Abstract
Purpose.
We applied a recently reported next-generation sequencing (NGS) strategy for screening the ABCA4 gene in a British cohort with ABCA4-associated disease and report novel mutations.
Methods.
We identified 79 patients with a clinical diagnosis of ABCA4-associated disease who had a single variant identified by the ABCA4 microarray. Comprehensive phenotypic data were obtained, and the NGS strategy was applied to identify the second allele by means of sequencing the entire coding region and adjacent intronic sequences of the ABCA4 gene. Identified variants were confirmed by Sanger sequencing and assessed for pathogenicity by in silico analysis.
Results.
Of the 42 variants detected by prescreening with the microarray, in silico analysis suggested that 34, found in 66 subjects, were disease-causing and 8, found in 13 subjects, were benign variants. We detected 42 variants by NGS, of which 39 were classified as disease-causing. Of these 39 variants, 31 were novel, including 16 missense, 7 splice-site–altering, 4 nonsense, 1 in-frame deletion, and 3 frameshift variants. Two or more disease-causing variants were confirmed in 37 (47%) of 79 patients, one disease-causing variant in 36 (46%) subjects, and no disease-causing variant in 6 (7%) individuals.
Conclusions.
Application of the NGS platform for ABCA4 screening enabled detection of the second disease-associated allele in approximately half of the patients in a British cohort where one mutation had been detected with the arrayed primer extension (APEX) array. The time- and cost-efficient NGS strategy is useful in screening large cohorts, which will be increasingly valuable with the advent of ABCA4-directed therapies.
Keywords: ABCA4, next generation sequencing, Stargardt disease
PCR-enrichment–based next-generation sequencing with an amplicon tagging protocol revealed two or more disease-causing variants in 37 of 79 patients with ABCA4-associated retinal disease, who had only one variant detected in prescreening with arrayed primer extension technology.
Introduction
Stargardt disease is the most common form of inherited macular dystrophy and is caused by recessive mutations in the ABCA4 gene.1,2 Stargardt disease typically presents with central macular atrophy and yellow-white flecks at the posterior pole, primarily at the level of the RPE.2,3 A highly variable phenotype and progression of Stargardt disease have been documented, and mutations in ABCA4 also have been implicated in cone dystrophy, cone-rod dystrophy, and “retinitis pigmentosa.”4–12 In this report, we will use the term “ABCA4-associated retinal disease” to refer to the broad range and variability of clinical manifestations of retinopathy due to ABCA4 variants.
The carrier frequency of likely pathogenic ABCA4 alleles has been reported to be as high as 1:2013,14 and more than 700 ABCA4 variants have been identified so far.1,2,5–29 The high allelic heterogeneity makes molecular genetic analyses of ABCA4-associated retinal disease very challenging. It has been reported that direct Sanger sequencing of the entire ABCA4 coding region (50 exons) detects between 66% and 80% of disease-causing alleles13,21; however, this approach has significant limitations in large patient cohorts due to the prohibitive time and cost implications.3,5
Since the development of the ABCA4 genotyping microarray, using arrayed primer extension (APEX) technology,14 systematic screening of all known previously reported ABCA4 variants has been available26,30; APEX detects approximately 65% to 75% of all disease-associated alleles. However, by definition, novel variants are not detected by APEX technology, necessitating the use of other methodologies for high-throughput systematic screening of the entire coding region, especially in cases where one or both disease-causing alleles have failed to be identified by the array.
Zernant et al. recently reported the capability of a next-generation sequencing (NGS) strategy to detect new ABCA4 variants that were not included on the APEX array; all 50 ABCA4 exons of 168 patients were amplified in parallel using an amplicon tagging PCR protocol and NGS was applied to the resulting amplicons.5 The purpose of this study was to apply this novel NGS strategy for ABCA4 screening in a large, well-characterized British cohort of patients with likely ABCA4-associated phenotypes and report novel disease-causing variants.
Materials and Methods
Patients
Prescreening with APEX technology was performed in a cohort of 232 patients seen at Moorfields Eye Hospital with a clinical diagnosis of retinopathy compatible with ABCA4-associated retinal disease. Two or more variants were identified in 103 patients, one variant in 79 subjects, and no variants in 50 individuals. The 79 patients with only one ABCA4 allele were recruited for this study. After informed consent was obtained, blood samples were taken from all individuals for NGS of ABCA4. The protocol of the study adhered to the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Moorfields Eye Hospital. The age at onset was defined as the age at which visual loss was first noted by the patient. The duration of disease was calculated as the difference between age at onset and age at the latest examination.
Clinical Assessment
A full medical history was obtained and a comprehensive ophthalmologic examination was performed for all patients. Clinical assessment included best-corrected Snellen visual acuity (converted to equivalent logMAR visual acuity), fundus photography, autofluorescence (AF) imaging, spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT), and electrophysiologic assessment.
