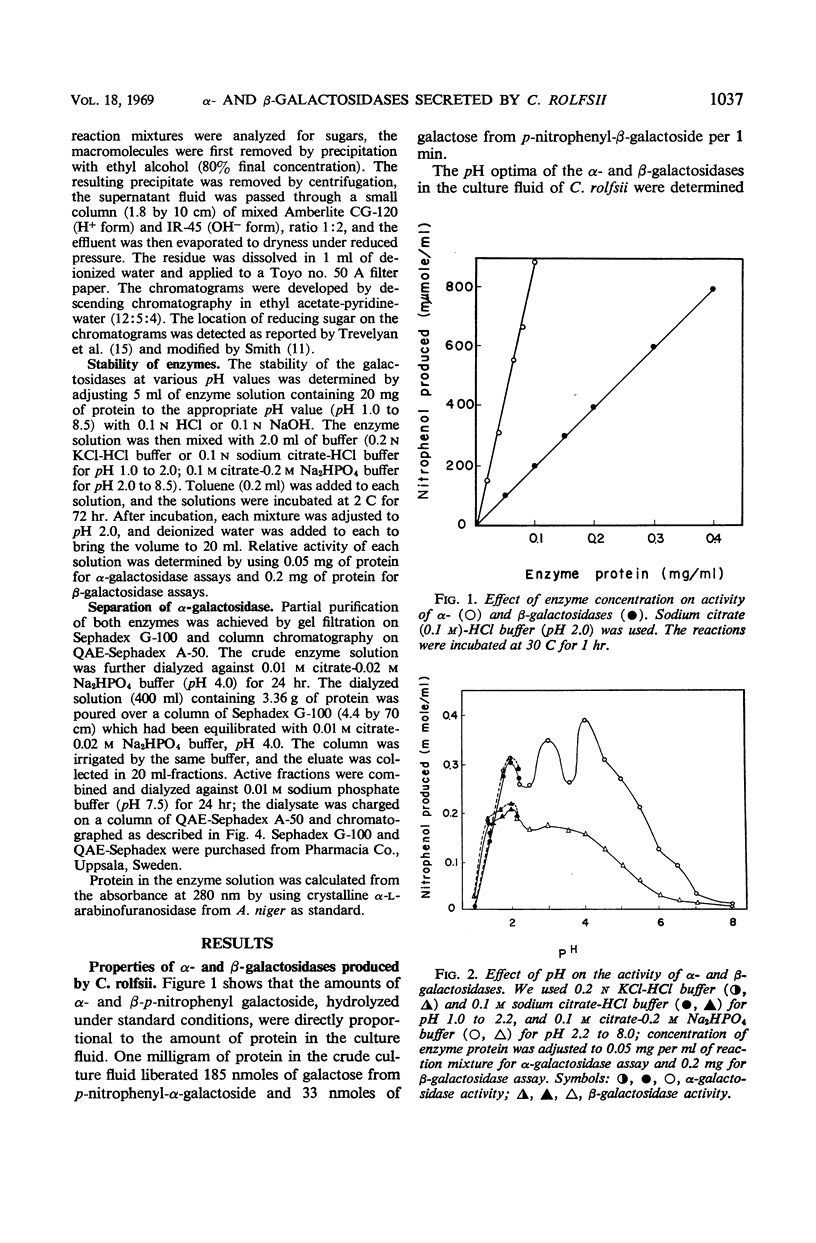
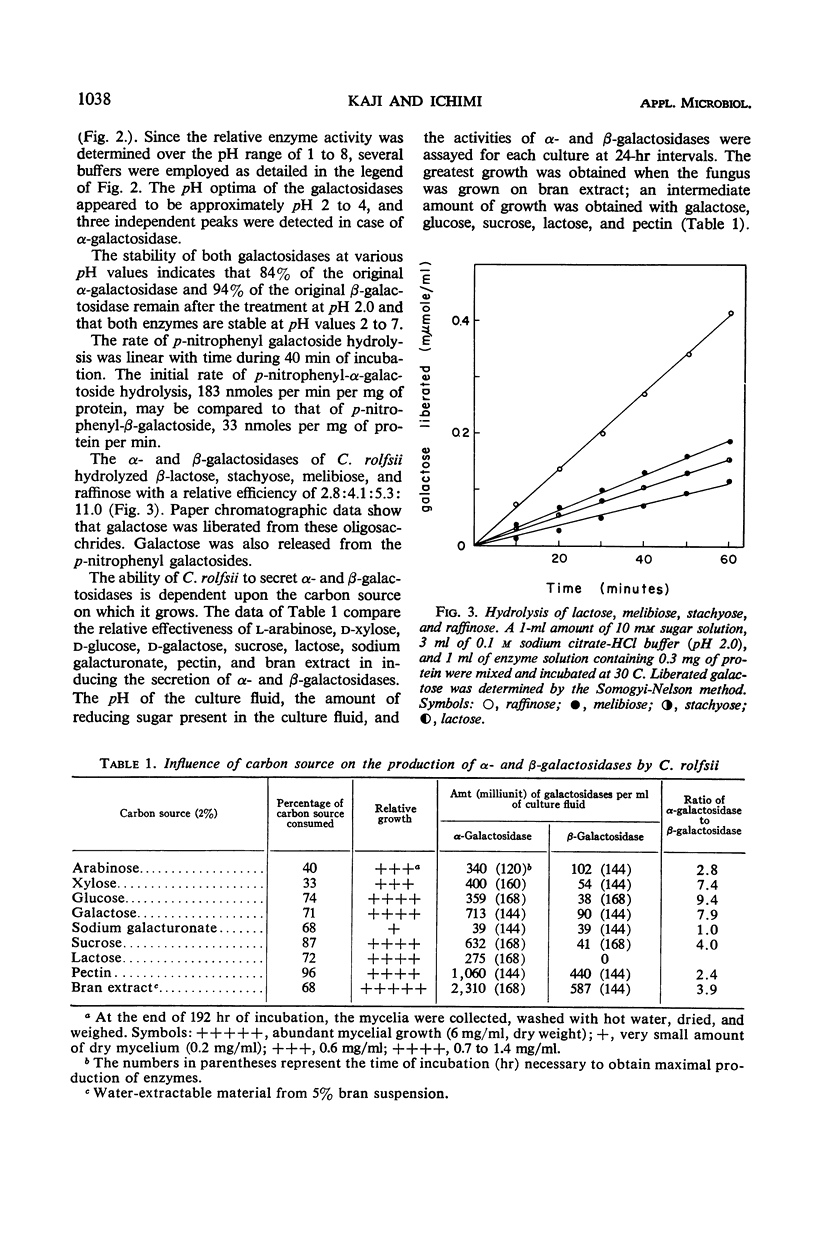
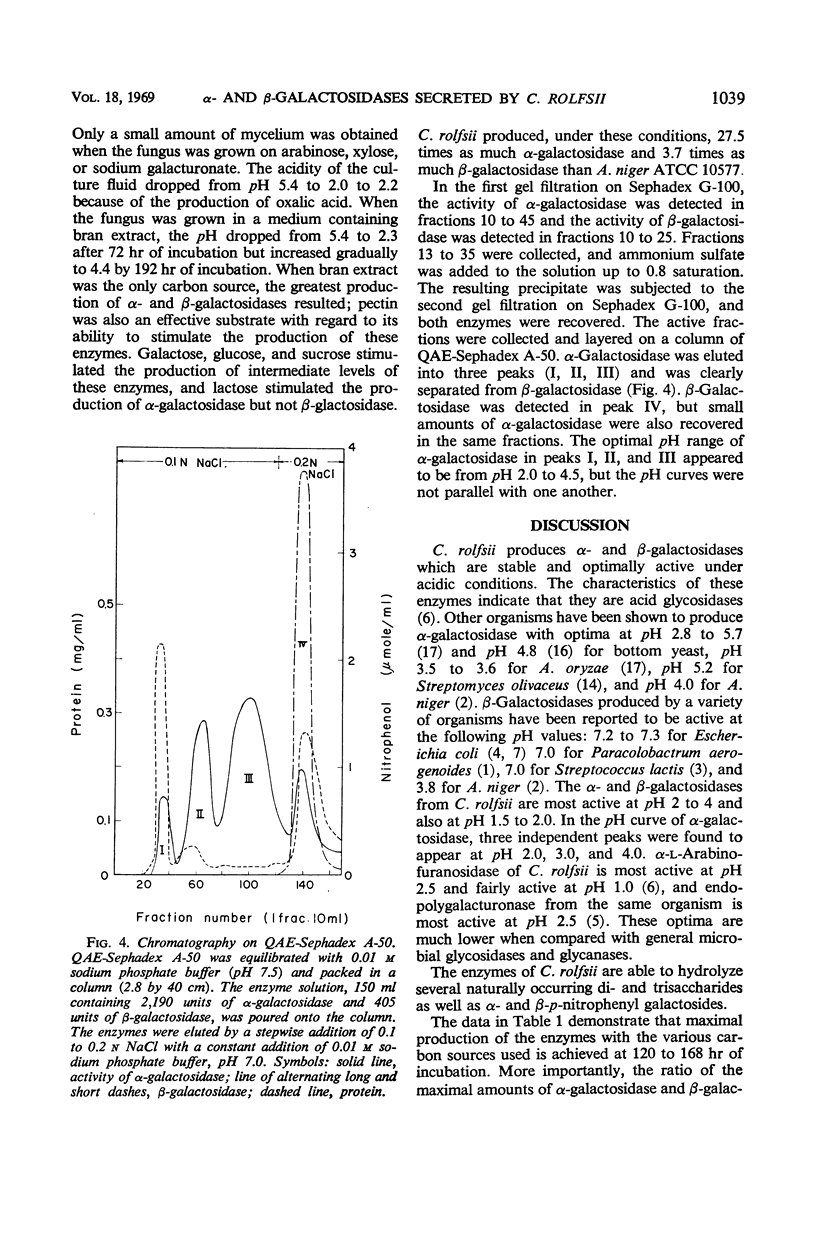
Abstract
When Corticum rolfsii was grown in a medium containing bran extract under aerobic conditions, it secreted α-D-galactosidase and β-D-galactosidase into the culture fluid. Pectin also stimulated the production of these enzymes, whereas galactose, glucose, and sucrose stimulated their production to a lesser degree. C. rolfsii produced greater amounts of both enzymes than Aspergillus niger. Both galactosidases in the culture medium hydrolyzed α- and β-p-nitrophenyl-D-galactosides as well as lactose, stachyose, melibiose, and raffinose. Both exhibited optimal activity at pH 2 to 4 and were quite stable under acidic conditions. α-Galactosidase was separated from β-galactosidase by column chromatography.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON J. M., RICKENBERG H. V. beta-Galactosidase of Paracolobactrum aerogenoides. J Bacteriol. 1960 Sep;80:297–304. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.3.297-304.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahl O. P., Agrawal K. M. Glycosidases of Aspergillus niger. I. Purification and characterization of alpha- and beta-galactosidases and beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 10;244(11):2970–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CITTI J. E., SANDINE W. E., ELLIKER P. R. BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF STREPTOCOCCUS LACTIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:937–942. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.937-942.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deere C. J., Dulaney A. D., Michelson I. D. The Lactase Activity of Escherichia coli-mutabile. J Bacteriol. 1939 Apr;37(4):355–363. doi: 10.1128/jb.37.4.355-363.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji A., Okada T. Purification and properties of an unusually acid-stable endo-polygalacturonase produced by Corticium rolfsii. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Apr;131(1):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji A., Yoshihara O. Production and Properties of alpha-L-Arabinofuranosidase from Corticium rolfsii. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jun;17(6):910–913. doi: 10.1128/am.17.6.910-913.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., COHN M. La biosynthèse induite des enzymes; adaptation enzymatique. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1952;13:67–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOGYI M. Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLENFELS K., MALHOTRA O. P. Galactosidases. Adv Carbohydr Chem. 1961;16:239–298. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60264-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


