Abstract
Baicalin is one of the main bioactive flavone glucuronides derived as a medicinal herb from the dried roots of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, and it is widely used for the treatment of fever, inflammation, and other conditions. Due to baicalin’s poor solubility in water, its absolute bioavailability after oral administration is only 2.2%. The objective of this study was to develop a novel baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion to improve the oral bioavailability of baicalin. Based on the result of pseudoternary phase diagram, the nanoemulsion formulation consisting of soy-lecithin, tween-80, polyethylene glycol 400, isopropyl myristate, and water (1:2:1.5:3.75:8.25, w/w) was selected for further study. Baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions (BAN-1 and BAN-2) were prepared by internal or external drug addition and in vivo and in vitro evaluations were performed. The results showed that the mean droplet size, polydispersity index, and drug content of BAN-1 and BAN-2 were 91.2 ± 2.36 nm and 89.7 ± 3.05 nm, 0.313 ± 0.002 and 0.265 ± 0.001, and 98.56% ± 0.79% and 99.40% ± 0.51%, respectively. Transmission electron microscopy revealed spherical globules and confirmed droplet size analysis. After dilution 30-fold with water, the solubilization capacity of BAN-1 and BAN-2 did not change. In vitro release results showed sustained-release characteristics. BAN-1 formulation was stable for at least 6 months and was more stable than BAN-2. In rats, the area under the plasma drug concentration-time curve value of BAN-1 was 1.8-fold and 7-fold greater than those of BAN-2 and free baicalin suspension after oral administration at a dose of 100 mg/kg. In conclusion, these results demonstrated that the baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion formulation, in particular BAN-1, was very effective for improving the oral bioavailability of baicalin and exhibited great potential for future clinical application.
Keywords: nanoemulsion, baicalin, oral bioavailability, pharmacokinetics
Introduction
Baicalin (7-glucuronic acid 5, 6-dihydroxyflavone) is one of the main single active constituents isolated from the dried roots of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi as a medicinal herb; its aglycone form is called baicalein (Figure 1). Current studies have shown various strong pharmacological properties of baicalin,1–5 such as antioxidative, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antiradical, antiproliferative, cardioprotective, and so on. However, it can be observed from the molecular structure of the currently marketed preparation of baicalin (Figure 1), including capsules and tablets, that both flavones and glucuronide can form intramolecular hydrogen bonds that result in poor solubility in water, which causes low oral bioavailability.6 In previous studies, baicalin was found to be moderately absorbed in the stomach and poorly absorbed in the small intestine and colon; in contrast, its aglycone moiety (baicalein; Figure 1) was well absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and then restored to baicalin in the body.4,7,8 After oral administration of baicalin and baicalein in rats, the absolute bioavailability was 2.2% and 27.8%, respectively.9 It was concluded that the oral bioavailability of baicalin was greatly improved after administration of baicalein. However, the baicalein content in Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi is very low; it is irrational to obtain baicalein by the extracting and purging process. In addition, baicalin is transformed to baicalein by enzyme hydrolysis and strong acid hydrolysis, which is costly and produces environmental pollution. Therefore, it is necessary to develop new drug dosages and new techniques for increasing baicalin’s solubility and dissolution rate and improving its oral bioavailability.
Figure 1.
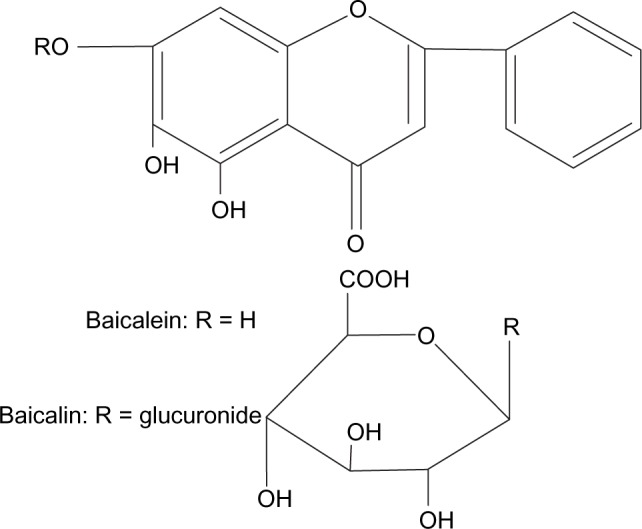
Chemical structures of baicalein and baicalin.
Nanoemulsions composed of oil, water, surfactant, and cosurfactant are thermodynamically stable and isotropically clear dispersion systems that are stabilized by an interfacial film of surfactant and cosurfactant.10 Nanoemulsions exhibit unique advantages and properties, such as reduced droplet size with larger surface area, improved drug solubility and dissolution rates, and enhanced drug absorption from the gastrointestinal tract by surfactant-induced mucosal permeability changes.11–19 Nanoemulsion formulations have been widely used to overcome problems related to the poor water solubility and low oral bioavailability of some drugs.20–26 Therefore, amongst the various drug delivery systems, nanoemulsions are considered an ideal alternative for the oral administration of drugs with poor water solubility, as they improve absorption and bioavailability. At present, the US Food and Drug Administration has approved nanoemulsions of compounds with poor water solubility, including cyclosporin (Neoral®, Gengraf®),27,28 saquinavir (Fortovase®),29,30 and ritonavir (Norvir®),31 for clinical use. However, to our knowledge, no related studies have demonstrated that nanoemulsion could improve the oral bioavailability of baicalin.
In the present study, a novel nanoemulsion formulation was developed to enhance oral absorption and bioavailability of baicalin. The optimized nanoemulsion formulation was obtained according to the results of ternary phase diagram experiment. Afterward, both baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions, BAN-1 and BAN-2, were prepared by internal and external addition of the drug, respectively. The physicochemical properties and pharmacokinetics were investigated in comparison with a free baicalin suspension (baicalin control), which was baicalin suspended in 0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution.
Materials and methods
Materials
Baicalin (≥98.0%) was purchased from Mianyang Dongfangyuan Bio-Technology Co, Ltd (Sichuan, People’s Republic of China). Rutin (internal standard) was obtained from Chengdu Mansite Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd (Sichuan, People’s Republic of China). Isopropyl myristate (IPM), glyceryl monooleate, isopropyl palmitate (IPP), soy-lecithin, tween-80, polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG400), propylene glycol, and ethanol were obtained from Luzhou Juhe Chemical Co, Ltd (Sichuan, People’s Republic of China). All other chemicals and reagents used in this study were of analytical or high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) grade.
