Abstract
Plant growth and development are regulated by interactions between the environment and endogenous developmental programs. Of the various environmental factors controlling plant development, light plays an especially important role, in photosynthesis, in seasonal and diurnal time sensing, and as a cue for altering developmental pattern. Recently, several laboratories have devised a variety of genetic screens using Arabidopsis thaliana to dissect the signal transduction pathways of the various photoreceptor systems. Genetic analysis demonstrates that light responses are not simply endpoints of linear signal transduction pathways but are the result of the integration of information from a variety of photoreceptors through a complex network of interacting signaling components. These signaling components include the red/far-red light receptors, phytochromes, at least one blue light receptor, and negative regulatory genes (DET, COP, and FUS) that act downstream from the photoreceptors in the nucleus. In addition, a steroid hormone, brassinolide, also plays a role in light-regulated development and gene expression in Arabidopsis. These molecular and genetic data are allowing us to construct models of the mechanisms by which light controls development and gene expression in Arabidopsis. In the future, this knowledge can be used as a framework for understanding how all land plants respond to changes in their environment.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowler C., Chua N. H. Emerging themes of plant signal transduction. Plant Cell. 1994 Nov;6(11):1529–1541. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.11.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan M. T., Quail P. H. Oat Phytochrome Is Biologically Active in Transgenic Tomatoes. Plant Cell. 1989 Aug;1(8):765–773. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.8.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle L. A., Meinke D. W. A FUSCA gene of Arabidopsis encodes a novel protein essential for plant development. Plant Cell. 1994 Jan;6(1):25–41. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs K. L., Cordonnier-Pratt M. M., Pratt L. H., Morgan P. W. Genetic Regulation of Development in Sorghum bicolor: VII. ma(3) Flowering Mutant Lacks a Phytochrome that Predominates in Green Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1992 Jun;99(2):765–770. doi: 10.1104/pp.99.2.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chory J., Nagpal P., Peto C. A. Phenotypic and Genetic Analysis of det2, a New Mutant That Affects Light-Regulated Seedling Development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 1991 May;3(5):445–459. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.5.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chory J. Out of darkness: mutants reveal pathways controlling light-regulated development in plants. Trends Genet. 1993 May;9(5):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90163-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. P., Roth S. Y., Simpson R. T. The global transcriptional regulators, SSN6 and TUP1, play distinct roles in the establishment of a repressive chromatin structure. Genes Dev. 1994 Jun 15;8(12):1400–1410. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.12.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Cashmore A. R. Binding of a pea nuclear protein to promoters of certain photoregulated genes is modulated by phosphorylation. Plant Cell. 1989 Nov;1(11):1069–1077. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.11.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W. Fresh view of light signal transduction in plants. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Matsui M., Wei N., Wagner D., Chu A. M., Feldmann K. A., Quail P. H. COP1, an Arabidopsis regulatory gene, encodes a protein with both a zinc-binding motif and a G beta homologous domain. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):791–801. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90555-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin P. F., Rood S. B., Somers D. E., Quail P. H., Whitelam G. C. Photophysiology of the Elongated Internode (ein) Mutant of Brassica rapa: ein Mutant Lacks a Detectable Phytochrome B-Like Polypeptide. Plant Physiol. 1992 Nov;100(3):1442–1447. doi: 10.1104/pp.100.3.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Weinzierl R. O., Admon A., Tjian R. The dTAFII80 subunit of Drosophila TFIID contains beta-transducin repeats. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):176–179. doi: 10.1038/363176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon K. M., Shacklock P. S., Trewavas A. J. Detection in Vivo of Very Rapid Red Light-Induced Calcium-Sensitive Protein Phosphorylation in Etiolated Wheat (Triticum aestivum) Leaf Protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1993 Mar;101(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1104/pp.101.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D. The price of repression. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):655–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90524-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. M., Cochran D. S., Lamerson P. M., Evans M. L., Cohen J. D. Red light-regulated growth. I. Changes in the abundance of indoleacetic acid and a 22-kilodalton auxin-binding protein in the maize mesocotyl. Plant Physiol. 