Abstract
We report that CNS directed expression of Interferon (IFN) -γ results in basal ganglia calcification, reminiscent of human idiopathic basal ganglia calcification (IBGC), and nigrostriatal degeneration. Our results show that IFN-γ mediates age-progressive nigrostriatal degeneration in the absence of exogenous stressors. Further study of this model may provide unique insight into selective nigrostriatal degeneration in human IBGC and other Parkinson syndromes.
Keywords: IFN-γ, gliosis, nigrostriatal degeneration, basal ganglia calcification
IFN-γ is a pro-inflammatory cytokine which acts as a potent activator of microglia and astrocytes1. In the context of an initiative to evaluate the effects of various immune-modulatory factors in mouse models of neurodegenerative disease2–3, we noted that expression of murine IFN-γ (mIFN-γ) in wild type mice results in previously unreported central nervous system (CNS) phenotype mimicking human IBGC, a neurodegenerative syndrome distinguished by bilateral calcification of the basal ganglia4, and age-progressive nigrostriatal degeneration. All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. In these studies, B6C3 mice pups were injected in the cerebral ventricles (ICV) with recombinant adeno-associated viruses expressing mIFN-γ (rAAV2/1-mIFN-γ) or enhanced green fluorescent protein (rAAV2/1-EGFP) on neonatal day P2. This results in transgene expression largely within the choroid plexus and ependymal cells of the ventricle and a limited number of cells within the parenchyma surrounding the ventricles (Suppl. Fig. 1a–h)2. rAAV2/1-EGFP were used as controls in subsequent experiments as expression of rAAV2/1-EGFP has no appreciable effect on gliosis or CNS pathology when compared to non-injected or PBS-injected mice2–3.
rAAV2/1-mIFN-γ expression recapitulated a number of features that were previously observed in Ifn-γ transgenic mice5–6. mIFN-γ expression following P2 injection results in significantly increased brain mIFN-γ levels, ~50% mortality by 5 months of age, and runting (Suppl. Fig. 1i–k). These mice showed extensive microgliosis and astrocytosis in the CNS, consistent with the induction of M1 macrophage phenotype (Fig. 1a–d and Suppl. Fig. 2a–h) indicating that the effect of rAAV2/1-mIFN-γ expression is non-cell autonomous. There was no evidence for T-cell infiltration in these mice (Suppl. Fig. 2i–l). We also observed significant demyelination in the corpus callosum and cerebellar granule cell abnormalities consistent with migratory defect (Suppl. Fig. 2m–v; p<0.05) that are similar to previous reports5–6. Expression of rAAV2/1-mIFN-γ resulted in unique pathologies not previously reported. Brain sections stained with H&E revealed numerous intensely basophilic lesions in the basal ganglia identified as mineralized calcified deposits (Fig. 1e–h and Suppl. Fig. 3a–h). These deposits formed in the thalamus and midbrain and occasionally in the cerebellum with no deposits apparent in the cortex. Calcification was evident in both 5 month and 8 month old cohorts and was evident in B6/C3H and B6SJL backgrounds. This pathology is reminiscent of human IBGC or striopallidodentate calcification, characterized by neurological features including parkinsonism7, dystonia, tremor and chorea as well as neuropsychiatric symptoms including psychosis and cognitive decline4. It is clinically and biochemically distinct from disorders of systemic calcium or phosphate metabolism such as parathyroid disease.
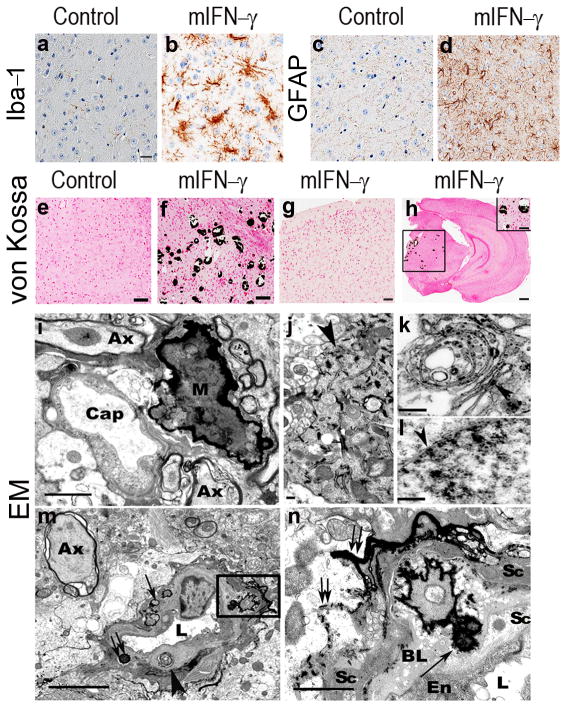
Fig 1. rAAV2/1 mediated mIFN-γ expression leads to extensive gliosis and selective basal ganglia calcification in wild type mice brain.
