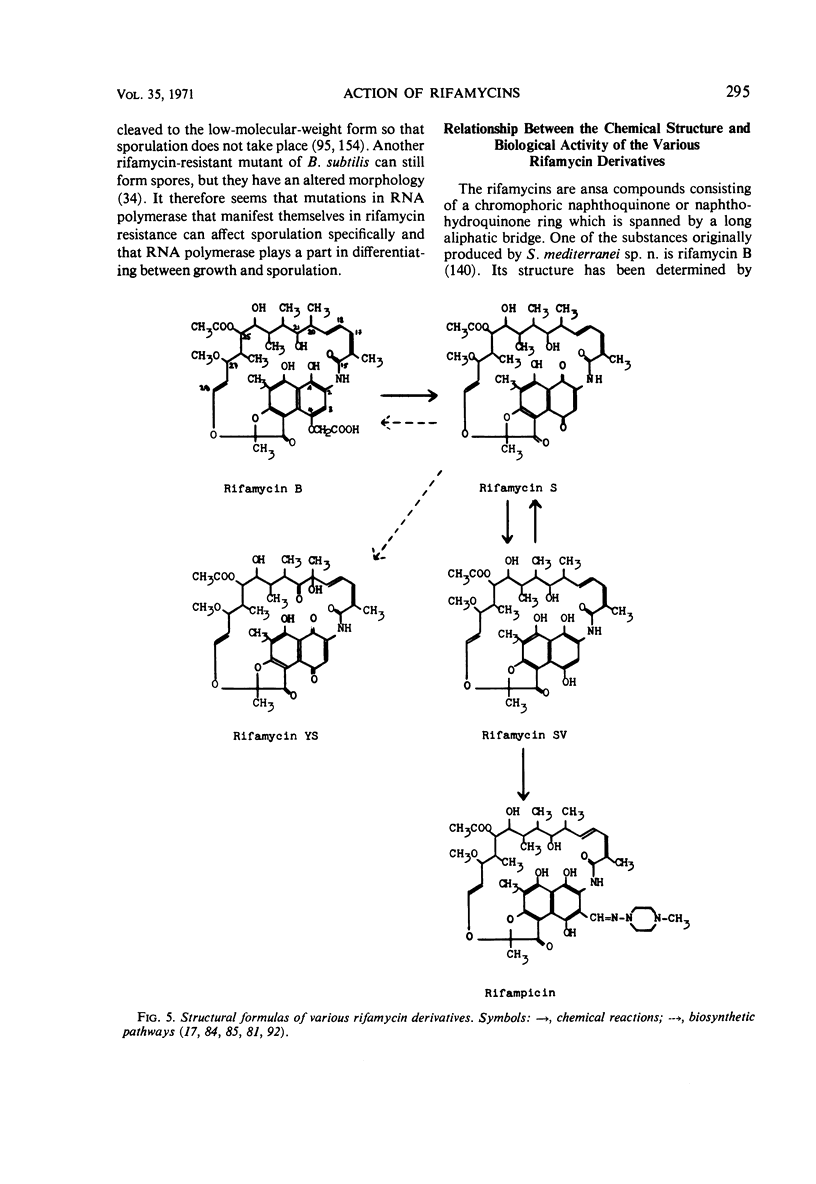
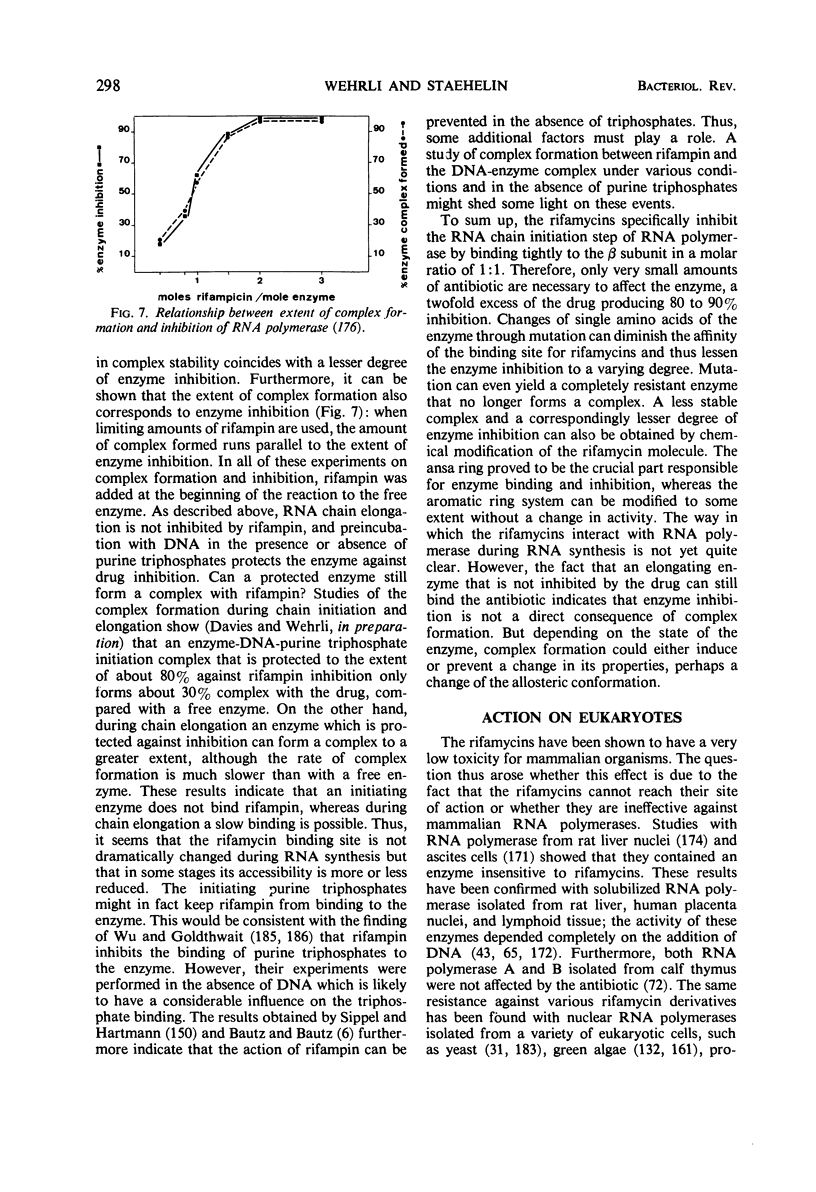
Full text
PDF

















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arioli V., Pallanza R., Furesz S., Carniti G. Rifampicin: a new rifamycin. I. Bacteriological studies. Arzneimittelforschung. 1967 May;17(5):523–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin S., Scaife J. A new method for selecting RNA polymerase mutants. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 14;49(1):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90394-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1209–1211. doi: 10.1038/2261209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandle E., Weissmann C. Rifampicin and the replication of the RNA-containing bacteriophage Q-beta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 18;199(2):551–553. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90105-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautz E. K., Bautz F. A. Initiation of RNA synthesis: the function of sigma in the binding of RNA polymerase to promoter sites. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1219–1222. doi: 10.1038/2261219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker Y., Asher Y., Himmel N., Zakay-Rones Z. Anti-trachoma activity of rifampicin and rifamycin SV derivatives. Nature. 1970 Jan 31;225(5231):454–455. doi: 10.1038/225454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker Y., Asher Y., Himmel N., Zakay-Rones Z., Maythar B. Rifapicin inhibition of trachoma agent in vivo. Nature. 1969 Oct 4;224(5214):33–34. doi: 10.1038/224033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker Y., Zakay-Rones Z. Rifampicin--a new antitrachoma drug. Nature. 1969 May 31;222(5196):851–853. doi: 10.1038/222851a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeuwkes H., Buytendijk H. J., Maesen F. P. Der Wert des Rifampicin bei der Behandlung von Patienten mit bronchopulmon-ären Affektionen. Eine klinisch-bakteriologische Studie. Arzneimittelforschung. 1969 Aug;19(8):1283–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ishai Z., Heller E., Goldblum N., Becker Y. Rifampicin and poxvirus replication. Nature. 1969 Oct 4;224(5214):29–32. doi: 10.1038/224029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergamini N., Fowst G. Rifamycin SV. A review. Arzneimittelforschung. 1965 Aug;15(8 Suppl):951–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickel H., Knüsel F., Kump W., Neipp L. New derivatives of rifamycin antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1966;6:352–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bread N. S., Jr, Armentrout S. A., Weisberger A. S. Inhibition of mammalian protein synthesis by antibiotics. Pharmacol Rev. 1969 Sep;21(3):213–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brufani M., Fedeli W., Giacomello G., Vaciago A. The x-ray analysis of the structure of rifamycin B. Experientia. 1964 Jun 15;20(6):339–342. doi: 10.1007/BF02171085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brufani M., Fedeli W., Giacomello G., Vaciago A. The x-ray analysis of the structure of rifamycin Y. Experientia. 1967 Jul 15;23(7):508–512. doi: 10.1007/BF02137935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Travers A. A., Dunn J. J., Bautz E. K. Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Jan 4;221(5175):43–46. doi: 10.1038/221043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byfield J. E., Lee Y. C., Bennett L. R. Similarity of Tetrahymeana and mammalian RNA polymerases based on rifampicin resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 15;204(2):610–613. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvori C., Frontali L., Leoni L., Tecce G. Effect of rifamycin on protein synthesis. Nature. 1965 Jul 24;207(995):417–418. doi: 10.1038/207417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canetti G., Le Lirzin M., Porven G., Rist N., Grumbach F. Some comparative aspects of rifampicin and isoniazid. Tubercle. 1968 Dec;49(4):367–376. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(68)80017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassani G., Burgess R. R., Goodman H. M., Gold L. Inhibition of RNA polymerase by streptolydigin. Nat New Biol. 1971 Apr 14;230(15):197–200. doi: 10.1038/newbio230197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M., McGrath J., Waskell L. New RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T7. Nature. 1970 Oct 17;228(5268):227–231. doi: 10.1038/228227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelala C. A., Hirschbein L., Torres H. N. Interconvertible forms of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):152–154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J., Wallace A. The susceptibility of mycobacteria to rifamide and rifampicin. Tubercle. 1967 Jun;48(2):144–148. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(67)80009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo F., Fiume L., La Placa M., Mannini-Palenzona A., Novello F., Stirpe F. Ribonucleic acid polymerase induced by vaccinia virus: lack of inhibition by rifampicin and alpha-amanitin. J Virol. 