Abstract
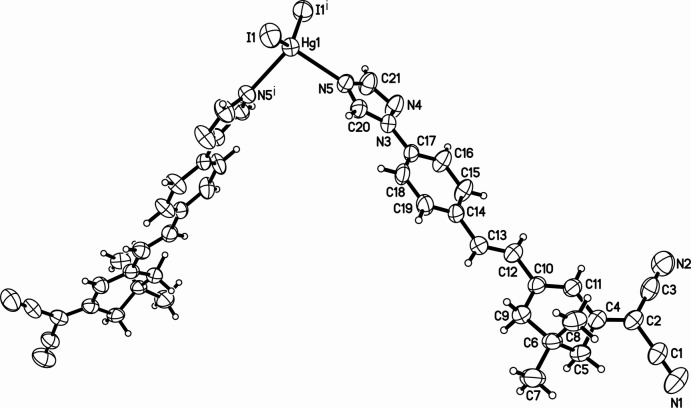
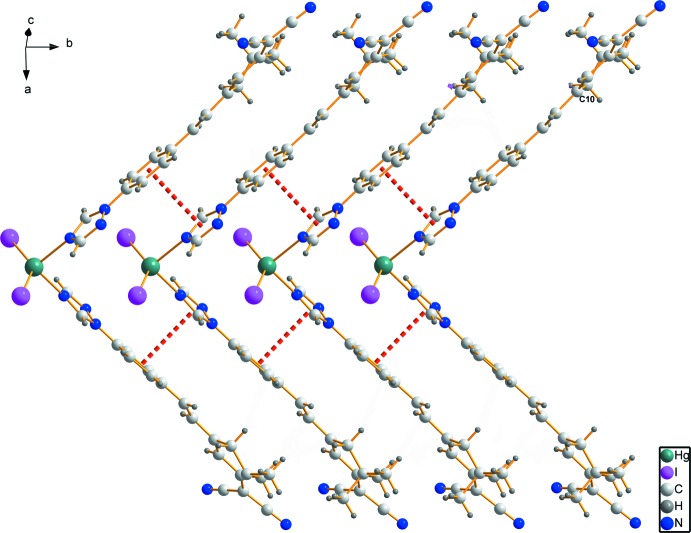
In the title complex, [HgI2(C21H19N5)2], the HgII ion is located on a twofold rotation axis and is coordinated by two I atoms and two N atoms from two (E)-2-{5,5-dimethyl-3-[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)styryl]cyclohex-2-enylidene}malononitrile ligands in a distorted tetrahedral geometry. In the crystal, the molecules are linked by intermolecular π–π interactions between the triazole and benzene rings [centroid–centroid distance = 3.794 (3) Å] into a band extending in [010]. These bands are further connected by C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds into a two-dimensional network parallel to (100).
Related literature
For background to metal-organic complexes, see: Haneda et al. (2007 ▶); Li et al. (2006 ▶); Liu et al. (2010 ▶, 2011 ▶); Satapathy et al. (2012 ▶); Sun et al. (2012 ▶). For the organic ligand of the title compound, see: Zheng et al. (2013 ▶). For related structures, see: Jin, Wang et al. (2013 ▶); Jin, Zhang et al. (2013 ▶); Zhou et al. (2009 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
[HgI2(C21H19N5)2]
M r = 1137.21
Monoclinic,
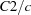
a = 38.9622 (16) Å
b = 5.5684 (12) Å
c = 21.9564 (14) Å
β = 117.738 (2)°
V = 4216.2 (10) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 5.16 mm−1
T = 291 K
0.30 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEX CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2001 ▶) T min = 0.307, T max = 0.457
14961 measured reflections
4078 independent reflections
3384 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.032
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.027
wR(F 2) = 0.071
S = 1.01
4078 reflections
251 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.78 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.52 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: XP in SHELXTL and DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 1999 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, Global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302518X/hy2634sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302518X/hy2634Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C20—H20⋯N2i | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.354 (7) | 157 |
Symmetry code: (i) 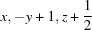 .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in Universities (China), the Doctoral Program Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (grant No. 20113401110004), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant Nos. 21271003 and 21271004), the Natural Science Foundation of the Education Committee of Anhui Province (grant No. KJ2012A024), the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (grant No. 1208085MB22) and the 211 Project of Anhui University.