a–d. Upregulation of microglia (Iba-1) and astrocytes (GFAP) in midbrain of 5 month old rAAV2/1-mIFN-γ or rAAV2/1-EGFP (Control) expressing wild type mice. For corresponding whole brain images, see Suppl. Fig. 2a–d. Scale Bar, 25μm (e–h). (n=5/group).
e-h. Von Kossa stained sections of 5 month old (e–g) and 8 month old (h and inset) rAAV2/1-mIFN-γ mice (f–h) and rAAV2/1-EGFP (e) expressing control mice showing selective calcification in the thalamus (f, h inset) following mIFN-γ expression. No calcification is seen in the cortex of young (g) or old (h) mIFN-γ mice. For whole brain images, see Suppl. Fig. 3a–h. Scale Bar, 125μm (e–f), 250μm (g–h), 50μm (inset, h). (n=5/group).
i–n. Electron micrograph from 5 month old mIFN-γ mice brain showing neuropil mineralization (M) adjacent to a capillary (Cap) (i) and intracellular mineralization in the axonal processes (j, arrowhead), neuronal golgi (k, arrowhead) and nuclear envelope of a neuron (l, arrowhead). Mineralized nodules can be seen inside the basal lamina of a small arteriole (double arrows, arrowhead), and along the outer margins of the basal lamina (single arrow) (m). Enlargement of boxed area of interest from panel m shows mineralized nodules (arrow) in the expanded vascular basal lamina (n). Double arrows depict mineral deposits along the outer basal lamina (n). Ax, swollen axon, BL, Basal lamina, En, endothelial cell, L, vascular lumen, Sc, Smooth muscle cell. Scale bar, 2 μm (i), 0.2μm (j), 0.5μm (k), 0.6μm (l), 5 μm (m), 1μm (n).
Further examination of the mIFN-γ mice and IBGC patients revealed spatially similar calcification patterns (Suppl. Fig. 3a–j) and focal activation of microglia and astrocytes (Suppl. Fig. 3k–p). Electron microscopy (Fig. 1i–n) showed that calcification in mIFN-γ mice was primarily extracellular, occurring both in the parenchyma and in perivascular spaces, but sparse intracellular calcification was also observed, with features previously noted in IBGC patients4. Swollen axons with accumulation of neurofilaments were also apparent. Silver impregnation techniques demonstrated degenerative changes, axonal swelling and intracellular argyrophilic inclusions in the midbrain of mIFN-γ mice (Suppl. Fig. 4). This pathology has not been previously described in oligodendrocyte-specific promoter driven Ifn-γ transgenic mouse models 5–6.
Clinical and pathological data indicate that there is dopaminergic dysfunction in IBGC patients8–9. To evaluate whether mIFN-γ resulted in nigrostriatal degeneration in these mice, we examined protein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 1B (DARPP32 or PPP1R1B) and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) levels. At 3 months, there was no change in DARPP32 (Fig. 2c–e) or TH (Fig. 2i–k) immunoreactivity between mIFN-γ mice and controls, despite the presence of calcinosis. At 5 months, there was a 50% decrease (p< 0.05) in DARPP32 immunoreactive cell bodies and a 74% decrease (p< 0.001) in DARPP32 protein levels assessed by immunoblotting in the mIFN-γ mice (Fig. 2a, b, e, f, and Suppl. Fig. 5). Similarly, there was a marked 84% loss (p<0.001) of TH immunoreactivity at 5 months, consistent with nigrostriatal denervation (Fig. 2g, h, k). Estimates of remaining cells showed an 84% decrease (p<0.001) in the number of total TH cells in the midbrain and pons and a 65% loss (p<0.001) in substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) TH neurons in mIFN-γ mice (Fig. 2l–n). In contrast there was no change in hippocampal cell number in mIFN-γ mice (Fig. 2o–p; 2% decrease), indicating that the nigrostriatal neurons are more vulnerable to the effects of mIFN-γ than hippocampal neurons. AAV2/1-mIFN-γ expression in ex vivo TH-positive mouse primary neuronal or mixed neuroglial striatal cultures resulted in apoptosis as well as necrosis as evident by Tunel (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)- mediated dUTP nick end labeling) assay and increased Annexin V immunostaining (Suppl. Fig. 6a–l). Though it appears that mIFN-γ expression causes toxicity in cultured neurons as well as neuroglial cultures, additional studies will be needed to understand the mechanism underlying the neurotoxicity of mIFN-γ in culture and in vivo.
