Abstract
This study determined whether higher patient volume of skilled nursing facility (SNF) care was associated with a lower hospital transfer rate. Using the nursing home Minimum Data Set and the On-line Survey, Certification, and Reporting file, we assembled a national cohort of Medicare SNF post-acute care admissions between January and September of 2008. Multivariable analyses based on Cox proportional hazards models found that patients admitted to high-volume SNFs (annual number of admissions in the top tertile group) showed an approximately 15% reduced risk for 30-day rehospitalization and an approximately 25% reduced risk for 90-day rehospitalization, compared to patients admitted to low-volume SNFs (annual number of admissions in the bottom tertile group, or<45). Similar patterns of volume-outcome associations were found for hospital-based and freestanding facilities separately. The inverse volume-outcome association in post-acute SNF care may reflect a “practice makes perfect” effect, a “selective referral” effect, or both.
Keywords: skilled nursing facilities, post-acute care, volume-outcome association, rehospitalization, Minimum Data Set
INTRODUCTION
Patients admitted to the skilled nursing facility (SNF) typically have recent hospital stay for an acute episode of illness. During their skilled facility stay, the post-acute SNF patients receive daily recuperative or rehabilitation services with the goals of stabilization of post-surgical or medical problems and recovery from functional losses. The post-acute SNF patients are medically complex with over half of them having five or more comorbidities and at least one impairment in activities of daily living (Liu, Garrett, & Wissoker, 2007). Medicare covers beneficiaries’ SNF care for up to one hundred days if they meet certain skilled care criteria. Recent estimates showed that each year between 1.3 and 1.8 million Medicare beneficiaries received an episode of post-acute care (Donelan-McCall, Eilertsen, Fish, & Kramer, 2006; Grabowski, Feng, Intrator, & Mor, 2010; Stearns, Dalton, Holmes, & Seagrave, 2006).
Rehospitalization of skilled nursing care patients – estimated at a rate between 15 and 40 percent within Medicare-covered stay (Donelan-McCall, et al., 2006; Grabowski, et al., 2010; Grabowski, Stewart, Broderick, & Coots, 2008; Konetzka, Spector, & Limcangco, 2008; Mor, Intrator, Feng, & Grabowski, 2010; Stearns, et al., 2006) – is a common problem that affects both quality of life of the transferred beneficiaries and overall efficiency of the Medicare program (Ouslander, Weinberg, & Phillips, 2000). Transfers of frail SNF patients back to the hospital often are deemed clinically inappropriate or preventable (Intrator, Zinn, & Mor, 2004; Saliba, et al., 2000), expose them to iatrogenic problems and medical errors (Boockvar, et al., 2004; Gorbien, et al., 1992), cause additional physical and psychological suffering (Covinsky, et al., 2003; Ouslander, et al., 2000), and increase system care cost (Ouslander, et al., 2010). As such, the rehospitalization rate is an important outcome indicator for SNF care quality. Policy interventions – such as bundled Medicare payment across alternative care settings (MedPAC, 2008) and “pay for performance”(Abt, 2006) – have been designed to create financial incentives for nursing facilities to reduce rehospitalization rate.
Focusing on this important outcome of skilled nursing facility care, this study was designed to determine whether Medicare beneficiaries admitted to higher-volume nursing facilities were less likely to be rehospitalized within 30 days and 90 days of admission, ie, the inverse volume-outcome association for SNF rehospitalization rates. Although an understudied topic in the post-acute care setting, the volume-outcome association has long been documented for hospital and physician services (Birkmeyer, Finlayson, & Birkmeyer, 2001; Glance, Li, Osler, Dick, & Mukamel, 2006; Luft, Bunker, & Enthoven, 1979; Thiemann, Coresh, Oetgen, & Powe, 1999) and, most recently, for custodial nursing home care (Li, Cai, Mukamel, & Glance, 2010). As suggested by the acute care literature, the volume-outcome relationship may exist due to a “selective referral” effect, a “practice makes perfect” effect, or both (Halm, Lee, & Chassin, 2002; Li, Cai, et al., 2010; Luft, et al., 1979).
Under the selective referral effect – as has been shown in hospital services (Luft, et al., 1990; Luft, Hunt, & Maerki, 1987) – skilled nursing facilities with superior outcomes of care (eg, low hospital transfer rate) would be able to attract more patients and thus increase volume. If, alternatively or simultaneously, practice makes perfect in the delivery of skilled nursing care, skilled facilities caring for a high volume of Medicare beneficiaries would be able to gain more experience, possess more resources and well-trained personnel, and operate more efficiently, thereby achieving better outcomes.