1991;97:352–358. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.1.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan E. T., Hatfield P. M., Hondred D., Talon M., Zeevaart J. A., Vierstra R. D. Phytochrome A overexpression in transgenic tobacco. Correlation of dwarf phenotype with high concentrations of phytochrome in vascular tissue and attenuated gibberellin levels. Plant Physiol. 1995 Mar;107(3):797–805. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.3.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Redd M. J., Schultz J., Carlson M., Johnson A. D. Ssn6-Tup1 is a general repressor of transcription in yeast. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Shanklin J., Vierstra R. D., Hershey H. P. Expression of a functional monocotyledonous phytochrome in transgenic tobacco. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1005–1012. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. F., Piekos B., Misera S., Deng X. W. A complement of ten essential and pleiotropic arabidopsis COP/DET/FUS genes is necessary for repression of photomorphogenesis in darkness. Plant Physiol. 1996 Mar;110(3):731–742. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyoku I., Yokota M., Kitano M., Mizuhara H., Sakamoto K., Uesaka T., Hasegawa S., Park S., Muraoka R. [Successful treatment by using a pedicled omental flap for mediastinal infection in the presence of a external valved conduit]. Nihon Geka Hokan. 1990 Mar 1;59(2):168–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. M., Altschmied L., Chory J. Arabidopsis mutants define downstream branches in the phototransduction pathway. Genes Dev. 1994 Feb 1;8(3):339–349. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Hm., Culligan K., Dixon R. A., Chory J. CUE1: A Mesophyll Cell-Specific Positive Regulator of Light-Controlled Gene Expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 1995 Oct;7(10):1599–1610. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.10.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Nagpal P., Vitart V., McMorris T. C., Chory J. A role for brassinosteroids in light-dependent development of Arabidopsis. Science. 1996 Apr 19;272(5260):398–401. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5260.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C., Robertson D. E., Ahmad M., Raibekas A. A., Jorns M. S., Dutton P. L., Cashmore A. R. Association of flavin adenine dinucleotide with the Arabidopsis blue light receptor CRY1. Science. 1995 Aug 18;269(5226):968–970. doi: 10.1126/science.7638620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin X., Feng X. H., Watson J. C. Differential accumulation of transcripts encoding protein kinase homologs in greening pea seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6951–6955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Juez E., Kobayashi M., Sakurai A., Kamiya Y., Kendrick R. E. Phytochrome, Gibberellins, and Hypocotyl Growth (A Study Using the Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) long hypocotyl Mutant). Plant Physiol. 1995 Jan;107(1):131–140. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNellis T. W., von Arnim A. G., Araki T., Komeda Y., Miséra S., Deng X. W. Genetic and molecular analysis of an allelic series of cop1 mutants suggests functional roles for the multiple protein domains. Plant Cell. 1994 Apr;6(4):487–500. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.4.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNellis T. W., von Arnim A. G., Deng X. W. Overexpression of Arabidopsis COP1 results in partial suppression of light-mediated development: evidence for a light-inactivable repressor of photomorphogenesis. Plant Cell. 1994 Oct;6(10):1391–1400. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.10.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar A. J., Straume M., Chory J., Chua N. H., Kay S. A. The regulation of circadian period by phototransduction pathways in Arabidopsis. Science. 1995 Feb 24;267(5201):1163–1166. doi: 10.1126/science.7855596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miséra S., Müller A. J., Weiland-Heidecker U., Jürgens G. The FUSCA genes of Arabidopsis: negative regulators of light responses. Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Aug 2;244(3):242–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00285451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mushegian A. R., Koonin E. V. A putative FAD-binding domain in a distinct group of oxidases including a protein involved in plant development. Protein Sci. 1995 Jun;4(6):1243–1244. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560040623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks B. M., Hangarter R. P. Blue light sensory systems in plants. Semin Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;5(5):347–353. doi: 10.1006/scel.1994.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
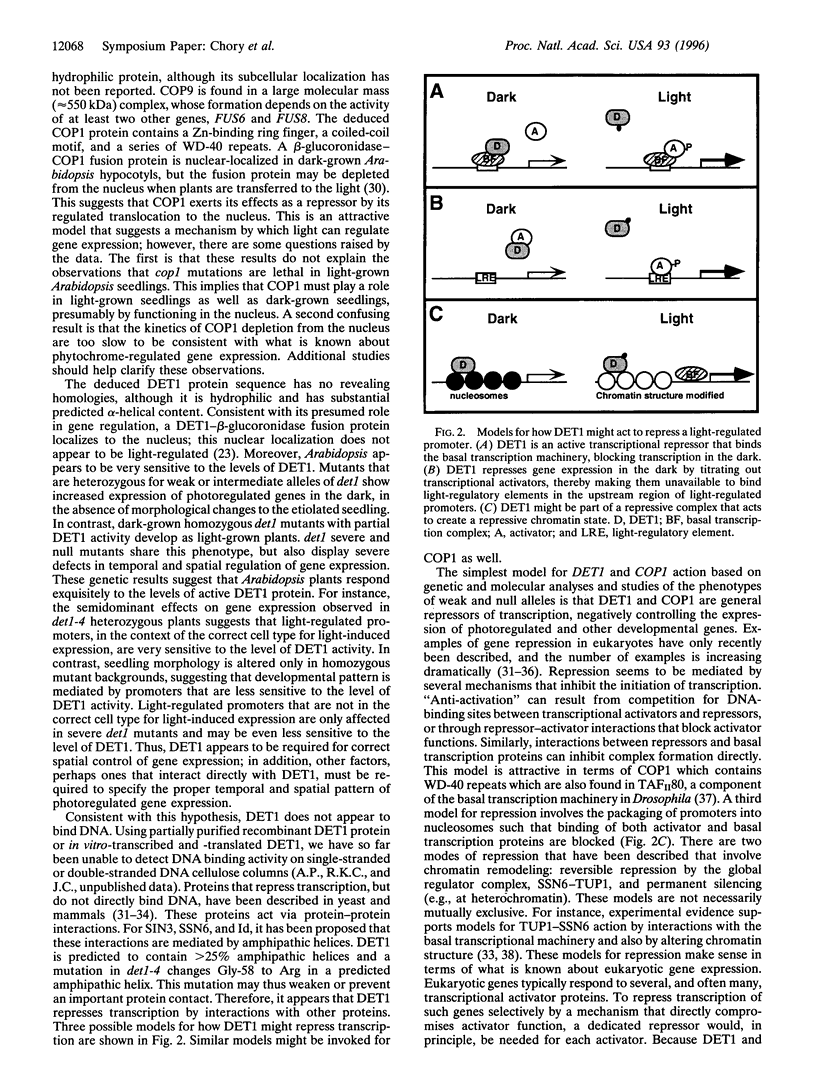
