Abstract
Background
Hippocampal atrophy is a well-known feature of Alzheimer's disease (AD), but sensitivity and specificity of hippocampal volumetry are limited. Neuropathological studies have shown that hippocampal subfields are differentially vulnerable to AD; hippocampal subfield volumetry may thus prove to be more accurate than global hippocampal volumetry to detect AD.
Methods
CA1, subiculum and other subfields were manually delineated from 40 healthy controls, 18 AD, 17 amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment (aMCI), and 8 semantic dementia (SD) patients using a previously developed high resolution MRI procedure. Non-parametric group comparisons and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses were conducted. Complementary analyses were conducted to evaluate differences of hemispheric asymmetry and anterior-predominance between AD and SD patients and to distinguish aMCI patients with or without β-amyloid deposition as assessed by Florbetapir-TEP.
Results
Global hippocampi were atrophied in all three patient groups and volume decreases were maximal in the CA1 subfield (22% loss in aMCI, 27% in both AD and SD; all p < 0.001). In aMCI, CA1 volumetry was more accurate than global hippocampal measurement to distinguish patients from controls (areas under the ROC curve = 0.88 and 0.76, respectively; p = 0.05) and preliminary analyses suggest that it was independent from the presence of β-amyloid deposition. In patients with SD, whereas the degree of CA1 and subiculum atrophy was similar to that found in AD patients, hemispheric and anterior–posterior asymmetry were significantly more marked than in AD with greater involvement of the left and anterior hippocampal subfields.
Conclusions
The findings suggest that CA1 measurement is more sensitive than global hippocampal volumetry to detect structural changes at the pre-dementia stage, although the predominance of CA1 atrophy does not appear to be specific to AD pathophysiological processes.
Abbreviations: Aβ, β-amyloid; AD, Alzheimer's disease; aMCI, amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment; ANOVA, Analysis of variance; AUC, Area Under the receiver operating characteristic Curve; HC, healthy controls; MRI, Magnetic resonance imaging; NFT, neurofibrillary tangles; PET, Positon Emission Tomography; ROC, receiver operating characteristic; SUVr, Standardized Uptake Value ratio; TIV, Total intracranial volume
Keywords: Hippocampal subfields, CA1, Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Alzheimer's disease, Semantic dementia, Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Highlights
-
•
Using 3 T MRI, hippocampal subfields were measured in aMCI, AD and SD and controls.
-
•
CA1 atrophy was found to be predominant in all patient groups.
-
•
CA1 volume was the best discriminating measure between controls and aMCI patients.
-
•
AD and SD differed in asymmetry and anterior-predominance, not in subfield atrophy.
1. Introduction
Hippocampal atrophy is a major feature of Alzheimer's disease (AD) (Frisoni et al., 2010) that strongly correlates with AD neuropathology (Bobinski et al., 1996; Jack et al., 2002). Using MRI, this atrophy is detectable prior to the diagnosis of AD, at the stage of amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment (aMCI) (Convit et al., 1997; Shi et al., 2009) or even earlier, in asymptomatic elderly up to 10 years before the diagnosis of dementia (Smith et al., 2007; Tondelli et al., 2012). Hippocampal volume has thus been proposed as a neuroimaging biomarker for early AD diagnosis (Albert et al., 2011; Dubois et al., 2010). Yet, the accuracy of this measurement is limited by a moderate sensitivity and a rather low specificity to AD pathophysiological processes (Frisoni et al., 2010). Indeed, hippocampal atrophy has been highlighted in various neurological and psychiatric conditions (Geuze et al., 2005), and notably in other neurodegenerative disorders such as semantic dementia (SD) (Chan et al., 2001; Davies et al., 2004; Desgranges et al., 2007; Galton et al., 2001; Nestor et al., 2006).
Interestingly, neuropathological studies have shown a differential vulnerability of hippocampal subfields to AD, with CA1 showing the earliest and strongest changes in terms of both neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) (Braak & Braak, 1991; Schönheit et al., 2004) and neuronal loss (Rössler et al., 2002; West et al., 1994). In vivo measurement of CA1 atrophy may thus constitute a better surrogate marker for AD pathology than global hippocampal volumetry. Recently MRI acquisition and processing techniques have been developed to assess the hippocampus in more detail, including high-resolution hippocampus scans allowing visualization and measurement of hippocampal subfields (Mueller et al., 2010; Pluta et al., 2012; Wisse et al., 2012).
In this study, we aimed at identifying the pattern of hippocampal subfield atrophy in patients with AD, aMCI and SD using a previously developed technique based on high-resolution 3-Tesla MRI and adapted delineation guidelines (La Joie et al., 2010). In addition we assessed the diagnosis accuracy of these measures, hypothesizing that specific measurement of the most vulnerable subfield(s), e.g. CA1, would be more accurate than global hippocampal volumetry to detect AD-related hippocampal atrophy (Mueller et al., 2010; Pluta et al., 2012).
2. Material and methods
2.1. Participants
Eighty-three right-handed native French-speaking participants from the IMAP project (La Joie et al., 2010) were included in the present study: 40 healthy controls (HC), 17 aMCI patients, 18 AD patients, and eight SD patients (see Table 1). They were all aged over 50 years, had at least 7 years of education and had no history of alcoholism, drug abuse, head trauma or psychiatric disorder.
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of participants.
Abbreviations: HC = healthy controls; aMCI = amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment; AD = Alzheimer's disease; SD = semantic dementia; IQR = interquartile range; MMSE = mini-mental state examination; ANOVA = Analysis of variance.
