Abstract
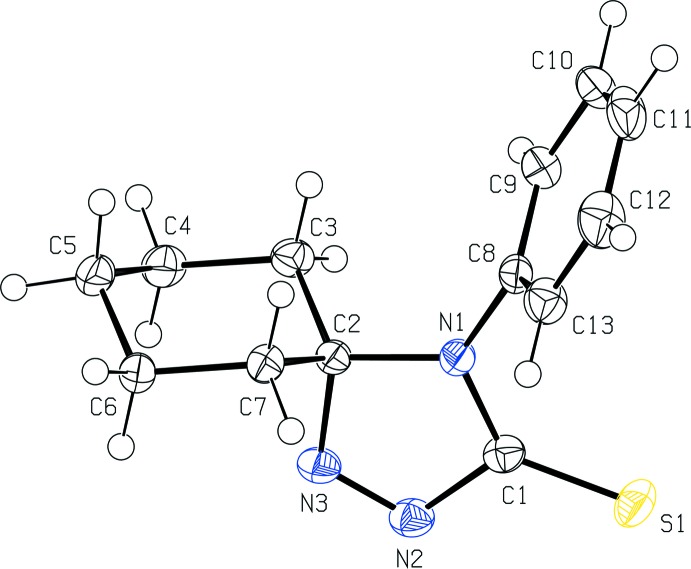
In the title compound, C13H15N3S, the 4,5-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole ring is nearly planar [maximum deviation = 0.020 (1) Å], while the cyclohexane ring adopts a chair conformation. The dihedral angle between the 4,5-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole ring and the phenyl ring is 74.68 (7)°. No specific intermolecular interactions are discerned in the crystal packing.
Related literature
For wide-spectrum medicinal applications of spiro compounds incorporating heterocyclic substructures, see: Patil et al. (2010 ▶); Pawar et al. (2009 ▶); Thadhaney et al. (2010 ▶); Chin et al. (2008 ▶); Wang et al. (2007 ▶); Chande et al. (2005 ▶); Obniska et al. (2006 ▶); Kamiński et al. (2008 ▶); Sarma et al. (2010 ▶); Shimakawa et al. (2003 ▶). For ring-puckering parameters, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶).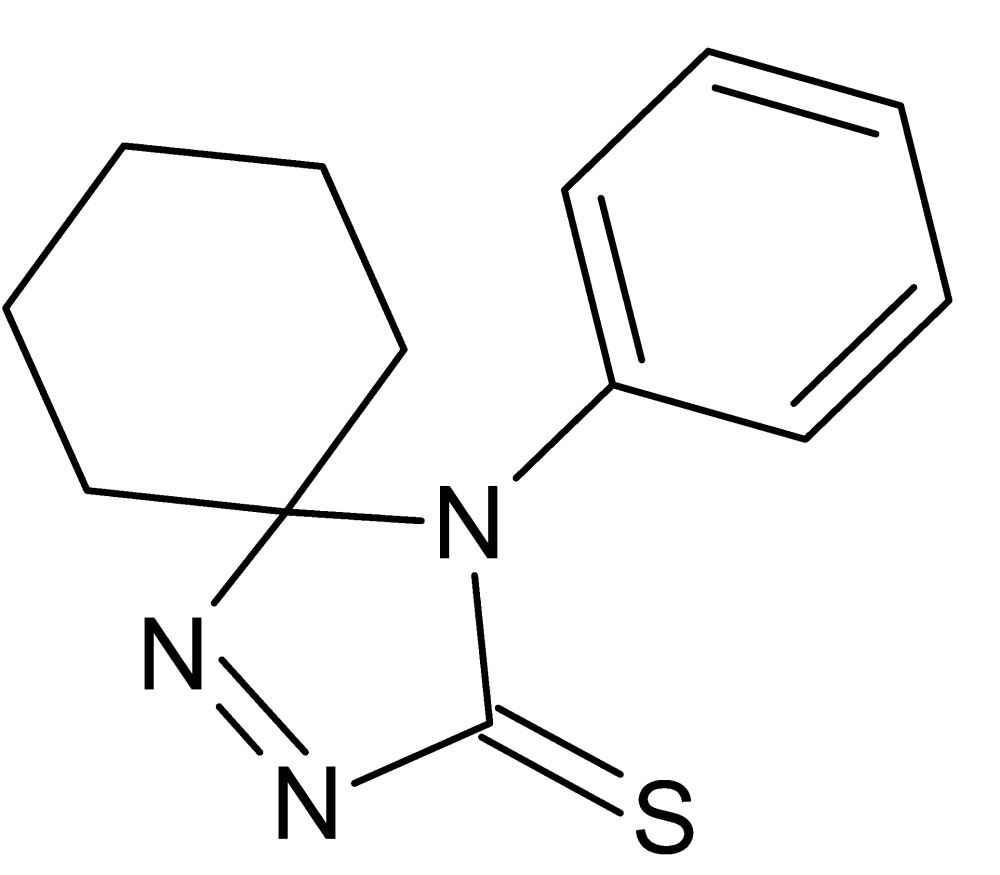
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H15N3S
M r = 245.34
Orthorhombic,
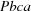
a = 9.4952 (9) Å
b = 7.4845 (7) Å
c = 34.692 (3) Å
V = 2465.5 (4) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.24 mm−1
T = 150 K
0.28 × 0.22 × 0.17 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2013 ▶) T min = 0.810, T max = 0.960
41202 measured reflections
3168 independent reflections
2899 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.046
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.104
S = 1.10
3168 reflections
154 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.40 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2013 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2013 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813019120/tk5237sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813019120/tk5237Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813019120/tk5237Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