Animals
Male Sprague Dawley rats weighing between 150–180 g were obtained from the Laboratory Animal Center of Luzhou Medical College (Sichuan, People’s Republic of China). All animal experimental procedures were approved by the Luzhou Medical College Animal Ethical Experimentation Committee. The rats were housed at a temperature of 20°C ± 2°C, a relative humidity of 50%–60%, and 12-hour light–dark cycles. Free access to food and water was allowed. All the animals were fasted overnight with free access to water prior to the experiment.
Solubility study
The saturation solubility of baicalin in oil phases, surfactant, and cosurfactant was investigated in this study. Briefly, an excess amount of baicalin was added into sealed tubes of each vehicle described above and then was carried out by nitrogen-filled protection followed by vortex mixing for about 1 minute. The tubes were shaken continually at room temperature for 24 hours, followed by equilibrium for 24 hours. The mixture was then centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes to obtain a clear solution and then was diluted with methanol and determined by HPLC. In in vitro and in vivo experiments, baicalin was quantified using a Dionex UltiMate® 3000 series HPLC system (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) that included a pump (LPG-3400SD), UV-vis detector (VWD-3100), auto injector (WPS-3000), and column oven (TCC-3000). Separation was performed on a reverse-phase Inertsil ODS-SP C18 column (GL Sciences, Inc., Torrance, CA, USA; 4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 μm particle size, made in Japan) with a Phenomenex C18 guard column (Torrance, CA, USA; 4.0 mm × 3.0 mm). The elution was isocratic at 1.0 mL/minute with a mobile phase consisting of methanol and 0.4% (v/v) aqueous phosphoric acid (6:4) at the detection wavelength of 278 nm. The column temperature was maintained at 30°C and the injection volume was 20 μL.
Construction of ternary phase diagrams
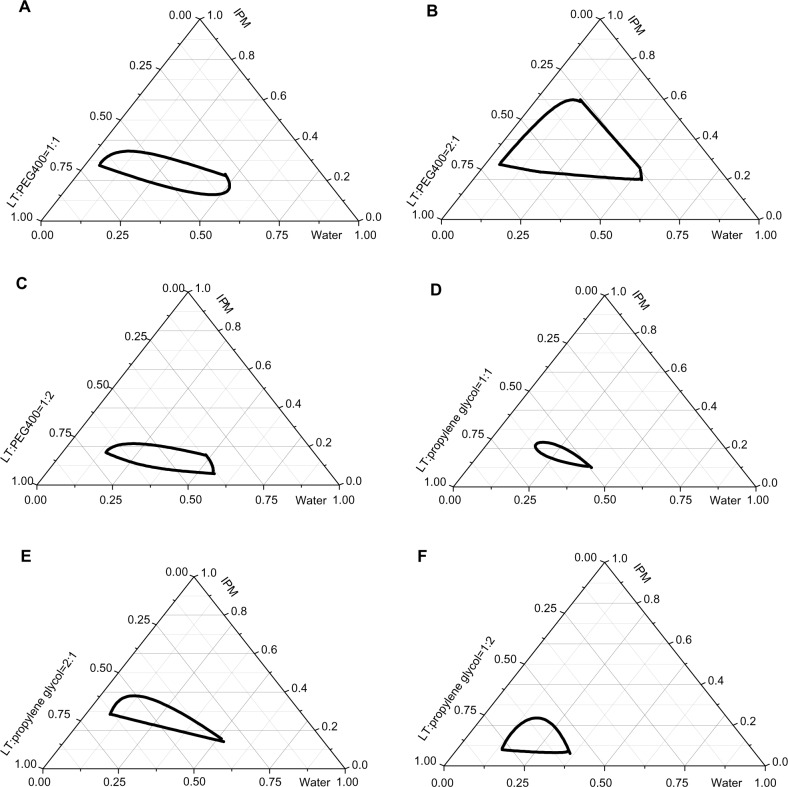
Pseudoternary phase diagrams of various oil, water, and surfactant/cosurfactant mixtures were developed by using the water titration method at room temperature to ascertain the concentration range of ingredients that could form a nanoemulsion region. According to the results of preliminary experiments, a combination of soy-lecithin and tween-80 at 1:2 weight ratio (LT) was used as a mixed surfactant; PEG400 and propylene glycol were chosen as cosurfactants. The LT and cosurfactant were combined at 1:2, 1:1, and 2:1 weight ratios, then mixed with IPM as oil phase at certain weight ratios (1/9, 2/8, 3/7, 4/6, 5/5, 6/4, 7/3, 8/2 and 9/1, w/w), and titrated with water in a dropwise manner under magnetic agitation, until the mixture became clear and flowable at a certain point.24,32 The concentrations of components were recorded to construct the pseudoternary phase diagrams.
Preparation of baicalin nanoemulsions
According to the results of solubility studies and the nanoemulsion regions in the pseudoternary phase diagram, in combination with safety, the nanoemulsion formulation composed of soy-lecithin, tween-80, PEG400, IPM, and water (1:2:1.5:3.75:8.25, w/w) was selected and developed into baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions. Baicalin was first dissolved in PEG400 and mixed with soy-lecithin, tween-80, and IPM, after which the required amount of water was added and the solution stirred to obtain a clear and transparent liquid ie, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion (BAN-1). The resulting nanoemulsions were filled with nitrogen gas and tightly sealed and stored at room temperature.
In addition, baicalin was dissolved in the final nanoemulsion formulations to obtain baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions (BAN-2).
Characteristics of baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions
Transmission electron microscopy
The morphologies of the baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions were examined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (JEM-1400; JEOL Ltd Tokyo, Japan). Prior to the analysis, the sample was diluted in distilled water (1:50) and a sample drop was placed on a copper grid. After the samples were dried they were stained with saturated solution of uranyl acetate and investigated.