All variables were compared using non-parametric tests.
a: Mattis scores were lower in AD and SD groups as compared to HC and aMCI but no difference was found between AD and SD.
| HC (n = 40) | aMCI (n = 17) | AD (n = 18) | SD (n = 8) | Group comparison | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age median (IQR) |
66 (56, 72) | 72 (69, 75) | 66 (58, 76) | 62.5 (59.5, 65.5) | pANOVA = 0.027 aMCI > HC; aMCI > SD |
| Gender females: n (%) |
23 (58%) | 9 (53%) | 12 (67%) | 5 (63%) | pChi-squared = 0.86 |
| Years of education median (IQR) |
12 (9.5, 15) | 10 (8, 12) | 10 (7, 14) | 12 (5.8, 15.5) | pANOVA = 0.19 |
| MMSE median (IQR) |
30 (29, 30) | 27 (26, 28) | 20.5 (20, 24) | – | pANOVA < 0.001 HC > aMCI > AD |
| Mattis median (IQR) |
143 (142, 144) | 137 (134, 138) | 123 (114, 128) | 118 (111, 125.5) | pANOVA < 0.001 HC > aMCI > AD, SDa |
All patients were recruited from local memory clinics and selected according to corresponding internationally agreed criteria: Petersen's criteria for aMCI (Petersen & Morris, 2005), NINCDS-ADRDA criteria for probable Alzheimer's disease (McKhann et al., 1984) and Neary et al. criteria for SD (Neary et al., 1998).
HC were recruited from the community and performed in the normal range on a neuropsychological examination assessing multiple domains of cognition including episodic and semantic memory, executive and visuo-spatial functions, language and praxis.
In addition to this clinically based selection, the majority of aMCI and AD patients underwent a Florbetapir PET scan allowing to classify them as β-amyloid (Aβ)-positive or Aβ-negative as recommended in the new research criteria for AD (Albert et al., 2011; Dubois et al., 2010) (see Sections 2.3.3 and 2.4 below).
The IMAP Study was approved by regional ethics committee (Comité de Protection des Personnes Nord-Ouest III) and is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (number NCT01638949). All participants gave written informed consent to the study prior to the investigation.
2.2. Neuroimaging data acquisition
All participants were scanned on the same MRI and PET cameras at the Cyceron center (Caen, France).
2.2.1. MRI data
A high-resolution proton density-weighted MR sequence, perpendicular to the long axis of the hippocampus (repetition time/echo time = 3500/19 ms; flip angle = 90°; 13 slices with 2 mm gap; slice thickness = 2 mm; in-plane resolution = 0.375 × 0.375 mm) was acquired on a Philips (Eindhoven, The Netherlands) Achieva 3 T scanner. A sagittal T1-weighted anatomical image was obtained beforehand using a 3D fast field echo sequence (repetition time/echo time = 20/4.6 ms; flip angle = 20°; 180 slices with no gap; slice thickness = 1 mm in-plane resolution = 1 × 1 mm) for the purpose of PET data preprocessing and total intracranial volume (TIV) measurement (see below).
2.2.2. PET data
Florbetapir PET scans were acquired on a Discovery RX VCT 64 PET-CT device (General Electric Healthcare) with a resolution of 3.76 × 3.76 × 4.9 mm (field of view = 157 mm). Forty-seven planes were obtained with a voxel size of 2.7 × 2.7 × 3.27 mm. A transmission scan was performed for attenuation correction before the PET acquisition. Participants underwent a 20-min PET scan, starting 50 min after the intravenous injection of ≈ 4 MBq/kg of Florbetapir.
2.3. Neuroimaging data processing
2.3.1. Hippocampal subfield delineation
Three regions of interest (subiculum, CA1 and “other” subfields — encompassing CA2–CA3–CA4 and the dentate gyrus) were delineated on both hippocampi of all individual high-resolution MRI images, following guidelines developed in the lab and described in full details elsewhere (La Joie et al., 2010). These guidelines were based on the anatomical description from an atlas of the human hippocampus (Harding et al., 1998). Delineations were performed on slices perpendicular to the long axis of the hippocampus by a single rater, blind to the identity (age, gender, clinical status) of the participants. Illustrations are provided in Fig. 1 (see also Supplementary Fig. 1 for further details and additional examples).
Fig. 1.
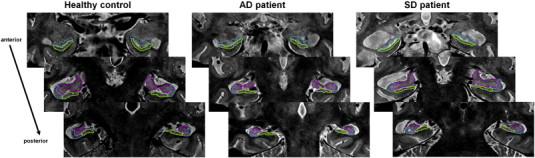
Illustration of hippocampal subfield delineation.
Three regions were manually delineated within each hippocampus: CA1 (blue), subiculum (green) and other (pink). Subfields were delineated on 9 slices on average; for the purpose of illustration, examples are displayed on three slices along the anterior–posterior axis of the hippocampus. Images correspond to a healthy control (left), a patient with Alzheimer's disease (middle) and a patient with semantic dementia (right). Images are in the neurological convention (right is right). Additional examples are available in Supplementary Fig. 1. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
Unlike other groups with comparable high-resolution anisotropic images (Mueller et al., 2010; Pluta et al., 2012) we delineated subfields along the head and body of the hippocampus (versus in the body only for these previous articles). Yet, because of the difficulty of distinguishing landmarks for subfields delineation in the hippocampal head, we only considered 3 regions of interest (therefore combining CA2–3–4 and the dentate gyrus in the same “subfield”) to ensure sufficient reliability and reproducibility (versus 4 or 5 subfields in previous studies (Mueller et al., 2010; Pluta et al., 2012)). As previously mentioned (Mueller et al., 2010; Wisse et al., 2012), measurements of hippocampal subfields not only rely on landmarks derived from anatomical atlases, but also on arbitrary rules that are fixed by the investigators to reach a compromise between reliability/reproducibility and validity. We acknowledge that existing protocols show differences in their definition of hippocampal subfields but, in the absence of direct comparison between in vivo imaging methods (ideally including a confrontation to neuropathological gold standard), the importance of these variations and their influence on results remains unknown. However, a recently formed initiative led by experts in the field is specifically meant to address this issue and to potentially develop a unified hippocampal subfield segmentation protocol (to know more about this group, visit http://www.hippocampalsubfields.com/).
Moreover, it is to note that high-resolution scans such as those used here are particularly prone to motion artifacts. To prevent the rejection of a large proportion of individuals from analyses, a procedure was settled to obtain high quality data from all individuals participating to imaging studies in our lab (including, but not restricted to the controls and patients from the present article). Indeed, a visual quality check was performed immediately after or within a few days of the MRI acquisition and was carried out by the same person who analyzes the data (RLJ). If image quality was considered insufficient for subfield delineation, the scan was repeated within a few weeks during a second MRI session (this occurred for about 15–20% of healthy controls and 30–40% of the patients included in our total imaging cohort). Rarely, a third scan was proposed. In the end, we failed to obtain an image of sufficient quality in some participants (roughly 5–10% of the controls and 15–20% of the patients) as they could not come back for a repeated scan or because the repeated scan(s) was/were still of insufficient quality; in this case, data were disregarded and excluded from all analyses. The 83 participants included in the present study had high quality data.