Selective referral might exist in skilled nursing care for 3 reasons. First, the current SNF care market is relatively competitive and due, in part, to the rapid increase in community-based long-term and post-acute care alternatives such as home health care and assisted living in the past 2 decades (Gruneir, Lapane, Miller, & Mor, 2007; MedPAC, 2009), the overall nursing home occupancy rate continued to decline, down to 83% nationally in 2005 (Li, Harrington, Spector, & Mukamel, 2010). The reduced occupancy rate made possible consumer choices of alternative SNF beds in local markets. Second, performance-based referrals have likely evolved in local markets as nursing facilities acquire reputations as “the best” or “the worst” in the area for patients with post-acute care needs. Such reputations often develop as prospective patients, their families, and hospital discharge planners observe over time the experience and outcomes of patients in these facilities. Finally, explicit outcomes data for nursing home care were made available to the public by CMS as of 2002 (GAO, 2002). These quality “report cards” are expected to be able to reinforce selection based on informal performance information, and bring about market share changes among competing facilities (Mukamel, Weimer, & Mushlin, 2007; Mukamel, Weimer, Zwanziger, Gorthy, & Mushlin, 2004; Werner, Stuart, & Polsky, 2010).
It is likely that the “practice makes perfect” mechanism also exists in the delivery of SNF care, particularly with regard to hospital transfers of post-acute SNF patients. The decision to transfer a SNF patient to the hospital may be affected by a variety of factors that include the acuity and severity of disease, family and patient preferences, and facility-related factors such as practice routines, available resources & expertise, and overall capacity to respond to emergent situations (Buchanan, et al., 2006; Grabowski, et al., 2008; Hutt, Ecord, Eilertsen, Frederickson, & Kramer, 2002; Intrator, et al., 2004; Teresi, Holmes, Bloom, Monaco, & Rosen, 1991). It has been established that improved staffing levels of physician assistants and geriatric nurse practitioners reduce hospitalizations (Grabowski, et al., 2008; Intrator, et al., 2004). It has also been suggested that a lack of technological resources in skilled nursing facilities such as X-rays and intravenous therapy increases hospital transfers (Buchanan, et al., 2006; Intrator, et al., 2004; Teresi, et al., 1991). In light of these findings, one would believe that higher-volume facilities exhibit lower rehospitalization rates because, at least in part, they tend to have better access to medical staff when faced with emergency situations, and be more able to provide the array of technologically sophisticated services – such as oxygen monitoring and therapy, specialized wound care, or intravenous medications – that otherwise could only be provided in emergency rooms or hospitals.
Given these considerations, this study performed a national cohort analysis on Medicare beneficiaries admitted to skilled nursing facilities, and determined whether their risks for being rehospitalized within 30 days and 90 days of admission varied as a function of facility volume of patients. We tested the potential volume-outcome association for hospital-based and freestanding SNFs separately, given their important differences in case mix, staffing and care patterns, as well as patient outcomes (Donelan-McCall, et al., 2006; Liu & Black, 2003; Stearns, et al., 2006).
NEW CONTRIBUTION
The relationship between higher volume of patients and better clinical outcomes in acute care settings has been extensively reported in the United States (Birkmeyer, et al., 2001; Glance, et al., 2006; Luft, et al., 1979; Thiemann, et al., 1999). For a broad array of surgical and medical conditions, patients admitted to higher-volume hospitals have been shown to have improved outcomes including lower mortality rates (Halm, et al., 2002). Policymakers responded to this evidence of volume-outcome associations by suggesting minimum volume requirements and encouraging regionalization of hospital care for certain complex conditions, whereby patients are referred to high-volume centers of excellence for superior outcomes (Birkmeyer, et al., 2001). Until now, however, little research has been undertaken to explore the volume-outcome association in the delivery of post-acute or long-term care. To our knowledge, only one recent study has examined this issue in nursing homes. That study found that long-term care residents in higher-volume nursing homes were less likely to experience functional decline (Li, Cai, et al., 2010). The present study contributes to the nursing home health services research literature by determining whether a similar volume-outcome association exists in skilled nursing facilities – one of the most common post-acute care settings (MedPAC, 2009).
METHODS
Data source and sample
We obtained the 2008 nursing home Minimum Data Set (MDS) file from CMS and created a retrospective cohort of all Medicare admissions to federally-certified skilled nursing facilities between January 1 and September 30 of 2008. It is estimated that over 90% of nursing facilities in the US are federally certified (Jones, Dwyer, Bercovitz, & Strahan, 2009). The MDS contains detailed information about patient demographics, socio-economic characteristics, physical and mental health status, disease diagnoses, and treatments received. Nursing home staff perform MDS assessments on all patients at admission, regularly thereafter, and when a significant change of health status occurs. MDS records are shown to be accurate and valid (Lawton, et al., 1998; Mor, et al., 2003), and have been used for a variety of regulatory and research purposes such as setting the Medicare payment rate (Liu, et al., 2007), public reporting of nursing home performances (Abt, 2006; Donelan-McCall, et al., 2006), and tracking outcomes based on large database analyses (Intrator, et al., 2004; Li, Cai, et al., 2010).