supplementary crystallographic information
1. Comment
The design and synthesis of metal-organic hybrid complexes based on strong coordinate bonds and multiple weak non-covalent forces have become one of the most active fields in coordination chemistry and crystal engineering not only for their fascinating structural features but also for their interesting properties as new functional materials with tremendous potential applications in the areas of luminescence, catalysis, separation, adsorption, biological chemistry (Haneda et al., 2007; Li et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2010, 2011; Satapathy et al., 2012; Sun et al., 2012). The organic ligand of the title compound had been investigated for its optical properties (Zheng et al., 2013). A variety of mercury(II) complexes have been reported (Jin, Wang et al., 2013). Besides, triazole and isophorone-malononitrile complexes have been reported (Jin, Zhang et al., 2013; Zhou et al., 2009). In this paper, we report the synthesis and crystal structure of the title complex (Fig. 1). In the crystal, intermolecular π–π interactions between the triazole and benzene rings [centroid–centroid distance = 3.794 (3) Å] link the molecules into a band extending in [010] (Fig. 2). The neighboring bands are further linked into a two-dimensional network parallel to (100) through C—H···N hydrogen bonds (Fig.3).
2. Experimental
For the preparation of the title complex, (E)-2-(3-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)styryl)- 5,5-dimethylcyclohex-2-enylidene)malononitrile (0.341 g, 1 mmol) in 25 ml of dichloromethane was added into a 50 ml colorimeter tube, carefully layered with a clear acetonitrile and benzene solution (25 ml) of HgI2 (0.227 g, 0.5 mmol). Crystals were obtained by slow interlayer diffusion (yield: 0.427 g, 75.1%).
3. Refinement
All H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with C—H = 0.93 (CH), 0.97 (CH2) and 0.96 (CH3) Å and with Uiso(H) = 1.2(1.5 for methyl)Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title complex. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. [Symmetry code: (i) -x, y, 3/2-z.]
Fig. 2.
The one-dimensional structure of the title complex, showing π–π interactions (dashed lines).
Fig. 3.
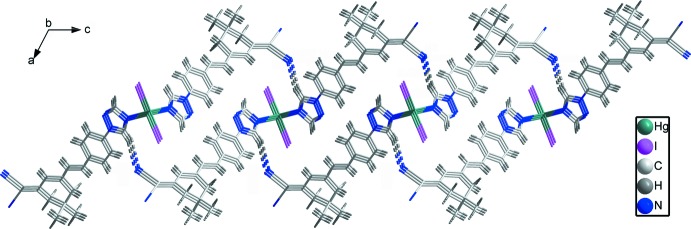
The two-dimensional structure of the title complex, showing C—H···N hydrogen bonds (dashed lines).