2.3.2. Total intracranial volume (TIV)
Individual TIV values were obtained from the T1-weighted images using the VBM5 toolbox implemented in the Statistical Parametric Mapping software (SPM5; Wellcome Trust Center for Neuroimaging, Institute of Neurology, London, England).
2.3.3. Florbetapir PET
PET data were processed as described in reference (La Joie et al., 2012). Briefly, each individual T1-weighted MRI was segmented into gray and white matter using the VBM5 toolbox (http://dbm.neuro.uni-jena.de/vbm/vbm5-for-spm5/). These segments were used for partial volume effect correction of raw PET data using the PMOD software. Using the Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) software, resulting images were coregistered onto corresponding MRI and normalized into Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space using the deformation parameters defined from the VBM procedure. The mean Florbetapir value in the cerebellum GM was extracted for each subject from the normalized TEP images. Each Florbetapir image was then divided by its corresponding mean cerebellar value, resulting in Florbetapir-PET SUVr data. The global neocortical Florbetapir-PET SUVr value was then computed for each subject from the Florbetapir-PET SUVr data using a neocortex mask (including all regions but the cerebellum, hippocampus, amygdala and subcortical gray nuclei).
2.4. Statistical analyses
Raw volumes of each hippocampal subfield and of the whole hippocampus (corresponding to the sum of the three subfields) were first normalized by the TIV to account for inter-individual variability in head size (normalized volume = 1000 × raw volume / TIV) and then transformed into W-scores, i.e. age and gender-adjusted Z-scores (Jack et al., 2002). W-scores provide information about the difference between a patient's value and the value that would be expected in the control group for his/her age and gender. In the present study, the use of W-score is of particular interest because of the rather wide age range of the participants and significant age difference between aMCI and both HC and SD groups (see Table 1). Due to the relative limited size of the patient groups, Kruskal–Wallis non-parametric analyses of variance (ANOVAs) were then performed on hippocampal subfield and whole hippocampus W-scores, and when a significant effect of group was found (p < 0.05), Mann–Whitney U tests were used for pairwise comparisons.
As previous studies reported a stronger hemispheric asymmetry and an anterior predominance of hippocampal atrophy in SD compared with AD (Chan et al., 2001; Nestor et al., 2006), complementary indices were calculated to characterize these gradients within each subfield. First, hemispheric asymmetry was measured as the absolute difference between left and right hippocampal volumes expressed as a percentage of the total volume (100 x | right volume – left volume | / bilateral hippocampal volume). Second, an index of anterior–posterior gradient was calculated as the percentage of each subfield volume located in the anterior hippocampus (100 x anterior volume / total hippocampal volume), with the anterior portion corresponding to the hippocampal head (Jack et al., 1997; Malykhin et al., 2007; Pruessner & Li, 2000). These indices were compared between HC, AD and SD using Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA and Mann–Whitney U tests.
Discriminant analyses were performed to assess the ability of each hippocampal subfield and of the whole hippocampus volume to distinguish i) AD patients from HC, ii) aMCI patients from HC, and iii) SD patients from AD. Areas Under the receiver operating characteristic Curve (AUC) of global hippocampus versus subfield volumes were then compared to test the hypothesis that subfield is more accurate than global hippocampal volumetry to discriminate between the groups.
Finally, preliminary analyses were conducted to assess the impact of the presence of Aβ on the different hippocampal volumes. All AD patients (n = 18) and 15 patients with aMCI (out of 17) underwent a Florbetapir PET scan and were classified using a previously determined Florbetapir neocortical SUVr of 1.1 (see reference (La Joie et al., 2012)). All AD patients were classified as Aβ-positive and 9 aMCI patients (60% of aMCI patients who underwent Florbetapir-PET) were classified as Aβ-positive. Aβ-positive and Aβ-negative aMCI did not differ in age, gender or education (all p-values > 0.8). Statistical analyses on hippocampal volumes included both Spearman's correlation between Aβ load and hippocampal atrophy within the 15 aMCI patients, and comparisons between Aβ-positive versus Aβ-negative aMCI, and between each subgroup and HC. For the latter analysis, because aMCI was significantly older than the whole HC group (see Table 1), a subgroup of age, gender and education-matched HC (n = 28) was used.
3. Results
3.1. Atrophy of hippocampal subfields in patients
Comparisons of W-scores are illustrated in Fig. 2. Briefly, the volume of the whole hippocampus was significantly decreased in all three patient groups as compared to HC (mean volume loss = − 12% for aMCI, − 22% for AD and − 17% for SD). In aMCI, atrophy was highly significant in CA1 (− 22%, p < 0.001) and to a lesser extent in the subiculum (− 17%, p = 0.01). In AD, volume decreases were highly significant (p < 0.001) for all three subfields, but atrophy in the other region (− 17%) was significantly lower (p < 0.005 using Wilcoxon rank-sum test) than in both CA1 and subiculum (both − 27%). In the SD group, both CA1 and subiculum volumes were significantly reduced relative to HC (− 27% and − 24% respectively, both p < 0.001). Similarly to the findings in the AD group, comparing degrees of atrophy (expressed as W-scores) between the three subfields in SD showed that both CA1 and subiculum were significantly more affected than the other subfield (both p < 0.05 Wilcoxon rank-sum test). None of the volumes differed between AD and SD patients (all p values > 0.15). Note that the main results were unchanged when performing comparisons on raw volumes or TIV-normalized volumes instead of age- and gender-adjusted W-scores as presented here (see Supplementary Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
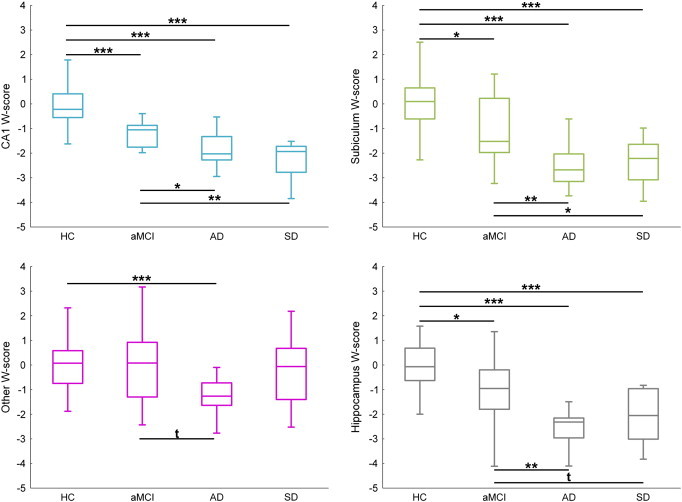
Between-group comparisons of hippocampal measurements.
