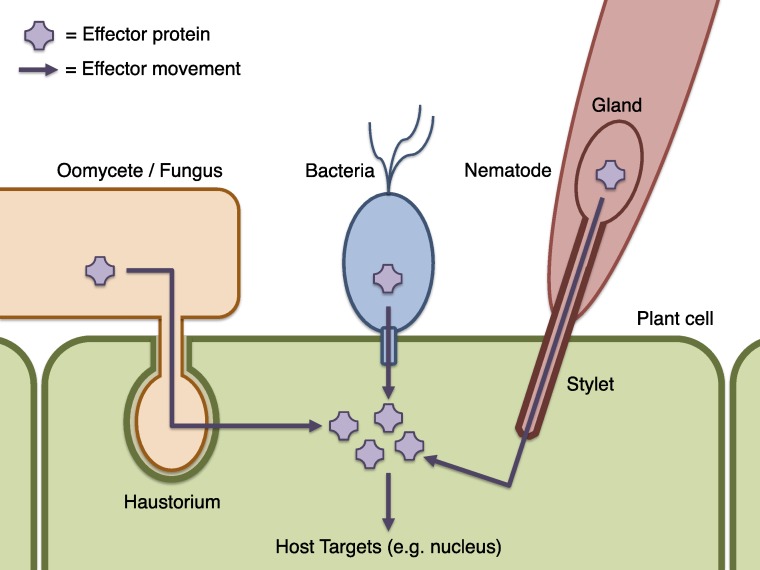
Figure 1. Schematic of effector infiltration into a host plant cell.
Plant pests and pathogens introduce effector proteins into the host plant cell (green), where they can target and manipulate plant biochemistry to the benefit of the pathogen (Dodds & Rathjen, 2010). Effectors may be delivered by haustorial ingression from a fungus or oomycete such as P. infestans (orange), via the bacterial Type III secretion system mechanism (blue), by nematodes via injection into the plant cell though a needle-like stylet (red), or many other processes (not illustrated). Where effectors may be identified by sequence properties, candidate effector proteins can be computationally predicted using Galaxy.