Tulane University, Erciyes University and Minia University are gratefully acknowledged for supporting this study.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Heterocyclic compounds such as 1.2.4-triazoles exhibit a wide range of biological activities (Patil et al., 2010). Several spiro-compounds incorporating different heterocyclic structures have showed significant industrial and pharmaceutical applications such as anti-microbial (Pawar et al., 2009; Thadhaney et al., 2010), anti-cancer (Chin et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2007), anti-tubercular (Chande et al., 2005) and anti-convulsant activities (Obniska et al., 2006; Kamiński et al., 2008) as well as functioning as antioxidants (Sarma et al., 2010; Shimakawa et al., 2003). In view of such facts and as part of our on-going study on the synthesis of bio-active molecules, we herein report the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound (I).
As shown in Fig. 1, the 4,5-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole ring (N1–N3/C1/C2) of (I) is nearly planar with a maximum deviation of 0.020 (1) Å for N1 and it makes a dihedral angle of 74.68 (7)° with the phenyl ring (C8–C13). The cyclohexane ring (C2–C7) adopts a chair conformation with the puckering parameters (Cremer & Pople, 1975) of QT = 0.5610 (14) Å, θ = 1.74 (14)° and φ = 342 (4)°.
The stabilization of the molecular packing of (I) is assisted by a number of non-bonded forces including van der Waals.
Experimental
A solution of 2-cyclohexylidene-N-phenylhydrazinecarbothioamide (1 mmol) in dry ethyl acetate (15 ml) was added drop wise over 2 h to a stirred solution of 4,5-dichloro-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,2-dicarbonitrile (227 mg, 1 mmol) in dry ethyl acetate (10 ml). The pink coloration of the reaction mixture turned quickly to red brown and the mixture was left to stand at room temperature for 48 h. The precipitated DDQ-H2 [JM1] was filtered off and washed with few drops of ethyl acetate. The filtrate was collected, concentrated under vacuum and left at room temperature to afford the title compound as red brown crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction.
IR: 3052 (Ar—CH), 2941, 2863 (Ali – CH), 1594 (Ar—C=C), 1350 (C═S); 1H-NMR (CDCl3) 1.26, 1.65, 1.94 and 2.20 (10H, cyclohexane–CH2), 7.707, 7.51, 7.55 (5H, Ar–H); 13C–NMR (CDCl3) 23.58, 24.52 and 33.90 (cyclohexane-CH2), 112.19 (spiro Cx b), 127.81, 129.87, 130.22 (Ar—CH), 135.07 (Ar-c), 187.83 (C═S).