We identified the cohort of Medicare SNF admissions by including all MDS admission assessments during the study period (January 1 to September 30 of 2008) that were also administratively designated as Medicare PPS (prospective payment system) assessments – This same approach has been used by CMS to define post-acute SNF admissions in its on-line publication of the “Nursing Home Compare” measures (Abt, 2004). This admission cohort was then linked to MDS discharge tracking records using a unique encrypted patient identifier in order to define the discharge status of patients within 30 days and 90 days of admission (such as discharge to a hospital). The patient sample was finally merged with the 2008 Online Survey, Certification, and Reporting (OSCAR) file, which is a facility-level database maintained by CMS. In this study, the OSCAR was used to obtain key SNF characteristics including whether a SNF was affiliated with a hospital (hospital based) or freestanding, profit status (for-profit, non-for-profit, and government), chain affiliation (yes/no), and geographic location (rural/urban).
Outcomes and predictors
The primary outcomes of interest were whether a SNF patient had at least one discharge to hospital within 30 days and within 90 days of admission. The key independent variable was skilled nursing facility volume which was defined as the annual tallied number of Medicare PPS admissions for each facility in 2008.
We identified an extensive set of patient covariates that were available in the admission assessment and that might affect patients’ risk for rehospitalization.(Donelan-McCall, et al., 2006; Grabowski, et al., 2008; Intrator, et al., 2007; Intrator, et al., 2004; Stearns, et al., 2006) Socio-demographic covariates included age (categorized as <65 years, 65–74 years, 75–84 years, and ≥85 years), male gender, race/ethnicity (non-Hispanic white, black, Hispanic, and other), education (<high school diploma, high school diploma, some college/technical school, and bachelor degree or higher), primary language (English vs. non-English), and marital status (married or not).
Patient clinical and diagnostic covariates included whether the patient was admitted to the SNF directly from a hospital, whether the patient had a do-not-resuscitate order at admission, the number of activities of daily living (ADLs) that each patient could perform at admission, whether the patient had cognitive impairment, and a set of binary variables (1/0) indicating presence (at admission) of diabetes, other endocrine disease, cardiovascular disease, musculoskeletal disease, dementia, neurological disease except dementia, anxiety disorder, depression, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, pulmonary disease, sensory disease, and other diseases. ADLs included bed mobility, transfer, dressing, eating, toilet use, personal hygiene, and bathing; each ADL component was coded in 5 categories from 0 (independence) to 4 (total dependence), resulting in a total range of the aggregate ADL score between 0 and 28. Patients were defined as having cognitive impairment if they had impaired short-term memory and were dependent in daily decision making.
Statistical analyses
We first ranked facility volume in an increasing order and categorized facilities into approximate tertile groups, that is, those of low volume (<45 admissions), medium volume (45–107 admissions) and high volume (≥108 admissions). We performed bivariate analyses to compare patient and key facility characteristics between volume groups, using σ2 tests for discrete variables and analyses of variance for continuous variables. In both bivariate and multivariable analyses (described below), we excluded patients who had a do-not-hospitalize order at admission (n=16,975). Of note, this exclusion was made after patient volume was calculated and thus although excluded patients were not used for analyses, they contributed to SNF patient volume.
We further performed survival analyses for hospital-based and freestanding SNFs separately. In each set of analyses, we first used the Kaplan-Meier survival curve and the log-rank test to determine the bivariate relationship between facility volume and risk for rehospitalization. In the Kaplan-Meier analyses, we included “volume tertiles” as 2 categorical variables for the high-volume and medium-volume groups, with the low volume group being the reference group. For the analyses of patients admitted to hospital-based facilities, the volume tertile groups were defined as <45 admissions (low-volume hospital-based SNFs), 45–126 admissions (medium-volume hospital-based SNFs), and ≥127 admissions (high-volume hospital-based SNFs). For the analyses of admissions to freestanding SNFs, the volume tertile groups were categorized as <45 admissions (low-volume freestanding SNFs), 45–107 admissions (medium-volume freestanding SNFs), and ≥108 admissions (high-volume freestanding SNFs).
To determine the independent association of volume with 30-day (or 90-day) rehospitalization, we estimated multivariable Cox proportional hazards models where the independent variables were volume tertiles defined for hospital-based and freestanding SNFs separately. The Cox proportional hazards models controlled for the patient covariates described in the previous section and accounted for left censoring or loss of follow up before 30 days (or 90 days) of admission due to death, discharge to home (with or without home health services), or transfer (to other SNFs, rehabilitation centers or other types of post-acute care settings). The unit of all survival analyses was each admission.
Lastly, we performed sensitivity analyses for alternative definitions of volume groups in multivariable analyses, where facilities (hospital-based, or freestanding) were re-categorized to 1) two groups (≥median volume vs. otherwise), 2) quartile group, or 3) quintile groups. Results of these sensitivity analyses were essentially identical to those of the base analyses, and thus are not reported. All analyses were conducted using SAS (SAS Corp, Cary, NC) Version 9.1.
