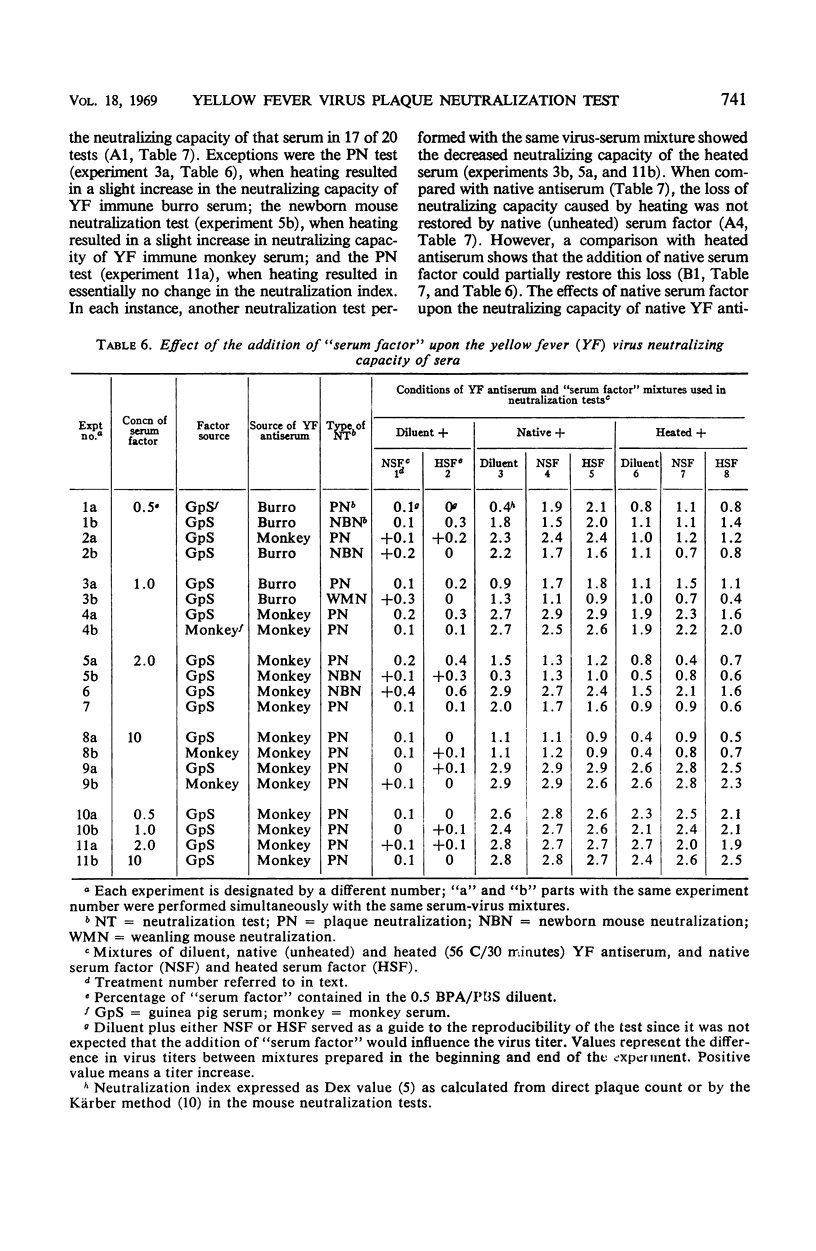
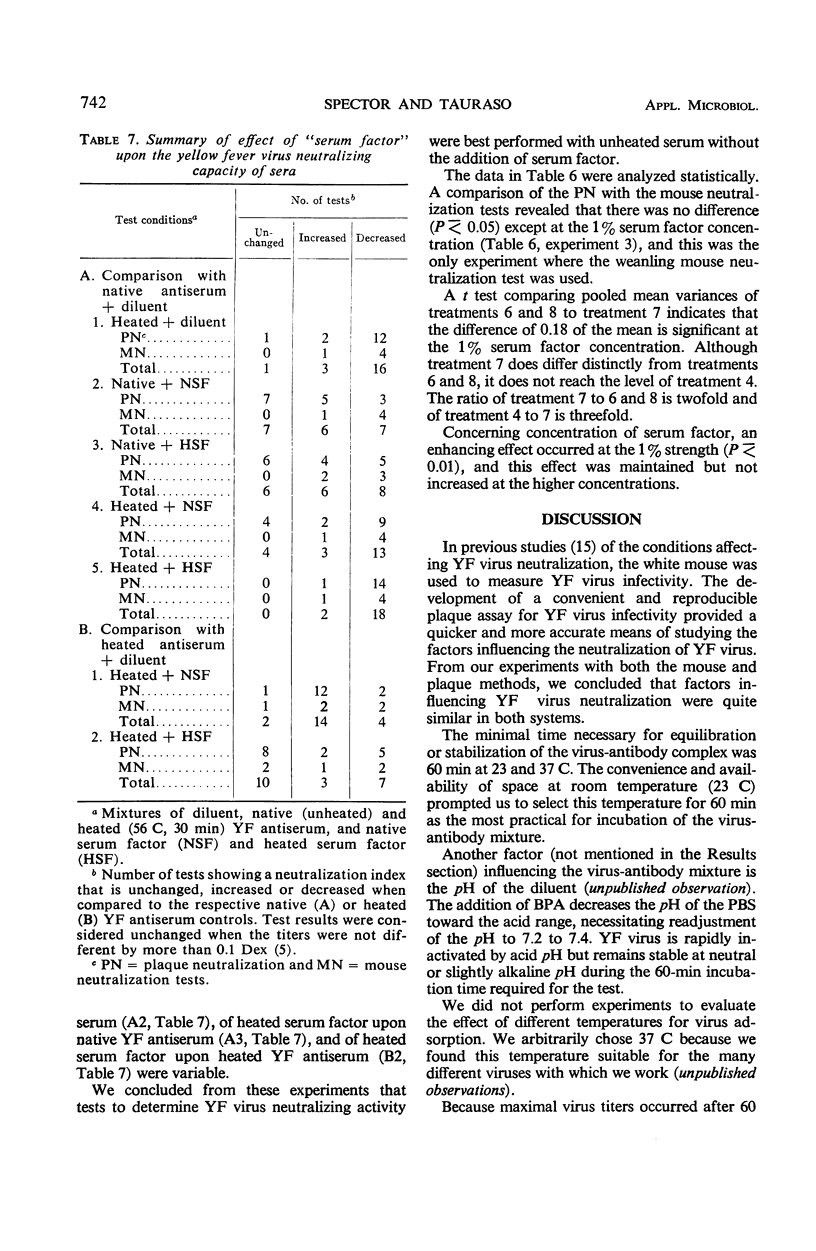
Abstract
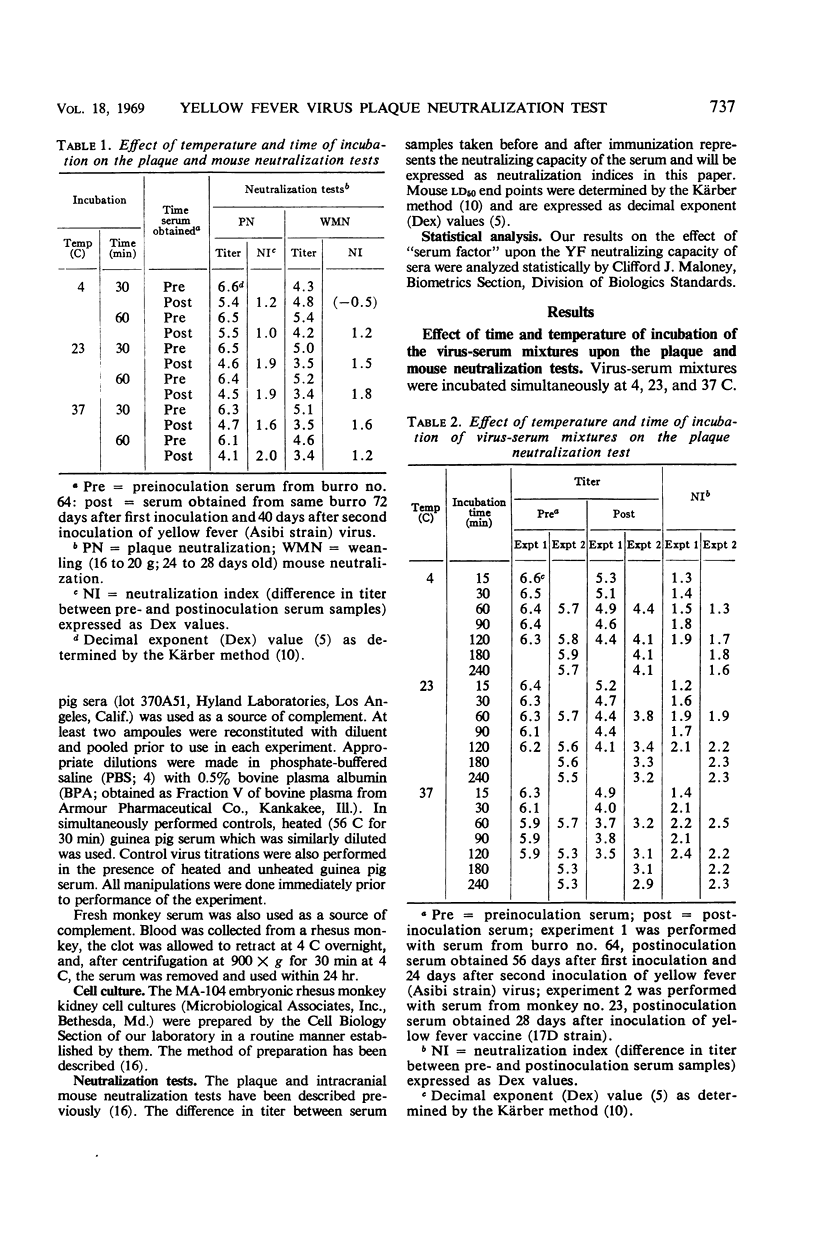
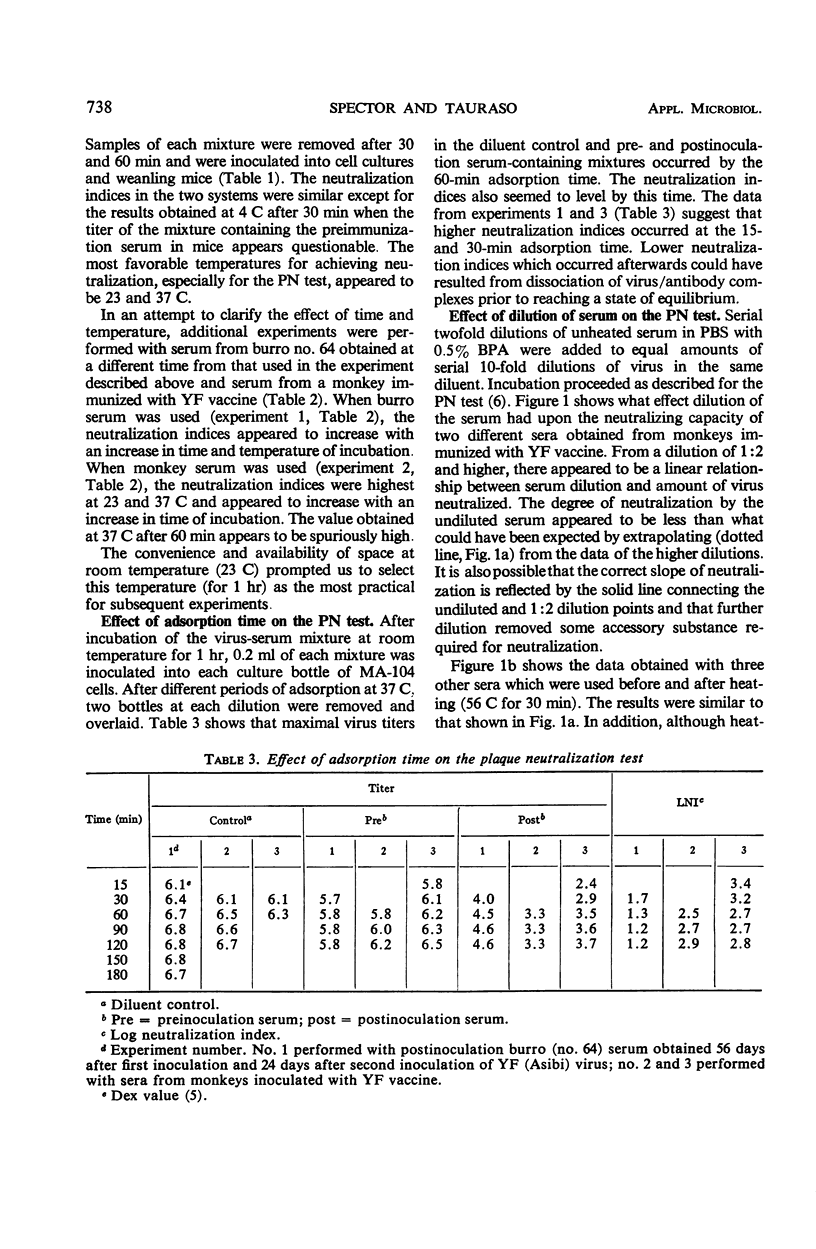
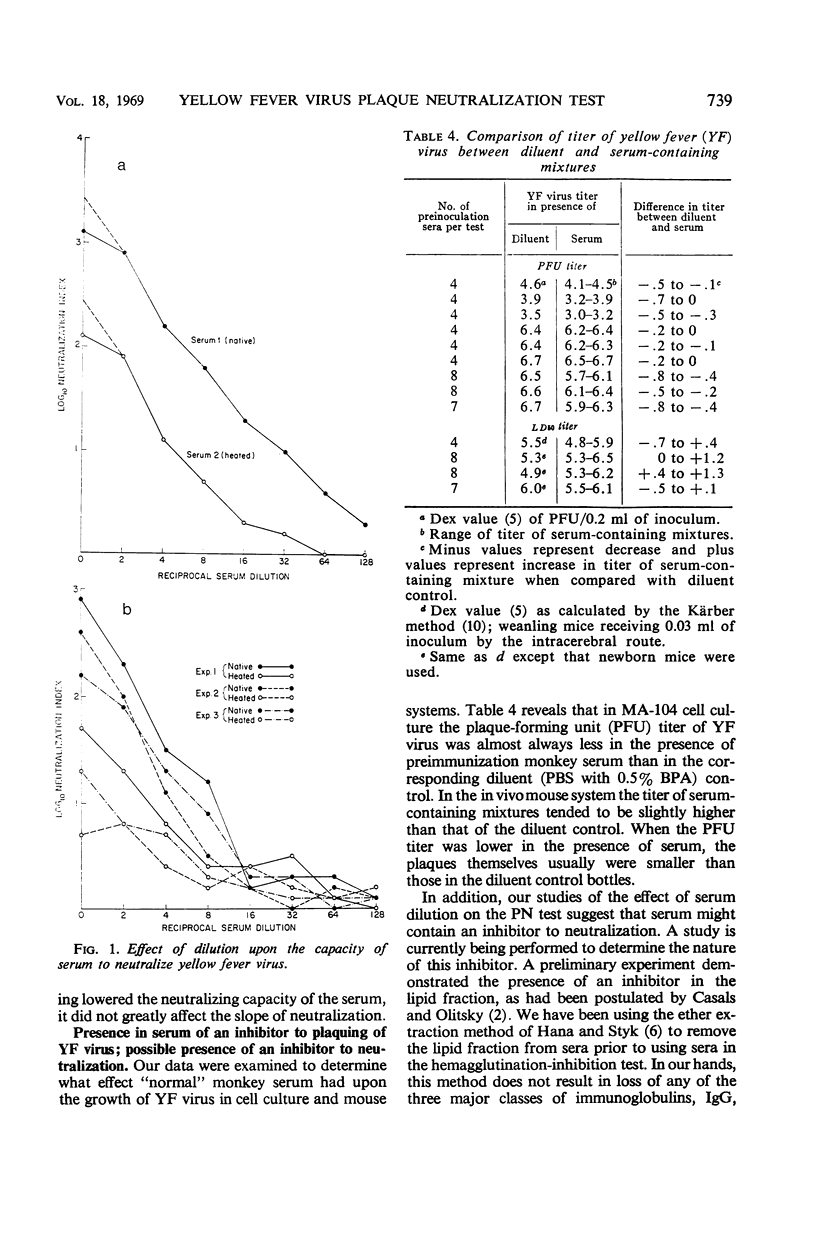
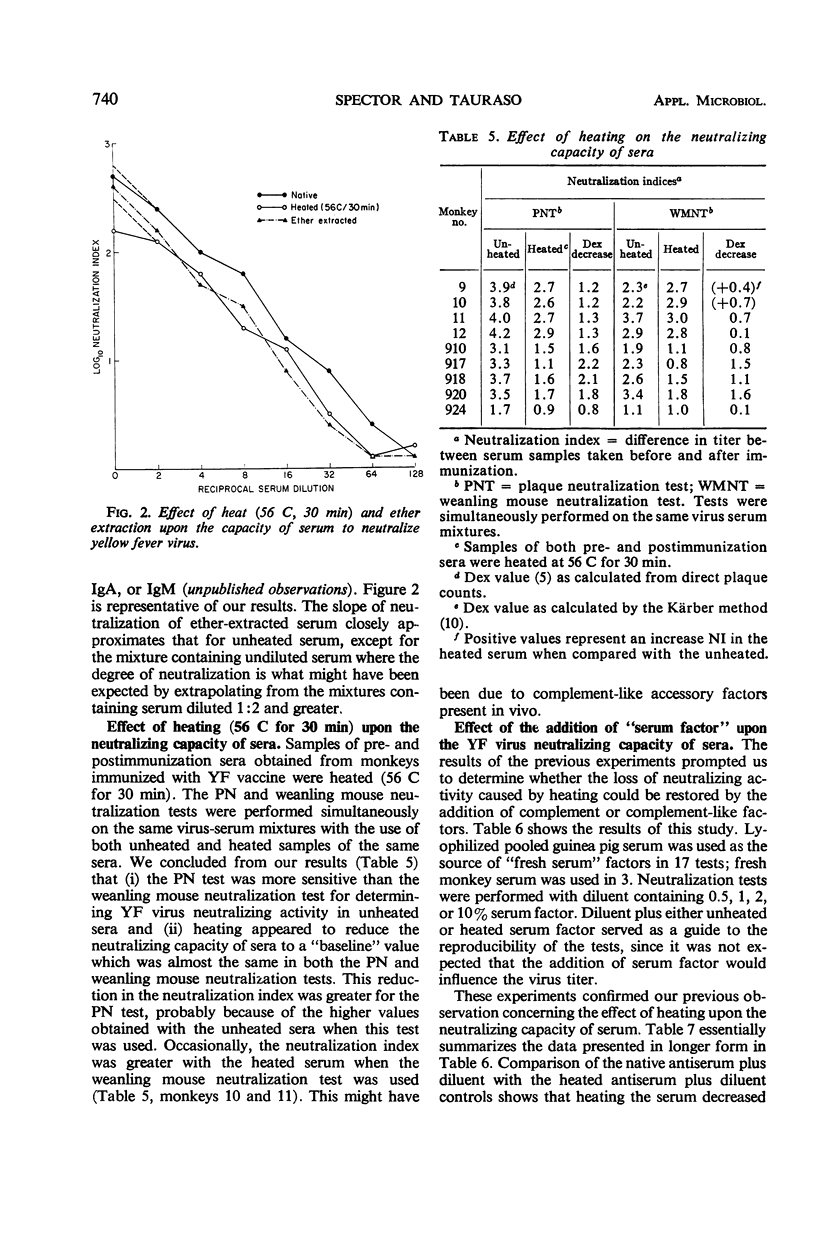
In studies on the factors and conditions influencing the yellow fever (YF) virus plaque neutralization test, 60 min was found to be the minimal time necessary for equilibration of the virus-antibody complex at 23 and 37 C. Maximal virus titers in the diluent controls and the pre- and postinoculation serum-containing mixtures occurred by the 60-min adsorption time. Serum neutralization indices also seemed to level by this time. Heating (56 C