Full text
PDF
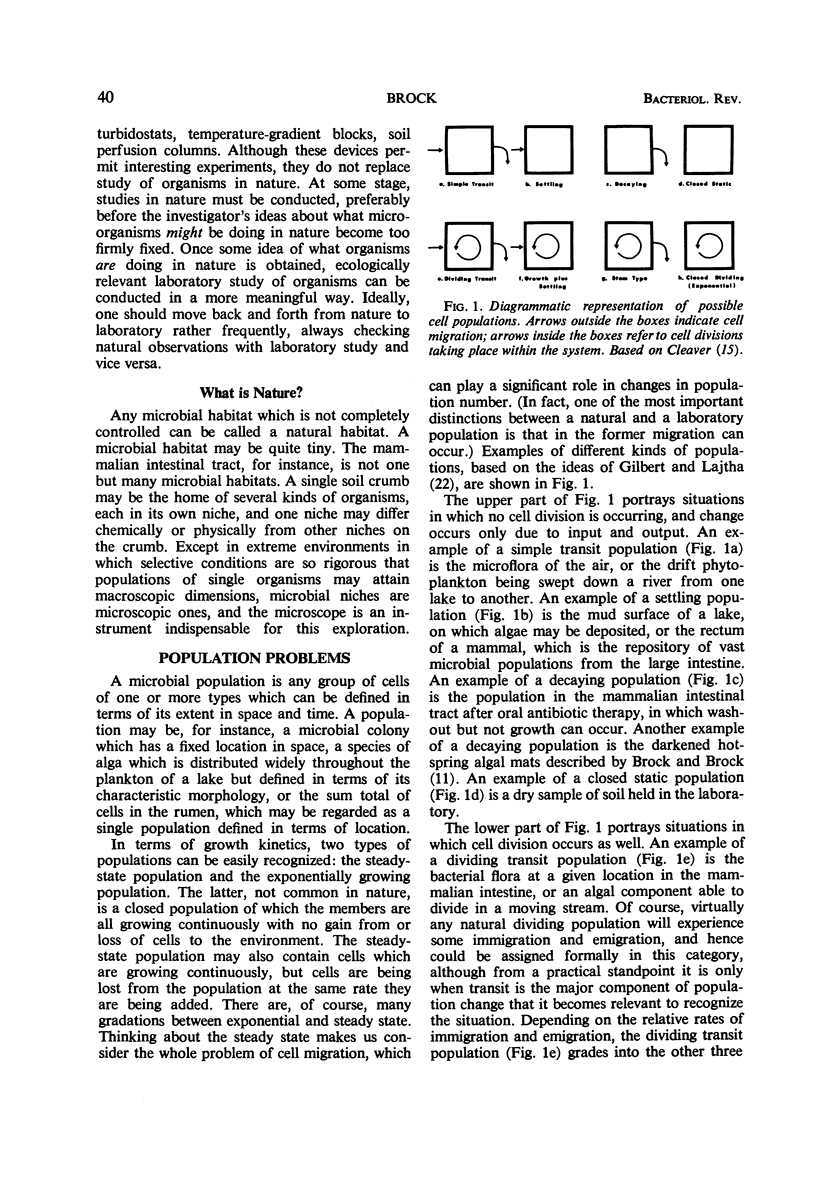


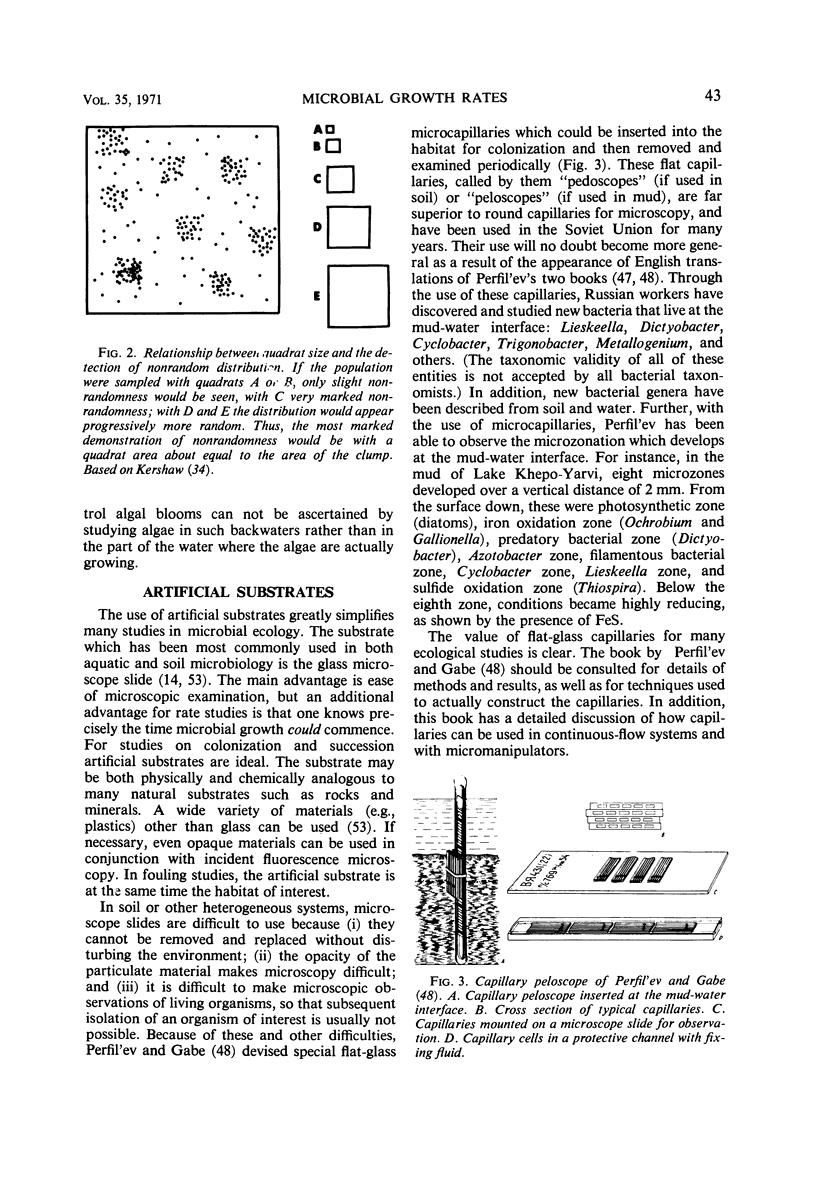



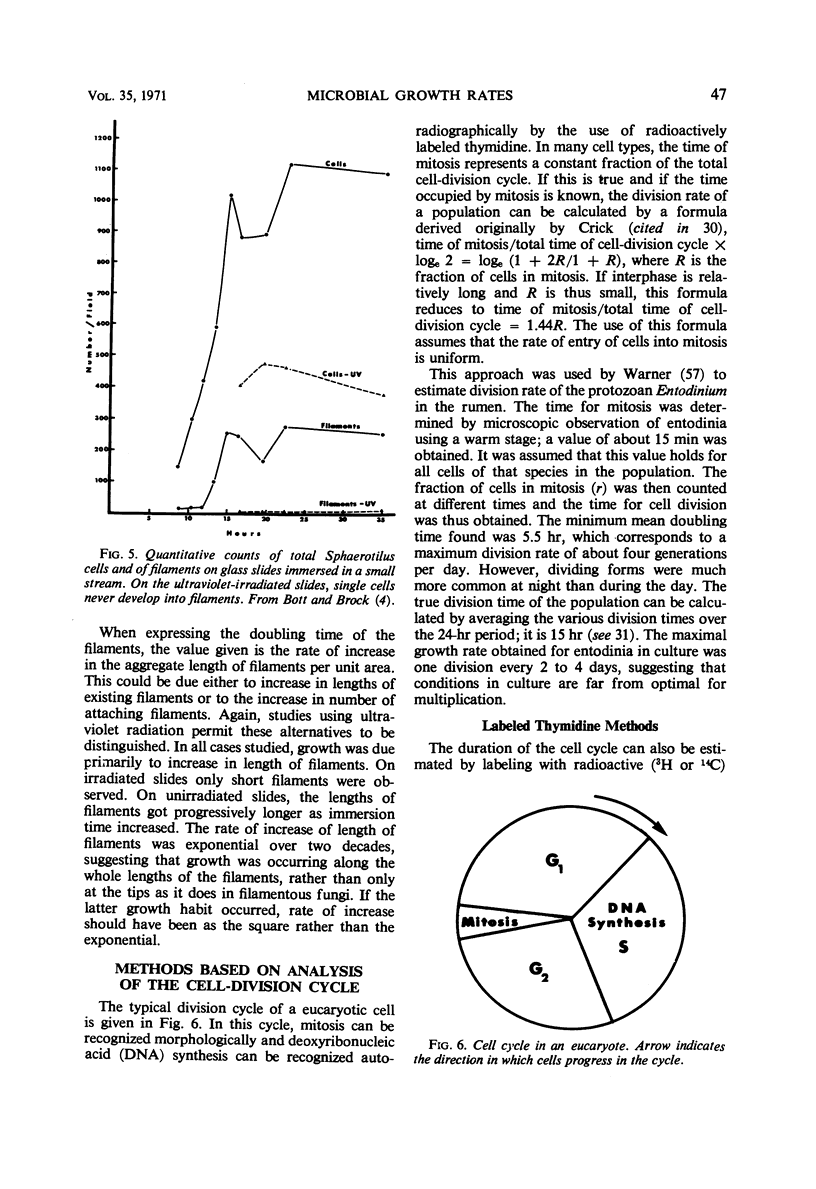
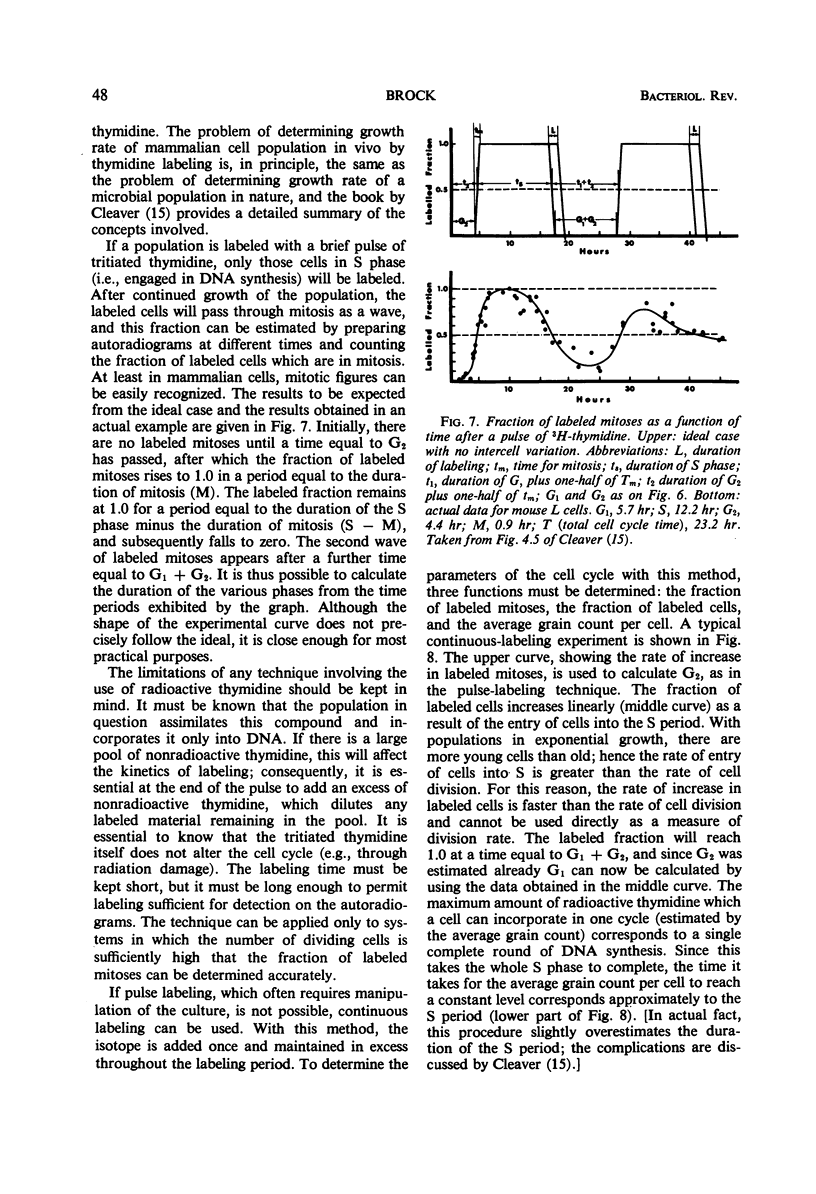







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bott T. L., Brock T. D. Bacterial growth rates above 90 degrees C in Yellowstone hot springs. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1411–1412. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott T. L., Brock T. D. Growth rate of Sphaerotilus in a thermally polluted environment. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):100–102. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.100-102.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D. Bacterial growth rate in the sea: direct analysis by thymidine autoradiography. Science. 1967 Jan 6;155(3758):81–83. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3758.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