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with C—H = 0.95 and 0.99 Å, with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Uiso(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the title compound (I) with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Crystal data
| C13H15N3S | F(000) = 1040 |
| Mr = 245.34 | Dx = 1.322 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 9973 reflections |
| a = 9.4952 (9) Å | θ = 2.5–28.6° |
| b = 7.4845 (7) Å | µ = 0.24 mm−1 |
| c = 34.692 (3) Å | T = 150 K |
| V = 2465.5 (4) Å3 | Block, red-brown |
| Z = 8 | 0.28 × 0.22 × 0.17 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 3168 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2899 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.046 |
| Detector resolution: 8.3660 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 28.7°, θmin = 2.4° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −12→12 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2013) | k = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.810, Tmax = 0.960 | l = −46→46 |
| 41202 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.104 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.10 | W = 1/[Σ2(FO2) + (0.0483P)2 + 1.0447P] where P = (FO2 + 2FC2)/3 |
| 3168 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 154 parameters | Δρmax = 0.40 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.53002 (4) | 1.40579 (5) | 0.84564 (2) | 0.0310 (1) | |
| N1 | 0.50442 (11) | 1.06645 (14) | 0.87249 (3) | 0.0199 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.53364 (11) | 1.27385 (15) | 0.91860 (3) | 0.0252 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.51796 (11) | 1.13018 (15) | 0.93661 (3) | 0.0233 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.52216 (12) | 1.24250 (17) | 0.87698 (4) | 0.0219 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.49469 (12) | 0.97820 (16) | 0.91027 (3) | 0.0188 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.60868 (13) | 0.83732 (18) | 0.91727 (4) | 0.0241 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.59589 (15) | 0.75735 (19) | 0.95773 (4) | 0.0282 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.44880 (15) | 0.68348 (18) | 0.96539 (4) | 0.0280 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.33484 (14) | 0.82248 (17) | 0.95781 (3) | 0.0240 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.34706 (13) | 0.90101 (16) | 0.91725 (3) | 0.0209 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.47802 (13) | 0.97938 (17) | 0.83642 (3) | 0.0208 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.58094 (15) | 0.87142 (18) | 0.82019 (4) | 0.0273 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.55240 (17) | 0.7858 (2) | 0.78557 (4) | 0.0346 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.42447 (19) | 0.8099 (2) | 0.76734 (4) | 0.0377 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.32316 (18) | 0.9190 (2) | 0.78367 (4) | 0.0369 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.34905 (15) | 1.00429 (19) | 0.81847 (4) | 0.0283 (4) | |
| H3A | 0.70270 | 0.89270 | 0.91420 | 0.0290* | |
| H3B | 0.59970 | 0.74110 | 0.89790 | 0.0290* | |
| H4A | 0.66580 | 0.66010 | 0.96070 | 0.0340* | |
| H4B | 0.61770 | 0.85060 | 0.97710 | 0.0340* | |
| H5A | 0.43240 | 0.57840 | 0.94860 | 0.0340* | |
| H5B | 0.44270 | 0.64330 | 0.99250 | 0.0340* | |
| H6A | 0.34290 | 0.91980 | 0.97700 | 0.0290* | |
| H6B | 0.24110 | 0.76650 | 0.96090 | 0.0290* | |
| H7A | 0.27600 | 0.99650 | 0.91390 | 0.0250* | |
| H7B | 0.32760 | 0.80660 | 0.89800 | 0.0250* | |
| H9 | 0.66940 | 0.85640 | 0.83260 | 0.0330* | |
| H10 | 0.62130 | 0.71000 | 0.77430 | 0.0410* | |
| H11 | 0.40610 | 0.75150 | 0.74360 | 0.0450* | |
| H12 | 0.23540 | 0.93560 | 0.77100 | 0.0440* | |
| H13 | 0.27940 | 1.07870 | 0.82980 | 0.0340* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0373 (2) | 0.0214 (2) | 0.0344 (2) | −0.0050 (1) | 0.0002 (1) | 0.0067 (1) |