Droplet size measurement
The droplet size and polydispersity index (PDI) of the nanoemulsions were measured by Malvern ZEN3600 (Malvern Instruments Ltd Worcestershire, UK). The sample was prepared by diluting the baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions with distilled water (50-fold v/v).
Changes in baicalin solubility in nanoemulsions after dilution
To investigate the solubilization capacity of baicalin in the diluted nanoemulsions, BAN-1 and BAN-2 containing 7.5 mg/mL baicalin were diluted 30 times with normal saline at 37°C. The samples (100 μL) were withdrawn at various time points over 24 hours and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes to remove the precipitated baicalin, if any. The concentration of baicalin in nanoemulsions was determined by using HPLC, as described above, after appropriate dilution with methanol.
In vitro release studies
The in vitro release of baicalin from nanoemulsions compared with drug suspensions was studied using a dialysis bag method (molecular weight cut-off [MWCO] 8,000–14,000) in 400 mL of artificial gastric juice (0.1 M HCl, pH 1.1) and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 6.8) as a release medium. Three mL of freshly prepared BAN-1, BAN-2, and free baicalin suspension as control (baicalin suspended in 0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution) containing baicalin 7.5 mg/mL was placed into the dialysis bags and tightly sealed. The test bags were soaked in release medium at a stirring rate of 100 rpm at 37°C ± 0.5°C. At predetermined time points, 0.2 mL of sample solution was taken; meanwhile, the same volume of fresh release medium at 37°C ± 0.5°C was added to maintain the same volume. The sample solution was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes and the supernatant liquid was measured by using HPLC, as described in the “Solubility study” section.
Stability studies
In accordance with the Technical Standard of Drug Stability Test (Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2010, appendix XIX C), stability studies were carried out for baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions (BAN-1 and BAN-2). For the accelerate stability test, samples were filled in amber-colored containers with nitrogen gas protection and stored at 40°C ± 2°C, RH 75% ± 5% for 6 months. Samples were withdrawn at time intervals of 1, 2, 3, and 6 months. After that, the samples were centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes to remove the precipitated baicalin, if any. The baicalin content in the supernatant liquid was determined by using HPLC, as described above. Changes in appearance from centrifugation and drug content were chosen as markers for stability evaluation in this study.
In vivo pharmacokinetic evaluations
Animal experiment
The rats used in this study were randomly divided into three main groups (BAN-1, BAN-2, and free baicalin suspension groups, n = 10 per group). Rats fasted overnight prior to the experiment, with free access to water. BAN-1 (7.5 mg/mL), BAN-2 (7.5 mg/mL), and free baicalin suspension (7.5 mg/mL) were administered to rats by oral gavage at a dose equivalent to 100 mg/kg of baicalin. Blood samples (0.25 mL each) were collected at 5 minutes, 15 minutes, 30 minutes, 60 minutes, 120 minutes, 150 minutes, 180 minutes, 300 minutes, 480 minutes, 720 minutes, and 1,440 minutes after oral administration. Plasma samples were separated immediately by centrifugation at 4,000 rpm for 5 minutes and stored at −20°C for further analysis.
Sample extraction
Baicalin was extracted from the plasma samples by a liquid–liquid extraction method. Briefly, 50 μL of rutin solution (internal standard) and 600 μL of methanol were added to 100 μL of rat plasma samples in turn, vortexed for 3 minutes, and then treated by sonication at room temperature for 10 minutes. After centrifugation at 8,000 rpm for 5 minutes, the supernatant was collected and evaporated to dryness at 40°C under nitrogen. The residue was reconstituted with 200 μL of mobile phase and centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 5 minutes, after which 20 μL of the clear supernatant was injected into the HPLC system for analysis.
Data analysis
According to the data of plasma drug concentration-time, we calculated the main pharmacokinetic parameters, including the area under the plasma drug concentration-time curve (AUC0–∞), the time to reach the maximum plasma drug concentration (Tmax), the maximum plasma drug concentration (Cmax), the elimination half-life (t1/2), and the mean residence time (MRT), by noncompartmental modeling using a software program, DAS 2.0 (Mathematical Pharmacology Professional Committee of China, People’s Republic of China).
The results were represented as mean ± standard deviation, and differences between the pharmacokinetic data of BAN-1, BAN-2 and free baicalin suspension as control were evaluated using a two-tailed t-test. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
Results and discussion
Solubility studies
For nanoemulsion formulations, oil phase is an important ingredient that can solubilize lipophilic drugs and enhance the amount of lipophilic drug transported through the intestinal lymphatic system. Therefore, the solubility of drug in oil phase is crucial for the development of nanoemulsion formulations. The solubilities of baicalin in oil phase, including glyceryl monooleate, IPM, and IPP, were investigated (Figure 2). Among these oil phases, the highest solubilization capacity was observed in IPM (0.0138 ± 0.0036 mg/mL), followed by glyceryl monooleate (0.0054 ± 0.0009 mg/mL) and IPP (0.0039 ± 0.0007 mg/mL). In addition, IPM was widely used to develop oral nanoemulsion formulations.33 As a result, IPM was chosen for further investigation in this study. Cosurfactant was also an important component for the development of nanoemulsion formulations, because a suitable cosurfactant is used to overcome problems related to the poor solubility and low oral bioavailability of drug.11 Thus, the solubilities of baicalin in three different cosurfactants were studied (Figure 2). Among the cosurfactants examined, PEG400 showed the highest solubility of baicalin (9.328 ± 0.259 mg/mL), followed by propylene glycol (7.056 ± 0.308 mg/mL); ethanol showed the lowest solubility (1.214 ± 0.115 mg/mL). To increase drug-loading efficiency, in combination with evaporation of ethanol, PEG400 and propylene glycol were selected as cosurfactants for further investigation.
Figure 2.
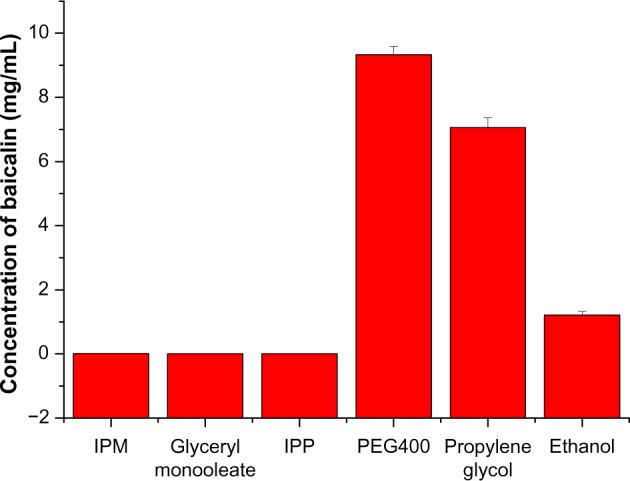
Solubility of baicalin in various oil phases and cosurfactants.