1970 Feb;5(2):266–269. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.2.266-269.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mattia R. Tavola rotonda sulla rifampicina. Torino, 18 dicembre 1968. Minerva Med. 1969 Dec 1;60(96):4781–4782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBoer C., Meulman P. A., Wnuk R. J., Peterson D. H. Geldanamycin, a new antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Sep;23(9):442–447. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deal W. B., Sanders E. Efficacy of rifampin in treatment of meningococcal carriers. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 18;281(12):641–645. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909182811203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine L. F., Johnson D. P., Hagerman C. R., Pierce W. E., Rhode S. L., 3rd, Peckinpaugh R. O. Rifampin. Levels in serum and saliva and effect on the meningococcal carrier state. JAMA. 1970 Nov 9;214(6):1055–1059. doi: 10.1001/jama.214.6.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dezelee S., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Study on yeast RNA polymerase. Effect of alpha-amanitan and rifampicin. FEBS Lett. 1970 Apr 16;7(3):220–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diggelmann H., Weissmann C. Rifampicin inhibits focus formation in chick fibroblasts infected with Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1969 Dec 27;224(5226):1277–1279. doi: 10.1038/2241277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi R. H., Brown L. R., Rodgers G., Hsu Y. Bacillus subtilis mutant altered in spore morphology and in RNA polymerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):404–410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle W. F., Pace N. R. Synthesis of 5S ribosomal RNA in Escherichia coli after rifampicin treatment. Nature. 1970 Oct 10;228(5267):125–129. doi: 10.1038/228125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engle C. G., Lasinski E., Gelzer J. Rifampin inhibition of H-1 virus infection in hamsters. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1190–1191. doi: 10.1038/2281190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekiel D. H., Hutchins J. E. Mutations affecting RNA polymerase associated with rifampicin resistance in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1968 Oct 19;220(5164):276–277. doi: 10.1038/220276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRONTALI L., LEONI L., TECCE G. ACTION OF RIFAMYCIN ON INCORPORATION OF AMINO-ACIDS INTO PROTEIN IN CELL-FREE SYSTEMS FROM B. SUBTILIS. Nature. 1964 Jul 4;203:84–85. doi: 10.1038/203084b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follett E. A., Pennington T. H. Antiviral effect of constituent parts of the rifampicin molecule. Nature. 1971 Mar 12;230(5289):117–118. doi: 10.1038/230117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromageot H. P., Zinder N. D. Growth of bacteriophage f2 in E. coli treated with rifampicin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):184–191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furesz S., Scotti R., Pallanza R., Mapelli E. Rifampicin: a new rifamycin. 3. Absorption, distribution, and elimination in man. Arzneimittelforschung. 1967 May;17(5):534–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth J. J., Nicholson A., Austin G. E. The enzymatic synthesis of ribonucleic acid in animal tissue. 3. Further purification of soluble RNA polymerase from lymphoid tissue and some general properties of the enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 16;213(1):124–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadaleta M. N., Greco M., Saccone C. The effect of rifampicin on mitochondrial RNA polymerase from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1970 Sep 18;10(1):54–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80414-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Yang S. S., Ting R. C. RNA dependent DNA polymerase of human acute leukaemic cells. Nature. 1970 Dec 5;228(5275):927–929. doi: 10.1038/228927a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. G., McCluer R. H. In vitro studies with rifampicin on the stability of heart mitochondrial RNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 14;53(3):557–560. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Haselkorn R. Messenger RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:647–676. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.003243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Sklar J. Continual requirement for a host RNA polymerase component in a bacteriophage development. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):833–836. doi: 10.1038/221833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand D. H., Hayashi M. In vitro synthesis of a DNA dependent RNA polymerase coded on coliphage T7 genome. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1162–1165. doi: 10.1038/2281162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimley P. M., Rosenblum E. N., Mims S. J., Moss B. Interruption by Rifampin of an early stage in vaccinia virus morphogenesis: accumulation of membranes which are precursors of virus envelopes. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):519–533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.519-533.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurgo C., Ray R. K., Thiry L., Green M. Inhibitors of the RNA and DNA dependent polymerase activities of RNA tumour viruses. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 27;229(4):111–114. doi: 10.1038/newbio229111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann G., Honikel K. O., Knüsel F., Nüesch J. The specific inhibition of the DNA-directed RNA synthesis by rifamycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;145(3):843–844. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselkorn R., Vogel M., Brown R. D. Conservation of the rifamycin sensitivity of transcription during T4 development. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):836–838. doi: 10.1038/221836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Green M. H. Effect of the lambda repressor on the binding of RNA polymerase to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):962–969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heil A., Zillig W. Reconstitution of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA-polymerase from isolated subunits as a tool for the elucidation of the role of the subunits in transcription. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec;11(3):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80519-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller E., Argaman M., Levy H., Goldblum N. Selective inhibition of vaccinia virus by the antibiotic rifampicin. Nature. 1969 Apr 19;222(5190):273–274. doi: 10.1038/222273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemphill H. E., Whiteley H. R., Brown L. R., Doi R. H. The effect of rifampin on the production of beta22 phage by Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Nov 6;37(4):559–566. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90845-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzfeld F. The insensitivity of RNA synthesis to rifampicin in Neurospora mitochondria. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 May;351(5):658–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobby G. L., Lenert T. F., Maier-Engallena J. In vitro activity of rifampin against the H37RV strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Mar;99(3):453–456. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.99.3.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobby G. L., Lenert T. F. The action of rifampin alone and in combination with other antituberculous drugs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Sep;102(3):462–465. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.102.3.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horgen P. A., Griffin D. H. Specific inhibitors of the three RNA polymerases from the aquatic fungus Blastocladiella emersonii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):338–341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Sajdel E. M., Munro H. N. Altered characteristics of mammalian RNA polymerase following solubilization from nuclei. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Sep 6;32(5):831–838. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jockusch H., Ball L. A., Kaesberg P. Synthesis of polypeptides directed by the RNA of phage Q beta. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):401–414. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90283-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya K., Sugino T., Wada Y., Nishikawa M., Kishi T. The x-ray analysis of tolypomycinone tri-m-bromobenzoate. Experientia. 1969 Sep 15;25(9):901–903. doi: 10.1007/BF01898050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J. R., McAuslan B. R. Poxvirus DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):134–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E., Grimley P., Moss B. Reversal of anti-viral effects of rifampicin. Nature. 1970 Sep 5;227(5262):1050–1051. doi: 10.1038/2271050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E., Moss B. Formation of a vaccinia virus structural polypeptide from a higher molecular weight precursor: inhibition by rifampicin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):677–684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E., Moss B. Vaccinia virus structural polypeptide derived from a high-molecular-weight precursor: formation and integration into virus particles. J Virol. 1970 Dec;6(6):717–726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.6.717-726.