Abbreviations: HC = healthy controls; aMCI = amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment; AD = Alzheimer's disease; SD = semantic dementia.
Volumes are expressed as W-scores (i.e. age- and gender-adjusted Z-scores as compared to the control group).
Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA was significant for all regions and post-hoc tests were performed with the Mann–Whitney test (t: p < 0.10; *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001).
3.2. Hemispheric asymmetry and anterior–posterior gradient in AD and SD
The results of the between-group comparisons of the hippocampal indices are reported in Table 2. Greater hemispheric asymmetry was found in SD patients compared to HC for all volumes (all p values < 0.03). Asymmetry was significantly stronger in SD than in AD for the whole hippocampus (p = 0.001), subiculum (p = 0.02), other (p = 0.01) and a trend was found for CA1 (p = 0.06).
Table 2.
Hemispheric asymmetry and anterior–posterior gradients of subfield atrophy in AD and SD patients.
Abbreviations: HC = healthy controls; AD = Alzheimer's disease; SD = semantic dementia; IQR = interquartile range. ANOVA were conducted with the Kruskal & Wallis H test and when significant (p < 0.05), two-by-two comparisons were assessed with the Mann–Whitney test. Significant (p < 0.05) results are shown in bold.
Increased hemispheric asymmetry indicates a stronger left/right volume difference but not the direction of this difference. Increased anterior–posterior gradient index indicates an increase in the volume of the anterior hippocampal compared to that of the total hippocampal volume. See main text (Section 2.4) for further information.
| Values: median (IQR) |
Statistical comparisons |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC | AD | SD | ANOVA | HC/AD | HC/SD | AD/SD | |
| Hemispheric asymmetry | |||||||
| CA1 | 5.4 (1.8, 8.5) |
7.8 (4.2, 17.0) |
15.3 (13.1, 18.5) |
H = 14.7 p < 10− 3 |
Z = 1.94 p = 0.05 |
Z = 3.67 p < 10− 3 |
Z = 1.86 p = 0.06 |
| Subiculum | 3.8 (1.6, 6.5) |
6.6 (1.8, 8.1) |
17.7 (12.7, 23.8) |
H = 16.1 p < 10− 3 |
Z = 1.64 p = 0.10 |
Z = 3.91 p < 10− 3 |
Z = 2.42 p = 0.02 |
| Other | 5.2 (2.8, 9.8) |
5.1 (1.9, 8.1) |
11.4 (7.2, 14.4) |
H = 7.2 p = 0.03 |
Z = − 0.82 p = 0.42 |
Z = 2.31 p = 0.021 |
Z = 2.53 p = 0.01 |
| Global hippocampus | 2.1 (1.2, 4.0) |
4.7 (2.8, 7.1) |
14.2 (11.2, 16.1) |
H = 27.1 p < 10− 3 |
Z = 3.17 p = 0.002 |
Z = 4.41 p < 10− 3 |
Z = 3.25 p = 0.001 |
| Anterior–posterior gradient | |||||||
| CA1 | 66.2 (63.4, 70.0) |
66.6 (59.7, 70.1) |
56.5 (52.9, 57.6) |
H = 14.7 p < 10− 3 |
Z = − 0.33 p = 0.74 |
Z = − 3.80 p < 10− 3 |
Z = 3.08 p = 0.002 |
| Subiculum | 57.2 (53.2, 61.5) |
60.1 (53.3, 65.6) |
52.4 (44.8, 54.9) |
H = 8.3 p = 0.02 |
Z = 1.02 p = 0.31 |
Z = 2.59 p = 0.01 |
Z = 2.47 p = 0.01 |
| Other | 62.8 (57.5, 66.7) |
65.8 (57.1, 70.4) |
59.7 (55.5, 61.9) |
H = 3.03 p = 0.22 |
– | – | – |
| Global hippocampus | 62.4 (59.0, 65.1) |
64.6 (58.2, 68.5) |
55.6 (52.0, 59.0) |
H = 9.3 p = 0.009 |
Z = 0.60 p = 0.55 |
Z = 2.95 p = 0.003 |
Z = 2.53 p = 0.01 |
Finally, the anterior–posterior index was significantly lower in SD compared to both HC and AD for the whole hippocampus, CA1 and subiculum, indicating a predominance of atrophy in the anterior hippocampus in SD.
3.3. Evaluation of diagnostic accuracy
For the AD versus HC discrimination, the AUC of all subfields was significantly higher than 0.5 (mean [95% CI] = 0.92 [0.85–0.99] for CA1, 0.88 [0.76–1] for subiculum, 0.81 [0.67–0.94] for other) but none of them was significantly higher than that of the whole hippocampus (0.91 [0.78–1]). For the discrimination between HC and aMCI, the AUC of CA1 (0.88 [0.78–0.98]) was significantly higher than 0.5 and higher than the AUC of the whole hippocampus (0.76 [0.60–0.93], p = 0.05; see Fig. 3), whereas the subiculum AUC (0.74 [0.59–0.90]) was significantly higher than 0.5 but did not perform better than the whole hippocampus, and the AUC for the other subfields was not significantly different from 0.5 (0.53 [0.34–0.72]). Finally, none of the volume measurements were allowed to separate AD from SD as none of the AUCs was significantly different from 0.5: 0.51 [0.27–0.74] for CA1, 0.64 [0.43–0.85] for subiculum, 0.69 [0.45–0.94] for other, and 0.69 [0.47–0.90] for the whole hippocampus.