Crystal data
| [HgI2(C21H19N5)2] | F(000) = 2184 |
| Mr = 1137.21 | Dx = 1.792 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 38.9622 (16) Å | Cell parameters from 3126 reflections |
| b = 5.5684 (12) Å | θ = 2.1–23.6° |
| c = 21.9564 (14) Å | µ = 5.16 mm−1 |
| β = 117.738 (2)° | T = 291 K |
| V = 4216.2 (10) Å3 | Needle, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEX CCD diffractometer | 4078 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3384 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.032 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2001) | h = −47→47 |
| Tmin = 0.307, Tmax = 0.457 | k = −6→6 |
| 14961 measured reflections | l = −26→26 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.027 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.071 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.01 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.04P)2 + 0.22P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4078 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 251 parameters | Δρmax = 0.78 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.52 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Hg1 | 0.0000 | 1.49817 (4) | 0.7500 | 0.04679 (9) | |
| I1 | 0.06739 (2) | 1.65983 (6) | 0.84809 (2) | 0.06479 (11) | |
| C19 | 0.11064 (13) | 0.4748 (8) | 0.6784 (2) | 0.0541 (11) | |
| H19 | 0.1329 | 0.4209 | 0.7164 | 0.065* | |
| C15 | 0.06588 (13) | 0.4500 (8) | 0.5599 (2) | 0.0560 (11) | |
| H15 | 0.0575 | 0.3788 | 0.5170 | 0.067* | |
| C16 | 0.04479 (12) | 0.6381 (8) | 0.5667 (2) | 0.0540 (10) | |
| H16 | 0.0227 | 0.6937 | 0.5288 | 0.065* | |
| N5 | 0.01215 (9) | 1.2154 (6) | 0.67843 (16) | 0.0452 (7) | |
| N3 | 0.03392 (9) | 0.9312 (6) | 0.63805 (16) | 0.0409 (7) | |
| C13 | 0.12305 (12) | 0.1699 (7) | 0.6110 (2) | 0.0485 (9) | |
| H13 | 0.1406 | 0.1013 | 0.6525 | 0.058* | |
| C21 | −0.01308 (12) | 1.1596 (8) | 0.6130 (2) | 0.0590 (11) | |
| H21 | −0.0370 | 1.2354 | 0.5892 | 0.071* | |
| C20 | 0.04150 (12) | 1.0708 (7) | 0.6927 (2) | 0.0447 (9) | |
| H20 | 0.0641 | 1.0659 | 0.7344 | 0.054* | |
| C17 | 0.05698 (10) | 0.7431 (6) | 0.63072 (19) | 0.0401 (8) | |
| C14 | 0.09914 (11) | 0.3646 (7) | 0.6153 (2) | 0.0439 (9) | |
| N4 | −0.00144 (11) | 0.9900 (6) | 0.58534 (19) | 0.0614 (10) | |
| C18 | 0.08964 (12) | 0.6650 (8) | 0.6862 (2) | 0.0528 (10) | |
| H18 | 0.0979 | 0.7374 | 0.7290 | 0.063* | |
| C10 | 0.14855 (11) | −0.1065 (7) | 0.5526 (2) | 0.0430 (9) | |
| C9 | 0.17746 (11) | −0.2203 (7) | 0.61823 (19) | 0.0481 (9) | |
| H9A | 0.1640 | −0.3332 | 0.6333 | 0.058* | |
| H9B | 0.1885 | −0.0966 | 0.6532 | 0.058* | |
| C11 | 0.14662 (11) | −0.1692 (7) | 0.4915 (2) | 0.0468 (9) | |
| H11 | 0.1295 | −0.0878 | 0.4520 | 0.056* | |
