Abstract
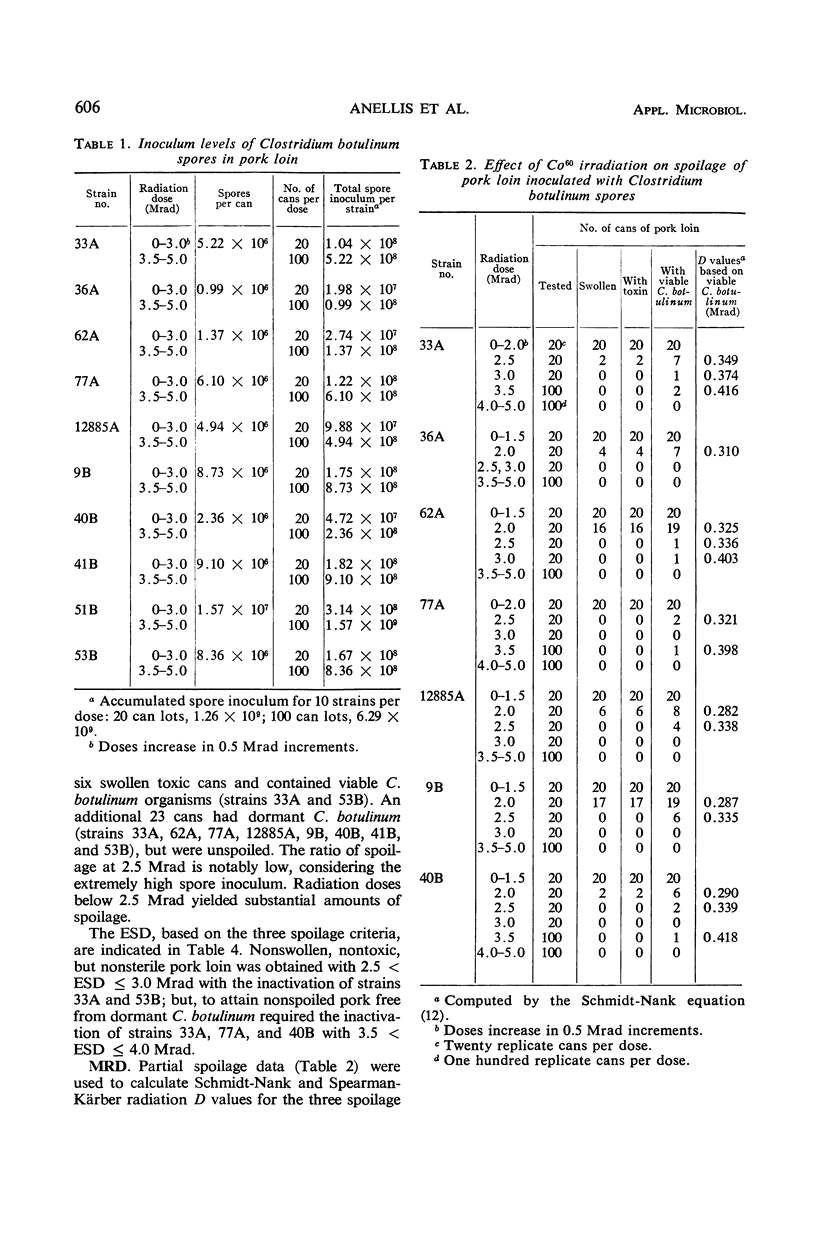
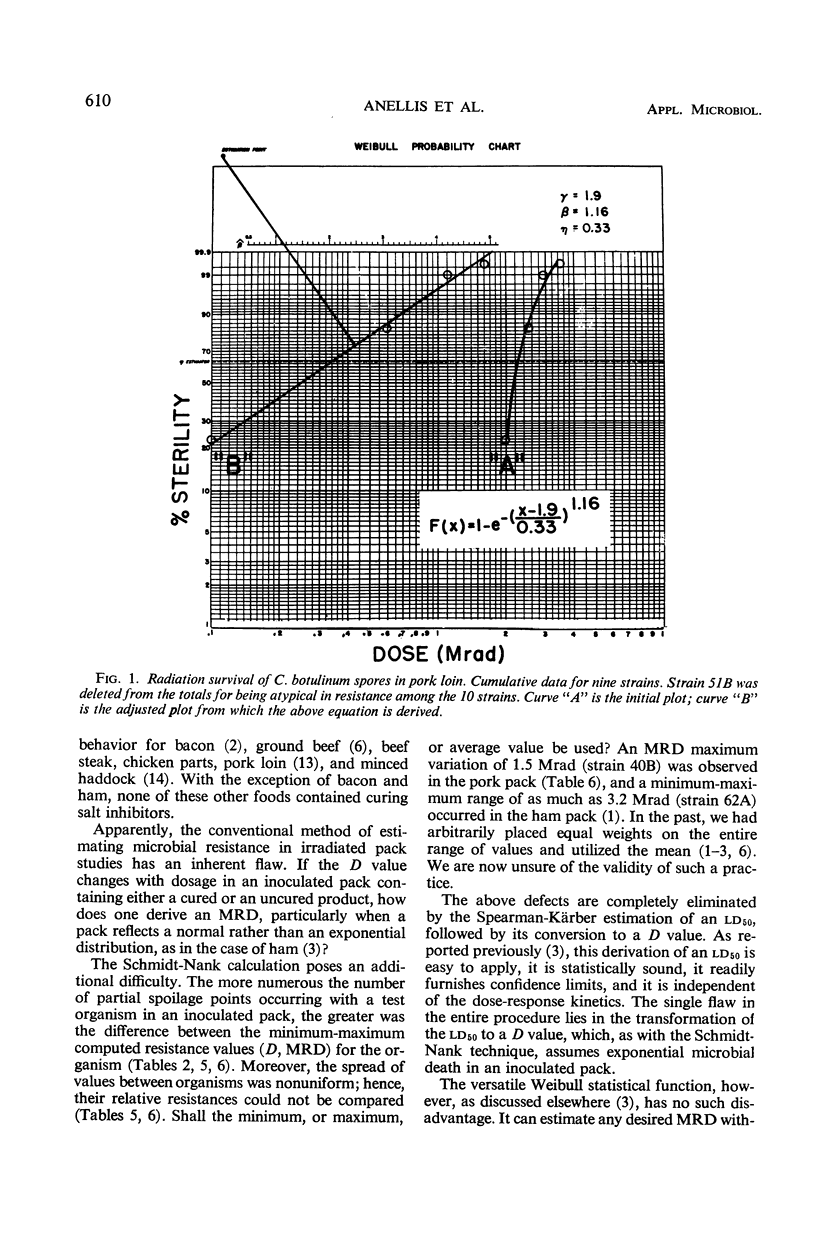
Ten lots of pork loin, packed in cans, were inoculated with approximately 106Clostridium botulinum spores per can. Each lot was seeded with a different strain; five type A and five type B strains were used. The pack comprised 5,690 cans, including controls, and contained about 109 spores per dose. The cans were irradiated with Co60 in the range of 0 to 5.0 Mrad (0.5 Mrad increments) at 5 to 25 C, incubated for 6 months at 30 C, and examined for swelling, toxicity, and recoverable C. botulinum. The minimal experimental sterilizing dose (ESD) based on nonswollen, nontoxic, but nonsterile end points was 2.5 < ESD ≤ 3.0 Mrad, and based on non-spoiled sterile cans was 3.5 < ESD ≤ 4.0 Mrad. The theoretical minimal radiation dose (MRD), the 12D equivalent, varied with the method of computation: 4.74, 4.33 ± 0.17, and 4.19 to 4.99 Mrad were obtained by the Weibull, Spearman-K̈arber, and Schmidt-Nank techniques, respectively. Calculation of D and MRD values by the conventional Schmidt-Nank method produced increasing values with rising dosage; this finding was compared with the data derived by the other two methods of calculation. Suggestions for estimating the MRD of a prototype radiation process are offered.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANELLIS A., GRECZ N., HUBER D. A., BERKOWITZ D., SCHNEIDER M. D., SIMON M. RADIATION STERILIZATION OF BACON FOR MILITARY FEEDING. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Jan;13:37–42. doi: 10.1128/am.13.1.37-42.