Fig. 3.
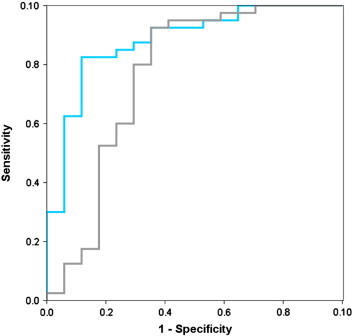
ROC Curve for CA1 and total hippocampal volume in aMCI patients versus HC.
ROC curves for CA1 (blue) and total hippocampal volume (gray) in the comparison between healthy controls (HC) and patients with amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment (aMCI). The area under the curve (AUC) is significantly higher (p = 0.05) for CA1 (AUC = 0.881) than for total hippocampal volume (0.763). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
3.4. Volume of hippocampal subfields versus neocortical amyloid load in aMCI patients
A Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA with three groups (HC, Aβ-positive aMCI, Aβ-negative aMCI) was performed on TIV-normalized hippocampal measurements. A significant effect of group was found for CA1 (H = 13.8; p = 0.001), subiculum (H = 5.99; p = 0.05) and global hippocampus (H = 5.98; p = 0.05). Post-hoc analyses revealed that Aβ-positive aMCI had significantly lower CA1 (p < 0.001), subiculum (p = 0.01) and hippocampal volumes (p = 0.01) as compared to HC, while Aβ-negative aMCI only showed lower CA1 volume (p = 0.04) as compared to HC, as illustrated in Fig. 4. The direct comparison between Aβ-positive aMCI and Aβ-negative aMCI did not show any significant difference (all p values > 0.25). Similarly, none of the volumes significantly correlated with Florbetapir neocortical SUVr in the whole group of 15 aMCI (CA1: Spearman's ρ = − 0.34, p = 0.22; subiculum ρ = − 0.26, p = 0.34; other ρ = − 0.01, p = 0.96; whole hippocampus ρ = − 0.23, p = 0.41). All the results remained unchanged when using W-scores instead of TIV-normalized volumes (data not shown).
Fig. 4.
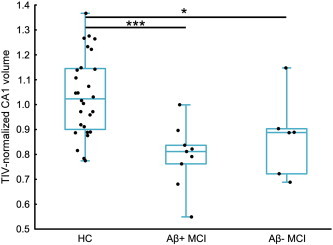
CA1 atrophy in aMCI patients classified as Aβ-positive or Aβ-negative according to their neocortical Florbetapir SUVr.
Abbreviations: HC = healthy controls; Aβ + aMCI = β-amyloid—positive patients with amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment; Aβ − aMCI = β-amyloid—negative patients with amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment.
For this analysis, a subsample of 28 age-, gender-, and education-matched HC was selected.
Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA was significant (p = 0.001) and post-hoc tests were performed with the Mann–Whitney test (*: p < 0.05; ***: p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
Using a high-resolution sequence on a 3 T MRI scanner, hippocampal subfields were delineated in healthy controls and patients with aMCI, AD or SD. Analyses showed that the pathologies had a differential effect on the hippocampal subfields, with a preferential involvement (i.e. stronger and earlier atrophy) of CA1 and subiculum. This pattern was not discriminant at the dementia stage as i) no differences were found between AD and SD and ii) hippocampal subfields did not perform better than the whole hippocampus in discriminating AD from HC. By contrast, at the aMCI stage, CA1 volume loss predominated and was found to better discriminate aMCI patients from HC than global hippocampal volume.
4.1. Hippocampal subfield atrophy in AD
The finding of a differential atrophy of the hippocampal subfields in AD, with a stronger and earlier alteration of CA1 and subiculum, is in agreement with neuropathological studies (Braak & Braak, 1991; Rössler et al., 2002; Schönheit et al., 2004; West et al., 1994). For instance, West et al. (1994) reported a reduction in the number of neurons in AD patients compared to HC of 68% in CA1, 47% in the subiculum and 25% in the hilus of the dentate gyrus. The higher vulnerability of CA1 neurons is likely to be at least partly due to the neurofibrillary pathology as the CA1 subfield is the first hippocampal area to be affected by NFT (Braak & Braak, 1991; Schönheit et al., 2004). Moreover, several studies have reported a strong negative correlation between neuronal counts and NFT number in the CA1 subfield (Fukutani et al., 2000; Von Gunten et al., 2006) suggesting that the progression of brain atrophy and the progression of NFT are strongly associated (Whitwell et al., 2008).
Using a variety of neuroimaging approaches such as radial atrophy (Frisoni et al., 2006), large-deformation high-dimensional brain mapping (Wang et al., 2003), voxel-based morphometry (Chételat et al., 2008) or manual delineation (Mueller et al., 2010), the predominance of atrophy in CA1 (and to a lesser extent in the subiculum) in patients with clinical AD or aMCI has already been shown in vivo. In the present study, we confirmed this point using a refined methodology in patients with both a clinical diagnosis of AD and a positive Florbetapir PET-scan. Our study showed that all subfields were atrophied at this AD dementia stage and subfield measurements were not more accurate than the global hippocampus in discriminating AD from HC. By contrast, and in agreement with previous volumetric studies (Hanseeuw, 2011; Mueller et al., 2010; Pluta et al., 2012), we showed that subfield measurements were more accurate than global hippocampal volumetry to differentiate aMCI from HC, highlighting the interest of these methods for early AD detection. However, discrepancies exist as regards to the area of largest difference between HC and aMCI patients (CA1 (Pluta et al., 2012), CA1–CA2 transition area (Mueller et al., 2010) or subiculum (Hanseeuw, 2011), probably reflecting variations in the anatomical landmarks used for subfield delineation as further discussed in previous publications (La Joie et al., 2010; Wisse et al., 2012) (see the method Section 2.3.1 for further discussion).
4.2. Comparison of the pattern of hippocampal atrophy in AD versus SD
AD and SD patients did not differ in terms of subfield volumetry. Although the absence of significant difference could be due to a lack of statistical power, preferential atrophy of both CA1 and subiculum was found in both groups and this finding is consistent with a recent surface-based study of the hippocampus in SD (Lindberg et al., 2012). Yet, the pathological substrate of hippocampal atrophy in SD is not clear, notably because patients with SD can present with heterogeneous pathological features (Davies et al., 2005). Despite this variability, a severe neuronal loss in the CA1 subfield together with a preservation of neurons in the dentate gyrus, consistent with our imaging findings, was reported independently of the histopathological subtypes (Davies et al., 2005).
