Abstract
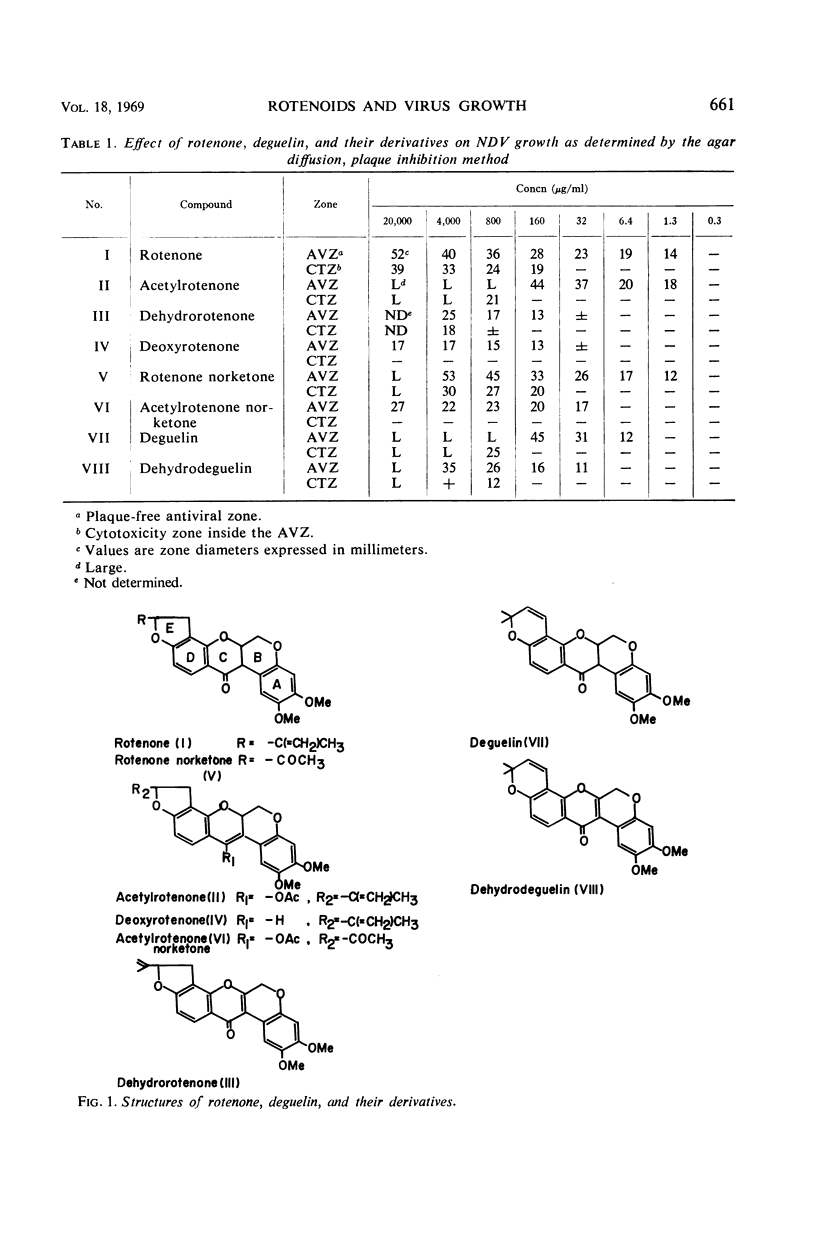
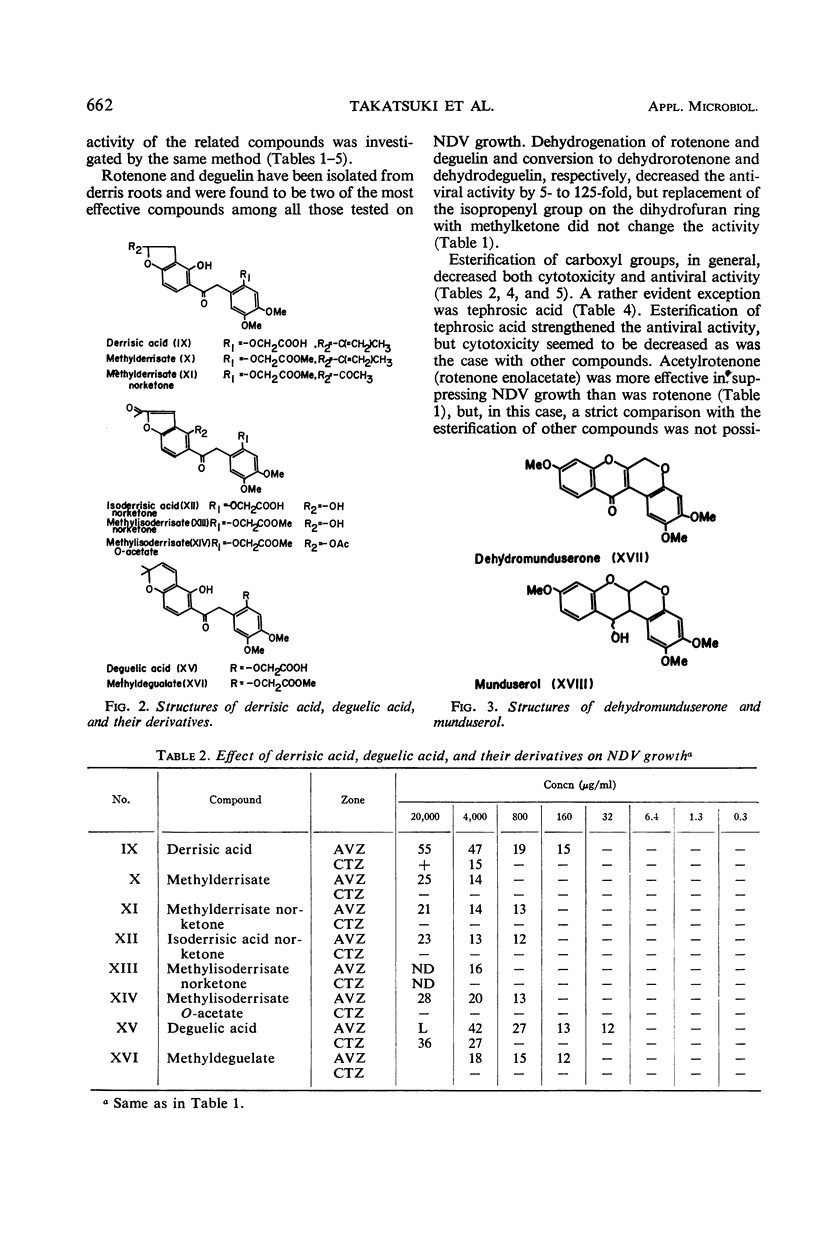
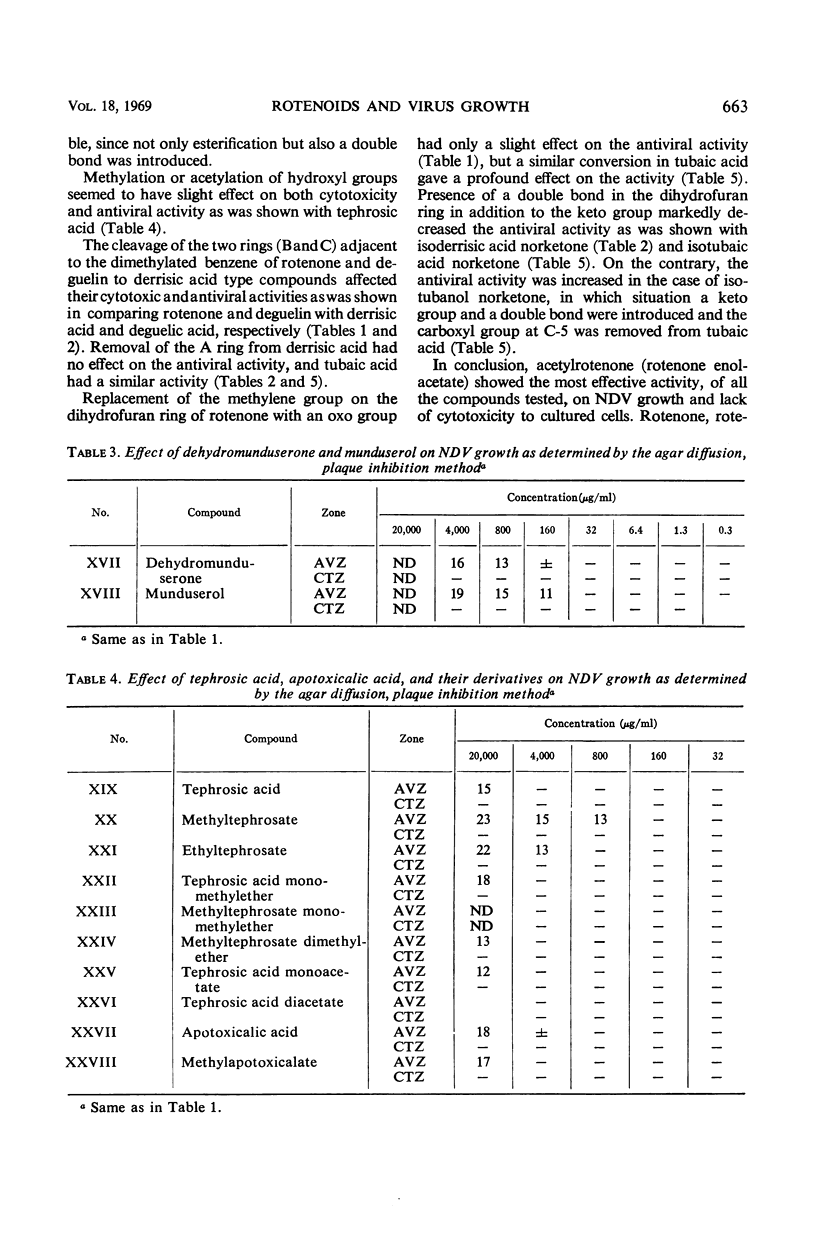
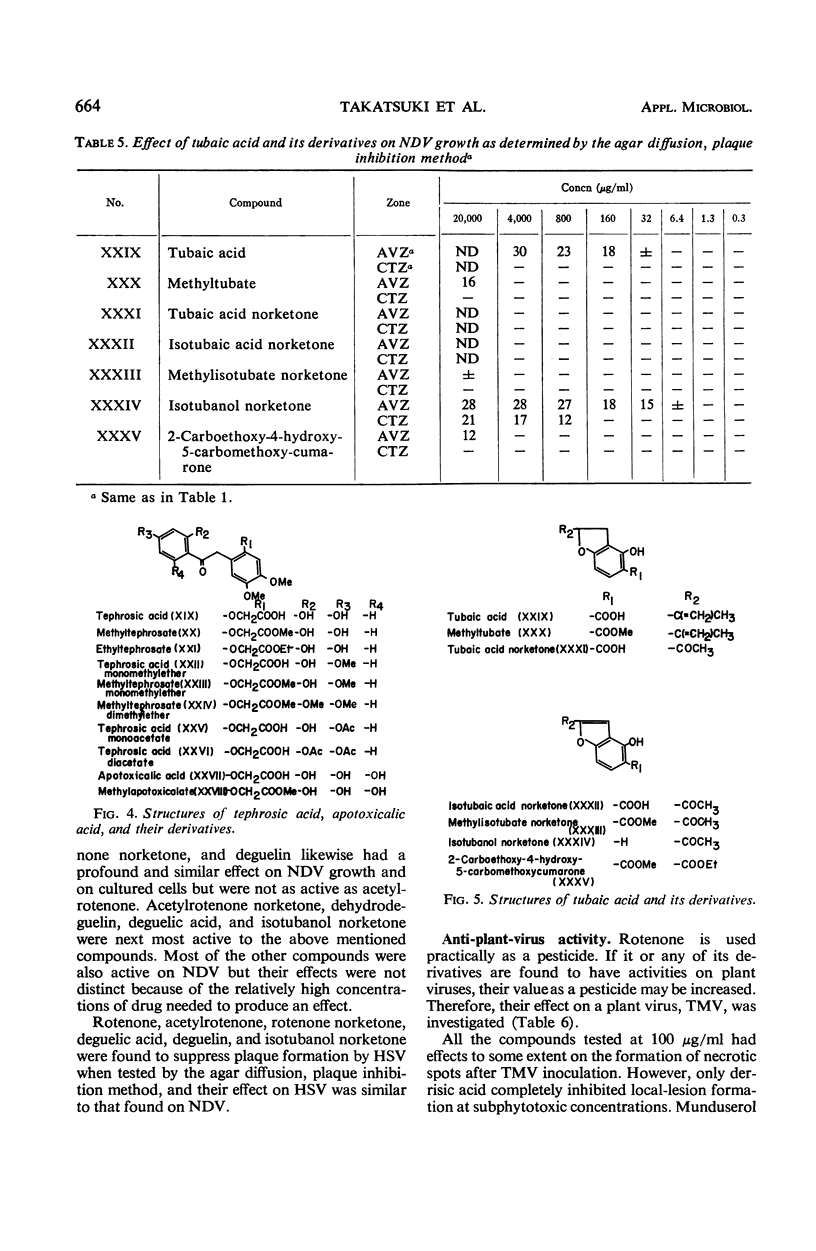
Rotenoids and related compounds were investigated for their effects on animal and plant viruses. Of 35 compounds examined, rotenone, rotenone norketone, acetylrotenone, acetylrotenone norketone, deguelin, deguelic acid, dehydrodeguelin, and isotubanol norketone, all used at low concentrations, suppressed the growth of Newcastle disease and herpes simplex viruses as determined by the agar diffusion, plaque inhibition method. Most of the compounds likewise decreased the number of necrotic spots on tobacco mosaic virus-infected leaf discs. Only derrisic acid completely inhibited the local lesion formation at subphytotoxic concentrations. Correlation of antiviral activity with respiratory inhibition of these compounds is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HAGIHARA B. Techniques for the application of polarography to mitochondrial respiration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jan 1;46:134–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90656-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRMANN E. C., Jr, GABLIKS J., ENGLE C., PERLMAN P. L. Agar diffusion method for detection and bioassay of antiviral antibiotics. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Mar;103:625–628. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDAHL P. E., OBERG K. E. The effect of rotenone on respiration and its point of attack. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Mar;23:228–237. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsuki A., Tamura G., Arima K. Antiviral and antitumor antibiotics. XIV. Effects of ascochlorin and other respiration inhibitors on multiplication of Newcastle disease virus in cultured cells. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jun;17(6):825–829. doi: 10.1128/am.17.6.825-829.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsuki A., Tamura G., Arima K. New antiviral antibiotics; xanthocillin X mono- and dimethylether, and methoxy-xanthocillin X dimethylether. II. Biological aspects of antiviral activity. (Studies on antiviral and antitumor antibiotics. VI). J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Dec;21(12):676–680. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


