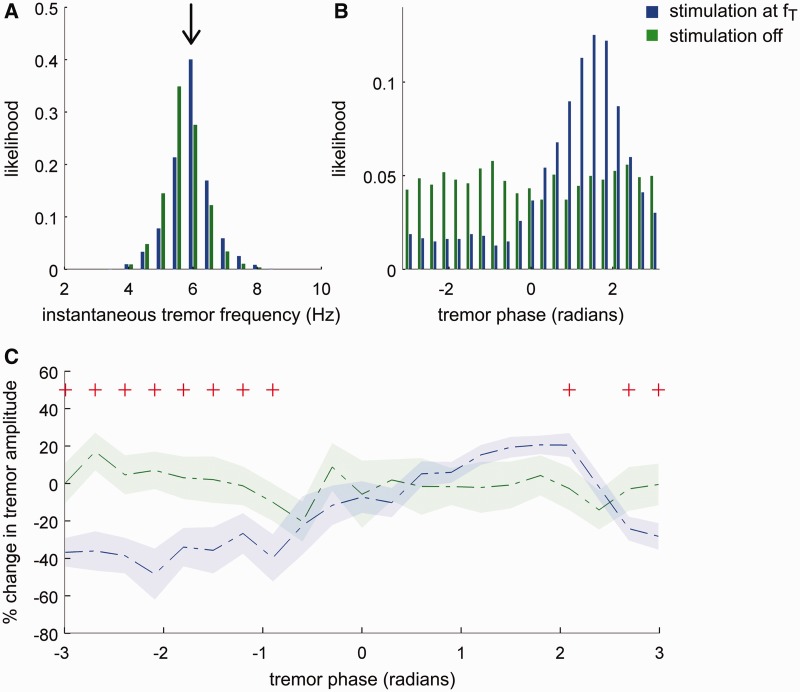
Figure 2.
Exemplar effect of DBS on essential tremor in Patient 6. DBS at near postural tremor frequency (fT) alters various tremor properties, ranging from tremor frequency to tremor entrainment. Moreover, tremor amplitude is modulated differentially depending on the timing of the thalamic DBS pulses with respect to the tremor cycle. (A) Tremor frequency is altered due to stimulation at fT Hz and pulled towards stimulation frequency (fT = 6 Hz indicated with an arrow). (B) When DBS is off, tremor phase sampled at 6 Hz is uniformly distributed. During DBS at fT Hz (e.g. 6 Hz), tremor phase sampled at stimulation instances gets pulled to certain phases, indicating that DBS at fT Hz entrains postural tremor. (C) Median percentage change in tremor amplitude relative to corresponding tremor phase during fT Hz stimulation (phase-amplitude profile) and when DBS is switched off are indicated with dashed lines; while shaded regions indicate standard error of the mean (red plus sign indicates amplitude changes during fT Hz stimulation, which are significantly different from tremor amplitude variability when stimulation is switched off (two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test at each phase bin, FDR corrected for multiple comparisons). Thalamic stimulation at particular instances of the tremor cycle can attenuate or increase tremor amplitude.