Contrastingly, hippocampal atrophy differed between SD and AD patients in terms of hemispheric and anterior–posterior asymmetry, in agreement with previous reports (Chan et al., 2001; Davies et al., 2004; Galton, 2001; Nestor et al., 2006), and we showed that these two gradients were mostly independent of subfields. Previous authors (Chan et al., 2001; Davies et al., 2004; Galton, 2001) hypothesized that this asymmetric nature of hippocampal atrophy in SD could partly explain the intriguing relative preservation of episodic memory in SD as compared to AD (Hornberger & Piguet, 2012) in spite of similarly severe hippocampal atrophy (Pleizier et al., 2012). According to these authors, the relatively spared hippocampal areas (posterior areas and most of the time the right hippocampus) in SD could therefore be sufficient to support essential episodic memory abilities (Chan et al., 2001; Davies et al., 2004; Galton, 2001). Alternatively, it has been proposed (Nestor et al., 2006) that differential alterations of cortical areas that are crucial for episodic memory, such as the posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) that shows a strong hypometabolism in AD but not in SD, are more likely to account for the differential alteration of episodic memory between AD and SD. Yet, these two hypotheses are not necessarily independent as hippocampal atrophy has been shown to induce PCC hypometabolism through a disconnection process in AD (Villain et al., 2008). Besides, the connectivity of the hippocampus varies along its anterior–posterior axis, with the posterior part being more strongly connected to the PCC (Poppenk et al., 2013). It is thus possible that the predominance of atrophy in the anterior hippocampus in SD at least partly accounts for differences in distant cortical alterations (e.g. the lack of PCC hypometabolism) compared to AD, themselves underlying differences in the cognitive deficits. This would also be consistent with the idea that SD and AD target two large-scale brain networks that would underlie different cognitive functions and differentially include anterior versus posterior hippocampi (Ranganath & Ritchey, 2012).
4.3. Relationships between hippocampal subfield atrophy and Aβ in aMCI
Because the presence of Aβ deposition significantly increases the likelihood of having AD pathology in patients with aMCI according to current diagnosis recommendations (Albert et al., 2011; Dubois et al., 2010), we also investigated hippocampal subfield atrophy in aMCI patients as a function of Aβ load. We did not find a significant influence of the presence of Aβ on the pattern of hippocampal subfield atrophy as both Aβ-positive and Aβ-negative aMCI showed a predominant atrophy of the CA1 subfield (Fig. 4). However, these findings should be considered as preliminary given the small size of the aMCI samples when dichotomized in Aβ-positive and Aβ-negative. Yet, this finding is in line with recent studies showing that AD-type atrophy and/or hypometabolism can be found in both Aβ-negative healthy controls (Jack et al., 2012) and Aβ-negative MCI patients (Prestia et al., 2013). While it may reflect methodological issues related to biomarker measurements (Jack et al., 2013), it is possible that CA1 atrophy in Aβ-negative patients reflect non-AD pathophysiological processes. This would be consistent with the finding of CA1 atrophy in other disorders (Gemmell et al., 2012; Jack et al., 2002; Zarow et al., 2012) and the idea that aMCI in Aβ-negative patients is unlikely due to AD etiology (Albert et al., 2011). Alternatively, recent findings suggest that neuronal injury biomarkers known to be closely related to tau pathology such as hippocampal atrophy (see above), may occur independently and possibly prior to Aβ in the course of AD (Chételat, 2013; Knopman et al., 2013). This would rather support hypotheses suggesting that tau pathology could occur independently from Aβ accumulation (Small, 2008), than the amyloid hypothesis where tau-related neurodegeneration is supposed to appear downstream to Aβ. Further investigations are needed not only to test these hypotheses but also to replicate our findings regarding the relationships between hippocampal subfield atrophy and Aβ in a larger sample given the limited size of our aMCI subgroups.
It should also be noted that subfield volumetry as performed in the present study only provides approximations of the exact volumes of the hippocampal subfields, based on anatomical landmarks derived from histological atlases (see the method Section 2.3.1 for further discussion).
4.4. Conclusion
Overall, our findings in AD and SD are consistent with the topography of neuronal loss described in post-mortem studies as well as with previous imaging studies that used different methods. They suggest that hippocampal subfield volumetry is a promising biomarker for early AD detection at a predementia or even presymptomatic stage, especially with the widespread use of high-resolution MR sequences in the last years (Mueller et al., 2010; Wisse et al., 2012) and the on-going development of automatic subfield segmentation procedures (Van Leemput et al., 2009; Yushkevich et al., 2010). Further studies are therefore needed to assess the diagnostic and prognostic accuracies of this novel technique in larger samples and in comparison to other established AD biomarkers.
Acknowledgments
Funding: This work was supported by the Fondation Plan Alzheimer (Alzheimer Plan 2008–2012), Programme Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique (PHRC National 2011), Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR LONGVIE 2007), Région Basse Normandie, and Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM), including the Inserm-Liliane Bettencourt School (MD–PhD Program). These funding sources were not involved in study design, data collection, statistical analysis, results interpretation, writing of the report or in the decision to submit the article for publication. The authors have no disclosure.
Additional contributions: The authors are grateful to A. Bejanin, J. Dayan, C. Duval, M. Fouquet, A. Manrique, K. Mevel, A. Pélerin, A. Quillard, C. Schupp, N. Villain, and the Cyceron MRI-PET staff members for their help with patients and imaging examination. We thank L. Barré, A. Abbas, D. Guilloteau, for the radiotracer; F. Mézenge, and B. Landeau, for their technical support and A. Hammers, for his careful reading of the manuscript.
Footnotes
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License, which permits non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
Supplementary figure 1:Additional examples of hippocampal subfield delineation in 3 patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), two patients with semantic dementia (SD) and a healthy control. For each individual, different slices are shown with and without annotations to enable a better visualization of the hippocampus.
