Abstract
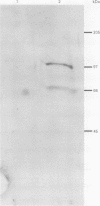
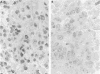
AIMS: To determine, by in situ immunohistochemistry, whether ovarian carcinomas have increased expression of DNA topoisomerase I. METHODS: Paraffin wax blocks obtained from 15 samples of normal human tissues and from 14 cases of ovarian cancer were cut on to glass slides and immunohistochemically stained for topoisomerase I. The primary antibody was a mouse monoclonal that recognises topoisomerase I in western blots. Colour was detected using a peroxidase system with diaminobenzidine as the chromogen. The expression of topoisomerase I in the tissues and tumours was graded subjectively from 0 to 3+ based on the colour intensity of the immunostain. RESULTS: In normal tissues, topoisomerase I expression was strongest in the mucosal lymphocytes in the gastrointestinal tract and in the germinal centres of the tonsil. Weak topoisomerase I staining was found in the columnar epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract and in squamous mucosa. In the series of ovarian carcinomas, raised topoisomerase I was observed in 43% (6 of 14) of the tumours. Of the tumours with raised topoisomerase I, only three contained a population of rapidly cycling cells. Therefore, 21% of our series of ovarian carcinomas (3 of 14) had raised topoisomerase I expression and were proliferating rapidly. CONCLUSIONS: Topoisomerase I expression in formalin fixed, paraffin wax embedded human tissues can be evaluated by immunohistochemical staining. Increases in topoisomerase I occur in some cases of ovarian cancer.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. D., Wadkins R. M., Stewart C. F., Beck W. T., Danks M. K. Cell cycle analysis of amount and distribution of nuclear DNA topoisomerase I as determined by fluorescence digital imaging microscopy. Cytometry. 1995 Feb 1;19(2):134–145. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990190208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauman M. E., Holden J. A., Brown K. A., Harker W. G., Perkins S. L. Differential immunohistochemical staining for DNA topoisomerase II alpha and beta in human tissues and for DNA topoisomerase II beta in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Mod Pathol. 1997 Mar;10(3):168–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti P., Fiorani P., Capuani L., Wang J. C. Camptothecin resistance from a single mutation changing glycine 363 of human DNA topoisomerase I to cysteine. Cancer Res. 1993 Sep 15;53(18):4343–4348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornsti M. A., Benedetti P., Viglianti G. A., Wang J. C. Expression of human DNA topoisomerase I in yeast cells lacking yeast DNA topoisomerase I: restoration of sensitivity of the cells to the antitumor drug camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1989 Nov 15;49(22):6318–6323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronstein I. B., Vorobyev S., Timofeev A., Jolles C. J., Alder S. L., Holden J. A. Elevations of DNA topoisomerase I catalytic activity and immunoprotein in human malignancies. Oncol Res. 1996;8(1):17–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruno S., Giaretti W., Darzynkiewicz Z. Effect of camptothecin on mitogenic stimulation of human lymphocytes: involvement of DNA topoisomerase I in cell transition from G0 to G1 phase of the cell cycle and in DNA replication. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Jun;151(3):478–486. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041510306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckwalter C. A., Lin A. H., Tanizawa A., Pommier Y. G., Cheng Y. C., Kaufmann S. H. RNA synthesis inhibitors alter the subnuclear distribution of DNA topoisomerase I. Cancer Res. 1996 Apr 1;56(7):1674–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño I. B., Heath-Pagliuso S., Sadoff B. U., Fitzhugh D. J., Christman M. F. A novel family of TRF (DNA topoisomerase I-related function) genes required for proper nuclear segregation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 Jun 15;24(12):2404–2410. doi: 10.1093/nar/24.12.2404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron M., Hancock R. DNA topoisomerase II is required for formation of mitotic chromosomes in Chinese hamster ovary cells: studies using the inhibitor 4'-demethylepipodophyllotoxin 9-(4,6-O-thenylidene-beta-D-glucopyranoside). Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 16;29(41):9531–9537. doi: 10.1021/bi00493a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti J. A., Kemeny N. E., Saltz L. B., Huang Y., Tong W. P., Chou T. C., Sun M., Pulliam S., Gonzalez C. Irinotecan is an active agent in untreated patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1996 Mar;14(3):709–715. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1996.14.3.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creemers G. J., Bolis G., Gore M., Scarfone G., Lacave A. J., Guastalla J. P., Despax R., Favalli G., Kreinberg R., Van Belle S. Topotecan, an active drug in the second-line treatment of epithelial ovarian cancer: results of a large European phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 1996 Dec;14(12):3056–3061. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1996.14.12.3056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danks M. K., Garrett K. E., Marion R. C., Whipple D. O. Subcellular redistribution of DNA topoisomerase I in anaplastic astrocytoma cells treated with topotecan. Cancer Res. 1996 Apr 1;56(7):1664–1673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguet M., Lavenot C., Harper F., Mirambeau G., De Recondo A. M. DNA topoisomerases from rat liver: physiological variations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):1059–1075. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng W. K., Faucette L., Johnson R. K., Sternglanz R. Evidence that DNA topoisomerase I is necessary for the cytotoxic effects of camptothecin. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;34(6):755–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng W. K., Pandit S. D., Sternglanz R. Mapping of the active site tyrosine of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13373–13376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florell S. R., Martinchick J. F., Holden J. A. Purification of DNA topoisomerase I from the spleen of a patient with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Anticancer Res. 1996 Nov-Dec;16(6B):3467–3474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimori A., Harker W. G., Kohlhagen G., Hoki Y., Pommier Y. Mutation at the catalytic site of topoisomerase I in CEM/C2, a human leukemia cell line resistant to camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1995 Mar 15;55(6):1339–1346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Elgin S. C. Localization of specific topoisomerase I interactions within the transcribed region of active heat shock genes by using the inhibitor camptothecin. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):141–148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Pflugfelder G., Wang J. C., Lis J. T. Topoisomerase I interacts with transcribed regions in Drosophila cells. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):401–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90461-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Hittelman W. N., Earnshaw W. C. Differential expression of DNA topoisomerases I and II during the eukaryotic cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1086–1090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden J. A., Perkins S. L., Snow G. W., Kjeldsberg C. R. Immunohistochemical staining for DNA topoisomerase II in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1995 Jul;104(1):54–59. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/104.1.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Stearns T., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II must act at mitosis to prevent nondisjunction and chromosome breakage. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):159–168. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Hertzberg R., Hecht S., Liu L. F. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14873–14878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Lihou M. G., Liu L. F. Arrest of replication forks by drug-stabilized topoisomerase I-DNA cleavable complexes as a mechanism of cell killing by camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 15;49(18):5077–5082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Mohler J. L., Seigler H. F., Besterman J. M. Elevation of topoisomerase I messenger RNA, protein, and catalytic activity in human tumors: demonstration of tumor-type specificity and implications for cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 1994 Jan 15;54(2):539–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwong C. L., Chen C. Y., Shang H. F., Hwang J. Increased synthesis and degradation of DNA topoisomerase I during the initial phase of human T lymphocyte proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18982–18986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzschmar M., Meisterernst M., Roeder R. G. Identification of human DNA topoisomerase I as a cofactor for activator-dependent transcription by RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11508–11512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden K. R., Champoux J. J. Overexpression of human topoisomerase I in baby hamster kidney cells: hypersensitivity of clonal isolates to camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 1;52(3):525–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod H. L., Douglas F., Oates M., Symonds R. P., Prakash D., van der Zee A. G., Kaye S. B., Brown R., Keith W. N. Topoisomerase I and II activity in human breast, cervix, lung and colon cancer. Int J Cancer. 1994 Dec 1;59(5):607–611. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910590506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merino A., Madden K. R., Lane W. S., Champoux J. J., Reinberg D. DNA topoisomerase I is involved in both repression and activation of transcription. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):227–232. doi: 10.1038/365227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitiss J. L., Wang J. C. Mechanisms of cell killing by drugs that trap covalent complexes between DNA topoisomerases and DNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1996 Nov;50(5):1095–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantazis P., Kozielski A. J., Mendoza J. T., Early J. A., Hinz H. R., Giovanella B. C. Camptothecin derivatives induce regression of human ovarian carcinomas grown in nude mice and distinguish between non-tumorigenic and tumorigenic cells in vitro. Int J Cancer. 1993 Mar 12;53(5):863–871. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910530526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E., Pantazis P., Bharti A., Toppmeyer D., Giovanella B., Kufe D. Identification of a mutant human topoisomerase I with intact catalytic activity and resistance to 9-nitro-camptothecin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2433–2439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. F., Schütz G. Camptothecin-induced in vivo topoisomerase I cleavages in the transcriptionally active tyrosine aminotransferase gene. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1109–1117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura H., Kohchi C., Yamada R., Ikeda T., Koiwai O., Patterson E., Keene J. D., Okada K., Kjeldsen E., Nishikawa K. Molecular cloning of a cDNA of a camptothecin-resistant human DNA topoisomerase I and identification of mutation sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanizawa A., Beitrand R., Kohlhagen G., Tabuchi A., Jenkins J., Pommier Y. Cloning of Chinese hamster DNA topoisomerase I cDNA and identification of a single point mutation responsible for camptothecin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25463–25468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Ohkura H., Adachi Y., Morino K., Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. DNA topoisomerase II is required for condensation and separation of mitotic chromosomes in S. pombe. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):917–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90518-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verschraegen C. F., Levy T., Kudelka A. P., Llerena E., Ende K., Freedman R. S., Edwards C. L., Hord M., Steger M., Kaplan A. L. Phase II study of irinotecan in prior chemotherapy-treated squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix. J Clin Oncol. 1997 Feb;15(2):625–631. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1997.15.2.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1996;65:635–692. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.65.070196.003223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Zee A. G., de Jong S., Keith W. N., Hollema H., Boonstra H., de Vries E. G. Quantitative and qualitative aspects of topoisomerase I and II alpha and beta in untreated and platinum/cyclophosphamide treated malignant ovarian tumors. Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 1;54(3):749–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]