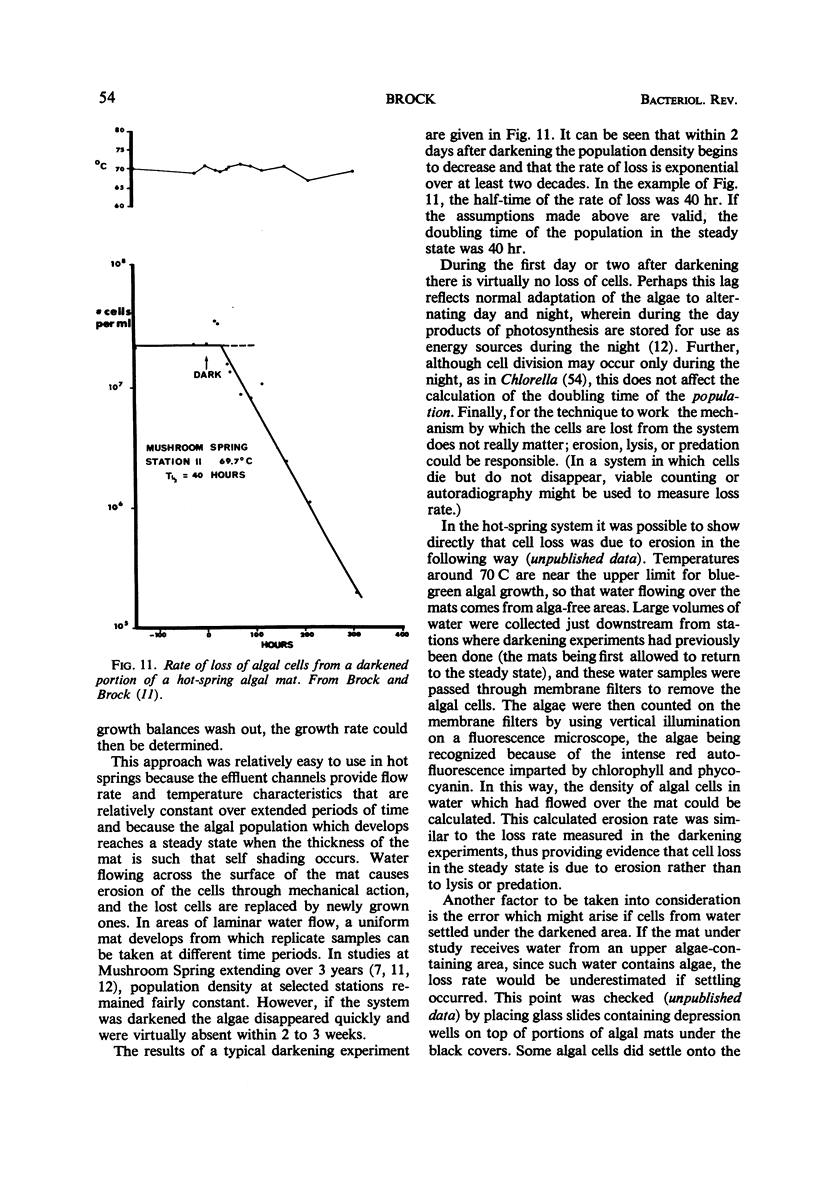
- Brock T. D., Brock M. L. Measurement of steady-state growth rates of a thermophilic alga directly in nature. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):811–815. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.811-815.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D. Mode of filamentous growth of Leucothrix mucor in pure culture and in nature, as studied by tritiated thymidine autoradiography. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):985–990. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.985-990.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casida L. E., Jr Observation of microorganisms in soil and other natural habitats. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Dec;18(6):1065–1071. doi: 10.1128/am.18.6.1065-1071.