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Gniazdowski M., Mandel J. L., Jr, Gissinger F., Chambon P. Alpha-amanitin: a specific inhibitor of one of two DNA-pendent RNA polymerase activities from calf thymus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 6;38(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khesin R. B., Gorlenko Z. M., Shemyakin M. F., Stvolinsky S. L., Mindlin S. Z., Ilyina T. S. Studies on the functions of the RNA polymerase components by means of mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1969;105(3):243–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00337475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi T., Asai M., Muroi M., Harada S., Mizuta E. Tolypomycin. I. Structure of tolypomycinone. Tetrahedron Lett. 1969 Jan;(2):91–95. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(01)88213-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi T., Harada S., Asai M., Muroi M., Mizuno K. Tolypomycin. II. Structures of tolyposamine and tolypomycin Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 1969 Jan;(2):97–100. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(01)88214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knüsel F., Bickel H., Kump W. A new group of ribamycin derivatives displaying activity against rifampicin-resistant mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Experientia. 1969 Nov 15;25(11):1207–1208. doi: 10.1007/BF01900281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knüsel F., Schiess B. Dominance study with rifampicin-resistant mutants of E. coli K 12. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(4):331–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00267770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka E. A., Zoganas H. C., Lewis L., Gelzer J. Chemotherapeutic activity of rifampin against gram-negative bacteria with reference to urinary-tract infection in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:519–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kradolfer F., Neipp L., Sackmann W. Chemotherapeutic activity of new derivatives of rifamycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1966;6:359–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kradolfer F., Schnell R. Incidence of resistant pulmonary tuberculosis in relation to initial bacterial load, Rifampicin and INH in experimental tuberculosis. Chemotherapy. 1970;15(4):242–249. doi: 10.1159/000220688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M., Brandt D., Wood H. Bacteriologic studies of rifampin, a new semisynthetic antibiotic. J Infect Dis. 1969 Feb;119(2):132–137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.2.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancini G. C., Sartori G. Rifamycins LXI: in vivo inhibition of RNA synthesis of rifamycins. Experientia. 1968 Nov 15;24(11):1105–1106. doi: 10.1007/BF02147783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancini G. C., Thiemann J. E., Sartori G., Sensi P. Biogenesis of rifamycins. The conversion of rifamycin B into rifamycin Y. Experientia. 1967 Nov 15;23(11):899–900. doi: 10.1007/BF02136207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancini G., Cricchio R., Thiry L. Antiviral activity of rifamycins and N-aminopiperazines. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Jan;24(1):64–66. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancini G., Pallanza R., Silvestri L. G. Relationships between bactericidal effect and inhibition of ribonucleic acid nucleotidyltransferase by rifampicin in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.761-768.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Huang S., Warner R. C. The preparation and properties of ribonucleic acid polymerase from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 25;244(14):3793–3802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitich J., Oppolzer W., Prelog V. Ueber die Konfiguration des Rifamycins B und verwandter Rifamycine. Experientia. 1964 Jun 15;20(6):343–344. doi: 10.1007/BF02171086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitich J., Prelog V., Sensi P. Rifamycin Y und seine Umwandlungsprodukte. Experientia. 1967 Jul 15;23(7):505–507. doi: 10.1007/BF02137934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liersch M., Auden J., Gruner J., Nüesch J. Biosynthesis of rifamycine. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1969;34(3):243–243. doi: 10.1159/000162159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorian V., Finland M. In vitro effect of rifampin on mycobacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Feb;17(2):202–207. doi: 10.1128/am.17.2.202-207.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Shorenstein R. G., Sonenshein A. L. Structural alteration of RNA polymerase during sporulation. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):910–913. doi: 10.1038/227910a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi N., Füresz S., Sensi P. The influence of the carboxyl group upon the antibacterial activity of rifamycins. J Med Chem. 1968 Mar;11(2):368–369. doi: 10.1021/jm00308a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi N., Pallanza R., Sensi P. New derivatives of rifamycin SV. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:765–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi N., Pasqualucci C. R., Ballotta R., Sensi P. Rifampicin: a new orally active rifamycin. Chemotherapy. 1966;11(5):285–292. doi: 10.1159/000220462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martelo O. J., Woo S. L., Reimann E. M., Davie E. W. Effect of protein kinase on ribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochemistry. 1970 Nov 24;9(24):4807–4813. doi: 10.1021/bi00826a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mcauslan B. R. Rifampicin inhibition of vaccinia replication. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Oct 8;37(2):289–295. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90733-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno S., Nitta K. Effect of streptovaricin on RNA synthesis in phage T4-infected Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 10;35(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90492-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno S., Yamazaki H., Nitta K., Umezawa H. Inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase reaction of Escherichia coli by an antimicrobial antibiotic, streptovaricin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 22;157(2):322–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno S., Yamazaki H., Nitta K., Umezawa H. Inhibition of initiation of DNA-dependent RNA synthesis by an antibiotic B44p. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Feb 26;30(4):379–385. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90755-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondal H., Mandal R. K., Biswas B. B. Factors and rifampicin influencing RNA polymerase isolated from chromatin of eukaryotic cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 10;40(5):1194–1200. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90922-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Katz E., Rosenblum E. N. Vaccinia virus directed RNA and protein synthesis in the presence of rifampicin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Aug 22;36(5):858–865. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90688-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Rosenblum E. N., Katz E., Grimley P. M. Rifampicin: a specific inhibitor of vaccinia virus assembly. Nature. 1969 Dec 27;224(5226):1280–1284. doi: 10.1038/2241280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosteller R. D., Yanofsky C. Transcription of the tryptophan operon in Escherichia coli: rifampicin as an inhibitor of initiation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):525–531. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Paoletti E., Grace J. T., Jr RNA polymerase activity in purified infectious vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2280–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaya A., Pogo B. G., Dales S. Biogenesis of vaccinia: separation of early stages from maturation by means of rifampicin. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90150-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhoff V., Schill W. B., Sternbach H. Mikro-Disk-elektrophoretische Analyse reiner DNA-abhängiger RNA-Polymerase aus Escherichia coli. 3. Differenzierung zwischen Syntheseort und Bindungsort für die Matrize. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Mar;350(3):335–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitta K., Nizuno S., Yamazaki H., Umezawa H. Streptovaricin- and rifampicin-resistance of RNA polymerase in a resistant clone of Escherichia coli B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Aug;21(8):521–522. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppolzer W., Prelog V., Sensi P. Konstitution des Rifamycins B und verwandter Rifamycine. Experientia. 1964 Jun 15;20(6):336–339. doi: 10.1007/BF02171084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallanza R., Arioli V., Furesz S., Bolzoni G. Rifampicin: a new rifamycin. II. Laboratory studies on the antituberculous activity and preliminary clinical observations. Arzneimittelforschung. 1967 May;17(5):529–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasqualucci C. R., Vigevani A., Radaelli P., Maggi N. Analisi spettrofotometrica della rifampicina. Farmaco Prat. 1969 Jan;24(1):46–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington T. H., Follett E. A., Szilágyi J. F. Events in vaccinia virus-infected cells following the reversal of the antiviral action of rifampicin. J Gen Virol. 1970 Dec;9(3):225–237. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-9-3-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington T. H. The inhibition of variola minor virus multiplication by rifampicin. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;31(3):281–292. doi: 10.1007/BF01253763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porpáczy P. Ein neues Antibiotikum in der Therapie der chronischen Pyelonephritis. Wien Med Wochenschr. 