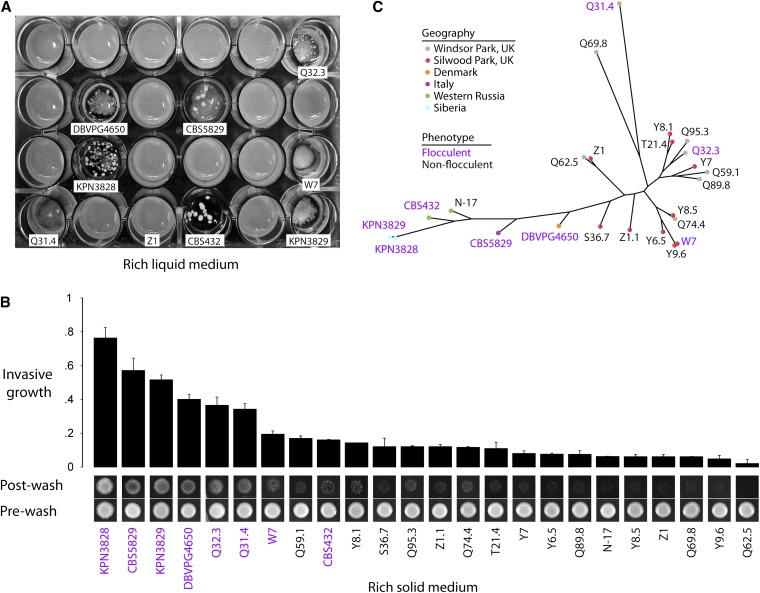
Figure 1.
Flocculation and invasive growth vary across European S. paradoxus. (A) Photograph of cultures of European S. paradoxus strains after overnight growth in rich liquid yeast peptone dextrose (YPD) medium containing 2% glucose. The eight flocculent strains and the nonflocculent strain Z1 are labeled with identifiers as in Liti et al. (2009). (B) Photographs at bottom are of invasive growth assays: a colony of each strain was grown on YPD solid medium for 5 days and then photographed before (“pre-wash”) and after (“post-wash”) removal of nonadherent cells by a water wash. At top, each bar height reports the ratio of cell density in colonies after and before a water wash as a mean of two replicate colonies; error bars represent one standard deviation. (C) Maximum-likelihood genome tree of European S. paradoxus. Branch lengths are proportional to the number of segregating sites that differentiate each pair of strains. In B and C, identifiers of flocculent strains are in purple.