| N1 | 0.0234 (5) | 0.0179 (5) | 0.0183 (5) | −0.0008 (4) | −0.0003 (4) | 0.0003 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0254 (5) | 0.0214 (5) | 0.0287 (6) | −0.0028 (4) | 0.0010 (4) | −0.0045 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0255 (5) | 0.0209 (5) | 0.0235 (5) | −0.0009 (4) | −0.0004 (4) | −0.0056 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0190 (5) | 0.0195 (6) | 0.0272 (6) | −0.0014 (4) | 0.0011 (4) | −0.0011 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0230 (5) | 0.0172 (6) | 0.0162 (5) | −0.0001 (4) | −0.0014 (4) | −0.0013 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0240 (6) | 0.0248 (6) | 0.0235 (6) | 0.0054 (5) | −0.0030 (5) | −0.0015 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0337 (7) | 0.0276 (7) | 0.0234 (6) | 0.0075 (6) | −0.0077 (5) | 0.0000 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0406 (7) | 0.0218 (6) | 0.0215 (6) | 0.0034 (5) | −0.0025 (5) | 0.0022 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0308 (6) | 0.0208 (6) | 0.0204 (6) | −0.0017 (5) | 0.0018 (5) | 0.0011 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0216 (5) | 0.0200 (5) | 0.0210 (6) | −0.0004 (5) | −0.0011 (4) | 0.0011 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0263 (6) | 0.0189 (6) | 0.0172 (5) | −0.0034 (5) | 0.0008 (4) | 0.0014 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0313 (7) | 0.0269 (6) | 0.0236 (6) | 0.0007 (5) | 0.0058 (5) | 0.0003 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0504 (9) | 0.0281 (7) | 0.0252 (7) | −0.0031 (6) | 0.0146 (6) | −0.0030 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0607 (10) | 0.0340 (8) | 0.0185 (6) | −0.0168 (7) | 0.0013 (6) | −0.0025 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0434 (8) | 0.0404 (8) | 0.0268 (7) | −0.0093 (7) | −0.0107 (6) | 0.0008 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0302 (7) | 0.0298 (7) | 0.0250 (6) | −0.0013 (5) | −0.0029 (5) | 0.0006 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C1 | 1.6375 (14) | C11—C12 | 1.383 (2) |
| N1—C1 | 1.3375 (17) | C12—C13 | 1.388 (2) |
| N1—C2 | 1.4706 (15) | C3—H3A | 0.9900 |
| N1—C8 | 1.4330 (15) | C3—H3B | 0.9900 |
| N2—N3 | 1.2525 (16) | C4—H4A | 0.9900 |
| N2—C1 | 1.4669 (17) | C4—H4B | 0.9900 |
| N3—C2 | 1.4757 (16) | C5—H5A | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.5305 (17) | C5—H5B | 0.9900 |
| C2—C7 | 1.5354 (17) | C6—H6A | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.531 (2) | C6—H6B | 0.9900 |
| C4—C5 | 1.525 (2) | C7—H7A | 0.9900 |
| C5—C6 | 1.5239 (19) | C7—H7B | 0.9900 |
| C6—C7 | 1.5293 (15) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| C8—C9 | 1.3874 (19) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| C8—C13 | 1.3864 (19) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C9—C10 | 1.388 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C10—C11 | 1.381 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C1—N1—C2 | 110.28 (10) | H3A—C3—H3B | 108.00 |
| C1—N1—C8 | 124.87 (11) | C3—C4—H4A | 109.00 |
| C2—N1—C8 | 124.27 (10) | C3—C4—H4B | 109.00 |
| N3—N2—C1 | 110.17 (10) | C5—C4—H4A | 109.00 |
| N2—N3—C2 | 111.76 (10) | C5—C4—H4B | 109.00 |
| S1—C1—N1 | 131.58 (11) | H4A—C4—H4B | 108.00 |
| S1—C1—N2 | 122.06 (10) | C4—C5—H5A | 109.00 |
| N1—C1—N2 | 106.36 (11) | C4—C5—H5B | 109.00 |
| N1—C2—N3 | 101.32 (9) | C6—C5—H5A | 109.00 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 113.98 (10) | C6—C5—H5B | 109.00 |
| N1—C2—C7 | 111.53 (9) | H5A—C5—H5B | 108.00 |
| N3—C2—C3 | 109.08 (9) | C5—C6—H6A | 109.00 |
| N3—C2—C7 | 109.21 (9) | C5—C6—H6B | 109.00 |
| C3—C2—C7 | 111.19 (10) | C7—C6—H6A | 109.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 111.03 (10) | C7—C6—H6B | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 111.97 (11) | H6A—C6—H6B | 108.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 111.88 (11) | C2—C7—H7A | 109.00 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 111.55 (10) | C2—C7—H7B | 109.00 |
| C2—C7—C6 | 111.04 (10) | C6—C7—H7A | 110.00 |
| N1—C8—C9 | 119.74 (11) | C6—C7—H7B | 109.00 |
| N1—C8—C13 | 119.05 (11) | H7A—C7—H7B | 108.00 |