Color fundus photography was performed with the TRC-50IA Retinal Fundus Camera (Topcon, Tokyo, Japan) and AF images were obtained using either an HRA 2 (excitation wavelength, 488 nm; barrier filter, 500 nm; field of view, 30 × 30°; Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany)31 or Spectralis with viewing module version 5.1.2.0 (excitation wavelength, 488 nm; barrier filter, 500 nm; fields of view, 30 × 30° and 55 × 55°; Heidelberg Engineering) after pupillary dilation.32 Patients were classified into one of three AF subtypes based on a recent report in ABCA4-associated retinal disease31: type 1—localized low AF signal at the fovea surrounded by a homogeneous background, type 2—localized low AF signal at the macula surrounded by a heterogeneous background, and type 3—multiple areas of low AF signal at the posterior pole with a heterogeneous background. SD-OCT imaging was obtained with the Spectralis with viewing module version 5.1.2.0.32
Electrophysiologic assessment included full-field electroretinography (ffERG) and pattern electroretinography (PERG) incorporating the standards of the International Society for Clinical Electrophysiology of Vision (ISCEV).33,34 All components of the ffERG and PERG were taken into account when classifying patients into one of the three electrophysiologic groups:4,35 group 1—patients with PERG P50 abnormality with normal ERGs, group 2—subjects with PERG P50 abnormality and additional generalized cone ERG abnormality (assessed with light adapted 30 Hz ERG and light adapted 3.0 ERG), and group 3—individuals with PERG P50 abnormality, and additional generalized cone and rod ERG abnormality (assessed using dark adapted 0.01 dim flash ERG and dark adapted 11.0 bright flash ERG).
Genetic Screening
Blood samples were collected in EDTA tubes and DNA was extracted with a Nucleon Genomic DNA extraction kit (BACC2; Tepnel Life Sciences, Manchester, UK). Mutation prescreening of ABCA4 was performed with the APEX microarray (ABCR400 chip or ABCR600 chip; Asper Ophthalmics, Tartu, Estonia; available in the public domain at http://www.asperbio.com/genetic-tests/panel-of-genetic-tests/stargardt-disease-cone-rod-dystrophy-abca4) in all probands.14 We screened 17 patients with ABCR400 (432 mutations on the chip) in 2005, 32 with updated ABCR400 (456 mutations) in 2006, 3 with further updated ABCR400 (480 mutations) in 2007, and 27 with ABCR500 (552 mutations) in 2011.
All 50 ABCA4 exons and exon-intron boundaries were amplified with tagged PCR primers using an amplicon tagging protocol (Access Array; Fluidigm, South San Francisco, CA; available in the public domain at http://www.fluidigm.com/products/access-array.html) and NGS on the Roche 454 platform (Roche Applied Science, Penzberg, Upper Bavaria, Germany) was performed as reported previously.5 Sequences of the barcoded samples were analyzed with the NextGENE software for next generation sequence analysis (SoftGenetics, State College, PA), which mapped reads to the reference genome (HG19) and identified all the differences compared to the reference sequence. All the identified variants were confirmed by Sanger sequencing. Segregation analysis was not performed in this study.
In Silico Molecular Genetic Analysis
All the missense variants identified were analyzed using two software prediction programs: Sorting Intolerant From Tolerant (SIFT; available in the public domain at http://sift.jcvi.org),36 and PolyPhen2 (available in the public domain at http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph/index.html).37 Predicted effects on splicing of all the missense and intronic variants were assessed with the Human Splicing Finder (HSF) program version 2.4.1 (available in the public domain at http://www.umd.be/HSF). The allele frequency of all the variants was estimated by reference to the Exome Variant Server (EVS; NHLBI Exome Sequencing Project, Seattle, WA; available in the public domain at http://snp.gs.washington.edu/EVS).
All the variants identified were classified into one of three categories based on the bioinformatics prediction protocol described in a previous report,5 namely disease-causing, possibly disease-causing, and benign. For the purpose of analysis in this study, variants predicted to be possibly disease-causing were included in the total number of variants described as disease-causing variants. The nomenclature of the variants was in the main in keeping with the internationally established guidelines (available in the public domain at http://www.hgvs.org/mutnomen).38
Results
Clinical Findings
The clinical findings of the cohort are summarized in Table 1. The study included 40 male (51%) and 39 female (49%) unrelated probands. The median age at onset was 22.0 years, with a median duration of disease of 10.0 years. The median age at the latest examination was 40.0 years, with the median logMAR visual acuities being 1.00. Color fundus photographs were obtained in 75 patients and AF imaging was undertaken in 71 subjects. There were 21 patients (30%) with a type 1 AF pattern, 34 (48%) with type 2, and 16 (22%) with type 3. Of the 70 patients with available electrophysiologic data, 34 subjects (49%) were in ERG group 1 (isolated macular dysfunction), 7 (10%) in ERG group 2 (macular and generalized cone dysfunction), and 29 (41%) in ERG group 3 (macular and generalized cone and rod dysfunction).