Supplementary figure 2: Influence of the correction for total intracranial volume and demographic factors on group comparisons.
References
- Albert M.S., DeKosky S.T., Dickson D., Dubois B., Feldman H.H., Fox N.C. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & Dementia. 2011;7:270–279. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobinski M., Wegiel J., Wisniewski H.M., Tarnawski M., Bobinski M., Reisberg B. Neurofibrillary pathology—correlation with hippocampal formation atrophy in Alzheimer disease. Neurobiology of Aging. 1996;17:909–919. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(97)85095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braak H., Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathologica. 1991;82:239–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00308809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan D., Fox N.C., Scahill R.I., Crum W.R., Whitwell J.L., Leschziner G. Patterns of temporal lobe atrophy in semantic dementia and Alzheimer's disease. Annals of Neurology. 2001;49:433–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chételat G. Alzheimer disease: Aβ-independent processes—rethinking preclinical AD. Nature Reviews. Neurology. 2013;9:123–124. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2013.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chételat G., Fouquet M., Kalpouzos G., Denghien I., de La Sayette V., Viader F. Three-dimensional surface mapping of hippocampal atrophy progression from MCI to AD and over normal aging as assessed using voxel-based morphometry. Neuropsychologia. 2008;46:1721–1731. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.11.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Convit A., De Leon M.J., Tarshish C., De Santi S., Tsui W., Rusinek H. Specific hippocampal volume reductions in individuals at risk for Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging. 1997;18:131–138. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(97)00001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R.R., Graham K.S., Xuereb J.H., Williams G.B., Hodges J.R. The human perirhinal cortex and semantic memory. European Journal of Neuroscience. 2004;20:2441–2446. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R.R., Hodges J.R., Kril J.J., Patterson K., Halliday G.M., Xuereb J.H. The pathological basis of semantic dementia. Brain. 2005;128:1984–1995. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desgranges B., Matuszewski V., Piolino P., Chételat G., Mézenge F., Landeau B. Anatomical and functional alterations in semantic dementia: a voxel-based MRI and PET study. Neurobiology of Aging. 2007;28:1904–1913. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois B., Feldman H.H., Jacova C., Cummings J.L., Dekosky S.T., Barberger-Gateau P. Revising the definition of Alzheimer's disease: a new lexicon. Lancet Neurology. 2010;9:1118–1127. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisoni G.B., Sabattoli F., Lee A.D., Dutton R.A., Toga A.W., Thompson P.M. In vivo neuropathology of the hippocampal formation in AD: a radial mapping MR-based study. NeuroImage. 2006;32:104–110. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisoni G.B., Fox N.C., Jack C.R., Scheltens P., Thompson P.M. The clinical use of structural MRI in Alzheimer disease. Nature Reviews. Neurology. 2010;6:67–77. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2009.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukutani Y., Cairns N.J., Shiozawa M., Sasaki K., Sudo S., Isaki K. Neuronal loss and neurofibrillary degeneration in the hippocampal cortex in late-onset sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences. 2000;54:523–529. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1819.2000.00747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galton C.J., Patterson K., Graham K., Lambon-Ralph M.A., Williams G., Antoun N. Differing patterns of temporal atrophy in Alzheimer's disease and semantic dementia. Neurology. 2001;57:216–225. doi: 10.1212/wnl.57.2.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell E., Bosomworth H., Allan L., Hall R., Khundakar A., Oakley A.E. Hippocampal neuronal atrophy and cognitive function in delayed poststroke and aging-related dementias. Stroke. 2012;43:808–814. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.636498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuze E., Vermetten E., Bremner J.D. MR-based in vivo hippocampal volumetrics: 2. Findings in neuropsychiatric disorders. Molecular Psychiatry. 2005;10:160–184. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanseeuw B.J., Van Leemput K., Kavec M., Grandin C., Seron X., Ivanoiu A. Mild cognitive impairment: differential atrophy in the hippocampal subfields. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology. 2011;32:1658–1661. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A.J., Halliday G.M., Kril J.J. Variation in hippocampal neuron number with age and brain volume. Cerebral Cortex. 1998;8:710–718. doi: 10.1093/cercor/8.8.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornberger M., Piguet O. Episodic memory in frontotemporal dementia: a critical review. Brain. 2012;135:678–692. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack C.R., Jr., Petersen R.C., Xu Y.C., Waring S.C., O'Brien P.C., Tangalos E.G. Medial temporal atrophy on MRI in normal aging and very mild Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1997;49:786–794. doi: 10.1212/wnl.49.3.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack C.R., Jr., Dickson D.W., Parisi J.E., Xu Y.C., Cha R.H., O'Brien P.C. Antemortem MRI findings correlate with hippocampal neuropathology in typical aging and dementia. Neurology. 2002;58:750–757. doi: 10.1212/wnl.58.5.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack C.R., Jr., Knopman D.S., Weigand S.D., Wiste H.J., Vemuri P., Lowe V. An operational approach to National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer's Association criteria for preclinical Alzheimer disease. Annals of Neurology. 2012;71:765–775. doi: 10.1002/ana.22628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack C.R., Jr., Knopman D.S., Jagust W.J., Petersen R.C., Weiner M.W., Aisen P.S. Tracking pathophysiological processes in Alzheimer's disease: an updated hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers. Lancet Neurology. 2013;12:207–216. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70291-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopman D.S., Jack C.R., Wiste H.J., Weigand S.D., Vemuri P., Lowe V.J. Neuronal injury biomarkers are not dependent on β-amyloid in normal elderly. Annals of Neurology. 2013;73:472–480. doi: 10.1002/ana.23816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Joie R., Fouquet M., Mézenge F., Landeau B., Villain N., Mevel K. Differential effect of age on hippocampal subfields assessed using a new high-resolution 3 T MR sequence. NeuroImage. 2010;53:506–514. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Joie R., Perrotin A., Barré L., Hommet C., Mézenge F., Ibazizene M. Region-specific hierarchy between atrophy, hypometabolism, and β-amyloid (Aβ) load in Alzheimer's disease dementia. Journal of Neuroscience. 2012;32:16265–16273. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2170-12.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg O., Walterfang M., Looi J.C.L., Malykhin N., Ostberg P., Zandbelt B. Hippocampal shape analysis in Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration subtypes. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2012;30:355–365. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-112210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malykhin N.V., Bouchard T.P., Ogilvie C.J., Coupland N.J., Seres P., Camicioli R. Three-dimensional volumetric analysis and reconstruction of amygdala and hippocampal head, body and tail. Psychiatry Research. 