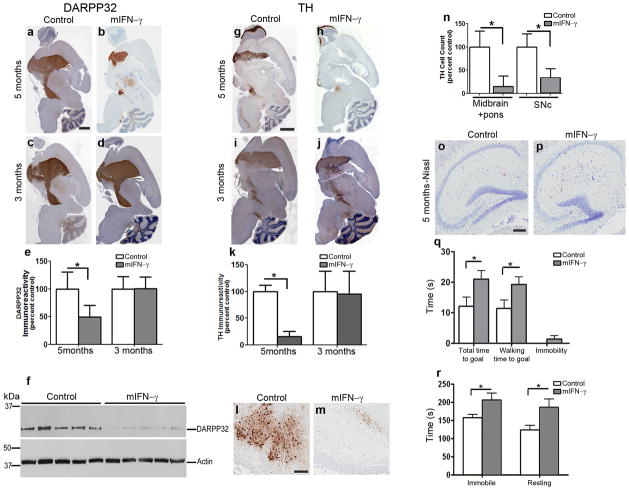
Fig 2. Selective and age-progressive nigrostriatal degeneration in rAAV2/1-mIFN-γ expressing wild type mice.
a–e. DARPP32 immunostained brain sections of 5 month old mice (a–b) or 3 month old mice (c–d) expressing rAAV2/1-mIFN-γ (b, d) or rAAV2/1-EGFP (Control) (a, c). Densitometric analysis of immunostaining is shown (e). Scale Bar, 600μm. (n=5/group; *p<0.05). Data represents mean + s.d.
f. Immunoblot showing DARPP32 and β-Actin (loading control) in 5 month old rAAV2/1-mIFN-γ expressing mice and control mice. The full length blot is depicted in Supplementary Figure 5. (n=5/group; *p<0.001).
g–k. TH immunostained brain sections of 5 month old mice (g–h) and 3 month old mice (i–j) expressing rAAV2/1-mIFN-γ (h, j) or EGFP (Control) (g, i). Densitometric analysis of immunoreactivity is shown (k). Scale Bar, 600μm. (n=5/group; *p<0.001). Data represents mean + s.d.
l–n. TH immunostained neurons in the SNc of 5 month old mIFN-γ (m) and EGFP (l) mice. Counts of TH immunoreactive cell bodies in SNc (n, “SNc”, n=5/group) and entire midbrain is depicted (n, “Midbrain+pons”; n=3/group). Scale bar, 120μm. (*p<0.001). Data represents mean + s.d.
o–p. Representative Nissl stained hippocampus from 5 month old mIFN-γ (p) and EGFP (o) mice. Scale Bar, 125μm. (n=5/group).
q–r. Locomotor and behavioral impairment is evident in 8 month old mIFN-γ mice compared to controls in the beam crossing test (q) and open field test (r). (n=8–12/group; *p<0.05). Data represents mean + s.e.m.
To test for basal ganglia dysfunction, we performed beam walking and open field exploratory tests on 8 month old mIFN-γ and EGFP mice. In beam walking test, mIFN-γ mice were immobile for longer periods of time and their walking time to reach the goal was significantly higher than control animals (Fig. 2q; p<0.05), though latency to initiate movement was the same in both the groups (Suppl. Fig. 7a). In an open field, mIFN-γ mice were more immobile and spent longer time resting (Fig. 2r; p<0.05); the path length traversed and latency periods were essentially unchanged (Suppl. Fig. 7b). Collectively these features are reminiscent of akinetic symptoms in dopamine deficient mice and human patients10. In contextual fear conditioning (Suppl. Fig. 7c), the mIFN-γ mice showed more freezing compared to controls, suggestive of parkinsonian freezing of gait10.
Encephalitis or viral infection can cause parkinsonism11. Interestingly, some sporadic forms of IBGC appear to have infectious etiologies such as intrauterine or perinatal infections associated with toxoplasmosis, rubella, herpesvirus and HIV14. To investigate whether neuroinflammation by itself leads to nigrostriatal degeneration, we tested the effect of murine Interleukin-6 (mIL-6), a pro-inflammatory cytokine, in wild type mice. rAAV2/1-mIL6 expression in the CNS causes widespread gliosis (Suppl. Fig. 8a–b, and2), similar to that observed in the mIFN-γ mice (Suppl. Fig. 2a–d), but does not cause midbrain calcification and does not increase mIFN-γ RNA or protein (Suppl. Fig. 8c–e). Notably, in mIL-6 mice, there were no alterations in TH or DARPP32 levels (Suppl. Fig. 8f–k). Moreover, rAAV2/1-mIFN-γ injection in thigh muscles of wild type neonatal mice elevates plasma mIFN-γ, and results in local macrophage activation, muscle dystrophy, and calcinosis at 5 months (Suppl. Fig. 9 and12). Therefore, calcification and neurodegeneration appear to be a direct result of mIFN-γ and not a non-specific consequence of chronic neuroinflammation.