Table 1.
Summary of Clinical Features of 79 Patients With ABCA4-Related Retinal Disease
| Median age of onset, y (range) | 22.0 (5–71) | |
| Median age at examination, y (range) | 40.0 (15–79) | |
| Median duration of disease, y (range) | 10.0 (0–54) | |
| LogMAR visual acuity (range) | R | 1.00 (−0.08–1.78) |
| L | 1.00 (−0.08–4.00) | |
| AF subtype, n = 71 | 1 | n = 21 |
| 2 | n = 34 | |
| 3 | n = 16 | |
| ERG group, n = 70 | 1 | n = 34 |
| 2 | n = 7 | |
| 3 | n = 29 | |
AF, autofluorescence; ERG, electroretinography; R, right eye; L, left eye.
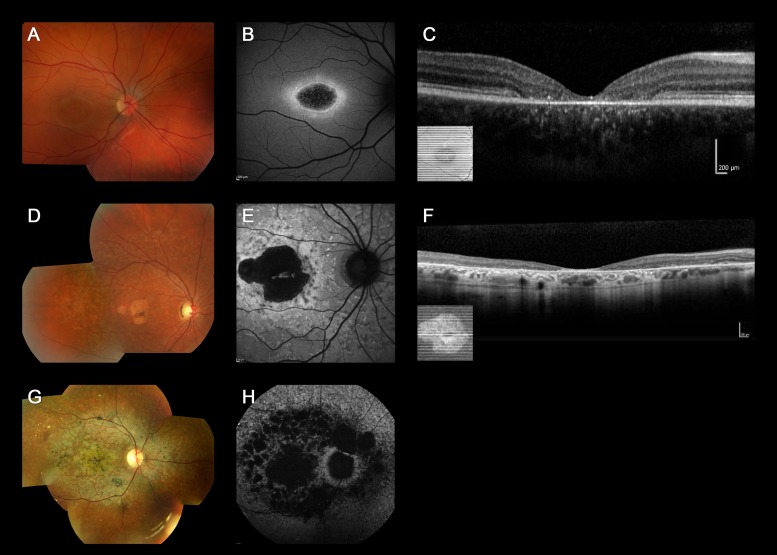
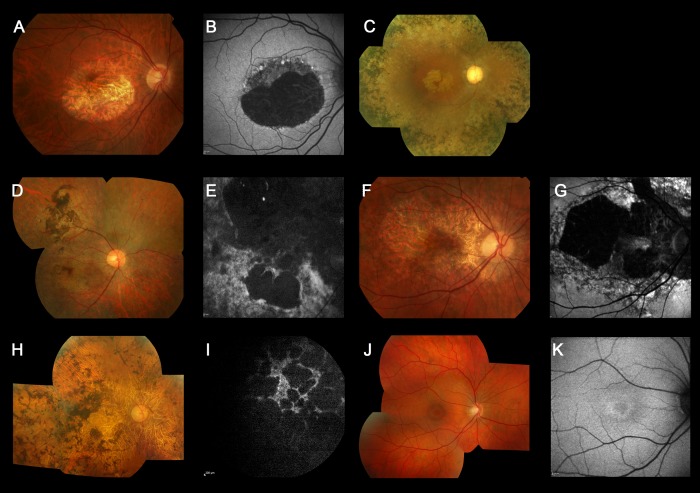
Color fundus photographs, AF images, and SD-OCT of three representative cases of “typical” ABCA4-associated retinal disease are shown in Figure 1 (patients 19, 36, and 17), all harboring two disease-causing variants. Six cases with an “atypical” phenotype for ABCA4-associated retinal disease are shown in Figure 2 (patients 74–79), all of them carried only one, likely benign, ABCA4 variant (Table 2).
Figure 1.
Color fundus photographs, autofluorescence images, and optical coherence tomography of three representative cases harboring two or more ABCA4 variants with “typical” ABCA4-associated retinal disease (patients 19, 36, and 17). Color fundus photograph of patient 19 shows macular atrophy (A) and AF imaging demonstrates a localized low AF signal at the fovea, with a high signal edge surrounded by a homogeneous background (B). SD-OCT demonstrates marked outer retinal loss at the central macula (C). Patient 36 has macular atrophy surrounded by numerous yellow-white flecks (D) and a localized low AF signal at the macula surrounded by a heterogeneous background, with peripapillary sparing (E). Generalized loss of outer retinal architecture is seen on SD-OCT. Patient 17 has widespread multiple areas of atrophy with patchy pigmentation (G) and multiple areas of low AF signal at the posterior pole with a heterogeneous background (H).
Figure 2.