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EL-SHAZLY K., HUNGATE R. E. FERMENTATION CAPACITY AS A MEASURE OF NET GROWTH OF RUMEN MICROORGANISMS. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Jan;13:62–69. doi: 10.1128/am.13.1.62-69.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Kapsimalis B. Estimates of the overall rate of growth of the intestinal microflora of hamsters, guinea pigs, and mice. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):510–512. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.510-512.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D. F., Cheers C. The steady state in cellular immunity. I. Chemotherapy and superinfection in murine tuberculosis. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1967 Aug;45(4):407–416. doi: 10.1038/icb.1967.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D. F., Cheers C. The steady state in cellular immunity. II. Immunological complaisance in murine pertussis. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1967 Aug;45(4):417–426. doi: 10.1038/icb.1967.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray T. R. Stereoscan electron microscopy of soil microorganisms. Science. 1967 Mar 31;155(3770):1668–1670. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3770.1668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
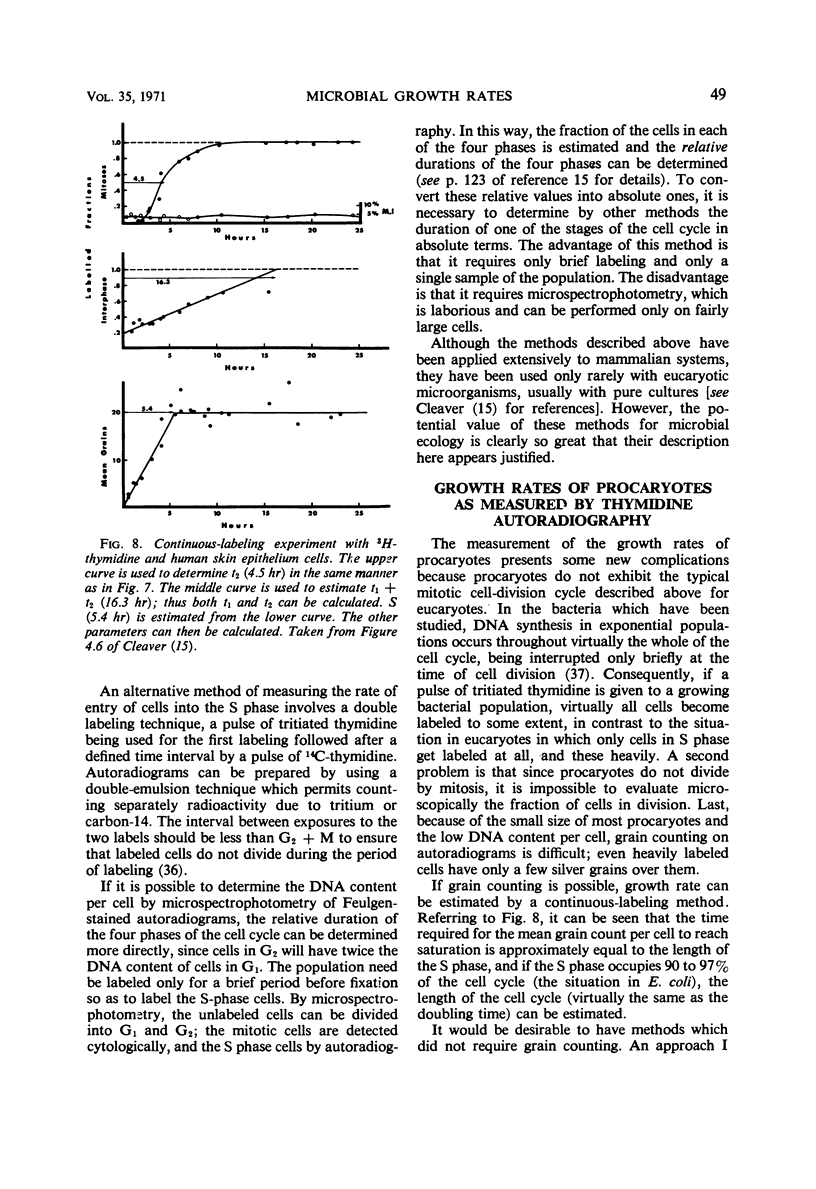
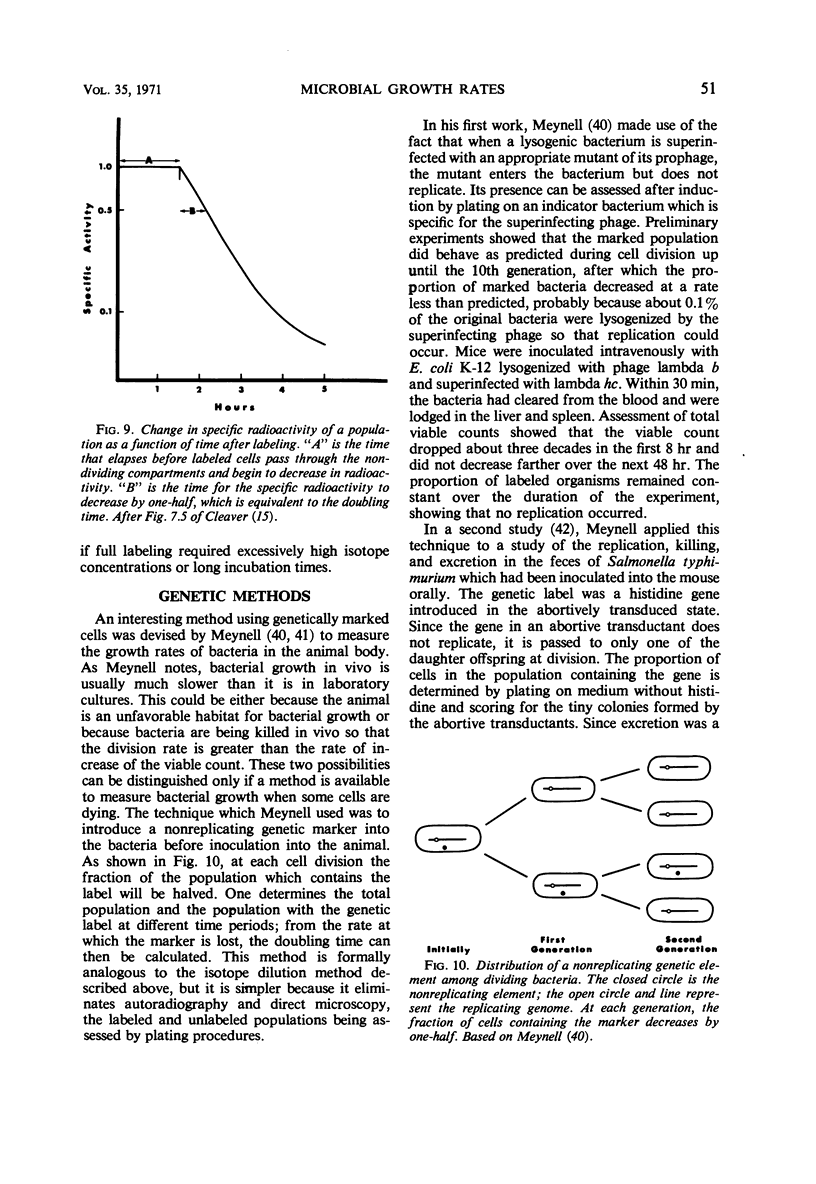
- Helmstetter C. E. Sequence of bacterial reproduction. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:223–238. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T., Brock T. D. Physiological ecology of Leucothrix mucor. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Dec;59(2):153–162. doi: 10.1099/00221287-59-2-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lala P. K. Measurement of S period in growing cell populations by a graphic analysis of double labeling with 3H- and 14C-thymidine. Exp Cell Res. 1968 May;50(2):459–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL G. G., SUBBAIAH T. V. Antibacterial mechanisms of the mouse gut. I. Kinetics of infection by Salmonella typhi-murium in normal and streptomycin-treated mice studied with abortive transductants. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Apr;44:197–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maw J., Meynell G. G. The true division and death rates of Salmonella typhimurium in the mouse spleen determined with superinfecting phage P22. Br J Exp Pathol. 1968 Dec;49(6):597–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POINDEXTER J. S. BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE CAULOBACTER GROUP. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:231–295. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.231-295.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter P. R., Marr A. G. Mathematics of microbial populations. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:519–548. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Dubos R., Schaedler R. W. The gastrointestinal epithelium and its autochthonous bacterial flora. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):67–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. L., Bakole R. O., Bohlool B. B. Fluorescent-antibody approach to study of rhizobia in soil. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):1987–1992. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.1987-1992.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER A. C. Some factors influencing the rumen microbial population. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Apr;28:129–146. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-1-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