RESULTS
Our analyses included 1,023,771 Medicare admissions to 14,857 SNFs between January and September of 2008 (Table 1), of whom 78,890 were admitted to low-volume facilities (annual admissions<45, n=4,952), 235,243 to medium-volume facilities (annual admissions of 45–107, n=4,952), and 709,638 to high-volume facilities (annual admissions≥108, n=4,953). Bivariate comparisons showed that the 30-day rehospitalization rate was 16.4% for low-volume facilities, 15.9% for medium-volume facilities, and 14.3% for high-volume facilities (p<0.0001), whereas the 90-day rehospitalization rate was 27.3%, 25.9%, and 21.5%, respectively, for the 3 volume groups (p<0.0001).
Table 1.
Patient and skilled nursing facility (SNF) characteristics in 2008, by SNF volume
| SNF patient volume*
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (<45) | Medium (45–107) | High (≥108) | |
| Number of patient admissions | 78890 | 235243 | 709638 |
| Number of facilities | 4952 | 4952 | 4953 |
| ------------Percent or Mean ± SD------------ | |||
| Patient characteristic | |||
| Discharge to hospital within 30 days of admission | 16.4 | 15.9 | 14.3 |
| Discharge to hospital within 90 days of admission | 27.3 | 25.9 | 21.5 |
| Age in Years | 79.0 ± 12.1 | 79.3 ± 11.5 | 79.6 ± 10.8 |
| <65 | 11.2 | 9.8 | 8.4 |
| 65–74 | 17.3 | 17.8 | 17.9 |
| 75–84 | 34.3 | 35.5 | 37.3 |
| ≥85 | 37.2 | 37.0 | 36.4 |
| Male | 38.3 | 36.6 | 34.1 |
| Race/Ethnicity | |||
| White | 83.4 | 83.4 | 85.1 |
| Black | 10.7 | 10.3 | 8.8 |
| Hispanic | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.4 |
| Other | 2.3 | 2.7 | 2.8 |
| Education | |||
| <High school diploma | 33.0 | 29.7 | 21.1 |
| High school diploma | 40.0 | 42.1 | 45.2 |
| Some college/technical school | 15.9 | 16.3 | 18.5 |
| Bachelor degree or higher | 9.0 | 9.5 | 12.7 |
| Missing | 2.1 | 2.4 | 2.5 |
| English as primary language | 96.6 | 95.7 | 95.8 |
| Married | 28.4 | 29.6 | 32.5 |
| Admitted from hospital | 80.2 | 87.1 | 93.3 |
| Presence of do-not-resuscitate order | 38.1 | 34.9 | 25.2 |
| Activities of daily living (0–28) | 16.0±6.5 | 16.7±5.8 | 16.9±5.1 |
| Cognitive impairment | 50.9 | 46.9 | 37.6 |
| Disease diagnosis | |||
| Diabetes | 33.8 | 35.0 | 33.4 |
| Other endocrine disease | 19.3 | 19.8 | 20.0 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 84.5 | 86.0 | 86.4 |
| Musculoskeletal disease | 42.4 | 43.7 | 45.9 |
| Dementia | 30.6 | 28.3 | 22.1 |
| Neurological disease except dementia | 28.4 | 27.4 | 24.0 |
| Anxiety disorder | 15.0 | 15.3 | 13.9 |
| Depression | 31.5 | 30.9 | 29.5 |
| Bipolar disorder | 2.8 | 2.1 | 1.6 |
| Schizophrenia | 3.3 | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| Pulmonary disease | 24.1 | 24.9 | 23.7 |
| Sensory disease | 11.5 | 11.0 | 10.8 |
| Other disease | 55.6 | 58.2 | 60.0 |
| SNF characteristic | |||
| SNF patient volume | 23.9 ±12.0 | 72.0 ±17.8 | 213.2 ±116.5 |
| Hospital-based | 6.6 | 5.3 | 7.8 |
| Profit status | |||
| For-profit | 65.8 | 70.3 | 70.2 |
| Non-for-profit | 27.2 | 25.5 | 26.9 |
| Government | 6.9 | 4.2 | 2.9 |
| Chain affiliated | 48.8 | 58.7 | 59.4 |
| Rural area | 45.6 | 32.2 | 13.7 |
P<0.001 for comparisons of all patient and facility characteristics across volume groups based on χ2 test or analysis of variance.
Table 1 also shows that certain patient characteristics were associated with admission to facilities of each volume group. For example, patients younger than 65 years, black patients, and patients with lowest education attainment showed decreased rate of admissions to high-volume facilities, while married patients and patients who were admitted directly from a hospital showed increased rate of admissions to high-volume facilities. Compared to low-volume SNFs, high-volume SNFs were more likely to be for profit, affiliated with a chain, and located in a non-rural area.
Although the average number of post-acute care admissions per year was 103 for all facilities (Table 2), hospital-based facilities (n=910, 6% of all facilities) tended to have higher number of admissions (117 on average) than freestanding facilities (102 on average). Unadjusted hospital discharge rate was much lower in hospital-based than in freestanding facilities – 8.9% versus 15.3% within 30 days of admission, and 12.0% versus 23.8% within 90 days of admission.