Color fundus photographs and autofluorescence images of six cases harboring a single, likely benign, missense variant with “atypical” clinical features for ABCA4-associated retinal disease (patients 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, and 79). Color photograph of patient 74 shows a geographic atrophy-like appearance (A), which on AF imaging is surrounded by foci of high and low AF signal (B). Patient 75 has evidence of generalized retinal atrophy in addition to marked macular atrophy, with dense pigmentation at the level of the RPE, and bone spicule formation, marked vessel attenuation, and optic disc pallor (C). Patient 76 has extensive macular atrophy extending beyond the arcades, with dense pigmentation at the level of the RPE and slight bone spicule pigmentation in the periphery (D). AF imaging demonstrates a heterogeneous background, but no peripapillary sparing (E). Patient 77 has a large area of macular atrophy extending to the optic disc (F), which on AF imaging is surrounded by an irregular low AF signal with foci of high and low signal, with no peripapillary sparing (G). Patient 78 has multiple widespread areas of atrophy with dense pigmentation at the level of RPE and bone spicule pigmentation in the periphery (H). AF imaging identifies multiple low signal areas with a heterogeneous background and no peripapillary sparing (I). Patient 79 has subtle atrophy confined to the fovea (J). AF imaging demonstrates a localized low AF signal at the fovea surrounded by a homogeneous background (K).
Table 2.
Molecular Genetic Status Identified by NGS in 79 Patients With ABCA4-Related Retinal Disease
|
Pt |
Allele 1 Detected by APEX |
Allele 2 Detected by NGS |
Allele 3 Detected by NGS |
Total
N
of DC Variants |
Comments |
||||||
|
DNA Change |
Protein Change/ Effect |
Pred. Patho. |
DNA Change |
Protein Change/ Effect |
Pred. Patho. |
DNA Change |
Protein Change/ Effect |
Pred. Patho. |
|||
| 1 | c.161G>A | p.C54Y | DC | c.2297G>T | p.G766V | DC | 2 | ||||
| 2 | c.223T>G | p.C75G | DC | c.5088C>G | p.S1696R | DC | 2 | ||||
| 3 | c.740A>C | p.N247T | DC | c.1433T>C | p.I478T | B | c.2345G>A | p.W782* | DC | 2 | |
| 4 | c.768G>T | Splice site | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 5 | c.1222C>T | p.R408* | DC | c.2568C>A | p.Y856* | DC | 2 | ||||
| 6 | c.1804C>T | p.R602W | DC | c.859-9T>C | Splice site | PDC | 2 | ||||
| 7 | c.1805G>A | p.R602Q | DC | c.5113C>T | p.R1705W | DC | 2 | ||||
| 8 | c.1922G>C | p.C641S | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 9 | c.1957C>T | p.R653C | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 10 | c.1957C>T | p.R653C | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 11 | c.2588G>C | p.G863A | DC | c.655A>T | p.R219* | DC | 2 | Allele 2 (p.R219*) was APEX-false-negative | |||
| 12 | c.2588G>C | p.G863A | DC | c.1906C>T | p.Q636* | DC | 2 | ||||
| 13 | c.2588G>C | p.G863A | DC | c.1906C>T | p.Q636* | DC | 2 | ||||
| 14 | c.2588G>C | p.G863A | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 15 | c.2588G>C | p.G863A | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 16 | c.2894A>G | p.N965S | DC | c.3322C>T | p.R1108C | DC | 2 | Allele 2 (p.R1108C) was APEX-false-negative | |||
| 17 | c.3064G>A | p.E1022K | DC | c.6729+4_+18delAGTTGGCCCTGGGGC | Splice site | DC | 2 | ||||
| 18 | c.3064G>A | p.E1022K | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 19 | c.3208_3209insGT | p.S1071fs | DC | c.2942C>T | p.P981L | DC | c.6529G>A | p.D2177N | B | 2 | |
| 20 | c.3208_3209insGT | p.S1071fs | DC | c.1519G>T | p.D507Y | DC | 2 | ||||
| 21 | c.3208_3209insGT | p.S1071fs | DC | c.4634G>A | p.S1545N | DC | 2 | ||||
| 22 | c.3208_3209insGT | p.S1071fs | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 23 | c.3292C>T | p.R1098C | DC | c.3299T>A | p.I1100N | DC | 2 | ||||
| 24 | c.3322C>T | p.R1108C | DC | c.4978delC | p.L1661* | DC | 2 | ||||
| 25 | c.3386G>A | p.R1129H | DC | c.3208_3209insGT | p.S1071fs | DC | c.4634G>A | p.S1545N | DC | 3 | Allele 2 (p.S1071fs) was APEX false-negative and allele 1 (p.R1129H) was NGS false-negative |
| 26 | c.4139C>T | p.P1380L | DC | c.3191-1G>T | Splice site | DC | 2 | ||||
| 27 | c.4139C>T | p.P1380L | DC | c.3398T>C | p.I1133T | PDC | 2 | ||||
