Full text
PDF








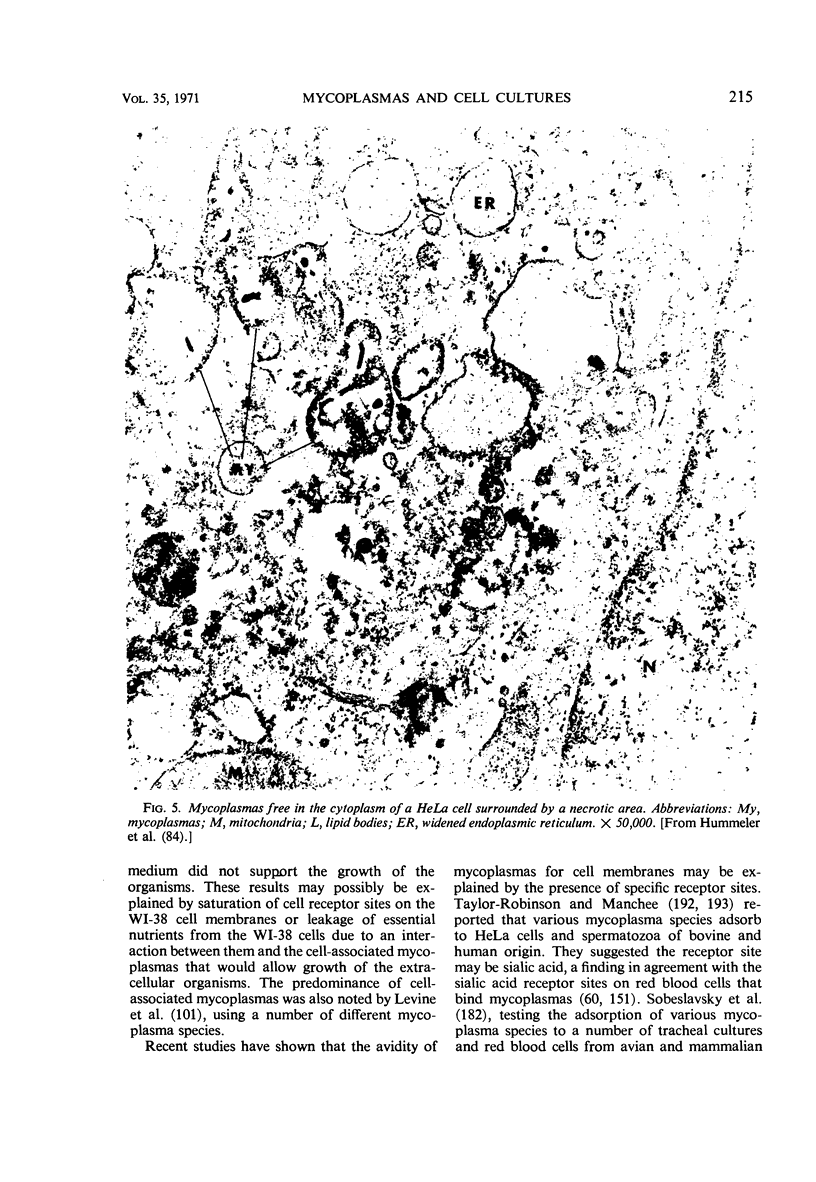












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG D., HENLE G., SOMERSON N. L., HAYFLICK L. CYTOPATHOGENIC MYCOPLASMAS ASSOCIATED WITH TWO HUMAN TUMORS. I. ISOLATION AND BIOLOGICAL ASPECTS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:418–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.418-424.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann W. W., Cox D. C., Kurtz H., Powers C. D., Davies S. J. Effect of poliovirus on deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in HeLa cells. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1943–1952. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1943-1952.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Afshar A. The growth of Mycoplasma bovigenitalium in cell cultures. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Apr;47(1):103–110. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison A. C., Paton G. R. Chromosomal abnormalities in human diploid cells infected with mycoplasma and their possible relevance to the aetiology of Down's syndrome (mongolism). Lancet. 1966 Dec 3;2(7475):1229–1230. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92308-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. R., Hopps H. E., Barile M. F., Bernheim B. C. Comparison of the ultrastructure of several rickettsiae, ornithosis virus, and Mycoplasma in tissue culture. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1387–1404. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1387-1404.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. R., Manaker R. A. Electron microscopic studies of Mycoplasma (PPLO strain 880) in artificial medium and in tissue culture. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1966 Jan;36(1):139–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai S., Yuri Y., Kudo A., Kikuchi M., Kumagai K. Effect of antibiotics on the growth of various strains of Mycoplasma. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1967 Sep;20(5):246–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D., Paucker K. Effect of mycoplasma on interferon production and interferon assay in cell cultures. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.97-101.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aula P., Nichols W. W. The cytogenetic effects of mycoplasma in human leukocyte cultures. J Cell Physiol. 1967 Dec;70(3):281–290. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040700308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARILE M. F., MALIZIA W. F., RIGGS D. B. Incidence and detection of pleuropneumonia-like organisms in cell cultures by fluorescent antibody and cultural procedures. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jul;84:130–136. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.1.130-136.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERG R. B., FROTHINGHAM T. E. Hemadsorption in monkey kidney cell cultures of Mycoplasma (PPLO) recovered from rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Dec;108:616–618. doi: 10.3181/00379727-108-27013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER M., LEACH R. H. A MYCOPLASMA WHICH INDUCES ACIDITY AND CYTOPATHIC EFFECT IN TISSUE CULTURE. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Feb;34:285–294. doi: 10.1099/00221287-34-2-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balduzzi P., Charbonneau R. J. Decontamination of pleuropneumonia-like organism (PPLO) infected tissue cultures. Experientia. 1964 Nov 15;20(11):651–652. doi: 10.1007/BF02144845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barile M. F., Leventhal B. G. Possible mechanism for Mycoplasma inhibition of lymphocyte transformation induced by phytohaemagglutinin. Nature. 1968 Aug 17;219(5155):750–752. doi: 10.1038/219751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barile M. F., Schimke R. T., Riggs D. B. Presence of the arginine dihydrolase pathway in Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):189–192. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.189-192.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard C. W., Anderson D. P. Aerosol studies with avian mycoplasma. I. Survival in the air. Avian Dis. 1967 Feb;11(1):54–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker Y., Olshevsky U., Levitt J. The role of arginine in the replication of herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1967 Oct;1(4):471–478. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-4-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. J., Cover M. S., Melchior F. W. Mycoplasma gallisepticum in a commercial laryngotracheitis vaccine. Avian Dis. 1967 Aug;11(3):426–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskirk H. H. Control of Pleuropneumonia-like Organisms in Cell Culture. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Nov;15(6):1442–1446. doi: 10.1128/am.15.6.1442-1446.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. Isolation and growth of mycoplasma in human embryo trachea cultures. Nature. 1969 Nov 8;224(5219):605–606. doi: 10.1038/224605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANTELL K., PAUCKER K. Studies on viral interference in two lines of HeLa cells. Virology. 1963 Jan;19:81–87. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARSKI T. R., SHEPARD C. C. Pleuropneumonia-like (mycoplasma) infections of tissue culture. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:626–635. