Fig. 3.
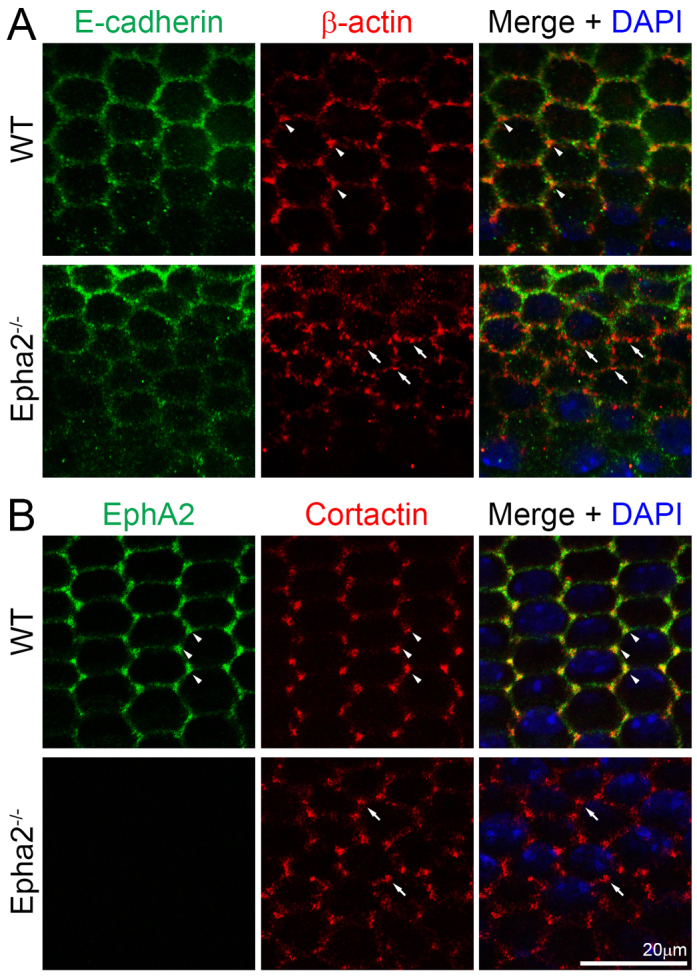
E-cadherin and total cortactin distribution in WT and Epha2-/- equatorial epithelial cells. (A) Double immunolabeling of E-cadherin (green) and β-actin (red) with DAPI staining (blue, nuclei) of equatorial lens epithelial cells from lens capsule flat-mounts of P21 WT and Epha2-/- mice. Confocal images reveal colocalization of β-actin and E-cadherin at the cell membranes of hexagonal epithelial cells in the WT sample. β-actin is enriched at the cell vertices of WT equatorial epithelial cells (arrowheads). However, there is only weak E-cadherin staining at the membranes of the Epha2-/- disorganized equatorial epithelial cells. β-actin (red) forms numerous abnormal aggregates on the membranes of Epha2-/- cells (arrows). (B) Double immunolabeling of EphA2 (green) and total cortactin (red) with DAPI staining (blue) of equatorial lens epithelial cells from lens capsule flat-mounts of P21 WT and Epha2-/- mice. EphA2 and total cortactin are enriched and colocalize at the vertices of hexagonal WT epithelial cells packed into organized meridional rows (arrowheads). By contrast, staining for total cortactin shows abnormal clusters at the cell membranes of disorganized equatorial Epha2-/- epithelial cells (arrows).