| 28 | c.4139C>T | p.P1380L | DC | c.4070C>A | p.A1357E | DC | 2 | ||||
| 29 | c.4139C>T | p.P1380L | DC | c.4773G>C | Splice site | DC | 2 | ||||
| 30 | c.4139C>T | p.P1380L | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 31 | c.4139C>T | p.P1380L | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 32 | c.4139C>T | p.P1380L | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 33 | c.4234C>T | p.Q1412* | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 34 | c.4319T>C | p.F1440S | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 35 | c.4328G>A | p.R1443H | DC | c.180delG | p.M61fs | DC | 2 | ||||
| 36 | c.4469G>A | p.C1490Y | DC | c.1726G>C | p.D576H | DC | 2 | ||||
| 37 | c.4469G>A | p.C1490Y | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 38 | c.4537_4538insC | p.Q1513fs | DC | c.5578C>T | p.R1860W | DC | 2 | Allele 1 (p.Q1513fs) was NGS-false-negative | |||
| 39 | c.4577C>T | p.T1526M | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 40 | c.4926C>G | p.S1642R | DC | c.5041_5055del GTGGTTGCCATCTGC | p.V1681_C1685del | DC | 2 | ||||
| 41 | c.4956T>G | p.Y1652* | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 42 | c.5018+2T>C | Splice site | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 43 | c.5461-10T>C | DC | c.6385A>G | p.S2129G | PDC | 2 | |||||
| 44 | c.5461-10T>C | DC | 1 | ||||||||
| 45 | c.5461-10T>C | DC | 1 | ||||||||
| 46 | c.5461-10T>C | DC | 1 | ||||||||
| 47 | c.5461-10T>C | DC | 1 | ||||||||
| 48 | c.5461-10T>C | DC | 1 | ||||||||
| 49 | c.5461-10T>C | DC | 1 | ||||||||
| 50 | c.5461-10T>C | DC | 1 | ||||||||
| 51 | c.5585-1G>A | Splice site | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 52 | c.5714+5G>A | Splice site | DC | c.6209C>G | p.T2070R | DC | 2 | ||||
| 53 | c.5882G>A | p.G1961E | DC | c.2686A>G | p.K896E | B | 1 | ||||
| 54 | c.5882G>A | p.G1961E | DC | c.3050+1G>C | Splice site | DC | 2 | ||||
| 55 | c.5882G>A | p.G1961E | DC | c.3392delC/3393C>G | p.A1131Gfs | DC | 2 | ||||
| 56 | c.5882G>A | p.G1961E | DC | c.4539+2T>G | Splice site | DC | 2 | ||||
| 57 | c.5882G>A | p.G1961E | DC | c.4552A>C | p.S1518R | DC | 2 | ||||
| 58 | c.5882G>A | p.G1961E | DC | c.5899-2delA | Splice site | DC | 2 | ||||
| 59 | c.5882G>A | p.G1961E | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 60 | c.6079C>T | p.L2027F | DC | c.1906C>T | p.Q636* | DC | 2 | ||||
| 61 | c.6079C>T | p.L2027F | DC | c.3322C>T | p.R1108C | DC | 2 | Allele 2 (p.R1108C) was APEX-false-negative | |||
| 62 | c.6079C>T | p.L2027F | DC | c.3370G>T | p.D1124Y | DC | 2 | ||||
| 63 | c.6079C>T | p.L2027F | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 64 | c.6089G>A | p.R2030Q | DC | c.4326C>A | p.N1442K | DC | 2 | ||||
| 65 | c.6445C>T | p.R2149* | DC | 1 | |||||||
| 66 | c.6709A>C | p.T2237P | DC | c.5899-3_5899-2delTA | Splice site | DC | 2 | ||||
| 67 | c.2971G>C | p.G991R | B | c.4538A>G | p.Q1513R | DC | 1 | ||||
| 68 | c.3602T>G | p.L1201R | B | c.1749G>C | p.K583N | DC | 1 | ||||
| 69 | c.3602T>G | p.L1201R | B | c.1982_1983insG | p.A662fs | DC | 1 | ||||
| 70 | c.3602T>G | p.L1201R | B | c.2972G>T | p.G991V | DC | 1 | ||||
| 71 | c.4685T>C | p.I1562T | B | c.3289A>T | p.R1097* | DC | 1 | ||||
| 72 | c.6320G>A | p.R2107H | B | c.2510T>C | p.L837P | DC | 1 | ||||
| 73 | c.6320G>A | p.R2107H | B | c.4352+1G>A | Splice site | DC | 1 | ||||
| 74 | c.2701A>G | p.T901A | B | 0 | |||||||
| 75 | c.3602T>G | p.L1201R | B | 0 | |||||||
| 76 | c.4283C>T | p.T1428M | B | 0 | |||||||
| 77 | c.466A>G | p.I156V | B | 0 | |||||||
| 78 | c.466A>G | p.I156V | B | 0 | |||||||
| 79 | c.4715C>T | p.T1572M | B | 0 | |||||||
Putative novel variants are shown in italics. Splice-site alteration (described as splice site) includes the change expected to affect splicing, for example, when the splice donor or splice acceptor site is changed, and the change that might affect splicing, for example, changes close to the splice donor or splice acceptor site, or in the first or last nucleotide of an exon. Two variants result in nucleotide substitution at the end of an exon and cause splice-site alteration (c.768G>T and c.4773G>C). B, benign; DC, disease-causing; PDC, possibly disease-causing; Pred. Patho, predicted pathogenicity; Pt, patient number.