| C12 | 0.12256 (12) | 0.0798 (7) | 0.5548 (2) | 0.0490 (10) | |
| H12 | 0.1040 | 0.1402 | 0.5129 | 0.059* | |
| C6 | 0.21068 (11) | −0.3527 (6) | 0.61357 (19) | 0.0451 (9) | |
| C5 | 0.19376 (13) | −0.5051 (6) | 0.5484 (2) | 0.0504 (10) | |
| H5A | 0.2147 | −0.5826 | 0.5437 | 0.061* | |
| H5B | 0.1775 | −0.6298 | 0.5524 | 0.061* | |
| C4 | 0.17029 (11) | −0.3582 (7) | 0.4857 (2) | 0.0448 (9) | |
| C1 | 0.19109 (13) | −0.6083 (9) | 0.4172 (2) | 0.0556 (10) | |
| C2 | 0.17018 (12) | −0.4045 (8) | 0.4249 (2) | 0.0493 (10) | |
| C3 | 0.14937 (13) | −0.2621 (9) | 0.3649 (2) | 0.0566 (11) | |
| N2 | 0.13295 (13) | −0.1425 (8) | 0.3170 (2) | 0.0772 (12) | |
| N1 | 0.20731 (13) | −0.7689 (8) | 0.4121 (2) | 0.0824 (13) | |
| C8 | 0.24041 (12) | −0.1776 (7) | 0.6121 (2) | 0.0580 (11) | |
| H8A | 0.2609 | −0.2658 | 0.6095 | 0.087* | |
| H8B | 0.2510 | −0.0819 | 0.6531 | 0.087* | |
| H8C | 0.2280 | −0.0748 | 0.5726 | 0.087* | |
| C7 | 0.23118 (16) | −0.5185 (7) | 0.6758 (3) | 0.0698 (14) | |
| H7A | 0.2131 | −0.6351 | 0.6761 | 0.105* | |
| H7B | 0.2411 | −0.4252 | 0.7173 | 0.105* | |
| H7C | 0.2522 | −0.5992 | 0.6732 | 0.105* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Hg1 | 0.05187 (14) | 0.04752 (14) | 0.04360 (14) | 0.000 | 0.02444 (11) | 0.000 |
| I1 | 0.0631 (2) | 0.0737 (2) | 0.05467 (19) | −0.01842 (15) | 0.02500 (15) | −0.00968 (15) |
| C19 | 0.056 (3) | 0.069 (3) | 0.043 (2) | 0.019 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.012 (2) |
| C15 | 0.053 (3) | 0.064 (3) | 0.050 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.023 (2) | −0.023 (2) |
| C16 | 0.044 (2) | 0.066 (3) | 0.046 (2) | 0.008 (2) | 0.0154 (18) | −0.016 (2) |
| N5 | 0.0489 (19) | 0.0457 (18) | 0.0442 (18) | 0.0023 (15) | 0.0242 (16) | −0.0050 (15) |
| N3 | 0.0427 (18) | 0.0461 (17) | 0.0376 (17) | 0.0000 (14) | 0.0219 (15) | −0.0028 (14) |
| C13 | 0.056 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.0027 (18) | 0.032 (2) | 0.0038 (19) |
| C21 | 0.048 (2) | 0.077 (3) | 0.048 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.019 (2) | −0.007 (2) |
| C20 | 0.049 (2) | 0.047 (2) | 0.039 (2) | 0.0000 (18) | 0.0210 (18) | −0.0038 (17) |
| C17 | 0.046 (2) | 0.0409 (19) | 0.043 (2) | −0.0022 (17) | 0.0285 (18) | −0.0026 (17) |
| C14 | 0.049 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.049 (2) | −0.0011 (18) | 0.0314 (19) | −0.0004 (18) |
| N4 | 0.050 (2) | 0.082 (3) | 0.044 (2) | 0.0147 (18) | 0.0156 (17) | −0.0155 (18) |
| C18 | 0.064 (3) | 0.065 (3) | 0.035 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.028 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| C10 | 0.047 (2) | 0.0361 (19) | 0.051 (2) | −0.0018 (17) | 0.0268 (19) | −0.0027 (18) |
| C9 | 0.057 (2) | 0.041 (2) | 0.051 (2) | −0.0002 (18) | 0.029 (2) | −0.0021 (19) |