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.626-635.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTREJON-DIEZ J., FISHER T. N., FISHER E., Jr Experimental infection of tissue cultures with certain mycoplasma (PPLO). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Mar;112:643–647. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., HAYFLICK L., BARILE M. F. Growth on artificial medium of an agent associated with atypical pneumonia and its identification as a PPLO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:41–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX W. A., D'ARCY P. F. A new cationic antimicrobial agent, N-dodecyl-4-aminoquinaldinium acetate (laurolinium acetate). J Pharm Pharmacol. 1963 Feb;15:129–137. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1963.tb12757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao F. C., Freeman G., Cummings J. G., Berridge B. J., Jr Amino acids of the ornithine cycle in transformed hamster fibroblasts carrying pleuropneumonia-like organisms. Cancer Res. 1967 Aug;27(8):1474–1481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterji J., Beswick T. S., Chapman J. A. Electron microscope observations of rubella virus in tissue culture cells. J Gen Virol. 1969 Apr;4(3):371–377. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-3-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry J. D., Taylor-Robinson D. Large-quantity production of chicken embryo tracheal organ cultures and use in virus and mycoplasma studies. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Apr;19(4):658–662. doi: 10.1128/am.19.4.658-662.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry J. D., Taylor-Robinson D. Peroxide production by mycoplasmas in chicken tracheal organ cultures. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1099–1100. doi: 10.1038/2281099a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G., Somerson N. L. Mycoplasma pneumoniae: hydrogen peroxide secretion and its possible role in virulence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):85–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr, Denny F. W. Biologic effects of Mycoplasma pneumoniae and other mycoplasmas from man on hamster tracheal organ culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Dec;132(3):1153–1158. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copperman R., Morton H. E. Reversible inhibition of mitosis in lymphocyte cultures by non-viable Mycoplasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Dec;123(3):790–795. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. F., Goodman M. R., Chatterji J., Beswick T. S., Chapman J. A. Another case of mistaken identity: rubella and mycoplasma. J Gen Virol. 1970 Jul;8(1):77–81. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-8-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. F., Goodman M. R., Shaw E. J. Detection and treatment of contaminating mycoplasmas in cell culture. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1967 Apr;45(2):201–212. doi: 10.1038/icb.1967.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M., Thomas L. Effect of gold on Mycoplasma. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1966;6:312–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS G. A., FOGH J. Fine structure of pleuropneumonia-like organisms in pure culture and in infected tissue culture cells. J Bacteriol. 1960 Feb;79:267–276. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.2.267-276.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FABRICANT C. G., FABRICANT J., VANDEMARK P. J. STUDIES ON THE NUTRITION AND GROWTH REQUIREMENTS OF MYCOPLASMA GALLISEPTICUM. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Apr;35:135–144. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALLON R. J., GRIST N. R., INMAN D. R., LEMCKE R. M., NEGRONI G., WOODS D. A. Further studies of agents isolated from tissue cultures inoculated with human leukaemic bone-marrow. Br Med J. 1965 Aug 14;2(5458):388–391. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOGH J., FOGH H. A METHOD FOR DIRECT DEMONSTRATION OF PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS IN CULTURED CELLS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Dec;117:899–901. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOGH J., FOGH H. CHROMOSOME CHANGES IN PPLO-INFECTED FL HUMAN AMNION CELLS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 May;119:233–238. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOGH J., HACKER C. Elimination of pleuropneumonia-like organisms from cell cultures. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Oct;21:242–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDKIN M., ROBERTS D. The enzymatic synthesis of nucleosides. II. Thymidine and related pyrimidine nucleosides. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):257–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher R. D., Milligan W. H., 3rd, Albertson J. N., Jr Contributing factor to Mycoplasma pneumoniae produced stimulation of rhinovirus-RNA synthesis. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1970;15(5):325–329. doi: 10.1007/BF02880097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogh J., Fogh H. Morphological and quantitative aspects of mycoplasma-human cell relationships. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jun;125(2):423–430. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogh J., Hahn E., 3rd, Fogh H. Effects of pleuropneumonia-like organisms on cultured human cells. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Sep;39(2):554–566. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogh J. Mycoplasma effects on SV40 transformation of human amnion cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 May;134(1):217–224. doi: 10.3181/00379727-134-34763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed J. J., Schatz S. A. Chromosome aberrations in cultured cells deprived of single essential amino acids. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Jun;55(3):393–409. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90574-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Patuleia M. C., Nelson J. B. Antibiotic effect of tylosin on a mycoplasma contaminant in a tissue culture leukemia cell line. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Apr;121(4):1009–1010. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODWIN R. F., WHITTLESTONE P. Production of enzootic pneumonia in pigs with an agent grown in tissue culture from the natural disease. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Jun;44:291–299. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORI G. B., LEE D. Y. A METHOD FOR ERADICATION OF MYCOPLASMA INFECTIONS IN CELL CULTURES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Dec;117:918–921. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIST N. R., MATTHEW H. ISOLATION OF VIRUSES FROM LEUKAEMIC PATIENTS. Br Med J. 1964 Nov 14;2(5419):1263–1264. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5419.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafford L. G., Sinclair F., Randall C. C. Growth cycle of fowlpox virus and change in plaque morphology and cytopathology by contaminating mycoplasma. Virology. 1969 Mar;37(3):464–472. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90230-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesner B., Thomas L. Sialic acid binding sites: role in hemagglutination by Mycoplasma gallisepticum. Science. 1966 Feb 4;151(3710):590–591. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3710.590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardi A. J., Hamparian V. V., Somerson N. L., Hayflick L. Mycoplasma isolates from primary cell cultures and human diploid cell strains. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Dec;120(3):760–770. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum N., Ravid Z., Becker Y. Effect of withdrawal of arginine and other amino acids on the synthesis of tumour and viral antigens of SV 40 virus. J Gen Virol. 1968 Jul;3(1):143–146. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-1-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKALA M. T., HOLLAND J. F., HOROSZEWICZ J. S. Change in pyrimidine deoxyribonucleoside metabolism in cell culture caused by Mycoplasma (PPLO) contamination. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Jun 20;11:466–471. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYFLICK L. Decontaminating tissue cultures infected with pleuropneumonia-like organisms. Nature. 1960 Mar 12;185:783–784. doi: 10.1038/185783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYFLICK L., STINEBRING W. R. Intracellular growth of pleuropneumonialike organisms (PPLO) in tissue culture and in ovo. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:433–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYFLICK L. THE LIMITED IN VITRO LIFETIME OF HUMAN DIPLOID CELL STRAINS. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Mar;37:614–636. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERDERSCHEE D., RUYS A. C., VAN RHIJNG PLEUROPNEUMONIALIKE ORGANISMS IN TISSUE CULTURES. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1963;29:368–376. doi: 10.1007/BF02046089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOOSER L. E., DAVIS E. V., MOORE M. L., SIEM R. A. ELIMINATION OF PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS FROM EMBRYONIC HUMAN LUNG TISSUE CULTURE WITH TETRACYCLINE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:237–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.237-237.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMELER K., ARMSTRONG D., TOMASSINI N. CYTOPATHOGENIC MYCOPLASMAS ASSOCIATED WITH TWO HUMAN TUMORS. II. MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECTS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:511–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.511-516.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. H., Mittelman A., Horoszewicz J., Grace J. T., Jr The RNA of Mycoplasma--880. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):799–800. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves F. D., Leach R. H. The influence of mycoplasma infection on the sensitivity of HeLa cells for growth of viruses. J Med Microbiol. 1970 May;3(2):259–265. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-2-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley E. H., Rees K. R., Cohen A. HeLa cell nucleic acid metabolism. The effect of Mycoplasma contamination. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 16;213(1):171–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwick H. J., Fekety F. R., Jr The antibiotic susceptibility of Mycoplasma hominis. J Clin Pathol. 1969 Jul;22(4):483–485. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.4.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L., Stanbridge E. Isolation and identification of mycoplasma from human clinical materials. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):608–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heneen W. K., Nichols W. W. Cell morphology of a human diploid cell strain (WI-38) after treatment with arabinosylcytosine. Cancer Res. 1967 Feb;27(2):242–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. F., Korn R., O'Malley J., Minnemeyer H. J., Tieckelmann H. 5-allyl-2'-deoxyuridine inhibition of nucleoside phosphorylase in HeLa cells containing mycoplasma. Cancer Res. 1967 Oct;27(10):1867–1873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House W., Waddell A. Detection of mycoplasma in cell cultures. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):125–132. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummeler K., Armstrong D. Observations on mycoplasma strains in tissue cultures. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):622–625. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INMAN D. R., WOODS D. A., NEGRONI G. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF VIRUS PARTICLES IN CELL CULTURES INOCULATED WITH PASSAGE FLUID FROM HUMAN LEUKAEMIC BONE-MARROW. Br Med J. 1964 Apr 11;1(5388):929–931. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5388.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jao R. L. Susceptibility of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to 21 antibiotics in vitro. Am J Med Sci. 1967 Jun;253(6):639–650. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196706000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jézéquel A. M., Shreeve M. M., Steiner J. W. Segregation of nucleolar components in mycoplasma-infected cells. Lab Invest. 1967 Feb;16(2):287–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNY G. E., POLLOCK M. E. Mammalian cell cultures contaminated with pleuropneumonia-like organisms. I. Effect of pleuropneumonia-like organisms on growth of established cell strains. J Infect Dis. 1963 Jan-Feb;112:7–16. doi: 10.1093/infdis/112.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAEMER P. M., DEFENDI V., HAYFLICK L., MANSON L. A. Mycoplasma (PPLO) strains with lytic activity for murine lymphoma cells in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Feb;112:381–387. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAEMER P. M. INTERACTION OF MYCOPLASMA (PPLO) AND MURINE LYMPHOMA CELL CULTURES: PREVENTION OF CELL LYSIS BY ARGININE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jan;115:206–212. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-28871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAEMER P. M. MYCOPLASMA (PPLO) FROM COVERTLY CONTAMINATED TISSUE CULTURES: DIFFERENCES IN ARGININE DEGRADATION BETWEEN STRAINS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Dec;117:910–918. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan G. Y. The results of some comparative experimental investigations of L-forms of bacteria and mycoplasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):734–748. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan R. Ia, Ershov F. I., Rakovskaia I. V., Tsareva A. A., Zhdanov V. M. Vliianie mikoplazma-infektsii na reproduktsiiu nekotorykh RNKsoderzhashchikh virusov. Vopr Virusol. 1967 Jul-Aug;12(4):478–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaklamanis E., Thomas L., Stavropoulos K., Borman I., Boshwitz C. Mycoplasmacidal action of normal tissue extracts. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):860–862. doi: 10.1038/221860b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingery F. A. When an ear nodule hurts. JAMA. 1966 Jul 11;197(2):137–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundsin R. B. Aerosols of mycoplasmas, L forms, and bacteria: comparison of particle size, viability, and lethality of ultraviolet radiation. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jan;16(1):143–146. doi: 10.1128/am.16.1.143-146.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMPEN J. O., GILL J. W., ARNOW P. M., MAGANA-PLAZA I. INHIBITION OF THE PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM MYCOPLASMA GALLISEPTICUM BY CERTAIN POLYENE ANTIFUNGAL ANTIBIOTICS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Nov;86:945–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.5.945-949.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larin N. M., Saxby N. V., Buggey D. Quantitative aspects of Mycoplasma pneumoniae-cell relationships in cultures of lung diploid fibroblasts. J Hyg (Lond) 1969 Sep;67(3):375–385. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400041796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larin N. M., Saxby N. V., Williamson G. M., Buggey D., Kenwright N. S. In vitro susceptibility of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to tetracyclines. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:680–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine E. M., Burleigh I. G., Boone C. W., Eagle H. An altered pattern of RNA synthesis in serially propagated human diploid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):431–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine E. M., Thomas L., McGregor D., Hayflick L., Eagle H. Altered nucleic acid metabolism in human cell cultures infected with mycoplasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):583–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman R. P., Clyde W. A., Jr The interrelationship of virulence, cytadsorption, and peroxide formation in Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Sep;131(4):1163–1167. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-34061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I. A., ALLNER K. L forms of bacteria as contaminants in tissue culture. Nature. 1960 Jun 18;186:992–992. doi: 10.1038/186992a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMION B. P., GOODBURN G. M. Effect of an organic gold salt on Eaton's primary atypical pneumonia agent and other observations. Nature. 1961 Jan 21;189:247–248. doi: 10.1038/189247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE G. E., MOUNT D., TARA G., SCHWARTZ N. GROWTH OF HUMAN TUMOR CELLS IN SUSPENSION CULTURES. Cancer Res. 1963 Dec;23:1735–1741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson I., Russell W. Transformations in hamster cells mediated by mycoplasmas. Nature. 1966 Jun 25;210(5043):1343–1345. doi: 10.1038/2101343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhavan H. N., Sharma K. B. Studies on mycobacteria isolated in Pondicherry. Indian J Chest Dis. 1969 Oct;11(4):196–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manchee R. J., Taylor-Robinson D. Studies on the nature of receptors involved in attachment of tissue culture cells to mycoplasmas. Br J Exp Pathol. 1969 Feb;50(1):66–75. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham J. G., Markham N. P. Mycoplasma laidlawii in human burns. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):827–828. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.827-828.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markov G. G., Bradvarova I., Mintcheva A., Petrov P., Shishkov N., Tsanev R. G. Mycoplasma contamination of cell cultures: interference with 32P-labelling pattern of RNA. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Oct;57(2):374–384. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90163-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzali R., Taylor-Robinson D. The behaviour of T-mycoplasmas in tissue culture. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Feb;4(1):125–138. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-1-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan W. H., 3rd, Fletcher R. D. Effect of Mycoplasma pneumoniae on rhinovirus ribonucleic acid synthesis in KB cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1969;9:196–199. doi: 10.1128/AAC.9.1.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morowitz H. J., Tourtellotte M. E., Pollack M. E. USE OF POROUS CELLULOSE ESTER MEMBRANES IN THE PRIMARY ISOLATION AND SIZE DETERMINATION OF PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85(1):134–136. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.134-136.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEGRONI G. ISOLATION OF VIRUSES FROM LEUKAEMIC PATIENTS. Br Med J. 1964 Apr 11;1(5388):927–929. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5388.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIMARK H. DEOXYRIBONUCLEASE ACTIVITY FROM 'LACTIC ACID PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS'. Nature. 1964 Aug 1;203:549–550. doi: 10.1038/203549b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWNHAM A. G., CHU H. P. AN IN VITRO COMPARISON OF THE EFFECT OF SOME ANTIBACTERIAL, ANTIFUNGAL AND ANTIPROTOZOAL AGENTS ON VARIOUS STRAINS OF MYCOPLASMA (PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS: P.P.L.O.). J Hyg (Lond) 1965 Mar;63:1–23. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400044922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardone R. M., Todd J., Gonzalez P., Gaffney E. V. Nucleoside incorporation into strain L cells: inhibition by pleuropneumonia-like organisms. Science. 1965 Sep 3;149(3688):1100–1101. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3688.1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufahrt A., Rolly H., Schütze E. Einfluss von Mykoplasmen auf die antivirale Wirkung von 5-Joduracil-desoxyribosid (JUdR) Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1969;209(4):470–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'CONNELL R. C., WITTLER R. G., FABER J. E. AEROSOLS AS A SOURCE OF WIDESPREAD MYCOPLASMA CONTAMINATION OF TISSUE CULTURES. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:337–342. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.337-342.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'MALLEY J. P., MEYER H. M., Jr, SMADEL J. E. Antibody in hepatitis patients against a newly isolated virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Oct;108:200–205. doi: 10.3181/00379727-108-26891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley J. P., McGee Z. A., Barile M. F., Barker L. F. Identification of the A-1 agent as Mycoplasma gallisepticum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):895–901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Koshimizu K. Isolation of Mycoplasmas from tissue cell lines and transplantable tumor cells. Jpn J Microbiol. 1967 Dec;11(4):289–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1967.tb00347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. E., KENNY G. E. Mammalian cell cultures contaminated with PPLO III. Elimination of PPLO with specific antiserum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Jan;112:176–181. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-27985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. E., KENNY G. E., SYVERTON J. T. Isolation and elimination of pleuropneumonia-like organisms from mammalian cell cultures. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Oct;105:10–15. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-25992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. E., TREADWELL P. E., KENNY G. E. MAMMALIAN CELL CULTURES CONTAMINATED WITH PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS. II. EFFECT OF PPLO ON CELL MORPHOLOGY IN ESTABLISHED MONOLAYER CULTURES. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Aug;31:321–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELSON D. M. Metabolism of animal cells infected with mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1961 Aug;82:288–297. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.2.288-297.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton G. R., Allison A. C. Chromosome breakage by deoxyribonuclease. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):707–708. doi: 10.1038/227707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton G. R., Jacobs J. P., Perkins F. T. Chromosome changes in human diploid-cell cultures infected with Mycoplasma. Nature. 1965 Jul 3;207(992):43–45. doi: 10.1038/207043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton G., Jacobs J. P., Perkins F. T. The effect of mycoplasma on the karyology of normal cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):626–627. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Rahman S. B., Semar J. B. Antibiotic control of Mycoplasma in tissue culture. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jan;15(1):82–85. doi: 10.1128/am.15.1.82-85.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. D., Razin S., Cleverdon R. C. Localization of Enzymes in Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1965 Sep;90(3):617–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.3.617-622.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDALL C. C., WALKER B. M. DEGRADATION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID AND ALTERATION NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM IN SUSPENSION CULTURES OF L-M CELLS INFECTED WITH EQUINE ABORTION VIRUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:138–146. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.138-146.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., COHEN A. Nutritional requirements and metabolism of Mycoplasma laidlawii. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jan;30:141–154. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-1-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., KNIGHT B. C. A partially defined medium for the growth of Mycoplasma. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Apr;22:492–503. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-2-492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., KNIGHT B. C. The effects of ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid on the growth of Myeoplasma. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Apr;22:504–519. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-2-504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., KNYSZYNSKI A., LIFSHITZ Y. NUCLEASES OF MYCOPLASMA. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Aug;36:323–332. doi: 10.1099/00221287-36-2-323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., MICHMANN J., SHIMSHONI Z. THE OCCURRENCE OF MYCOPLASMA (PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS, PPLO) IN THE ORAL CAVITY OF DENTULOUS AND EDENTULOUS SUBJECTS. J Dent Res. 1964 May-Jun;43:402–405. doi: 10.1177/00220345640430031101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S. Nucleic acid precursor requirements of Mycoplasma laidlawii. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jun;28:243–250. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON L. B., WICHELHAUSEN R. H. Contamination of human cell cultures by pleuropneumonialike organisms. Science. 1956 Dec 7;124(3232):1147–1148. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3232.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHBLAT G. H., MORTON H. E. Detection and possible source of contaminating pleuropneumonialike organisms (PPLO) in cultures of tissue cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jan;100(1):87–90. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHBLAT G. H. PPLO contamination in tissue cultures. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:430–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42708.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman S. B., Semar J. B., Perlman D. Antibiotic resistance in Mycoplasma isolates from tissue cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jul;15(4):970–970. doi: 10.1128/am.15.4.970-.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall C. C., Gafford L. G., Gentry G. A., Lawson L. A. Lability of host-cell DNA in growing cell cultures due to Mycoplasma. Science. 1965 Sep 3;149(3688):1098–1099. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3688.1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Structure and function in mycoplasma. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:317–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R. K., Hetrick F. M. Potential use of surface-active agents for controlling Mycoplasma contamination in animal cell cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Mar;17(3):405–411. doi: 10.1128/am.17.3.405-411.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano N., Brancato P. Inhibition of growth of measles virus by mycoplasma in cell-cultures and the restoring effect of arginine. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;29(1):39–43. doi: 10.1007/BF01253878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Pfendt E. A., Hayflick L. Sterol requirements of T-strain mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):323–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.323-330.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse H. C., Schlesinger R. W. An arginine-dependent step in the maturation of type 2 adenovirus. Virology. 1967 Nov;33(3):513–522. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. C., Becker Y. A maturation factor for adenovirus. Virology. 1968 May;35(1):18–27. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90301-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. C., Niven J. S., Berman L. D. Studies on the biology of the mycoplasma-induced "stimulation" of BHK21-C13 cells. Int J Cancer. 1968 Mar 15;3(2):191–202. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910030204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T., BARILE M. F. ARGININE METABOLISM IN PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS ISOLATED FROM MAMMALIAN CELL CULTURE. J Bacteriol. 1963 Aug;86:195–206. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.2.195-206.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T., BARILE M. F. Arginine breakdown in mammalian cell culture contaminated with pleuropneumonia-like organisms (PPLO). Exp Cell Res. 1963 May;30:593–596. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPARD M. C. Growth and development of T strain pleuropneumonia-like organisms in human epidermoid carcinoma cells (HeLa). J Bacteriol. 1958 Mar;75(3):351–355. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.3.351-355.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F. Amino acid metabolism by pleuropneumonialike organisms. I. General catabolism. J Bacteriol. 1955 Nov;70(5):552–556. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.5.552-556.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F. Amino acid metabolism of PPLO. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:543–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOMERSON N. L., COOK M. K. SUPPRESSION OF ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS GROWTH IN TISSUE CULTURES BY MYCOPLASMA ORALE. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:534–540. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.534-540.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B. Nature and source of mycoplasma in various tissue cultures. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):628–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27708.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Berlin C. M., Sweeney E. W., Carroll W. R. The generation of energy by the arginine dihydrolase pathway in Mycoplasma hominis 07. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2228–2236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Studies on the metabolism of arginine by Mycoplasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):573–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer H., Witzleb W., Blumöhr T. Zur Kontamination von Gewebekulturen mit Mykoplasmen. 3. Eliminierung von Mykoplasmen aus kontaminierten Gewebekulturen. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;30(2):130–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shedden W. I., Cole B. C. Rapid method for demonstrating intracellular pleuropneumonia-like organisms in a strain of hamster kidney cells (BHK 21 C13). Nature. 1966 May 21;210(5038):868–868. doi: 10.1038/210868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shedden W. I., Cole B. C. The use of sodium aurothiomalate in the eradication of pleuropneumonia-like organisms (PPLO) from a chronically infected strain of hamster kidney cells (BHK 21 C13). J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(2):574–576. doi: 10.1002/path.1700920238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard M. C., Lunceford C. D. Occurrence of urease in T strains of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1513–1520. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1513-1520.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simberkoff M. S., Thorbecke G. J., Thomas L. Studies of PPLO infection. V. Inhibition of lymphocyte mitosis and antibody formation by mycoplasmal extracts. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1163–1181. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. H., Barile M. F., Kirschstein R. L. Enhanced virus yields and decreased interferon production in mycoplasma-infected hamster cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Sep;131(4):1129–1134. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-34053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. H., Fitzgerald E. A., Barile M. F., Kirschstein R. L. Effect of mycoplasmas on vaccinia virus growth: requirement for arginine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Apr;133(4):1439–1442. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S., Kirschstein R. L., Barile M. F. Increased yields of stomatitis virus from hamster cells injected with mycoplasma. Nature. 1969 Jun 14;222(5198):1087–1088. doi: 10.1038/2221087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotkin R. I., Clyde W. A., Jr, Denny F. W. The effect of antibiotics on Mycoplasma pneumoniae in vitro and in vivo. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Jul;86(1):225–237. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Friedewald W. T., Chanock R. M. Shedding of Mycoplasma pneumoniae after tetracycline and erythromycin therapy. N Engl J Med. 1967 May 25;276(21):1172–1175. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196705252762103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobeslavsky O., Chanock R. M. Peroxide formation by mycoplasmas which infect man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Nov;129(2):531–535. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobeslavsky O., Prescott B., Chanock R. M. Adsorption of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to neuraminic acid receptors of various cells and possible role in virulence. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):695–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.695-705.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitler L., Cochrum K., Fudenberg H. H. Mycoplasma inhibition of phytohemagglutinin stimulation of lymphocytes. Science. 1967 Sep 13;161(3846):1148–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E., Onen M., Perkins F. T., Hayflick L. Karyological and morphological characteristics of human diploid cell strain WI-38 infected with mycoplasmas. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Oct;57(2):397–410. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. M., Burnet M. E., Young J. E. In-vitro sensitivity of strains of mycoplasmas from human sources to antibiotics and to sodium aurothiomalate and tylosin tartrate. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Aug;2(3):287–292. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-3-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock D. A., Gentry G. A. Mycoplasmal deoxyribonuclease activity in virus-infected L-cell cultures. J Virol. 1969 Mar;3(3):313–317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.3.313-317.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANKERSLEY R. W., Jr AMINO ACID REQUIREMENTS OF HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS IN HUMAN CELLS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:609–613. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.609-613.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Manchee R. J. Novel approach to studying relationships between mycoplasmas and tissue culture cells. Nature. 1967 Dec 30;216(5122):1306–1307. doi: 10.1038/2161306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Manchee R. J. Spermadsorption and spermagglutination by mycoplasmas. Nature. 1967 Jul 29;215(5100):484–487. doi: 10.1038/215484a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Aaronson S. A., Rands E. Rapid detection of mycoplasma-infected cell cultures. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Mar;65(1):256–257. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(71)80077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G. Mycoplasma granularum of swine origin as a tissue culture contaminant. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jun;122(2):565–568. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Razin S. Acholeplasma axanthum, sp. n.: a new sterol-nonrequiring member of the Mycoplasmatales. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):751–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.751-754.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Razin S. Characteristics of a new sterol-nonrequiring Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):970–978. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.970-978.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelzang A. A., Compeer-Dekker G. Elimination of mycoplasma from various cell cultures. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(4):393–408. doi: 10.1007/BF02219158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzleb W., Blumöhr T., Dziambor H., Schweizer H. Zur Kontamination von Gewebekulturen mit Mykoplasmen. II. Nachweis und serologische Identifizierung der Mykoplasmen. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;30(2):121–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzleb W. Zur Kontamination von Gewebekulturen mit Mykoplasmen. I. Beeinträchtigung der Zellphysiologie und die Auswirkungen auf die virologische Diagnostik. (Literaturübersicht) Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;30(2):113–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. N., Bailey G. D., Goldberg L. J. Effect of temperature on survival of airborne Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):491–495. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.491-495.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yershov F. I., Zhdanov V. M. Influence of PPLO on production of interferon in virus-infected cells. Virology. 1965 Nov;27(3):451–453. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90132-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zgorniak-Nowosielska I., Sedwick W. D., Hummeler K., Koprowski H. New assay procedure for separation of mycoplasmas from virus pools and tissue culture systems. J Virol. 1967 Dec;1(6):1227–1237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.6.1227-1237.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D., Davidson M., Thomas L. The interaction of mycoplasmas with mammalian cells. I. HeLa cells, neutrophils, and eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):521–532. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D., Davidson M., Thomas L. The interaction of mycoplasmas with mammalian cells. II. Monocytes and lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):533–542. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









