Abstract
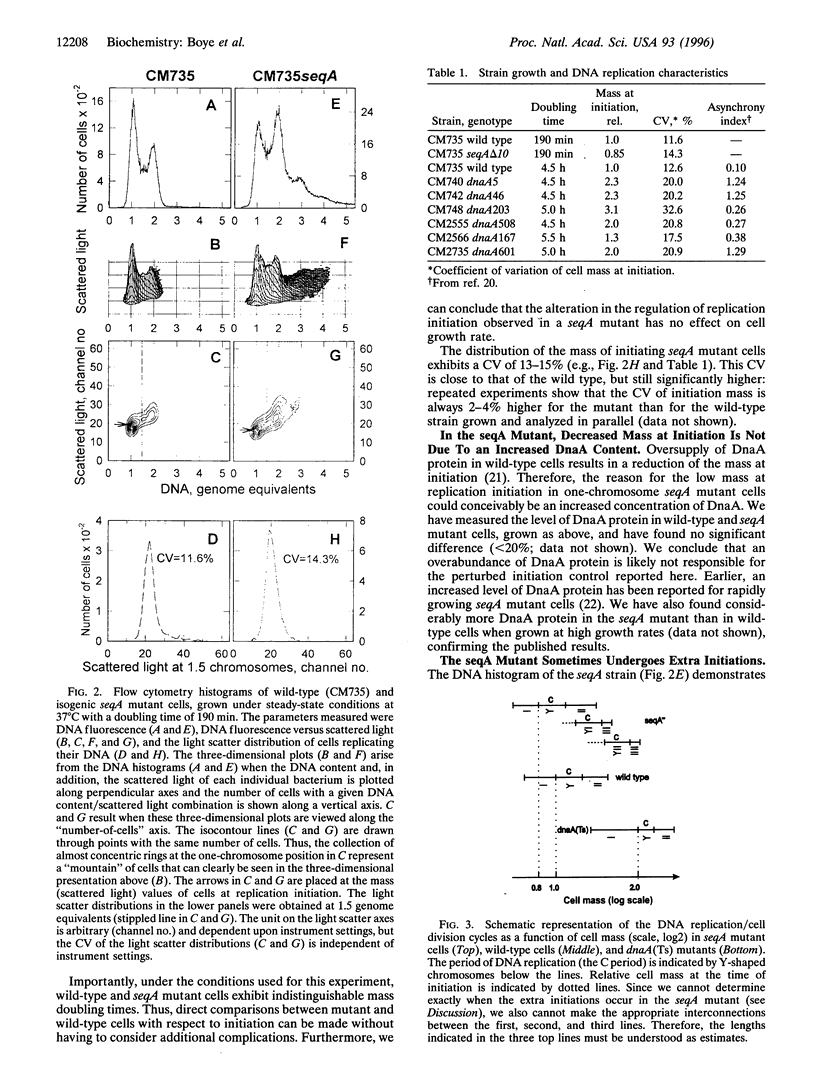
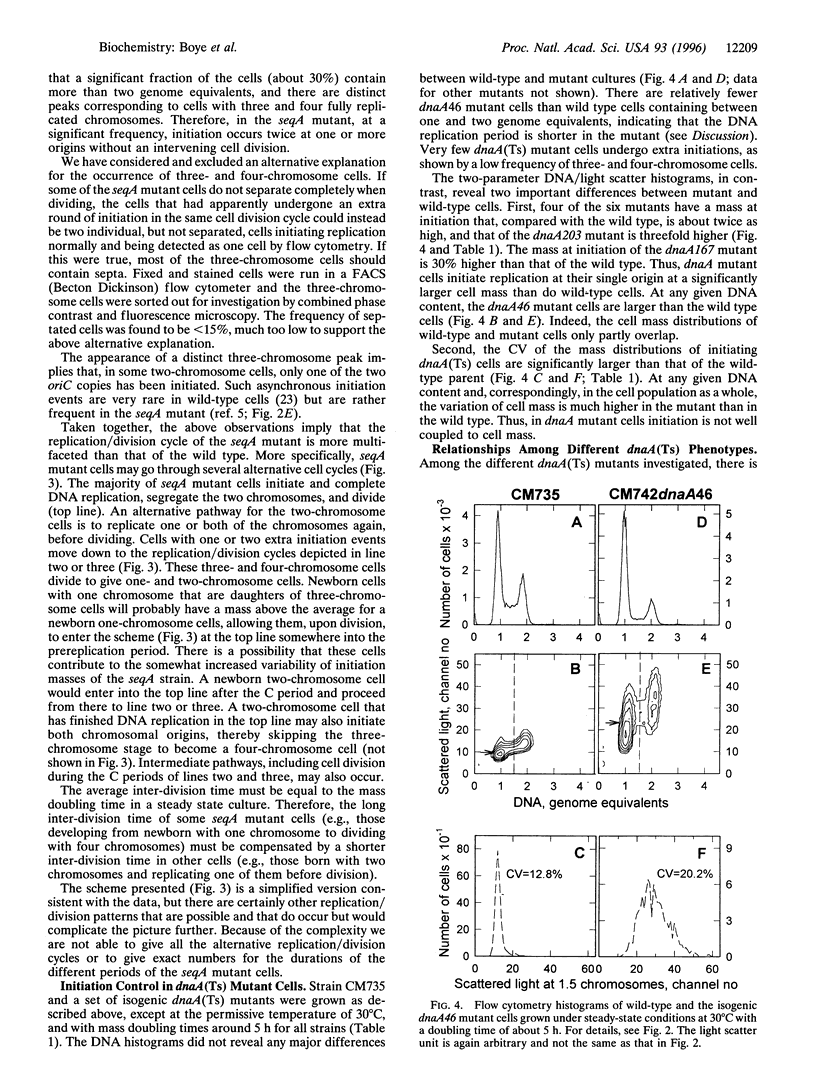
We describe here the development of a new approach to the analysis of Escherichia coli replication control. Cells were grown at low growth rates, in which case the bacterial cell cycle approximates that of eukaryotic cells with G1, S, and G2 phases: cell division is followed sequentially by a gap period without DNA replication, replication of the single chromosome, another gap period, and finally the next cell division. Flow cytometry of such slowly growing cells reveals the timing of replication initiation as a function of cell mass. The data show that initiation is normally coupled to cell physiology extremely tightly: the distribution of individual cell masses at the time of initiation in wild-type cells is very narrow, with a coefficient of variation of less than 9%. Furthermore, a comparison between wild-type and seqA mutant cells shows that initiation occurs at a 10-20% lower mass in the seqA mutant, providing direct evidence that SeqA is a bona fide negative regulator of replication initiation. In dnaA (Ts) mutants the opposite is found: the mass at initiation is dramatically increased and the variability in cell mass at initiation is much higher than that for wild-type cells. In contrast to wild-type and dnaA(Ts) cells, seqA mutant cells frequently go through two initiation events per cell division cycle, and all the origins present in each cell are not initiated in synchrony. The implications for the complex interplay amongst growth, cell division, and DNA replication are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atlung T., Løbner-Olesen A., Hansen F. G. Overproduction of DnaA protein stimulates initiation of chromosome and minichromosome replication in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jan;206(1):51–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00326535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernander R., Akerlund T., Nordström K. Inhibition and restart of initiation of chromosome replication: effects on exponentially growing Escherichia coli cells. J Bacteriol. 1995 Apr;177(7):1670–1682. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.7.1670-1682.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernander R., Dasgupta S., Nordström K. The E. coli cell cycle and the plasmid R1 replication cycle in the absence of the DnaA protein. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1145–1153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90269-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boye E., Løbner-Olesen A. Bacterial growth control studied by flow cytometry. Res Microbiol. 1991 Feb-Apr;142(2-3):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90020-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. L., Kleckner N. E. coli oriC and the dnaA gene promoter are sequestered from dam methyltransferase following the passage of the chromosomal replication fork. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):967–979. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90271-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casaregola S., D'Ari R., Huisman O. Role of DNA replication in the induction and turn-off of the SOS response in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):440–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00334136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchward G., Estiva E., Bremer H. Growth rate-dependent control of chromosome replication initiation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1232–1238. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1232-1238.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donachie W. D. Relationship between cell size and time of initiation of DNA replication. Nature. 1968 Sep 7;219(5158):1077–1079. doi: 10.1038/2191077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. B., Atlung T., Hansen F. G., Skovgaard O., von Meyenburg K. Fine structure genetic map and complementation analysis of mutations in the dnaA gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):387–396. doi: 10.1007/BF00436184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen F. G., Christensen B. B., Atlung T. The initiator titration model: computer simulation of chromosome and minichromosome control. Res Microbiol. 1991 Feb-Apr;142(2-3):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen F. G., von Meyenburg K. Characterization of the dnaA, gyrB and other genes in the dnaA region of the Escherichia coli chromosome on specialized transducing phages lambda tna. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Sep;175(2):135–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00425529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrick J., Bensimon D. Gene regulation under growth conditions. A model for the regulation of initiation of replication in Escherichia coli. J Theor Biol. 1991 Aug 7;151(3):359–366. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(05)80385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffé A., D'Ari R., Norris V. SOS-independent coupling between DNA replication and cell division in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):66–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.66-71.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Donachie W. D. Chromosome replication, transcription and control of cell division in Escherichia coli. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 23;243(125):100–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. Does the initiation of chromosome replication regulate cell division? Adv Microb Physiol. 1977;16:49–98. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppes L. H., Woldringh C. L., Nanninga N. Size variations and correlation of different cell cycle events in slow-growing Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):423–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.423-433.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu M., Campbell J. L., Boye E., Kleckner N. SeqA: a negative modulator of replication initiation in E. coli. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):413–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Løbner-Olesen A., Skarstad K., Hansen F. G., von Meyenburg K., Boye E. The DnaA protein determines the initiation mass of Escherichia coli K-12. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):881–889. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90802-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaffy J. M., Zyskind J. W. A model for the initiation of replication in Escherichia coli. J Theor Biol. 1989 Oct 23;140(4):453–477. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(89)80109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M., Gross J. Induction of prophage lambda in a mutant of E. coli K12 defective in initiation of DNA replication at high temperature. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;110(4):299–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00438272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata T., Meselson M. Periodic replication of DNA in steadily growing Escherichia coli: the localized origin of replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:553–557. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman C. N., Kubitschek H. E. Variation in periodic replication of the chromosome in Escherichia coli B/rTT. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jun 5;121(4):461–471. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90394-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström K., Bernander R., Dasgupta S. The Escherichia coli cell cycle: one cycle or multiple independent processes that are co-ordinated? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Apr;5(4):769–774. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden G. B., Pratt M. J., Schaechter M. The replicative origin of the E. coli chromosome binds to cell membranes only when hemimethylated. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90186-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Zinder N. D. Hemimethylation prevents DNA replication in E. coli. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1071–1079. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90173-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarstad K., Boye E., Steen H. B. Timing of initiation of chromosome replication in individual Escherichia coli cells. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1711–1717. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04415.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarstad K., Løbner-Olesen A., Atlung T., von Meyenburg K., Boye E. Initiation of DNA replication in Escherichia coli after overproduction of the DnaA protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jul;218(1):50–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00330564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarstad K., Steen H. B., Boye E. Cell cycle parameters of slowly growing Escherichia coli B/r studied by flow cytometry. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):656–662. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.656-662.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarstad K., Steen H. B., Boye E. Escherichia coli DNA distributions measured by flow cytometry and compared with theoretical computer simulations. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):661–668. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.661-668.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarstad K., von Meyenburg K., Hansen F. G., Boye E. Coordination of chromosome replication initiation in Escherichia coli: effects of different dnaA alleles. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):852–858. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.852-858.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater S., Wold S., Lu M., Boye E., Skarstad K., Kleckner N. E. coli SeqA protein binds oriC in two different methyl-modulated reactions appropriate to its roles in DNA replication initiation and origin sequestration. Cell. 1995 Sep 22;82(6):927–936. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90272-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold S., Skarstad K., Steen H. B., Stokke T., Boye E. The initiation mass for DNA replication in Escherichia coli K-12 is dependent on growth rate. EMBO J. 1994 May 1;13(9):2097–2102. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Freiesleben U., Rasmussen K. V., Schaechter M. SeqA limits DnaA activity in replication from oriC in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Nov;14(4):763–772. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