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anellis A., Berkowitz D., Jarboe C., el Bisi H. M. Radiation sterilization of prototype military foods. II. Cured ham. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jan;15(1):166–177. doi: 10.1128/am.15.1.166-177.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anellis A., Werkowski S. Estimation of radiation resistance values of microorganisms in food products. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1300–1308. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1300-1308.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRECZ N., ANELLIS A., SCHNEIDER M. D. Procedure for cleaning of Clostridium botulinum spores. J Bacteriol. 1962 Sep;84:552–558. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.3.552-558.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRECZ N., SNYDER O. P., WALKER A. A., ANELLIS A. EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE OF LIQUID NITROGEN ON RADIATION RESISTANCE OF SPORES OF CLOSTRIDIUM BOTULINUM. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Jul;13:527–536. doi: 10.1128/am.13.4.527-536.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEMPE L. L., GRAIKOSKI J. T. Gamma-ray sterilization and residual toxicity studies of ground beef inoculated with spores of Clostridium botulinum. Appl Microbiol. 1962 Jan;10:31–36. doi: 10.1128/am.10.1.31-36.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSHEROFF B. J., SLOCUM G. G., DECKER W. M. STATUS OF BOTULISM IN THE UNITED STATES. Public Health Rep. 1964 Oct;79:871–878. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