Note: Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3).
Abbreviations: IPM, isopropyl myristate; IPP, isopropyl palmitate; PEG400, polyethylene glycol 400.
Construction of pseudoternary phase diagram and formulation of baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions
Because phospholipids act as natural emulsifiers, soy-lecithin is generally considered to be safe for humans. Additionally, nonionic surfactants are less toxic than ionic surfactants.34 The combination of soy-lecithin and tween-80 as mixed surfactants was investigated in the preliminary experiment. The results showed that the highest emulsification efficiency was obtained in the case of LT (soy-lecithin and tween-80 with the weight ratio of 1:2 as mixed surfactants). Therefore, on the basis of results of solubility studies and preliminary experiments, we primarily chose nanoemulsion formulations composed of IPM, LT, and water in the presence of cosurfactant (PEG400 or propylene glycol). To determine the appropriate concentration range of components for the formation of nanoemulsion regions, we constructed pseudoternary phase diagrams with various weight ratios of LT/PEG400 or LT/propylene glycol (Figure 3). Figure 3 illustrates that the areas of nanoemulsion produced by various ratios (1:1, 2:1, 1:2) of LT/PEG400 or LT/propylene glycol were different. The area formed by LT/PEG400 was larger than that of LT/propylene glycol, indicating that the formation of nanoemul-sions was affected by the cosurfactant types. Furthermore, the largest area of nanoemulsion regions was observed in the case of LT/PEG400 (2:1).
Figure 3.
Pseudoternary phase diagrams of nanoemulsions composed of IPM or LT as mixed surfactants, PEG400 or propylene glycol as cosurfactants, and water.
Notes: (A–C) LT/PEG400 at the weight ratios of 1:1, 2:1, and 1:2, respectively. (D–F) LT/propylene glycol at the weight ratios of 1:1, 2:1, and 1:2, respectively. The dark outline represents the area of nanoemulsion produced by the surfactant/cosurfactant combination.
Abbreviations: IPM, isopropyl myristate; LT, soy-lecithin/tween-80 with the weight ratio of 1:2; PEG400, polyethylene glycol 400.
On the basis of the results of the pseudoternary phase diagrams, we selected the appropriate concentration of the components, ie, soy-lecithin, tween-80, PEG400, IPM, and water (1:2:1.5:3.75:8.25, w/w) to develop baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions. When baicalin was first dissolved in PEG400 to obtain baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions, BAN-1 was expressed. In addition, baicalin was dissolved in the final nanoemulsion formulations to obtain baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions (BAN-2). Nanoemulsions with a fixed concentration of 7.5 mg/mL of baicalin were prepared and used in the following studies.
Characteristics of nanoemulsions
The droplet size of nanoemulsions is an important factor because it influences drug-release behavior and stability.35 The PDI ranged from 0.0 to 1.0, representing the uniformity of droplet size. The closer to zero the PDI value, the more homogeneous the droplets are.36 In the current study, droplet size, PDI, and drug content of baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions are shown in Table 1. The results showed that the mean droplet size of BAN-1 and BAN-2 measured by Malvern ZEN3600 was less than 100 nm with a maximum PDI of 0.313, which demonstrated that the particle size distribution of baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions was homogeneous. The drug content of BAN-1 and BAN-2 was 98.56% ± 0.79% and 99.40% ± 0.51%, respectively, which meets the requirement of Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2010 edition, part II).
Table 1.
Droplet size, polydispersity index and drug content of baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions
| Samples | Droplet size (nm) | Polydispersity index | Drug content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BAN-1 | 91.2 ± 2.36 | 0.313 ± 0.002 | 98.56 ± 0.79 |
| BAN-2 | 89.7 ± 3.05 | 0.265 ± 0.001 | 99.40 ± 0.51 |
Note: Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3).
Abbreviations: BAN-1, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion created by dissolution of baicalin in PEG400 and mixing with soy-lecithin, tween-80, IPM, and water; BAN-2, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion created by dissolution of baicalin in the final nanoemulsion formulations.
To examine morphology and confirm droplet size analysis, TEM was used to investigate the baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions in this study. TEM images of BAN-1 and BAN-2 are shown in Figure 4 and show that spherical nanoemulsion globules had a diameter of less than 100 nm, in accordance with the results obtained by Malvern ZEN3600.
Figure 4.
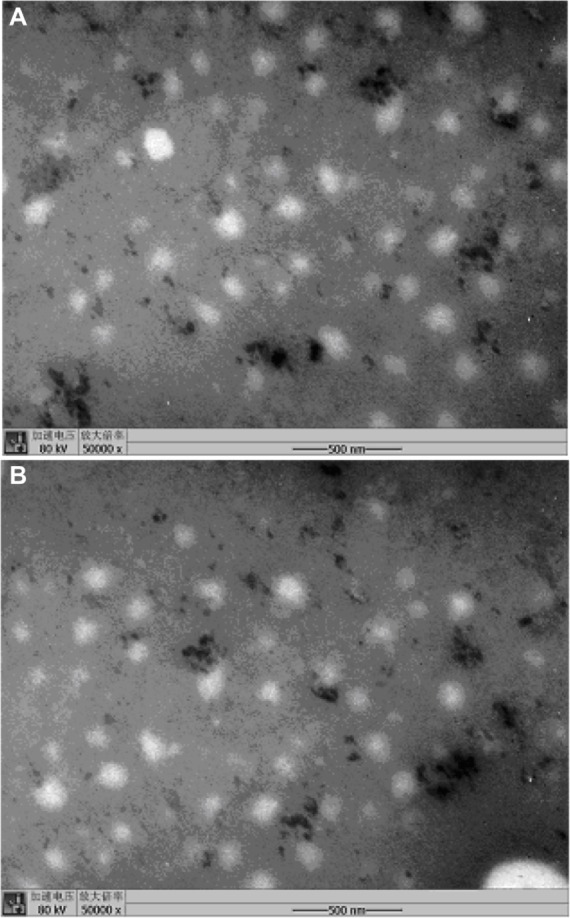
Transmission electron microscopy of baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions with 50-fold dilution in distilled water.