| C11 | 0.050 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.0068 (18) | 0.0219 (19) | −0.0007 (18) |
| C12 | 0.048 (2) | 0.048 (2) | 0.055 (3) | 0.0043 (19) | 0.027 (2) | −0.004 (2) |
| C6 | 0.055 (2) | 0.0315 (19) | 0.045 (2) | 0.0024 (17) | 0.0202 (18) | 0.0003 (17) |
| C5 | 0.061 (3) | 0.032 (2) | 0.061 (3) | 0.0023 (18) | 0.031 (2) | −0.0009 (19) |
| C4 | 0.042 (2) | 0.042 (2) | 0.053 (2) | −0.0049 (17) | 0.0240 (18) | −0.0077 (18) |
| C1 | 0.056 (3) | 0.056 (3) | 0.060 (3) | −0.002 (2) | 0.031 (2) | −0.014 (2) |
| C2 | 0.047 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.054 (3) | −0.0012 (19) | 0.023 (2) | −0.012 (2) |
| C3 | 0.053 (3) | 0.070 (3) | 0.045 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.021 (2) | −0.018 (2) |
| N2 | 0.081 (3) | 0.087 (3) | 0.055 (3) | 0.007 (2) | 0.024 (2) | −0.007 (2) |
| N1 | 0.082 (3) | 0.075 (3) | 0.103 (3) | 0.003 (2) | 0.053 (3) | −0.028 (3) |
| C8 | 0.051 (2) | 0.047 (2) | 0.071 (3) | −0.0008 (19) | 0.024 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C7 | 0.091 (4) | 0.048 (3) | 0.062 (3) | 0.014 (2) | 0.028 (3) | 0.009 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Hg1—N5 | 2.422 (3) | C10—C9 | 1.495 (5) |
| Hg1—I1 | 2.6606 (8) | C9—C6 | 1.533 (5) |
| C19—C14 | 1.385 (6) | C9—H9A | 0.9700 |
| C19—C18 | 1.397 (5) | C9—H9B | 0.9700 |
| C19—H19 | 0.9300 | C11—C4 | 1.444 (5) |
| C15—C16 | 1.381 (5) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C15—C14 | 1.384 (6) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C15—H15 | 0.9300 | C6—C5 | 1.524 (5) |
| C16—C17 | 1.386 (5) | C6—C8 | 1.526 (5) |
| C16—H16 | 0.9300 | C6—C7 | 1.531 (6) |
| N5—C20 | 1.312 (5) | C5—C4 | 1.494 (6) |
| N5—C21 | 1.346 (5) | C5—H5A | 0.9700 |
| N3—C20 | 1.342 (5) | C5—H5B | 0.9700 |
| N3—N4 | 1.364 (5) | C4—C2 | 1.357 (5) |
| N3—C17 | 1.437 (5) | C1—N1 | 1.131 (5) |
| C13—C12 | 1.324 (5) | C1—C2 | 1.452 (6) |
| C13—C14 | 1.461 (5) | C2—C3 | 1.424 (6) |
| C13—H13 | 0.9300 | C3—N2 | 1.153 (5) |
| C21—N4 | 1.313 (5) | C8—H8A | 0.9600 |
| C21—H21 | 0.9300 | C8—H8B | 0.9600 |
| C20—H20 | 0.9300 | C8—H8C | 0.9600 |
| C17—C18 | 1.360 (5) | C7—H7A | 0.9600 |
| C18—H18 | 0.9300 | C7—H7B | 0.9600 |
| C10—C11 | 1.354 (5) | C7—H7C | 0.9600 |
| C10—C12 | 1.466 (5) | ||
| N5i—Hg1—N5 | 98.89 (15) | C10—C9—H9A | 108.6 |
| N5i—Hg1—I1 | 96.43 (8) | C6—C9—H9A | 108.6 |
| N5—Hg1—I1 | 109.14 (7) | C10—C9—H9B | 108.6 |
| N5i—Hg1—I1i | 109.15 (7) | C6—C9—H9B | 108.6 |
| N5—Hg1—I1i | 96.43 (8) | H9A—C9—H9B | 107.5 |
| I1—Hg1—I1i | 140.450 (19) | C10—C11—C4 | 122.2 (4) |
| C14—C19—C18 | 121.6 (4) | C10—C11—H11 | 118.9 |
| C14—C19—H19 | 119.2 | C4—C11—H11 | 118.9 |
| C18—C19—H19 | 119.2 | C13—C12—C10 | 126.0 (4) |
| C16—C15—C14 | 121.7 (4) | C13—C12—H12 | 117.0 |