1970 Oct 17;120(42):743–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulitzer J. F., Geiduschek E. P. Function of T4 gene 55. II. RNA synthesis by temperature-sensitive gene 55 mutants. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 28;49(2):489–507. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90259-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintrell N. A., McAuslan B. R. Inhibition of Poxvirus replication by streptovaricin. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):485–491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.485-491.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RHULAND L. E., STERN K. F., REAMES H. R. Streptovaricin. III. In vivo studies in the tuberculous mouse. Am Rev Tuberc. 1957 Apr;75(4):588–593. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1957.75.4.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabussay D., Zillig W. A rifampicin resistent rna-polymerase from E. coli altered in the beta-subunit. FEBS Lett. 1969 Oct 21;5(2):104–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80305-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid P., Speyer J. Rifampicin inhibition of ribonucleic acid and protein synthesis in normal and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-treated Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):376–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.376-389.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E., Zillig W. Purification and properties of DNA-dependent RNA-polymerase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jan;7(3):318–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. RNA polymerase and the control of RNA synthesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1969;9:75–116. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60768-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinehart K. L., Jr, Mathur H. H., Sasaki K., Martin P. K., Coverdale C. E. Chemistry of the streptovaricins. V. Structures of streptovaricins A and C. J Am Chem Soc. 1968 Oct 23;90(22):6241–6243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Termination factor for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1168–1174. doi: 10.1038/2241168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Mosteller R. D., Yanofsky C. Tryptophan messenger ribonucleic acid elongation rates and steady-state levels of tryptophan operon enzymes under various growth conditions. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug;51(3):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Scolnick E. M., Todaro G. J., Aaronson S. A. Separation of murine cellular and murine leukaemia virus DNA polymerases. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 9;231(23):163–167. doi: 10.1038/newbio231163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SENSI P., GRECO A. M., BALLOTTA R. Rifomycin. I. Isolation and properties of rifomycin B and rifomycin complex. Antibiot Annu. 1959;7:262–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SENSI P., MAGGI N., BALLOTTA R., FUERESZ S., PALLANZA R., ARIOLI V. RIFAMYCINS. XXXV. AMIDES AND HYDRAZIDES OF RIFAMYCIN B3. J Med Chem. 1964 Sep;7:596–602. doi: 10.1021/jm00335a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SENSI P., TIMBAL M. T., MAFFII G. Rifomycin IX. Two new antibiotics of rifomycin family: rifomycin S and rifomycin SV. Preliminary report. Experientia. 1960 Sep 15;16:412–412. doi: 10.1007/BF02178838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMINOFF P., SMITH R. M., SOKOLSKI W. T., SAVAGE G. M. Streptovaricin. I. Discovery and biologic activity. Am Rev Tuberc. 1957 Apr;75(4):576–583. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1957.75.4.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Becker Y. RNA in the elementary bodies of trachoma agent. Nature. 1968 Mar 2;217(5131):849–852. doi: 10.1038/217849b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Rinehart K. L., Jr, Slomp G., Grostic M. F., Olson E. C. Geldanamycin. I. Structure assignment. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Dec 30;92(26):7591–7593. doi: 10.1021/ja00729a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. Isolation and characterization of streptolydigin resistant RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Sep 6;223(5210):1068–1069. doi: 10.1038/2231068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz T., Craig E., Kennell D. Inactivation and degradation of messenger ribnucleic acid from the lactose operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):299–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90431-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J., Parks W. P. RNA dependent DNA polymerase activity in mammalian cells. Nature. 1971 Jan 29;229(5283):318–321. doi: 10.1038/229318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmerling Z. G. The effect of rifamycin on RNA synthesis in the rat liver mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Dec 4;37(6):965–969. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90225-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddhikol C., Erbstoeszer J. W., Weisblum B. Mode of action of streptolydigin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):151–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.151-155.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel A. E., Hartmann G. R. Rifampicin resistance of RNA polymerase in the binary complex with DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;16(1):152–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel A., Hartmann G. Mode of action of rafamycin on the RNA polymerase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):218–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka A., Butler B., Echols H. Genetic control of transcription during development of phage gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):576–583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So A. G., Downey K. M. Studies on the mechanism of ribonucleic acid synthesis. II. Stabilization of the deoxyribonucleic acid-ribonucleic acid polymerase complex by the formation of a single phosphodiester bond. Biochemistry. 1970 Nov 24;9(24):4788–4793. doi: 10.1021/bi00826a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolova E. V., Ovadis M. I., Gorlenko Z. M., Khesin R. B. Localization of streptolydigin resistant mutation in E. coli chromosome and effect of streptolydigin on T2 phage development in stl-r and stl-s strains of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Nov 25;41(4):870–876. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenshein A. L., Losick R. RNA polymerase mutants blocked in sporulation. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):906–909. doi: 10.1038/227906a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman S., Burny A., Das M. R., Keydar J., Schlom J., Travnicek M., Watson K. DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity in oncogenic RNA viruses. Nature. 1970 Sep 5;227(5262):1029–1031. doi: 10.1038/2271029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straat P. A., Ts'o P. O. Ribonucleic acid polymerase from Micrococcus luteus (Micrococcus lysodeikticus). IV. Effect of rifampicin and oligomers on the homopolymer-directed reaction. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 17;9(4):926–931. doi: 10.1021/bi00806a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subak-Sharpe J. H., Timbury M. C., Williams J. F. Rifampicin inhibits the growth of some mammalian viruses. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):341–345. doi: 10.1038/222341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M., Okamoto T., Takanami M. RNA polymerase sigma-factor and the selection of initiation site. Nature. 1970 Feb 14;225(5233):598–600. doi: 10.1038/225598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C. The process of infection with coliphage T7. IV. Stability of RNA in bacteriophage-infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug;51(3):671–678. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surzycki S. J. Genetic functions of the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardi: effect of rifampin on chloroplast DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1327–1334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Oyama Y., Nakajima K., Yura T. Role of host RNA polymerase for lambda phage development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Aug 15;36(4):533–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90337-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. B., McAuslan B. R. Effect of rifampicin on poxvirus protein synthesis. J Virol. 1970 Sep;6(3):326–332. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.3.326-332.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. B., McAuslan B. R. Inhibition of nucleoside incorporation into HeLa cells by streptovaricin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 22;42(2):230–236. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Mizutani S. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1211–1213. doi: 10.1038/2261211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiry L., Lancini G. Inhibition of vaccinia virus growth by 1-methyl-4-aminopiperazine. Nature. 1970 Sep 5;227(5262):1048–1050. doi: 10.1038/2271048a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocchini-Valentini G. P., Marino P., Colvill A. J. Mutant of E. coli containing an altered DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Nature. 1968 Oct 19;220(5164):275–276. doi: 10.1038/220275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Burgessrr Cyclic re-use of the RNA polymerase sigma factor. Nature. 1969 May 10;222(5193):537–540. doi: 10.1038/222537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Kamen R. I., Schleif R. F. Factor necessary for ribosomal RNA synthesis. Nature. 1970 Nov 21;228(5273):748–751. doi: 10.1038/228748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. Control of transcription in bacteria. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 20;229(3):69–74. doi: 10.1038/newbio229069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. J., Michaelis G., Criddle R. S. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from yeast mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):473–477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Mizuno S., Yamazaki H., Nitta K. Inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA synthesis by rifamycins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Mar;21(3):234–236. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt H. -P., Kaufmann R., Matthaei H. Solubilized DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from human placenta: A Mn(2+)-dependent enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1970 Oct 16;10(4):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80642-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITFIELD G. B., OLSON E. C., HERR R. R., FOX J. A., BERGY M. E., BOYACK G. A. Streptovaricin. II. Isolation and properties. Am Rev Tuberc. 1957 Apr;75(4):584–587. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1957.75.4.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Zillig W., Palm P., Fuchs E. Initiation of DNA-dependent RNA synthesis and the effect of heparin on RNA polymerase. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Dec;3(2):194–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb19515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Knüsel F., Schmid K., Staehelin M. Interaction of rifamycin with bacterial RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):667–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Knüsel F., Staehelin M. Action of rifamycin on RNA-polymerase from sensitive and resistant bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 26;32(2):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90382-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Nüesch J., Knüsel F., Staehelin M. Action of rifamycins on RNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Staehelin M. The rifamycins--relation of chemical structure and action on RNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 20;182(1):24–29. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90516-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Davies J. Antibiotic inhibitors of the bacterial ribosome. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):493–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willcox R. R., Morrison G. D., Cobbold R. J. Rifampicin (Rimactane) in the treatment of gonorrhoea. Br J Vener Dis. 1970 Apr;46(2):145–148. doi: 10.1136/sti.46.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintersberger E. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from mitochondria of a cytoplasmic "petite" mutant of yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 10;40(5):1179–1184. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90919-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintersberger E., Wintersberger U. Rifamycin insensitivity of RNA synthesis in yeast. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jan 15;6(1):58–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. W., Goldthwait D. A. Studies of nucleotide binding to the ribonucleic acid polymerase by a fluoresence technique. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4450–4458. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. W., Goldthwait D. A. Studies of nucleotide binding to the ribonucleic acid polymerase by equilibrium dialysis. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4458–4464. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki H., Mizuno S., Nitta K., Utahara R., Umezawa H. Studies on antimicrobial substance B 44 P (streptovaricin) produced by a strain of actinomycetes. IV. Biochemical mechanism of action of substance B 44 P. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Mar;21(3):227–233. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S., Criddle R. S. In vitro biosynthesis of membrane proteins in isolated mitochondria from Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Biochemistry. 1970 Jul 21;9(15):3063–3072. doi: 10.1021/bi00817a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yura T., Igarashi K. RNA polymerase mutants of Escherichia coli. I. Mutants resistant to streptovaricin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1313–1319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakay-Rones Z., Becker Y. Anti-poxvirus activity of rifampicin associated with hydrazone side chain. Nature. 1970 Jun 20;226(5251):1162–1163. doi: 10.1038/2261162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G., Schwartz D., Beckwith J. Mechanism of activation of catabolite-sensitive genes: a positive control system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):104–110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Mauro E., Synder L., Marino P., Lamberti A., Coppo A., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Rifampicin sensitivity of the components of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 May 10;222(5193):533–537. doi: 10.1038/222533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