Prescreening With APEX Technology
The results of prescreening of ABCA4 in our cohort of 79 patients are summarized in Table 2. We detected 42 variants at the APEX prescreening stage. In silico analysis of these 42 variants suggested that 34 were disease-causing and 8 were considered benign. Therefore, these analyses confirmed at least one disease-causing variant in 66/79 patients, while 13/79 subjects had no disease-causing variants (Tables 2, 3).
Table 3.
In Silico Analysis for Previously Reported Variants Identified in 79 Patients With ABCA4-Related Retinal Disease
|
Exon/ IVS |
Nucleotide Substitution |
Protein Change/ Effect |
N
of Alleles Identified |
Pt |
Method |
Previous Report |
SIFT |
Polyphen 2 |
HSF Matrix |
Allele Freq. by EVS |
Reference |
Comment |
||||||
|
APEX |
NGS |
Pred. |
Tol. Index (0–1) |
Pred. |
Hum Var Score (0–1) |
Site |
Wt CV |
Mt CV |
CV % Variation |
|||||||||
| 3 | c.161G>A | p.C54Y | 1 | 1 | ✓ | ✓ | Lewis RA, et al.11 | Tol. | 0.11 | PRD | 0.994 | No change | 1/13006 | db SNP (rs150774447) | ||||
| 3 | c.223T>G | p.C75G | 1 | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | Lewis RA, et al.11 | Del. | NA | POD | 0.603 | No change | ND | |||||
| 5 | c.466A>G | p.I156V | 2 | 77, 78 | ✓ | ✓ | Papaioannou M, et al.16 | Tol. | 0.46 | B | 0.003 | No change | 16/13006 | db SNP (rs112467008) | Benign | |||
| 6 | c.655A>T | p.R219* | 1 | 11 | ✓ | Xi Q, et al.27 | ND | |||||||||||
| 6 | c.740A>C | p.N247T | 1 | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | APEX | Del. | NA | B | 0.135 | No change | ND | |||||
| 6 | c.768G>T | Splice site | 1 | 4 | ✓ | ✓ | Klevering BJ, et al.22 | Tol. | 0.56 | NA | Don. | 70.4 | 58 | Site broken (−17.51) | ND | |||
| 9 | c.1222C>T | p.R408* | 1 | 5 | ✓ | ✓ | Webster AR, et al.7 | ND | ||||||||||
| 12 | c.1726G>C | p.D576H | 1 | 36 | ✓ | Downs K, et al.25 | POD | 0.688 | Acc. | 68.1 | 39.1 | Site broken (−42.54) | 1/13006 | |||||
| 13 | c.1804C>T | p.R602W | 1 | 6 | ✓ | ✓ | Lewis RA, et al.11 | Del. | 0.00 | B | 0.129 | No change | ND | db SNP (rs 6179409) | ||||
| 13 | c.1805G>A | p.R602Q | 1 | 7 | ✓ | ✓ | Webster AR, et al.7 | Del. | 0.04 | PRD | 0.513 | Acc. | 48.9 | 77.9 | New site (+59.14) | 2/13006 | db SNP (rs61749410) | |
| 13 | c.1906C>T | p.Q636* | 3 | 12, 13, 60 | ✓ | Zernant J, et al.5 | No change | 1/13006 | db SNP (rs145961131) | |||||||||
| 13 | c.1922G>C | p.C641S | 1 | 8 | ✓ | ✓ | Stenirri S, et al.24 | Del. | 0.00 | No change | ND | db SNP (rs61749416) | ||||||
| 14 | c.1957C>T | p.R653C | 2 | 9, 10 | ✓ | ✓ | Rivera A, et al.17 | Del. | 0.00 | PRD | 0.999 | No change | ND | db SNP (rs61749420) | ||||
| 17 | c.2588G>C | p.G863A/ p.DelG863 | 5 | 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 | ✓ | ✓ | Lewis RA, et al.11/ Maugeri A, et al.29 | Del. | 0.00 | PRD | 0.996 | No change | 68/13006 | db SNP (rs76157638) | ||||
| 18 | c.2701A>G | p.T901A | 1 | 74 | ✓ | ✓ | APEX | Tol. | 0.82 | B | 0.008 | 23/13006 | db SNP (rs139655975) | Benign | ||||
| 19 | c.2894A>G | p.N965S | 1 | 16 | ✓ | ✓ | Lewis RA, et al.11 | Del. | 0.03 | PRD | 0.981 | Acc. | 53.4 | 82.3 | New site (+54.26) | ND | db SNP (rs201471607) | |