| C16—C15—H15 | 119.1 | C10—C12—H12 | 117.0 |
| C14—C15—H15 | 119.1 | C5—C6—C8 | 109.7 (3) |
| C15—C16—C17 | 119.3 (4) | C5—C6—C7 | 108.7 (3) |
| C15—C16—H16 | 120.4 | C8—C6—C7 | 108.6 (4) |
| C17—C16—H16 | 120.4 | C5—C6—C9 | 108.7 (3) |
| C20—N5—C21 | 103.6 (3) | C8—C6—C9 | 111.5 (3) |
| C20—N5—Hg1 | 131.0 (3) | C7—C6—C9 | 109.6 (4) |
| C21—N5—Hg1 | 125.2 (3) | C4—C5—C6 | 111.9 (3) |
| C20—N3—N4 | 109.6 (3) | C4—C5—H5A | 109.2 |
| C20—N3—C17 | 129.3 (3) | C6—C5—H5A | 109.2 |
| N4—N3—C17 | 121.1 (3) | C4—C5—H5B | 109.2 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 127.5 (4) | C6—C5—H5B | 109.2 |
| C12—C13—H13 | 116.3 | H5A—C5—H5B | 107.9 |
| C14—C13—H13 | 116.3 | C2—C4—C11 | 121.1 (4) |
| N4—C21—N5 | 115.0 (4) | C2—C4—C5 | 121.6 (4) |
| N4—C21—H21 | 122.5 | C11—C4—C5 | 117.3 (3) |
| N5—C21—H21 | 122.5 | N1—C1—C2 | 178.8 (5) |
| N5—C20—N3 | 109.7 (4) | C4—C2—C3 | 122.9 (4) |
| N5—C20—H20 | 125.1 | C4—C2—C1 | 121.2 (4) |
| N3—C20—H20 | 125.1 | C3—C2—C1 | 115.9 (4) |
| C18—C17—C16 | 120.7 (3) | N2—C3—C2 | 178.6 (5) |
| C18—C17—N3 | 120.3 (3) | C6—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| C16—C17—N3 | 119.0 (3) | C6—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C15—C14—C19 | 117.5 (3) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C15—C14—C13 | 124.2 (4) | C6—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C19—C14—C13 | 118.3 (4) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C21—N4—N3 | 102.1 (3) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C17—C18—C19 | 119.2 (4) | C6—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| C17—C18—H18 | 120.4 | C6—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C19—C18—H18 | 120.4 | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—C12 | 119.6 (4) | C6—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 121.0 (3) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C12—C10—C9 | 119.4 (3) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C6 | 114.9 (3) | ||
| C14—C15—C16—C17 | −0.6 (7) | N3—C17—C18—C19 | 177.2 (3) |
| C20—N5—C21—N4 | −0.1 (5) | C14—C19—C18—C17 | 0.4 (6) |
| Hg1—N5—C21—N4 | −175.7 (3) | C11—C10—C9—C6 | 16.2 (5) |
| C21—N5—C20—N3 | −0.8 (4) | C12—C10—C9—C6 | −162.3 (3) |
| Hg1—N5—C20—N3 | 174.5 (2) | C12—C10—C11—C4 | −177.3 (4) |
| N4—N3—C20—N5 | 1.4 (5) | C9—C10—C11—C4 | 4.1 (6) |
| C17—N3—C20—N5 | −178.0 (3) | C14—C13—C12—C10 | 176.2 (4) |
| C15—C16—C17—C18 | 1.0 (6) | C11—C10—C12—C13 | −175.1 (4) |
| C15—C16—C17—N3 | −177.2 (4) | C9—C10—C12—C13 | 3.4 (6) |
| C20—N3—C17—C18 | 8.1 (6) | C10—C9—C6—C5 | −45.2 (4) |
| N4—N3—C17—C18 | −171.2 (4) | C10—C9—C6—C8 | 75.8 (4) |
| C20—N3—C17—C16 | −173.8 (4) | C10—C9—C6—C7 | −163.9 (4) |
| N4—N3—C17—C16 | 6.9 (5) | C8—C6—C5—C4 | −66.4 (4) |
| C16—C15—C14—C19 | 0.1 (6) | C7—C6—C5—C4 | 175.1 (4) |
