Figure 1.
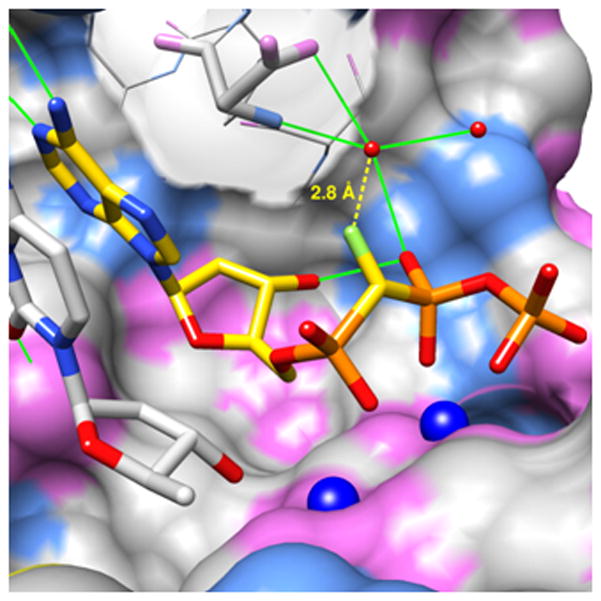
X-ray crystal structure of the DNA pol β active site containing (S)-α,β-CHF-dATP. The solvent-excluded pol β active site surface is colored by atom (carbon, gray; nitrogen, light blue; oxygen, pink; magnesium, dark blue spheres). The surface of Asp276 has been made transparent. The fluorine atom (light green) is 2.8 Å from the oxygen of a conserved water molecule (small red sphere) that is within hydrogen bonding distance (green solid lines) of the oxygen of an adjacent water (2.6 Å), the carboxyamide nitrogen (2.8 Å) and a carboxylate anion oxygen of Asp276 (2.9 Å), as well as the phosphoryl oxygen of Pβ (2.8 Å) which accepts a hydrogen bond from the 3′-OH (2.8 Å). The 3′-primer terminal nucleoside is shown (gray carbons), but its backbone is omitted for clarity.
