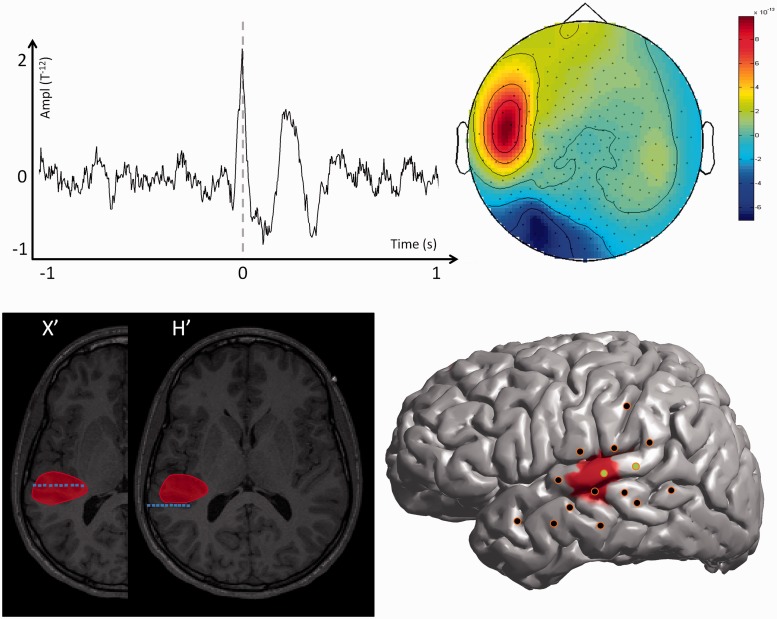
Figure 1.
MEG modelling of epileptic spikes and SEEG localization of the seizure-onset zone in a patient with a focal spiking volume (Patient 16). Top left: Example of one prototypical spike recorded with MEG for one single channel. Top right: Topographic map of the magnetic field recorded for all MEG channels at the main peak of the prototypical spike. Bottom left: The MEG spiking volume determined with VIES (red volume) is shown on representative MRI slices. On the same slices, the SEEG electrodes showing clear signal changes at seizure-onset are shown in blue. Bottom right: SEEG implantation scheme of Patient 16. The location of the penetrating points of intracranial electrodes is determined by co-registering the patient’s post-implantation MRI onto the cortical mesh extracted from the MRI. The MEG spiking volume projected onto the cortical surface is shown as a red area. SEEG electrodes showing clear signal change at seizure onset are shown in green and electrodes without ictal changes are shown in black. Notice that the spiking volume is spatially restricted and co-extensive with the seizure-onset zone determined with SEEG. The patient underwent surgery with a resection of the posterior part of the left temporal neocortex (superior and middle temporal gyrus) and is seizure free postoperatively after 22 months of follow-up.