2007;155:155–165. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2006.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E.M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1984;34:939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller Schuff N., Yaffe K., Madison C., Miller B., Weiner M.W. Hippocampal atrophy patterns in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Human Brain Mapping. 2010;31:1339–1347. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neary D., Snowden J.S., Gustafson L., Passant U., Stuss D., Black S. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a consensus on clinical diagnostic criteria. Neurology. 1998;51:1546–1554. doi: 10.1212/wnl.51.6.1546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestor P.J., Fryer T.D., Hodges J.R. Declarative memory impairments in Alzheimer's disease and semantic dementia. NeuroImage. 2006;30:1010–1020. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen R.C., Morris J.C. Mild cognitive impairment as a clinical entity and treatment target. Archives of Neurology. 2005;62:1160–1163. doi: 10.1001/archneur.62.7.1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleizier C.M., van der Vlies A.E., Koedam E., Koene T., Barkhof F., van der Flier W.M. Episodic memory and the medial temporal lobe: not all it seems. Evidence from the temporal variants of frontotemporal dementia. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry. 2012;83:1145–1148. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2012-302437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluta J., Yushkevich P., Das S., Wolk D. In vivo analysis of hippocampal subfield atrophy in mild cognitive impairment via semi-automatic segmentation of T2-weighted MRI. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2012;31:85–99. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-111931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppenk J., Evensmoen H.R., Moscovitch M., Nadel L. Long-axis specialization of the human hippocampus. Trends in Cognitive Science. 2013;17:230–240. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2013.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestia A., Caroli A., van der Flier W.M., Ossenkoppele R., Van Berckel B., Barkhof F. Prediction of dementia in MCI patients based on core diagnostic markers for Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2013;80:1048–1056. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182872830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruessner J.C., Li L.M., Serles W., Pruessner M., Collins D.L., Kabani N. Volumetry of hippocampus and amygdala with high-resolution MRI and three-dimensional analysis software: minimizing the discrepancies between laboratories. Cerebral Cortex. 2000;10:433–442. doi: 10.1093/cercor/10.4.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranganath C., Ritchey M. Two cortical systems for memory-guided behaviour. Nature Review Neuroscience. 2012;13:713–726. doi: 10.1038/nrn3338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rössler M., Zarski R., Bohl J., Ohm T.G. Stage-dependent and sector-specific neuronal loss in hippocampus during Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathologica. 2002;103:363–369. doi: 10.1007/s00401-001-0475-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönheit B., Zarski R., Ohm T.G. Spatial and temporal relationships between plaques and tangles in Alzheimer-pathology. Neurobiology of Aging. 2004;25:697–711. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2003.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi F., Liu B., Zhou Y., Yu C., Jiang T. Hippocampal volume and asymmetry in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: meta-analyses of MRI studies. Hippocampus. 2009;19:1055–1064. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small S.A., Duff K. Linking Abeta and tau in late-onset Alzheimer's disease: a dual pathway hypothesis. Neuron. 2008;60:534–542. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.11.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C.D., Chebrolu H., Wekstein D.R., Schmitt F.A., Jicha G.A., Cooper G. Brain structural alterations before mild cognitive impairment. Neurology. 2007;68:1268–1273. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000259542.54830.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tondelli M., Wilcock G.K., Nichelli P., De Jager C.A., Jenkinson M., Zamboni G. Structural MRI changes detectable up to ten years before clinical Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging. 2012;33(825):e25–e36. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.05.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leemput K., Bakkour A., Benner T., Wiggins G., Wald L.L., Augustinack J. Automated segmentation of hippocampal subfields from ultra-high resolution in vivo MRI. Hippocampus. 2009;19:549–557. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villain N., Desgranges B., Viader F., de La Sayette V., Mézenge F., Landeau B. Relationships between hippocampal atrophy, white matter disruption, and gray matter hypometabolism in Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Neuroscience. 2008;28:6174–6181. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1392-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Gunten A., Kövari E., Bussière T., Rivara C.-B., Gold G., Bouras C. Cognitive impact of neuronal pathology in the entorhinal cortex and CA1 field in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging. 2006;27:270–277. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Swank J.S., Glick I.E., Gado M.H., Miller M.I., Morris J.C. Changes in hippocampal volume and shape across time distinguish dementia of the Alzheimer type from healthy aging. NeuroImage. 2003;20:667–682. doi: 10.1016/S1053-8119(03)00361-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M.J., Coleman P.D., Flood D.G., Troncoso J.C. Differences in the pattern of hippocampal neuronal loss in normal ageing and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1994;344:769–772. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92338-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitwell J.L., Josephs K.A., Murray M.E., Kantarci K., Przybelski S.A., Weigand S.D. MRI correlates of neurofibrillary tangle pathology at autopsy. Neurology. 2008;71:743. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000324924.91351.7d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisse L.E.M., Gerritsen L., Zwanenburg J.J.M., Kuijf H.J., Luijten P.R., Biessels G.J. Subfields of the hippocampal formation at 7 T MRI: in vivo volumetric assessment. NeuroImage. 2012;61:1043–1049. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yushkevich P.A., Wang H., Pluta J., Das S.R., Craige C., Avants B.B. Nearly automatic segmentation of hippocampal subfields in in vivo focal T2-weighted MRI. NeuroImage. 2010;53:1208–1224. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarow C., Weiner M.W., Ellis W.G., Chui H.C. Prevalence, laterality, and comorbidity of hippocampal sclerosis in an autopsy sample. Brain Behavior. 2012;2:435–442. doi: 10.1002/brb3.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary figure 1:Additional examples of hippocampal subfield delineation in 3 patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), two patients with semantic dementia (SD) and a healthy control. For each individual, different slices are shown with and without annotations to enable a better visualization of the hippocampus.
Supplementary figure 2: Influence of the correction for total intracranial volume and demographic factors on group comparisons.