| C16—C15—C14—C13 | −178.7 (4) | C9—C6—C5—C4 | 55.8 (4) |
| C18—C19—C14—C15 | 0.0 (6) | C10—C11—C4—C2 | −174.5 (4) |
| C18—C19—C14—C13 | 178.9 (4) | C10—C11—C4—C5 | 7.5 (6) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | 15.6 (7) | C6—C5—C4—C2 | 143.5 (4) |
| C12—C13—C14—C19 | −163.3 (4) | C6—C5—C4—C11 | −38.5 (5) |
| N5—C21—N4—N3 | 0.9 (5) | C11—C4—C2—C3 | 4.7 (6) |
| C20—N3—N4—C21 | −1.3 (4) | C5—C4—C2—C3 | −177.4 (4) |
| C17—N3—N4—C21 | 178.1 (3) | C11—C4—C2—C1 | −174.2 (4) |
| C16—C17—C18—C19 | −0.9 (6) | C5—C4—C2—C1 | 3.7 (6) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x, y, −z+3/2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C20—H20···N2ii | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.354 (7) | 157 |
Symmetry code: (ii) x, −y+1, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HY2634).
References
- Brandenburg, K. (1999). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2001). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2007). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Haneda, S., Gan, Z. B., Eda, K. & Hayashi, M. (2007). Organometallics, 26, 6551–6555.
- Jin, F., Wang, H.-Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Kong, L., Hao, F.-Y., Yang, J.-X., Wu, J.-Y., Tian, Y.-P. & Zhou, H.-P. (2013). CrystEngComm, 15, 3687–3695.
- Jin, F., Zhang, Y., Wang, H.-Z., Zhu, H.-Z., Yan, Y., Zhang, J., Wu, J.-Y., Tian, Y.-P. & Zhou, H.-P. (2013). Cryst. Growth Des. 13, 1978–1987.
- Li, Y.-Y., Lin, C.-K., Zheng, G.-L., Cheng, Z.-Y., You, H., Wang, W.-D. & Lin, J. (2006). Chem. Mater. 18, 3463–3469.
- Liu, Q.-K., Ma, J.-P. & Dong, Y.-B. (2010). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 7005–7017. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.-K., Ma, J.-P. & Dong, Y.-B. (2011). Chem. Commun. 47, 12343–12345. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Satapathy, R., Wu, Y. H. & Lin, H. C. (2012). Org. Lett. 14, 2564–2567. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sun, L., Li, G.-Z., Xu, M.-H., Li, X.-J., Li, J. R. & Deng, H. (2012). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. pp. 1764–1772.
- Zheng, Z., Yu, Z.-P., Yang, M.-D., Jin, F., Zhang, Q., Zhou, H.-P., Wu, J.-Y. & Tian, Y.-P. (2013). J. Org. Chem. 78, 3222–3234. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.-P., Yin, J.-H., Zheng, L.-X., Wang, P., Hao, F.-Y., Geng, W.-Q., Gan, X.-P., Xu, G.-Y., Wu, J.-Y., Tian, Y.-P., Tao, X.-T., Jiang, M.-H. & Kan, Y.-H. (2009). Cryst. Growth Des. 9, 3789–3798.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, Global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302518X/hy2634sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302518X/hy2634Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report