Table 2.
Characteristics of Medicare-certified skilled nursing facilities
| All | Hospitalized-based | Freestanding | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of facilities | 14857 | 910 | 13947 |
| Annual volume of admissions | |||
| Mean | 103 | 117 | 102 |
| Median | 71 | 80 | 71 |
| Inter-quartile range | 33–136 | 31–164 | 35–135 |
| 30-day rate of discharge to hospital, % | 14.79 | 8.88 | 15.25 |
| 90-day rate of discharge to hospital, % | 22.95 | 12.04 | 23.80 |
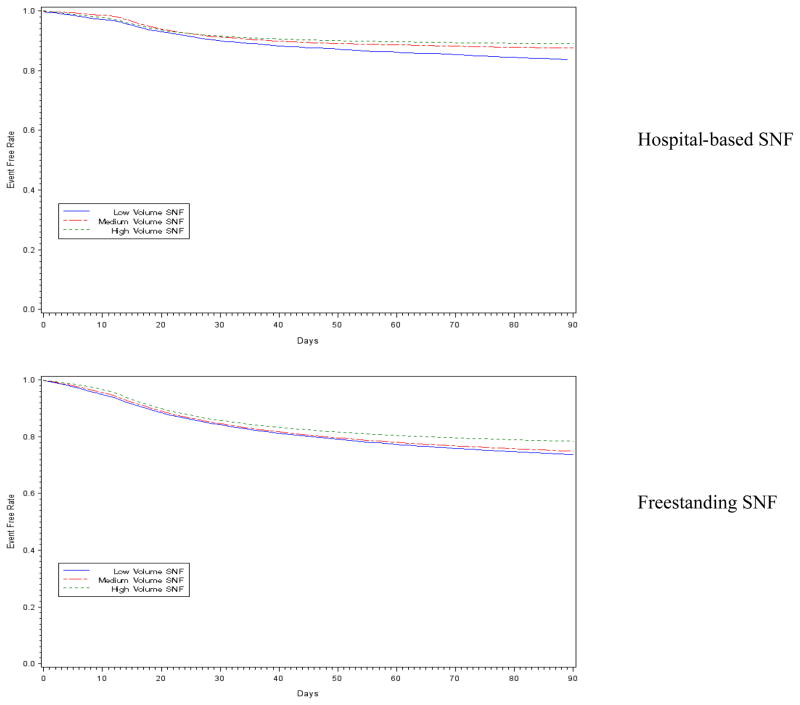
The Kaplan-Meier curves for both types of facilities (Figure 1) suggest a significant inverse bivariate association between higher volume and lower risk of rehospitalization (log-rank tests P<0.001). Table 3 shows that in multivariable Cox proportional hazards models considering censoring and for hospital-based facilities, the adjusted hazard ratios (HR) of 30-day rehospitalization were 0.87 (95% CI 0.79–0.97, p=0.010) for high-volume facilities, and 0.89 (95% CI 0.79–0.99, p=0.030) for medium-volume facilities, both compared to low-volume hospital-based SNFs; in addition, the adjusted HR of 90-day rehospitalization were 0.72 (95% CI 0.66–0.78, p<0.001) for high-volume facilities, and 0.79 (95% CI 0.73–0.86, p<0.001) for medium-volume facilities. Similar pattern of volume-outcome associations was found for freestanding facilities (Table 3).
Figure 1.
Skilled nursing facility (SNF) volume and time to acute care rehospitalization since SNF admission, stratified by SNF hospital affiliation status (log-rank tests P<0.001 in both cases)
Table 3.
Adjusted hazard ratios (HR) for skilled nursing facility (SNF) rehospitalization, by hospital affiliation status
| Hospital-based facility
|
Freestanding facility
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted HR | Adjusted HR*
|
Unadjusted HR | Adjusted HR*
|
|||||
| Point estimate | 95% CI | P-value | Point estimate | 95% CI | P-value | |||
| 30-day rehospitalization | ||||||||
| High volume§ | 0.84 | 0.87 | 0.79–0.97 | 0.010 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.84–0.87 | <0.001 |
| Medium volume¶ | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.79–0.99 | 0.030 | 0.97 | 0.92 | 0.90–0.94 | <0.001 |
| Low volume£ | 1.00 | 1.00 | … | … | 1.00 | 1.00 | … | … |
| 90-day rehospitalization | ||||||||
| High volume§ | 0.67 | 0.72 | 0.66–0.78 | <0.001 | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.78–0.81 | <0.001 |
| Medium volume¶ | 0.76 | 0.79 | 0.73–0.86 | <0.001 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.90–0.93 | <0.001 |
| Low volume£ | 1.00 | 1.00 | … | … | 1.00 | 1.00 | … | … |
Separate Cox proportional hazards regression models adjusted for patient characteristics listed in Table 1.
Annual admissions ≥127 for hospital-based facilities, and ≥108 for freestanding facilities.
Annual admissions of 45–126 for hospital-based facilities, and 45–107 for freestanding facilities.
