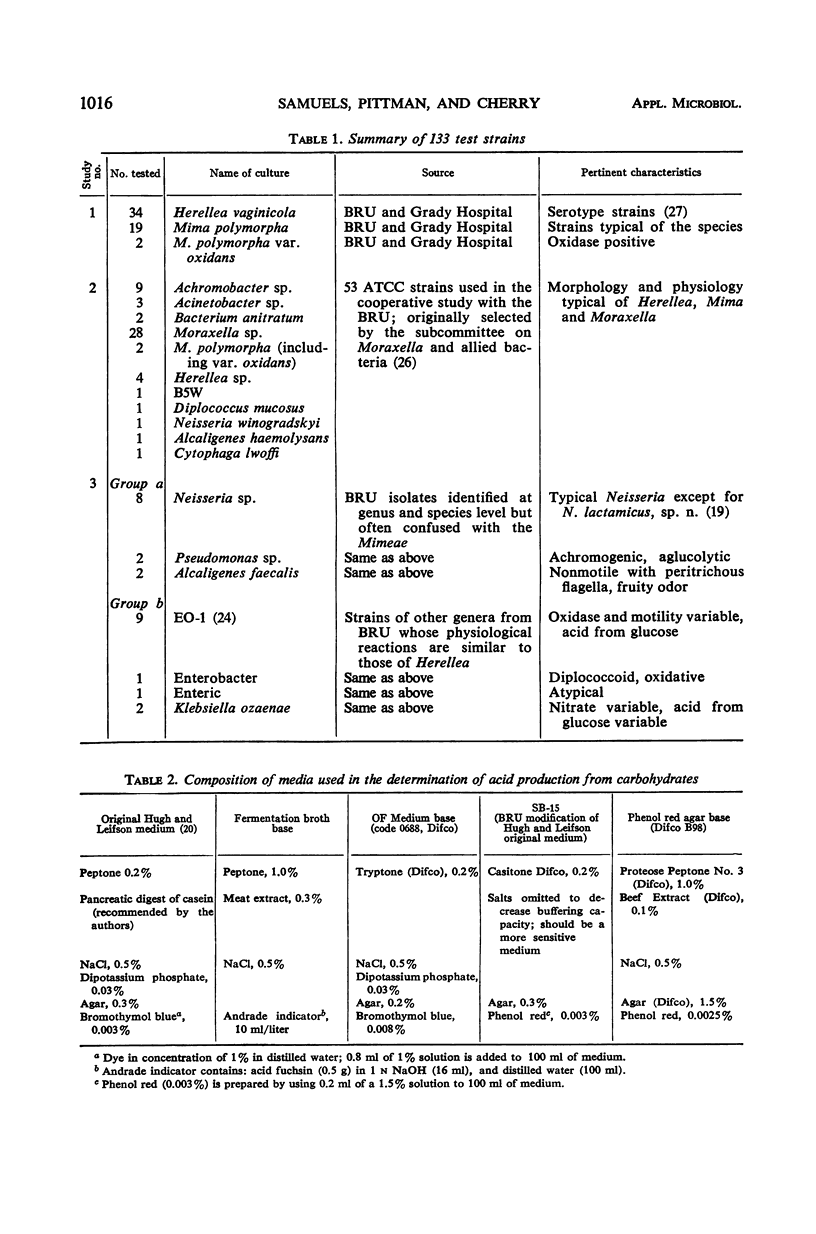
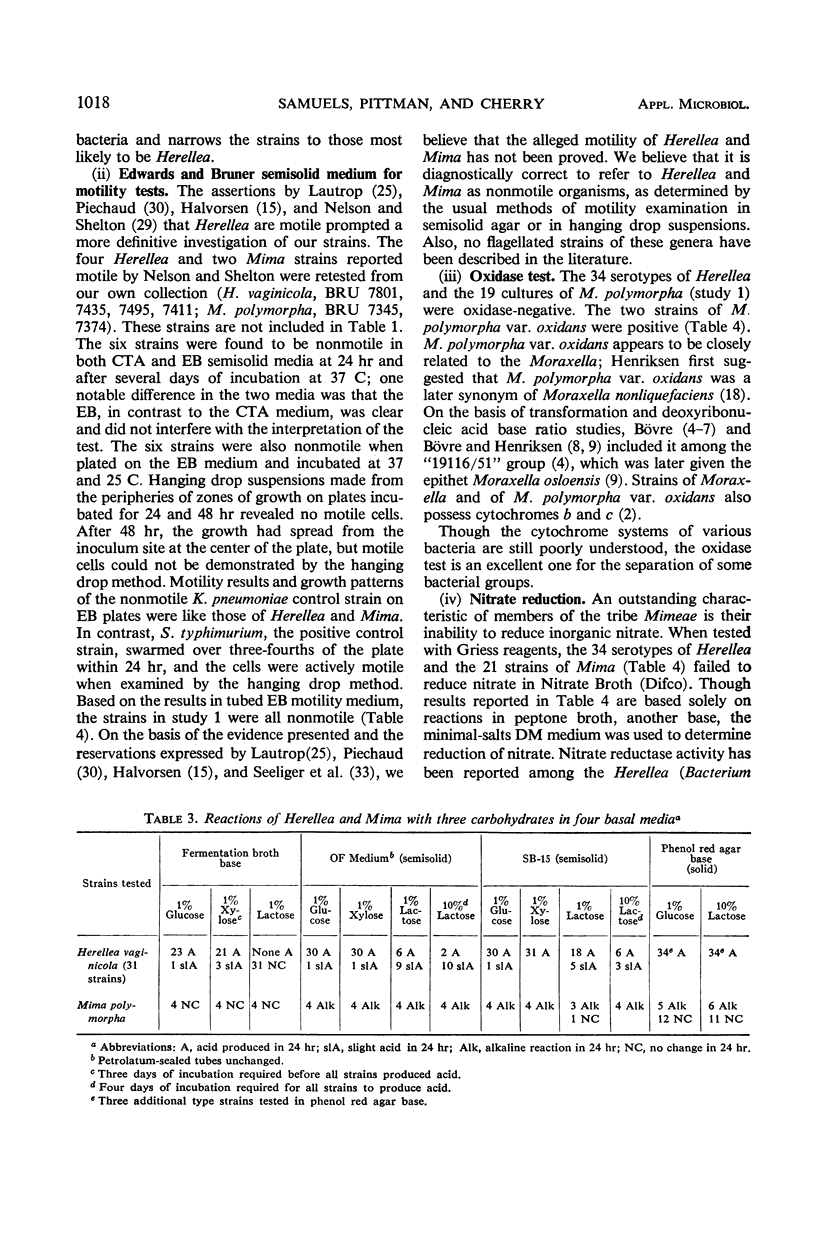
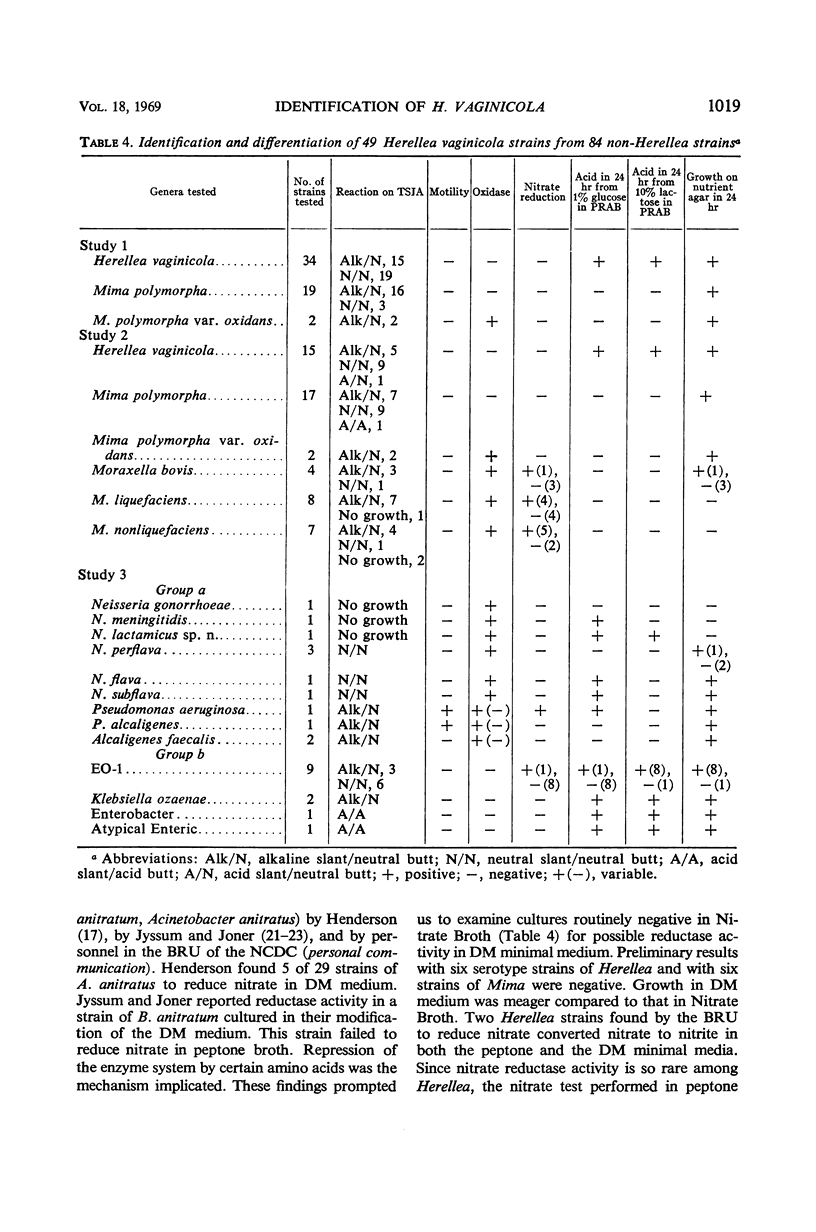
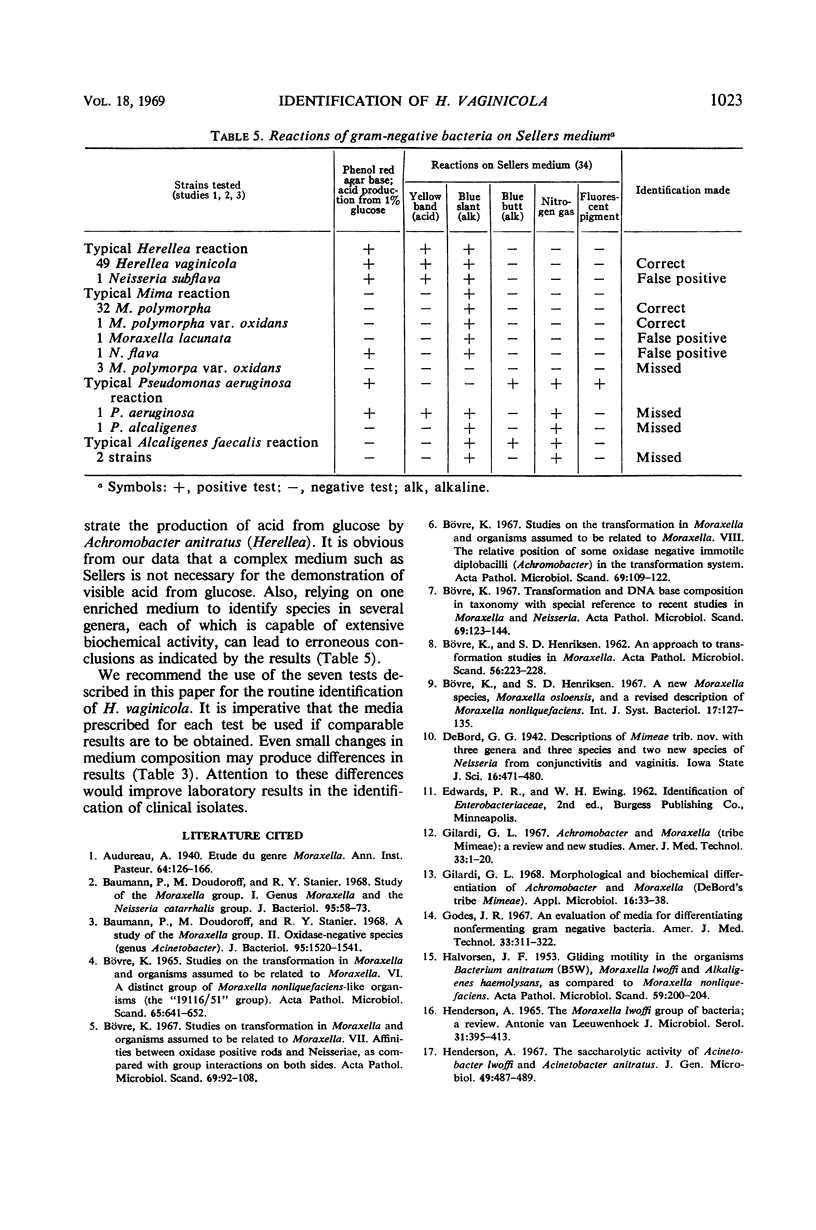
Abstract
A seven-test schema is presented that will identify Herellea vaginicola and differentiate it from Mima, Moraxella, and other gram-negative organisms whose biochemical reactions are similar to those of Herellea. Of 133 cultures examined, 49 were Herellea strains accurately identified by this schema: 34 of the 49 cultures were the capsular type strains of Herellea and 15 strains were from a group of 53 ATCC cultures listed under several different taxons. The remaining 84 non-Herellea cultures yielded 4 (4.7%) false positive identifications for Herellea; two were from a selected group of organisms (EO-1) whose taxonomic position is undetermined and two were Klebsiella ozaenae. Since neither of these groups is frequently encountered in clinical specimens, from a practical viewpoint they present no particular problem in the identification of Herellea. We recommend the use of the seven tests as described in this paper as a routine procedure for the identification of H. vaginicola.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOVRE K., HENRIKSEN S. D. An approach to transformation studies in Moraxella. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1962;56:223–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1962.tb04183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Doudoroff M., Stanier R. Y. A study of the Moraxella group. II. Oxidative-negative species (genus Acinetobacter). J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1520–1541. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1520-1541.