for 30 min) decreased the neutralizing capacity of serum. However, the slope of the neutralization curve was not affected. The addition of native (unheated) “serum factor” in the form of fresh guinea pig or monkey sera partially restored the neutralizing activity lost by heating in some, but not all, sera. Many sera contained nonspecific inhibitors of YF virus infectivity and neutralization. Preliminary studies with ether extraction suggest that these inhibitors are lipid in nature.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casals J., Olitsky P. K. Inactivation of Certain Neurotropic Viruses in Vitro by Serum Lipids. Science. 1947 Sep 19;106(2751):267–268. doi: 10.1126/science.106.2751.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASHIMOTO N., PRINCE A. M. Kinetic studies on the neutralization reaction between Japanese encephalitis virus and antiserum. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:261–272. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90063-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki Y., Tabeyi K. Studies on the neutralization of Japanese encephalitis virus. I. Application of kinetic neutralization to the measurement of the neutralizing potency of antiserum. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1218–1223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H. A VIRUS IN CHICK EMBRYOS WHICH INDUCES RESISTANCE IN VITRO TO INFECTION WITH ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Aug;46(8):1105–1119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.8.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABIN A. B. The dengue group of viruses and its family relationships. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Sep;14(3):225–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S., Tauraso N. M. Yellow fever virus. I. Development and evaluation of a plaque neutralization test. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Nov;16(11):1770–1775. doi: 10.1128/am.16.11.1770-1775.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauraso N. M., Spector S. L., Jahnes W. G., Shelokov A. Yellow fever vaccine. I. Development of a vaccine seed free from contaminating avian leukosis viruses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Apr;127(4):1116–1120. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISKRANTZ L. Effects of medial temporal lesions on taste preference in the monkey. Nature. 1960 Sep 3;187:879–880. doi: 10.1038/187879b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G. The neutralization of arboviruses. II. Neutralization in heterologous virus-serum mixtures with four group B arboviruses. Virology. 1965 Aug;26(4):528–537. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90314-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