Notes: (A) BAN-1. (B) BAN-2.
Abbreviations: BAN-1, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion created by dissolution of baicalin in PEG400 and mixing with soy-lecithin, tween-80, IPM, and water; BAN-2, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion created by dissolution of baicalin in the final nanoemulsion formulations.
In general, when nanoemulsions containing poor water-soluble drug are diluted with water in the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration, they can result in drug precipitation.23 Therefore, it is necessary to investigate solubilization capacity via dilution with water (Figure 5). Figure 5 indicates that the baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions showed satisfactory solubilization capacity for at least 24 hours, suggesting that both BAN-1 and BAN-2 would not cause drug precipitation upon contact with the water solution in the gastrointestinal tract.
Figure 5.
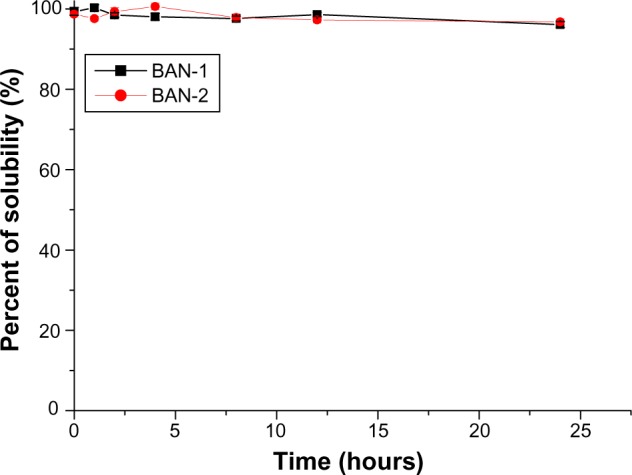
Change of baicalin solubility in nanoemulsions after 30 times dilution with normal saline at 37°C.
Note: Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3).
Abbreviations: BAN-1, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion created by dissolution of baicalin in PEG400 and mixing with soy-lecithin, tween-80, IPM, and water; BAN-2, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion created by dissolution of baicalin in the final nanoemulsion formulations.
In vitro release studies
To simulate drug-release behaviors in the gastrointestinal tract, the in vitro release of baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions (BAN-1 and BAN-2) was performed in 0.1 M HCl (pH 1.1) and PBS (pH 6.8) as release medium (Figure 6). According to the vitro release profiles of BAN-1 and BAN-2, the accumulative release amount of baicalin from the nanoemulsions in PBS was much higher than it was in 0.1 M HCl, which could be attributed to the higher solubility of baicalin at high pH values.36 A similar release behavior was observed for free baicalin suspension. However, in both release mediums, the release of baicalin from nanoemulsions was much higher than that from the free baicalin suspension, which could result from the solubilizing effect of nanoemulsions. The accumulative release of BAN-1 and BAN-2 in PBS was 19.302% and 16.940%, respectively, within 48 hours, while that in 0.1 M HCl was 4.666% and 5.152%, respectively. These results may be attributed to the presence of a diffusion membrane composed of oil phase and oil–water interface of nanoemulsions that constituted a hindrance against drug release.37 In conclusion, the baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion displayed sustained-release characteristics, and no significant difference in the in vitro release behavior between BAN-1 and BAN-2 was observed.
Figure 6.
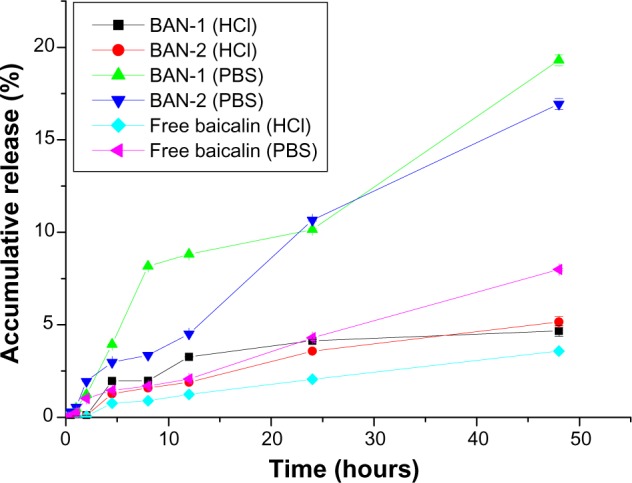
In vitro release profile of BAN-1 and BAN-2 and free baicalin suspension in 0.1 M HHI (pH 1.1) and PBS (pH 6.8) as release medium.
Note: Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3).
Abbreviations: BAN-1, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion created by dissolution of baicalin in PEG400 and mixing with soy-lecithin, tween-80, IPM, and water; BAN-2, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion created by dissolution of baicalin in the final nanoemulsion formulations; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.
Stability studies
Stability studies were performed because stability is a crucial marker for quality evaluation of new drug dosage forms (Table 2). For the BAN-1 formulation, the results showed no significant difference (P > 0.05) in baicalin content and no appearance changes after 6 months, compared with initial samples at 0 months. For BAN-2, a significant difference (P < 0.05) in baicalin content and some precipitation was observed after 3 months. Therefore, it is suggested that BAN-1 formulation is stable for at least 6 months – more stable than BAN-2.
Table 2.
Results of the accelerate stability test: difference in baicalin content over time compared with 0 months
| Items | Time (months)
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | |
| BAN-1 (%) | 98.56 ± 0.79 | 98.15 ± 0.66 | 98.95 ± 0.84 | 97.76 ± 0.65 | 97.25 ± 0.38* |
| BAN-2 (%) | 99.40 ± 0.51 | 96.24 ± 0.86* | 95.31 ± 0.57* | 90.19 ± 0.47† | 85.23 ± 0.58 |
Note: Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3).
Not significant compared with 0 months, P > 0.05.