Annual admissions <45 for both hospital-based and freestanding facilities.
CI=confidence interval.
To control for potential confounding of facility covariates on the estimated volume-outcome associations, we performed additional analyses where we incorporated several key (and exogenous) SNF characteristics into the multivariable analyses. These additional facility covariates included profit status (for-profit, non-for-profit, and government), chain affiliation status (yes/no), and rural/urban location (see Table 1 for descriptive statistics). These sensitivity analyses showed that the estimated volume-outcome associations were essentially the same as the estimates in main analyses (details of these sensitivity analyses are available from the authors upon request).
DISCUSSION
This study of the nation’s Medicare skilled nursing facility admissions revealed that those who were admitted to higher-volume facilities tended to show lower rehospitalization rates within 30 days and 90 days of admission. In multivariable analyses controlling for patient demographic, socio-economic, clinical, and diagnostic characteristics, high-volume facilities (annual number of admissions in the top tertile group) were associated with an approximately 15% reduced risk for 30-day rehospitalization and an approximately 25% reduced risk for 90-day rehospitalization, compared to low-volume facilities (annual number of admissions in the bottom tertile group, or< 45). This volume-outcome association was similarly found for both hospital-based and freestanding facilities.
Of the many ways in which hospital-based and freestanding SNFs can differ (Donelan-McCall, et al., 2006; Liu & Black, 2003; Stearns, et al., 2006), our analyses found that hospital-based units tended to admit more Medicare patients and showed lower rehospitalization rate than freestanding facilities (Table 2). This outcome difference is consistent with previous findings. For example, a MedPAC-commissioned study reported that compared to patients admitted to freestanding nursing facilities, those admitted to hospital-based facilities exhibited approximately 50 percent reduced odds of hospital transfers for any and each of 5 most common diagnoses (Donelan-McCall, et al., 2006). In addition, Stearns et al (Stearns, et al., 2006) similarly found that the 30-day rehospitalization rate for a hospital-based SNF cohort was nearly one-half of that for a matched cohort of freestanding admissions.
Our study confirmed that the volume-outcome association persisted and exhibited similar patterns for both types of facilities. This might be expected given the nature of skilled-level services provided in all facilities, and would suggest that similar referral and/or technological mechanisms drive the volume-outcome association in an across-the-board manner. In further regression analyses controlling for key SNF characteristics (profit status, chain affiliation, and rural versus urban location), we found that the volume-outcome associations tended to be similar for both hospital-based and freestanding facilities, confirming the robustness of our findings.
This study has several limitations. First, we focused on rehospitalization as an important outcome of skilled nursing facility care. There are, however, other important outcomes such as pain control or mobility and, in general, these outcomes do not tend to be correlated (Mukamel, et al., 2008). Therefore, the observed volume-outcome association found in this study may not be generalized to other aspects of SNF care outcomes. Second, this study only examined the association between facility volume and rehospitalization rate, and was not able to make causal inferences between them. Future work is needed to clarify the nature of the causal pathway between volume and outcome so as to better inform quality improvement efforts and policy interventions. Specifically, refined study designs such as longitudinal tracking of changes in both volume and outcome, and sophisticated statistical techniques such as simultaneous equation models (Luft, et al., 1987) would allow researchers to ascertain the relative contribution of the “selective referral” versus “practice makes perfect” mechanism. Future research can also be undertaken to control for unobserved and observed facility heterogeneity and explore the un-confounded (by specific facility characteristics such as resource availability and staffing levels) volume-outcome associations using 2-step fixed effects modeling (Milcent, 2005). These additional analyses, however, are beyond the scope of the present study.
Third, although our multivariable analyses controlled for over 30 patient covariates obtained from MDS assessment, it is still possible that the regression did not capture all clinical and nonclinical (such as patient preference) factors that affect individual risk for hospital admissions. Therefore, we cannot rule out the possibility that residual confounding may mediate a part of the estimated volume-outcome association. Fourth, our estimates of rehospitalization rate were slightly lower than the estimates of previous studies, which ranged from 17 percent (Donelan-McCall, et al., 2006; Stearns, et al., 2006) to over 20 percent (Grabowski, et al., 2010; Mor, et al., 2010) (within 30 days of SNF admission). These previous estimates, however, were derived from Medicare hospital claims data which only included fee-for-service admissions and excluded hospital admissions of Medicare HMO patients (Jencks, Williams, & Coleman, 2009). Given the effective control of expensive hospital resource use by HMO policies (Zhan, Miller, Wong, & Meyer, 2004), the lower rehospitalization rate estimated for overall Medicare beneficiaries in this study is expected. Finally, we examined all-cause rehospitalization within defined periods of SNF admission which receives much attention by current policy debates. However, we did not have information about the reasons for these hospital transfers from the MDS discharge disposition code, although it has been reported that a substantial number of SNF hospital transfers are “preventable”(Donelan-McCall, et al., 2006). Future work, in which the MDS assessments are linked to hospital diagnostic records, could attempt to refine our analyses and identify potentially preventable hospitalizations of SNF care patients before reexamining the volume-outcome association.