| 20 | c.2971G>C | p.G991R | 1 | 67 | ✓ | ✓ | Yatsenko AN, et al.13 | Del. | 0.02 | PRD | 0.999 | No change | 28/13006 | db SNP (rs147484266) | Benign | |||
| 22 | c.3064G>A | p.E1022K | 2 | 17, 18 | ✓ | ✓ | Webster AR, et al.7 | Del. | 0.00 | PRD | 1.000 | No change | ND | db SNP (rs61749459) | ||||
| 22 | c.3208_3209insGT | p.S1071fs | 5 | 19, 20, 21, 22, 25 | ✓ | ✓ | APEX | ND | False-negative in APEX in patient 25 | |||||||||
| 22 | c.3292C>T | p.R1098C | 1 | 23 | ✓ | ✓ | Rivera A, et al.17 | Del. | NA | PRD | 0.999 | No change | ND | |||||
| 22 | c.3322C>T | p.R1108C | 3 | 16, 24, 61 | ✓ | ✓ | Rozet JM, et al.10 | Del. | 0.00 | PRD | 0.986 | No change | 1/13006 | db SNP (rs61750120) | False-negative in APEX in patients 16 and 61 | |||
| 23 | c.3386G>A | p.R1129H | 1 | 25 | ✓ | Zernant J, et al.5 | PRD | 0.989 | No change | ND | False-negative in NGS in patient 25 | |||||||
| 24 | c.3602T>G | p.L1201R | 4 | 72, 73, 74, 79 | ✓ | ✓ | Lewis RA, et al.11 | Tol. | 0.37 | B | 0.052 | Don. | 61.3 | 73.7 | New site (20.08) | 416/13006 | db SNP (rs61750126) | Benign |
| 28 | c.4139C>T | p.P1380L | 7 | 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36 | ✓ | ✓ | Lewis RA, et al.11 | Del. | 0.01 | B | 0.377 | No change | 2/13006 | db SNP (rs61750130) | ||||
| 28 | c.4234C>T | p.Q1412* | 1 | 33 | ✓ | ✓ | Rivera A, et al.17 | ND | db SNP (rs61750137) | |||||||||
| 29 | c.4283C>T | p.T1428M | 1 | 76 | ✓ | ✓ | APEX | Tol. | 0.15 | B | 0.010 | No change | 2/13006 | db SNP (rs1800549) | Benign | |||
| 29 | c.4319T>C | p.F1440S | 1 | 34 | ✓ | ✓ | Lewis RA, et al.11 | Del. | 0.00 | POD | 0.744 | No change | ND | dbSNP (rs61750141) | ||||
| 29 | c.4326C>A | p.N1442K | 1 | 64 | ✓ | Zernant J, et al.5 | Tol. | NA | POD | 0.374 | No change | ND | ||||||
| 29 | c.4328G>A | p.R1443H | 1 | 35 | ✓ | ✓ | Rivera A, et al.17 | Del. | 0.02 | PRD | 0.999 | No change | 1/13006 | dbSNP (rs61750142) | ||||
| IVS29 | c.4352+1G>A | Splice site | 1 | 73 | ✓ | Zernant J, et al.5 | Don. | 82.3 | 55.4 | WT site broken (−32.62) | ND | |||||||
| 30 | c.4469G>A | p.C1490Y | 2 | 36, 37 | ✓ | ✓ | Lewis RA, et al.11 | Del. | 0.00 | PRD | 0.994 | No change | ND | dbSNP (rs61751402) | ||||
| 30 | c.4538A>G | p.Q1513R | 1 | 67 | ✓ | Webster AR, et al.7 | Tol. | NA | Benign | 0.043 | Acc. | 91.7 | 62.8 | Site broken (−31.55) | ND | |||
| 30 | c.4537_4538insC | p.G1513fs | 1 | 38 | ✓ | Briggs CE, et al.19 | ND | False-negative in NGS in patient 38 | ||||||||||
| 31 | c.4577C>T | p.T1526M | 1 | 39 | ✓ | ✓ | Lewis RA, et al.11 | Del. | 0.00 | PRD | 0.910 | No change | ND | db SNP (rs61750152) | ||||
| 33 | c.4685T>C | p.I1562T | 1 | 71 | ✓ | ✓ | Yatsenko, et al.13 | Tol. | NA | PRD | 0.783 | No change | ND | Benign | ||||
| 33 | c.4715C>T | p.T1572M | 1 | 79 | ✓ | ✓ | Pang CP and Lamm DS23 | Del. | 0.02 | B | 0.326 | No change | ND | db SNP (rs185093512) | Benign | |||
| 35 | c.4926C>G | p.S1642R | 1 | 40 | ✓ | ✓ | Birch DG, et al.22 | Tol. | 0.68 | B | 0.116 | No change | ND | db SNP (rs61753017) | ||||
| 35 | c.4956T>G | p.Y1652* | 1 | 41 | ✓ | ✓ | Fumagalli A, et al.16 | ND | db SNP (rs61750561) | |||||||||
| IVS35 | c.5018+2T>C | Splice site | 1 | 42 | ✓ | ✓ | APEX | Don. | 81.2 | 54.3 | WT site broken (−33.07) | ND | ||||||