Significant compared with 0 months, P < 0.05.
Abbreviations: BAN-1, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion created by dissolution of baicalin in PEG400 and mixing with soy-lecithin, tween-80, IPM, and water; BAN-2, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion created by dissolution of baicalin in the final nanoemulsion formulations.
Pharmacokinetic behavior
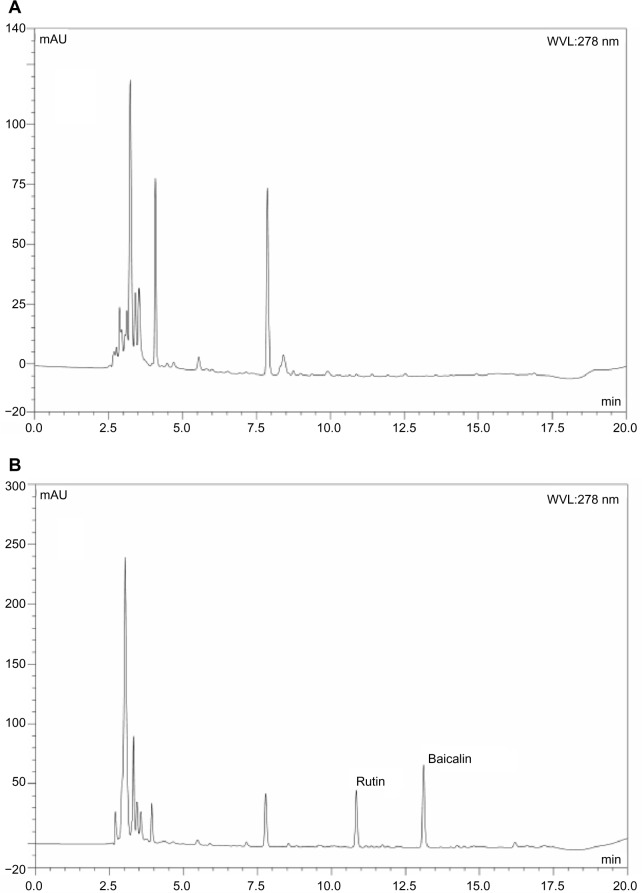
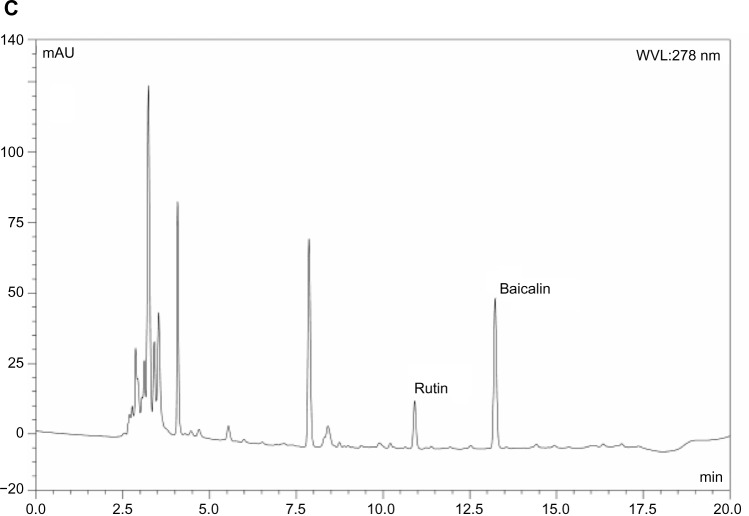
To investigate whether a nanoemulsion carrier system could increase the oral bioavailability of baicalin, the plasma drug concentration in rats was determined by HPLC to evaluate the pharmacokinetic behavior of BAN-1 and BAN-2 in comparison with free baicalin suspension after oral administration at a dose of 100 mg/kg. In this study, the reversephase HPLC method was developed and validated for the determination of baicalin in rat plasma. The analysis method had good specificity (Figure 7). Good linearity was obtained between 0.1 μg/mL and 12.5 μg/mL for plasma (r > 0.999). The intraday and interday assay of precision and accuracy for plasma samples ranged from 1.2% to 4.2% and from 92.5% to 95.2%, respectively. The extraction recoveries ranged from 80.2% to 81.7%.
Figure 7.
Representative HPLC chromatograms of baicalin and rutin in rat plasma determined by HPLC method.
Notes: (A) Blank plasma. (B) Blank plasma spiked with baicalin and rutin (internal standard). (C) Plasma samples collected 60 minutes after oral administration of baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions.
Abbreviations: HPLC, high-performance liquid chromatography; WVL, wavelength.
The plasma drug concentration-time curve is shown in Figure 8, and the main pharmacokinetic parameters are summarized in Table 3. A significant difference between the pharmacokinetic behavior of baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion and free baicalin suspension was observed (Figure 8). At each time point, the plasma drug concentration of BAN-1 and BAN-2 was much higher than that of free baicalin suspension. The peak concentration (Cmax) of baicalin from BAN-1 and BAN-2 was 3.155 ± 0.132 mg/L and 4.625 ± 0.203 mg/L, respectively, which was about 3–4 times that of free baicalin suspension (1.143 ± 0.105 mg/L) – a significant increase (P < 0.05). The AUC(0–∞) value of baicalin in rats treated with BAN-1 or BAN-2 was 98.439 ± 4.579 mg/L*h and 54.443 ± 3.879 mg/L*h, respectively, which was improved more than 7 and 4 times than that of free baicalin suspension (13.681 ± 1.092 mg/L*h) (P < 0.05). In addition, the MRT and t1/2 value of BAN-1 was about 3.5-fold greater than that of BAN-2 and the reference preparation. It was reported that the oral bioavailability of baicalin was enhanced approximately 2.6 times by solid lipid nanoparticles.38 However, in the present study, unexpected results demonstrated that the baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion BAN-1 was much more effective than nanoparticle, which could be attributed to enhanced permeability induced by surfactant and cosurfactant, uptake of BAN-1 in gastrointestinal tract, and the sustained-release of drug from BAN-1. In this study, the AUC(0–∞) value of BAN-1 was 1.8-fold higher that of BAN-2, which could have resulted from the longer MRT(0–∞) and t1/2 values, in combination with being more stable.
Figure 8.