In conclusion, this study of a national cohort of skilled nursing facility admissions reveals that patients admitted to higher-volume facilities were less likely to be hospitalized within 30 days and 90 days of admission than patients admitted to lower-volume facilities. This volume-outcome relationship is found for hospital-based and freestanding facilities separately. Future work is needed to understand the mechanisms underlying this finding in the context of skilled nursing care, and clarify the potential “selective referral” versus “practice makes perfect” hypothesis.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Li gratefully acknowledges funding from the National Institute on Aging (NIA) under grant R01AG032264. The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the NIA or the Department of Veterans Affairs.
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interests: no conflicts of interest for any authors.
References
- Abt Assoc, Inc. Quality Measures for National Public Reporting: User’s Manual. 2004 Nov1.2 [Google Scholar]
- Abt Associates Inc. Quality monitoring for Medicare global payment demonstrations: Nursing home quality-based purchasing demonstration. 2006 Jun [Google Scholar]
- Birkmeyer JD, Finlayson EV, Birkmeyer CM. Volume standards for high-risk surgical procedures: potential benefits of the Leapfrog initiative. Surgery. 2001;130(3):415–422. doi: 10.1067/msy.2001.117139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boockvar K, Fishman E, Kyriacou CK, Monias A, Gavi S, Cortes T. Adverse events due to discontinuations in drug use and dose changes in patients transferred between acute and long-term care facilities. Archieves of Internal Medicine. 2004;164(5):545–550. doi: 10.1001/archinte.164.5.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan JL, Murkofsky RL, O’Malley AJ, Karon SL, Zimmerman D, Caudry DJ, et al. Nursing home capabilities and decisions to hospitalize: a survey of medical directors and directors of nursing. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2006;54(3):458–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.00620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covinsky KE, Palmer RM, Fortinsky RH, Counsell SR, Stewart AL, Kresevic D, et al. Loss of independence in activities of daily living in older adults hospitalized with medical illnesses: increased vulnerability with age. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2003;51(4):451–458. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donelan-McCall N, Eilertsen TB, Fish R, Kramer A. Small patient population and low frequency event effects on the stability of SNF quality measures. Washington DC: Medicare Payment Advisory Commision; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- GAO General Accounting Office. Public reporting of quality indicators has merit, but national implementation is premature (Publication No GAO-03-187) Washington, D.C: 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Glance LG, Li Y, Osler TM, Dick A, Mukamel DB. Impact of patient volume on the mortality rate of adult intensive care unit patients. Critical Care Medicine. 2006;34(7):1925–1934. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000226415.93237.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbien MJ, Bishop J, Beers MH, Norman D, Osterweil D, Rubenstein LZ. Iatrogenic illness in hospitalized elderly people. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 1992;40(10):1031–1042. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1992.tb04483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski DC, Feng Z, Intrator O, Mor V. Medicaid Bed-Hold Policy and Medicare Skilled Nursing Facility Rehospitalizations. Health Services Research. 2010 doi: 10.1111/j.1475-6773.2010.01104.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski DC, Stewart KA, Broderick SM, Coots LA. Predictors of nursing home hospitalization: a review of the literature. Medical Care Research and Review. 2008;65(1):3–39. doi: 10.1177/1077558707308754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruneir A, Lapane KL, Miller SC, Mor V. Long-term care market competition and nursing home dementia special care units. Medical Care. 2007;45(8):739–745. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e3180616c7e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halm EA, Lee C, Chassin MR. Is volume related to outcome in health care? A systematic review and methodologic critique of the literature. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2002;137(6):511–520. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-137-6-200209170-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutt E, Ecord M, Eilertsen TB, Frederickson E, Kramer AM. Precipitants of emergency room visits and acute hospitalization in short-stay medicare nursing home residents. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2002;50(2):223–229. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Intrator O, Grabowski DC, Zinn J, Schleinitz M, Feng Z, Miller S, et al. Hospitalization of nursing home residents: the effects of states’ Medicaid payment and bed-hold policies. Health Services Research. 2007;42(4):1651–1671. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-6773.2006.00670.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Intrator O, Zinn J, Mor V. Nursing home characteristics and potentially preventable hospitalizations of long-stay residents. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2004;52(10):1730–1736. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jencks SF, Williams MV, Coleman EA. Rehospitalizations among patients in the Medicare fee-for-service program. New England Journal of Medicine. 2009;360(14):1418–1428. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa0803563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones AL, Dwyer LL, Bercovitz AR, Strahan GW. The National Nursing Home Survey: 2004 overview. Vital Health Statistics. 2009;13(167):1–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konetzka RT, Spector W, Limcangco MR. Reducing hospitalizations from long-term care settings. Medical Care Research and Review. 2008;65(1):40–66. doi: 10.1177/1077558707307569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawton MP, Casten R, Parmelee PA, Van Haitsma K, Corn J, Kleban MH. Psychometric characteristics of the minimum data set II: validity. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 1998;46(6):736–744. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1998.tb03809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Cai X, Mukamel DB, Glance LG. The volume-outcome relationship in nursing home care: an examination of functional decline among long-term care residents. Medical Care. 2010;48(1):52–57. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e3181bd4603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Harrington C, Spector WD, Mukamel DB. State regulatory enforcement and nursing home termination from the medicare and medicaid programs. Health Services Research. 2010;45(6 Pt 1):1796–1814. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-6773.2010.01164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu K, Black KJ. Hospital-based and freestanding skilled nursing facilities: any cause for differential Medicare payments? Inquiry. 2003;40(1):94–104. doi: 10.5034/inquiryjrnl_40.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu K, Garrett B, Wissoker D, et al. Options for improving medicare payment for skilled nursing facilities. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS); 2007. Available at: http://www.urban.org/url.cfm?ID=411526. [Google Scholar]
- Luft HS, Bunker JP, Enthoven AC. Should operations be regionalized? The empirical relation between surgical volume and mortality. New England Journal of Medicine. 1979;301(25):1364–1369. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197912203012503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft HS, Garnick DW, Mark DH, Peltzman DJ, Phibbs CS, Lichtenberg E, et al. Does quality influence choice of hospital? Journal of the American Medical Association. 1990;263(21):2899–2906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft HS, Hunt SS, Maerki SC. The volume-outcome relationship: practice-makes-perfect or selective-referral patterns? Health Services Research. 1987;22(2):157–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MedPAC. Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. Report to the Congress: Medicare payment policy. Washington DC: MedPAC; 2008. Jun, [Google Scholar]
- MedPAC. Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. A data book: health care spending and the Medicare program. Washington DC: MedPAC; 2009. Jun, [Google Scholar]
- Milcent C. Hospital ownership, reimbursement systems and mortality rates. Health Economics. 2005;14(11):1151–1168. doi: 10.1002/hec.1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mor V, Angelelli J, Jones R, Roy J, Moore T, Morris J. Inter-rater reliability of nursing home quality indicators in the U.S. BMC Health Services Research. 2003;3(1):20. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-3-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mor V, Intrator O, Feng Z, Grabowski DC. The revolving door of rehospitalization from skilled nursing facilities. Health Affairs (Millwood) 2010;29(1):57–64. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2009.0629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukamel DB, Glance LG, Li Y, Weimer DL, Spector WD, Zinn JS, et al. Does risk adjustment of the CMS quality measures for nursing homes matter? Medical Care. 2008;46(5):532–541. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e31816099c5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukamel DB, Weimer DL, Mushlin AI. Interpreting Market Share Changes as Evidence for Effectiveness of Quality Report Cards. Medical Care. 2007;45(12):1227–1232. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e31812f56bb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukamel DB, Weimer DL, Zwanziger J, Gorthy SF, Mushlin AI. Quality report cards, selection of cardiac surgeons, and racial disparities: a study of the publication of the New York State Cardiac Surgery Reports. Inquiry. 2004;41(4):435–446. doi: 10.5034/inquiryjrnl_41.4.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouslander JG, Lamb G, Perloe M, Givens JH, Kluge L, Rutland T, et al. Potentially avoidable hospitalizations of nursing home residents: frequency, causes, and costs: [see editorial comments by Drs. Jean F. Wyman and William R. Hazzard, pp 760–761] Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2010;58(4):627–635. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.02768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouslander JG, Weinberg AD, Phillips V. Inappropriate hospitalization of nursing facility residents: a symptom of a sick system of care for frail older people. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2000;48(2):230–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2000.tb03919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saliba D, Kington R, Buchanan J, Bell R, Wang M, Lee M, et al. Appropriateness of the decision to transfer nursing facility residents to the hospital. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2000;48(2):154–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2000.tb03906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns SC, Dalton K, Holmes GM, Seagrave SM. Using propensity stratification to compare patient outcomes in hospital-based versus freestanding skilled-nursing facilities. Medical Care Research and Review. 2006;63(5):599–622. doi: 10.1177/1077558706290944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teresi JA, Holmes D, Bloom HG, Monaco C, Rosen S. Factors differentiating hospital transfers from long-term care facilities with high and low transfer rates. The Gerontologist. 1991;31(6):795–806. doi: 10.1093/geront/31.6.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann DR, Coresh J, Oetgen WJ, Powe NR. The association between hospital volume and survival after acute myocardial infarction in elderly patients. New England Journal of Medicine. 1999;340(21):1640–1648. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199905273402106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner R, Stuart E, Polsky D. Public reporting drove quality gains at nursing homes. Health Affairs (Millwood) 2010;29(9):1706–1713. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2009.0556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan C, Miller MR, Wong H, Meyer GS. The effects of HMO penetration on preventable hospitalizations. Health Services Research. 2004;39(2):345–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-6773.2004.00231.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]