- Pepper A., Delaney T., Washburn T., Poole D., Chory J. DET1, a negative regulator of light-mediated development and gene expression in arabidopsis, encodes a novel nuclear-localized protein. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90577-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quail P. H., Boylan M. T., Parks B. M., Short T. W., Xu Y., Wagner D. Phytochromes: photosensory perception and signal transduction. Science. 1995 May 5;268(5211):675–680. doi: 10.1126/science.7732376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. W., Chory J. Mutational analyses of light-controlled seedling development in Arabidopsis. Semin Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;5(5):327–334. doi: 10.1006/scel.1994.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. W., Nagatani A., Elich T. D., Fagan M., Chory J. Phytochrome A and Phytochrome B Have Overlapping but Distinct Functions in Arabidopsis Development. Plant Physiol. 1994 Apr;104(4):1139–1149. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.4.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S. Y. Chromatin-mediated transcriptional repression in yeast. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Apr;5(2):168–173. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(95)80004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J., Marshall-Carlson L., Carlson M. The N-terminal TPR region is the functional domain of SSN6, a nuclear phosphoprotein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4744–4756. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomura T., Nagatani A., Chory J., Furuya M. The Induction of Seed Germination in Arabidopsis thaliana Is Regulated Principally by Phytochrome B and Secondarily by Phytochrome A. Plant Physiol. 1994 Feb;104(2):363–371. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler D. A., Laetsch W. M. Kinetin-induced chloroplast maturation in cultures of tobacco tissue. Science. 1965 Sep 17;149(3690):1387–1388. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3690.1387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susek R. E., Ausubel F. M., Chory J. Signal transduction mutants of Arabidopsis uncouple nuclear CAB and RBCS gene expression from chloroplast development. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):787–799. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90459-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekeres M., Németh K., Koncz-Kálmán Z., Mathur J., Kauschmann A., Altmann T., Rédei G. P., Nagy F., Schell J., Koncz C. Brassinosteroids rescue the deficiency of CYP90, a cytochrome P450, controlling cell elongation and de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Cell. 1996 Apr 19;85(2):171–182. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Gasch A., Nishizawa N., Chua N. H. The DIMINUTO gene of Arabidopsis is involved in regulating cell elongation. Genes Dev. 1995 Jan 1;9(1):97–107. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D., Fairchild C. D., Kuhn R. M., Quail P. H. Chromophore-bearing NH2-terminal domains of phytochromes A and B determine their photosensory specificity and differential light lability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 30;93(9):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.9.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. W., Cosgrove D. J., Arteca R. N. Brassinosteroid Stimulation of Hypocotyl Elongation and Wall Relaxation in Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis cv Lei-Choi). Plant Physiol. 1993 Mar;101(3):965–968. doi: 10.1104/pp.101.3.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei N., Chamovitz D. A., Deng X. W. Arabidopsis COP9 is a component of a novel signaling complex mediating light control of development. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):117–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90578-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller J. L., Nagatani A., Kendrick R. E., Murfet I. C., Reid J. B. New lv Mutants of Pea Are Deficient in Phytochrome B. Plant Physiol. 1995 Jun;108(2):525–532. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelam G. C., Johnson E., Peng J., Carol P., Anderson M. L., Cowl J. S., Harberd N. P. Phytochrome A null mutants of Arabidopsis display a wild-type phenotype in white light. Plant Cell. 1993 Jul;5(7):757–768. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.7.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. A., Weatherwax S. C., Bray E. A., Tobin E. M. NPR genes, which are negatively regulated by phytochrome action in Lemna gibba L. G-3, can also be positively regulated by abscisic acid. Plant Physiol. 1994 Jul;105(3):949–954. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. N., Heckman J. W., Somerville C. R. Gibberellin Is Required for Flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana under Short Days. Plant Physiol. 1992 Sep;100(1):403–408. doi: 10.1104/pp.100.1.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeevaart J. A., Gage D. A. ent-kaurene biosynthesis is enhanced by long photoperiods in the long-day plants Spinacia oleracea L. and Agrostemma githago L. Plant Physiol. 1993 Jan;101(1):25–29. doi: 10.1104/pp.101.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Arnim A. G., Deng X. W. Light inactivation of Arabidopsis photomorphogenic repressor COP1 involves a cell-specific regulation of its nucleocytoplasmic partitioning. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):1035–1045. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]