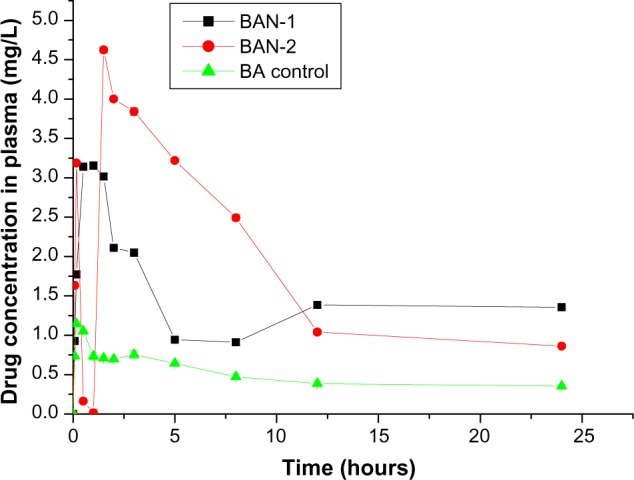
Plasma concentration-time profiles of baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions in rats after oral administration of BAN-1, BAN-2, and BA control.
Note: Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3).
Abbreviations: BAN-1, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion created by dissolution of baicalin in PEG400 and mixing with soy-lecithin, tween-80, IPM, and water; BAN-2, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion created by dissolution of baicalin in the final nanoemulsion formulations; BA control, free baicalin suspension (baicalin suspended in 0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution).
Table 3.
Pharmacokinetic parameters of baicalin in rats after oral administration of BAN-1, BAN-2, and free baicalin suspension as control
| Parameter | Unit | Value of parameter
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAN-1 | BAN-2 | Free baicalin suspension | ||
| AUC(0–∞) | mg/L*h | 98.439 ± 4.579 | 54.443 ± 3.879 | 13.681 ± 1.092 |
| MRT(0–∞) | h | 50.667 ± 3.479 | 15.210 ± 1.254 | 14.144 ± 1.125 |
| t1/2 | h | 33.097 ± 1.952 | 9.842 ± 0.486 | 9.296 ± 0.505 |
| Tmax | h | 1.000 ± 0.047 | 1.500 ± 0.078 | 0.167 ± 0.006 |
| Vz/F | L/kg | 48.517 ± 3.465 | 26.087 ± 2.09 | 98.054 ± 5.432 |
| CLz/F | L/h/kg | 1.016 ± 0.065 | 1.837 ± 0.106 | 7.310 ± 0.58 |
| Cmax | mg/L | 3.155 ± 0.132 | 4.625 ± 0.203 | 1.143 ± 0.105 |
Note: Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3).
Abbreviations: BAN-1, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion created by dissolution of baicalin in PEG400 and mixing with soy-lecithin, tween-80, IPM, and water; BAN-2, baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion created by dissolution of baicalin in the final nanoemulsion formulations; (AUC0–∞), area under the plasma drug concentration-time curve; MRT, mean residence time; (t1/2 elimination half-life; (Tmax), time to reach the maximum plasma drug concentration; Vz/F, apparent volume of distribution; CLz/F, clearance; (Cmax), maximum plasma drug concentration.
Conclusion
A novel baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion formulation consisting of soy-lecithin, tween-80, PEG400, IPM, and water (1:2:1.5:3.75:8.25, w/w) was developed to improve the oral bioavailability of baicalin. Baicalin-loaded nanoemulsions (BAN-1 and BAN-2) were prepared by internal and external drug addition. No significant differences between BAN-1 and BAN-2 in droplet size, PDI, drug content, in vitro release behavior, and solubilization capacity via dilution with water were observed. However, BAN-1 is stable for at least 6 months, more stable than BAN-2. The AUC(0–∞) value of BAN-1 was 1.8-fold and 7.0-fold that of BAN-1 and free baicalin suspension after oral administration at a dose of 100 mg/kg in rats. To sum up, these results demonstrated that the baicalin-loaded nanoemulsion formulation, in particular BAN-1, was effective for improving the oral bioavailability of baicalin and exhibited great potential for future clinical application.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81101678, 81172049), the Key Program of the Scientific Research Foundation of the Education Department of Sichuan Province (11ZZ024; 12ZZ020; 12ZB066), the Scientific Research Foundation of the Administration of Traditional Chinese of Sichuan Province (2012-F-026), the Key Program of the Scientific Research Foundation of Bureau of Science and Technology of Luzhou City (2011-S-32(1/4), and Produce-Learn-Research Projects of Luzhou Medical College (2012CXY-01).