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Doudoroff M., Stanier R. Y. Study of the Moraxella group. I. Genus Moraxella and the Neisseria catarrhalis group. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):58–73. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.58-73.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bövre K. Studies on transformation in Moraxella. and organisms assumed to be related to Moraxella 6. A distinct group of Moraxella nonliquefaciens-like organisms (the "19116/51" group). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;65(4):641–652. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.65.4.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi G. L. Morphological and biochemical differentiation of Achromobacter and Moraxella (DeBord's tribe Mimeae). Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jan;16(1):33–38. doi: 10.1128/am.16.1.33-38.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godes J. R. An evaluation of media for differentiating nonfermenting gram negative bacteria. Am J Med Technol. 1967 Jul-Aug;33(4):311–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALVORSEN J. F. GLIDING MOTILITY IN THE ORGANISMS BACTERIUM ANITRATUM (B5W), MORAXELLA LWOFFI AND ALKALIGENES HAEMOLYSANS, AS COMPARED TO MORAXELLA NONLIQUEFACIENS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;59:200–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1963.tb01789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGH R., LEIFSON E. The taxonomic significance of fermentative versus oxidative metabolism of carbohydrates by various gram negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):24–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.1.24-26.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. The Moraxella iwoffi group of bacteria; a review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1965;31(4):395–413. doi: 10.1007/BF02045919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis D. G., Wiggins G. L., Weaver R. E. Neisseria lactamicus sp. n., a lactose-fermenting species resembling Neisseria meningitidis. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jan;17(1):71–77. doi: 10.1128/am.17.1.71-77.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jyssum K., Joner P. E. Growth of Bacterium anitratum (B5W) with nitrate or nitrite as nitrogen source. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64(3):381–386. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.3.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jyssum K., Joner P. E. Hydroxylamine as a possible intermediate in nitrate reduction by Bacterium anitratum (B5W). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;67(1):139–148. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.67.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jyssum K., Joner P. E. Regulation of the nitrogen assimilation from nitrate and nitrite in Bacterium anitratum (B5W). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64(3):387–397. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.3.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus B. B., Samuels S. B., Pittman B., Cherry W. B. A serologic study of Herellea vaginicola and its identification by immunofluorescent staining. Am J Clin Pathol. 1969 Sep;52(3):309–319. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/52.3.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A., Von Riesen V. L. Carbohydrate metabolism of Bacterium antitratum. Am J Med Technol. 1968 Jan;34(1):30–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. D., Shelton S. Cultural, biochemical, and immunological properties of Mima, Herellea, and Flavobacterium species. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Sep;13(5):801–807. doi: 10.1128/am.13.5.801-807.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIECHAUD M. [Motility of the Moraxella]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1963 Feb;104:291–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintér M., Bende I. Computer analysis of Acinetobacter iwoffi (Moraxella iwoffii) and Acinetobacter anitratus (Moraxella glucidolytica) strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Feb;46(2):267–272. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-2-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON R. G., GARRISON R. G., BROWN R. W. EVALUATION OF THE CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF THE GENUS HERELLEA. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Jan;60:19–27. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-60-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELLERS W. MEDIUM FOR DIFFERENTIATING THE GRAM-NEGATIVE, NONFERMENTING BACILLI OF MEDICAL INTEREST. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:46–48. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.46-48.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornley M. J. A taxonomic study of Acinetobacter and related genera. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Nov;49(2):211–257. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



