Fig. 5.
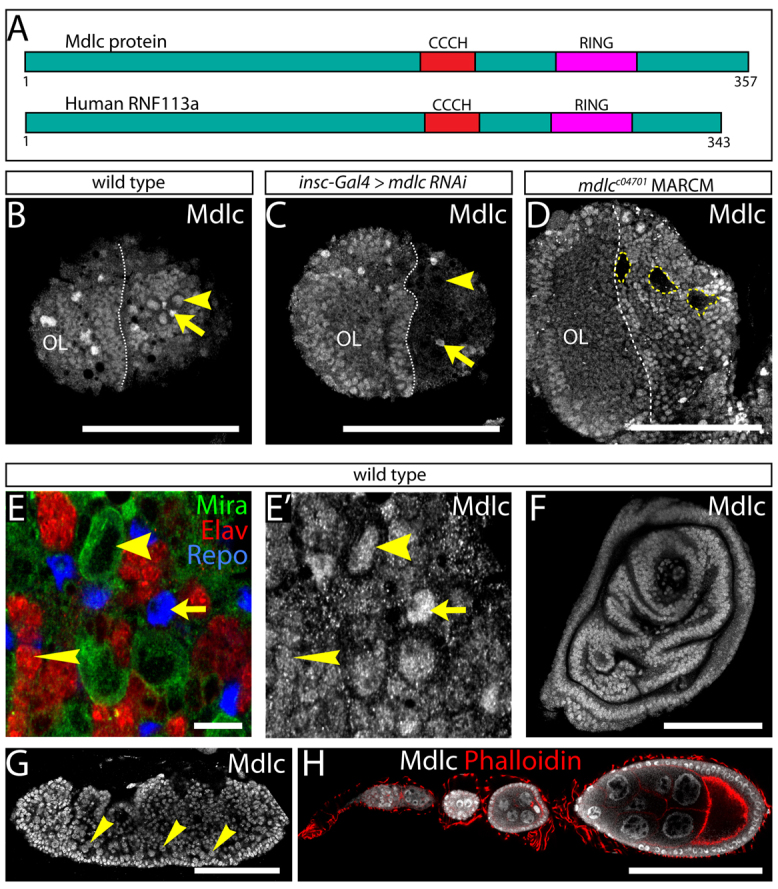
Mdlc is a zinc-finger protein with broad expression in the CNS and other tissues. (A) Mdlc protein and the human ortholog RNF113A have a conserved CCCH zinc finger and a C-terminal RING domain. Numbers indicate amino acids. (B-D) Anti-Mdlc shows ubiquitous nuclear localization of Mdlc, which is lost upon mdlc loss of function. (B) Wt Mdlc is expressed in larval brain neuroblasts (arrowhead) and glia (arrow). (C) mdlc RNAi in central brain neuroblasts and their immediate progeny reduces Mdlc protein staining in the central brain, particularly in neuroblasts (arrowhead), as identified by the presence of Dpn (not shown). Mdlc expression is still visible in glia (arrow) and in the optic lobe (OL), where the RNAi transgene was not expressed. (D) Homozygous mutant mdlcc04701 clones (yellow dashed lines) show a strong reduction in Mdlc protein. (E,E′) In the wt larval brain, Mdlc protein is detected in neuroblasts (wide arrowheads), neurons (narrow arrowheads) and glia (arrows), which can be identified based on staining with antibodies against Mira, Elav and Repo, respectively. (F-H) Mdlc is ubiquitously expressed in all tissues examined. (F) Representative imaginal disc. (G) Mdlc expression in the embryo, including in neuroblasts (arrowheads) identified by Mira expression (not shown). (H) Adult ovariole. Scale bars: 100 μm in B-D,F-H; 10 μm in E.