The striking feature of the neurodegeneration seen in rAAV2/1-mIFN-γ mice is its relative selectivity for the basal ganglia and nigrostriatal pathways. High serum levels of IFN-γ and TNFα are associated with IBGC14 as well as a number of other neurodegenerative movement disorders including Parkinson disease15. Interestingly, Parkinsonism can occur following viral encephalitis11 providing an intriguing link between post-encephalitic parkinsonism and IFNγ-mediated anti-viral response. Previous studies have demonstrated that IFN-γ driven microglial activation is required for dopaminergic neurodegeneration induced by paraquat, MPTP and rotenone (reviewed in13). Although innate immune mediators like IFN-γ, TNFα and IL-1β can exacerbate toxin-driven nigrostriatal degeneration13, frank nigrostriatal degeneration in the absence of an additional stressor has not been demonstrated. Our current studies provide compelling in vivo evidence that IFN-γ can directly mediate robust, selective and progressive nigrostriatal degeneration and antagonism of IFN-γ signaling may hold potential therapeutic benefit for diseases that result in nigrostriatal degeneration and basal ganglia calcification.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH/NIA (TEG), the Ellison Medical Foundation (TEG) and American Health Assistance Foundation (PD).
Footnotes
Author Contribution: PC conducted the experiments and wrote the manuscript; CC-D prepared the rAAV2/1 virus and performed Q-PCR; W-LL performed the electron micrography; AB and KJ-W provided technical assistance; CJ conducted the behavioral analysis; NRM and PD assisted with study design and interpretation; DD provided human tissue, conducted neuropathological analysis and interpretation; TEG coordinated the research, supervised the project and assisted in manuscript preparation.
References
- 1.Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T, Hume DA. Interferon-gamma: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;75:163–189. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0603252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chakrabarty P, et al. Massive gliosis induced by interleukin-6 suppresses Abeta deposition in vivo: evidence against inflammation as a driving force for amyloid deposition. FASEB J. 2010;24:548–559. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-141754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chakrabarty P, et al. IFN-gamma promotes complement expression and attenuates amyloid plaque deposition in amyloid beta precursor protein transgenic mice. J Immunol. 2010;184:5333–5343. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Baba Y, Broderick DF, Uitti RJ, Hutton ML, Wszolek ZK. Heredofamilial brain calcinosis syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80:641–651. doi: 10.4065/80.5.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Corbin JG, et al. Targeted CNS expression of interferon-gamma in transgenic mice leads to hypomyelination, reactive gliosis, and abnormal cerebellar development. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1996;7:354–370. doi: 10.1006/mcne.1996.0026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Horwitz MS, Evans CF, McGavern DB, Rodriguez M, Oldstone MB. Primary demyelination in transgenic mice expressing interferon-gamma. Nat Med. 1997;3:1037–1041. doi: 10.1038/nm0997-1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Manyam BV, Walters AS, Narla KR. Bilateral striopallidodentate calcinosis: clinical characteristics of patients seen in a registry. Mov Disord. 2001;16:258–264. doi: 10.1002/mds.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Paschali A, et al. Dopamine transporter SPECT/CT and perfusion brain SPECT imaging in idiopathic basal ganglia calcinosis. Clin Nucl Med. 2009;34:421–423. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0b013e3181a7d195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Savoldi F, Nappi G, Martignoni E, Bono G. Biochemical evidence of dopaminergic involvement in Fahr’s syndrome. Acta Neurol (Napoli) 1980;2:231–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Devos D, Defebvre L, Bordet R. Dopaminergic and non-dopaminergic pharmacological hypotheses for gait disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2010;24:407–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2009.00798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jang H, Boltz DA, Webster RG, Smeyne RJ. Viral parkinsonism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1792:714–721. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.08.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shelton GD, et al. Necrotizing myopathy induced by overexpression of interferon-gamma in transgenic mice. Muscle Nerve. 1999;22:156–165. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4598(199902)22:2<156::aid-mus3>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Frank-Cannon TC, Alto LT, McAlpine FE, Tansey MG. Does neuroinflammation fan the flame in neurodegenerative diseases? Mol Neurodegener. 2009;4:47. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-4-47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Morishima T, Morita M, Kato T, Hoshino Y, Kimura H. Natural killer cell proliferation and circulating cytokines in patients with bilateral basal ganglia calcification. Eur J Neurol. 2002;9:521–525. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-1331.2002.00449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mount MP, et al. Involvement of interferon-gamma in microglial-mediated loss of dopaminergic neurons. J Neurosci. 2007;27:3328–3337. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5321-06.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.