| C9—C8—C13 | 121.21 (11) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.00 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 118.85 (13) | C10—C9—H9 | 121.00 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 120.50 (14) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.00 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 120.08 (13) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.00 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 120.31 (15) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.00 |
| C8—C13—C12 | 119.04 (13) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.00 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 109.00 | C11—C12—H12 | 120.00 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 109.00 | C13—C12—H12 | 120.00 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 110.00 | C8—C13—H13 | 121.00 |
| C4—C3—H3B | 109.00 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.00 |
| C2—N1—C1—S1 | −175.88 (10) | N2—N3—C2—C7 | −116.28 (11) |
| C2—N1—C1—N2 | 3.52 (12) | N1—C2—C3—C4 | 177.48 (10) |
| C8—N1—C1—S1 | −4.33 (19) | N3—C2—C3—C4 | 65.07 (13) |
| C8—N1—C1—N2 | 175.07 (10) | C7—C2—C3—C4 | −55.43 (13) |
| C1—N1—C2—N3 | −3.14 (12) | N1—C2—C7—C6 | −175.60 (10) |
| C1—N1—C2—C3 | −120.14 (11) | N3—C2—C7—C6 | −64.44 (12) |
| C1—N1—C2—C7 | 112.94 (11) | C3—C2—C7—C6 | 55.98 (13) |
| C8—N1—C2—N3 | −174.76 (10) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 54.36 (15) |
| C8—N1—C2—C3 | 68.24 (14) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −53.80 (15) |
| C8—N1—C2—C7 | −58.67 (14) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | 54.12 (14) |
| C1—N1—C8—C9 | 110.43 (14) | C5—C6—C7—C2 | −55.15 (13) |
| C1—N1—C8—C13 | −69.89 (16) | N1—C8—C9—C10 | 178.89 (12) |
| C2—N1—C8—C9 | −79.16 (15) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | −0.8 (2) |
| C2—N1—C8—C13 | 100.51 (14) | N1—C8—C13—C12 | −179.57 (12) |
| C1—N2—N3—C2 | 0.53 (13) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 0.1 (2) |
| N3—N2—C1—S1 | 176.89 (9) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 1.0 (2) |
| N3—N2—C1—N1 | −2.58 (13) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.5 (2) |
| N2—N3—C2—N1 | 1.50 (12) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.2 (2) |
| N2—N3—C2—C3 | 122.02 (11) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | 0.4 (2) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: TK5237).
References
- Bruker (2013). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chande, M. S., Verma, R. S., Barve, P. A., Khanwelkar, R. R., Vaidya, R. B. & Ajaikumar, K. B. (2005). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 40, 1143–1148. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chin, Y.-W., Salim, A. A., Su, B.-N., Mi, Q., Chai, H.-B., Riswan, S., Kardono, L. B. S., Ruskandi, A., Farnsworth, N. R., Swanson, S. M. & Kinghorn, A. D. (2008). J. Nat. Prod. 3, 390–395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Kamiński, K., Obniska, J. & Dybala, M. (2008). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 43, 53–61. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Obniska, J., Kamiński, K. & Tatarczyńska, E. (2006). Pharmacol. Rep. 58, 207–214. [PubMed]
- Patil, B. S., Krishnamurthy, G., BhojyaNaik, H. S., Latthe, P. R. & Ghate, M. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 3329–3334. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Pawar, M. J., Burungale, A. B. & Karale, B. K. (2009). ARKIVOC, XIII, 97–107.
- Sarma, B. K., Manna, D., Minoura, M. & Mugesh, G. (2010). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 5364–5374. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shimakawa, S., Yoshida, Y. & Niki, E. (2003). Lipids, 38, 225–231. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Thadhaney, B., Sain, D., Pernawat, G. & Talesara, G. L. (2010). Indian J. Chem. Sect. B, 49, 368–373.
- Wang, W.-L., Zhu, T.-J., Tao, H.-W., Lu, Z.-Y., Fang, Y.-C., Gu, Q.-Q. & Zhu, W.-M. (2007). Chem. Biodivers. 4, 2913–2919. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813019120/tk5237sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813019120/tk5237Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813019120/tk5237Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report