Footnotes
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
References
- 1.Boyle SP, Doolan PJ, Andrews CE, Reid RG. Evaluation of quality control strategies in Scutellaria herbal medicines. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2011;54(5):951–957. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2010.11.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Franek KJ, Zhou Z, Zhang WD, Chen WY. In vitro studies of baicalin alone or in combination with Salvia miltiorrhiza extract as a potential anti-cancer agent. Int J Oncol. 2005;26(1):217–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mao W, Chen X, Yang T, et al. A rapid fluorescent screening method for cellular sensitivity to anti-cancer compound. Cytotechnology. 2012;64(4):451–457. doi: 10.1007/s10616-011-9423-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Srinivas NR. Baicalin, an emerging multi-therapeutic agent: pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and considerations from drug development perspectives. Xenobiotica. 2010;40(5):357–367. doi: 10.3109/00498251003663724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Huang Y, Tsang SY, Yao X, Chen ZY. Biological properties of baicalein in cardiovascular system. Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Hematol Disord. 2005;5(2):177–184. doi: 10.2174/1568006043586206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Li B, Wen M, Li W, He M, Yang X, Li S. Preparation and characterization of baicalin-poly-vinylpyrrolidone coprecipitate. Int J Pharm. 2011;408(1–2):91–96. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Taiming L, Xuehua J. Investigation of the absorption mechanisms of baicalin and baicalein in rats. J Pharm Sci. 2006;95(6):1326–1333. doi: 10.1002/jps.20593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Xing J, Chen X, Sun Y, Luan Y, Zhong D. Interaction of baicalin and baicalein with antibiotics in the gastrointestinal tract. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2005;57(6):743–750. doi: 10.1211/0022357056244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Xing J, Chen X, Zhong D. Absorption and enterohepatic circulation of baicalin in rats. Life Sci. 2005;78(2):140–146. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.04.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zheng WW, Zhao L, Wei YM, Ye Y, Xiao SH. Preparation and the in vitro evaluation of nanoemulsion system for the transdermal delivery of granisetron hydrochloride. Chem Pharm Bull. 2010;58(8):1015–1019. doi: 10.1248/cpb.58.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ryu JK, Yoo SD. Preparation and evaluation of bicyclol microemulsions for enhanced oral bioavailability. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2012;38(11):1313–1318. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2011.650643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ammar HO, Salama HA, Ghorab M, Mahmoud AA. Nanoemulsion as a potential ophthalmic delivery system for dorzolamide hydrochloride. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2009;10(3):808–819. doi: 10.1208/s12249-009-9268-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bali V, Ali M, Ali J. Study of surfactant combinations and development of a novel nanoemulsion for minimising variations in bioavailability of ezetimibe. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2010;76(2):410–420. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.11.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kuminek G, Kratz JM, Ribeiro R, et al. Pharmacokinetic study of a carbamazepine nanoemulsion in beagle dogs. Int J Pharm. 2009;378(1–2):146–148. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.05.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kuo F, Kotyla T, Wilson T, et al. A nanoemulsion of an anti-oxidant synergy formulation reduces tumor growth rate in neuroblastoma-bearing nude mice. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2007;6(2):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Singh KK, Vingkar SK. Formulation, antimalarial activity and biodistribution of oral lipid nanoemulsion of primaquine. Int J Pharm. 2008;347(1–2):136–143. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.06.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ganta S, Amiji M. Coadministration of Paclitaxel and curcumin in nanoemulsion formulations to overcome multidrug resistance in tumor cells. Mol Pharm. 2009;6(3):928–939. doi: 10.1021/mp800240j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Vyas TK, Shahiwala A, Amiji MM. Improved oral bioavailability and brain transport of Saquinavir upon administration in novel nanoemulsion formulations. Int J Pharm. 2008;347(1–2):93–101. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.06.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Constantinides PP. Lipid microemulsions for improving drug dissolution and oral absorption: physical and biopharmaceutical aspects. Pharm Res. 1995;12(11):1561–1572. doi: 10.1023/a:1016268311867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yong CS, Park BJ, Kim DH, et al. Short communication: in vivo evaluation of microemulsion system for oral and parenteral delivery of rutaecarpine to rats. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2007;33(5):531–534. doi: 10.1080/03639040600865199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hirunpanich V, Sato H. Improvement of cyclosporine A bioavailability by incorporating ethyl docosahexaenoate in the microemulsion as an oil excipient. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;73(2):247–252. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2009.06.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wu H, Lu C, Zhou A, Min Z, Zhang Y. Enhanced oral bioavailability of puerarin using microemulsion vehicle. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2009;35(2):138–144. doi: 10.1080/03639040801973495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yin YM, Cui FD, Mu CF, et al. Docetaxel microemulsion for enhanced oral bioavailability: preparation and in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Control Release. 2009;140(2):86–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Attivi D, Ajana I, Astier A, Demoré B, Gibaud S. Development of microemulsion of mitotane for improvement of oral bioavailability. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2010;36(4):421–427. doi: 10.3109/03639040903225083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.He CX, He ZG, Gao JQ. Microemulsions as drug delivery systems to improve the solubility and the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2010;7(4):445–460. doi: 10.1517/17425241003596337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hu L, Wu H, Niu F, Yan C, Yang X, Jia Y. Design of fenofibrate microemulsion for improved bioavailability. Int J Pharm. 2011;420(2):251–255. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.08.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kovarik JM, Mueller EA, van Bree JB, Arns W, Renner E, Kutz K. Within-day consistency in cyclosporine pharmacokinetics from a microemulsion formulation in renal transplant patients. Ther Drug Monit. 1994;16(3):232–237. doi: 10.1097/00007691-199406000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mueller EA, Kovarik JM, van Bree JB, Tetzloff W, Grevel J, Kutz K. Improved dose linearity of cyclosporine pharmacokinetics from a microemulsion formulation. Pharm Res. 1994;11(2):301–304. doi: 10.1023/a:1018923912135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mandal S, Mandal SS, Surti N, Patel VB. Design and development of saquinavir microemulsion for the oral bioavailability. Pharm Tech Res. 2009;1:1442–1448. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hugen PW, Burger DM, Koopmans PP, et al. Saquinavir soft-gel capsules (Fortovase) give lower exposure than expected, even after a high-fat breakfast. Pharm World Sci. 2002;24(3):83–86. doi: 10.1023/a:1016121100568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fatouros DG, Karpf DM, Nielsen FS, Mullertz A. Clinical studies with oral lipid based formulations of poorly soluble compounds. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2007;3(4):591–604. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Shafiq S, Shakeel F, Talegaonkar S, Ahmad FJ, Khar RK, Ali M. Development and bioavailability assessment of ramipril nanoemulsion formulation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2007;66(2):227–243. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2006.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chen H, Zhong YQ, Lu Y. Preparation of puerarin by microemulsion drug delivery system. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice. 2008;3:200–203. Chinese. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nepal PR, Han HK, Choi HK. Preparation and in vitro-in vivo evaluation of Witepsol H35 based self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) of coenzyme Q(10) Eur J Pharm Sci. 2010;39(4):224–232. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2009.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kohli K, Chopra S, Dhar D, Arora S, Khar RK. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: an approach to enhance oral bioavailability. Drug Discov Today. 2010;15(21–22):958–965. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2010.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tang SY, Manickam S, Wei TK, Nashiru B. Formulation development and optimization of a novel Cremophore EL-based nanoemulsion using ultrasound cavitation. Ultrason Sonochem. 2012;19(2):330–345. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2011.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kelmann RG, Kuminek G, Teixeira HF, Koester LS. Carbamazepine parenteral nanoemulsions prepared by spontaneous emulsification process. Int J Pharm. 2007;342(1–2):231–239. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hao J, Wang F, Wang X, et al. Development and optimization of baicalin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles prepared by coacervation method using central composite design. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2012;47(2):497–505. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2012.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]