| 36 | c.5113C>T | p.R1705W | 1 | 7 | ✓ | Ernest PJ, et al.26 | Del. | NA | PRD | 0.996 | Don. | 46.5 | 73.3 | No change | ND | |||
| IVS38 | c.5461-10T>C | 8 | 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50 | ✓ | ✓ | Briggs CE, et al.19 | No change | 3/13006 | db SNP (rs1800728) | |||||||||
| IVS39 | c.5585-1G>A | Splice site | 1 | 51 | ✓ | ✓ | Shroyer NF, et al.21 | Acc. | 86.3 | 57.4 | WT site broken (−33.53) | ND | ||||||
| IVS40 | c.5714+5G>A | Splice site | 1 | 52 | ✓ | ✓ | Cremers FP, et al.8 | Don. | 85.5 | 73.3 | Wild type site broken (−14.23) | ND | ||||||
| 42 | c.5882G>A | p.G1961E | 7 | 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59 | ✓ | ✓ | Lewis RA, et al.11 | Del. | 0.00 | PRD | 0.998 | No change | 41/13006 | db SNP (rs1800553) | ||||
| 44 | c.6079C>T | p.L2027F | 4 | 60, 61, 62, 63 | ✓ | ✓ | Lewis RA, et al.11 | Del. | 0.00 | PRD | 1.000 | No change | 4/13006 | db SNP (rs61751408) | ||||
| 44 | c.6089G>A | p.R2030Q | 1 | 64 | ✓ | ✓ | Lewis RA, et al.11 | Del. | 0.00 | PRD | 0.995 | No change | 8/13006 | db SNP (rs61750641) | ||||
| 46 | c.6320G>A | p.R2107H | 2 | 72, 73 | ✓ | ✓ | Fishman GA, et al.15 | Del. | 0.04 | PRD | 0.999 | No change | 91/13006 | db SNP (rs62642564) | Benign | |||
| 47 | c.6445C>T | p.R2149* | 1 | 65 | ✓ | ✓ | Lewis RA, et al.14 | 1/13006 | db SNP (rs61750654) | |||||||||
| 48 | c.6529G>A | p.D2177N | 1 | 19 | ✓ | Rivera A, et al.17 | Tol. | 0.41 | B | 0.004 | No change | 116/13006 | db SNP (rs1800555) | Benign | ||||
| 48 | c.6709A>C | p.T2237P | 1 | 66 | ✓ | ✓ | APEX | Del. | NA | POD | 0.719 | No change | ND | |||||
| IVS48 | c.6729+4_ +18del AGTTGGCCCTGGGGC | Splice site | 1 | 17 | ✓ | Littink KW, et al.28 | NA | ND | ||||||||||
Splice-site alteration (described as splice site) includes the change expected to affect splicing, for example, when the splice donor or splice acceptor site is changed, and the change that might affect splicing, for example, changes close to the splice donor or splice acceptor site, or in the first or last nucleotide of an exon. SIFT (version 4.0.4) results are reported to be tolerant if tolerance index is ≥0.05 or deleterious if tolerance index is <0.05. Polyphen-2 (vision 2.1) appraises mutations qualitatively as benign, possibly damaging or probably damaging based on the model's false positive rate. The cDNA is numbered according to Ensemble transcript ID ENST00000370225, in which +1 is the A of the translation start codon. Human splicing finder version 2.4.1 was applied to predict the effect of each variant on splicing. The result from the HSF matrix indicates the values for the wild type (Wt) and mutant sequences. The larger the difference in values between the Wt and the mutant sequences suggests a greater chance that the variant can affect splicing. EVS denotes variants in the Exome Variant Server, NHLBI Exome Sequencing Project, Seattle, WA (accessed 01/04/2013; available in the public domain at http://snp.gs.washington.edu/EVS). Acc., Acceptor; Allele freq., allele frequency; CV, consensus values; Del., deleterious; Don., donor; EVS, exome variant server; HSF, human splicing finder; IVS, intervening sequence; Mt, mutant; NA, not available; ND, not detected; POD, possibly damaging; PRD, probably damaging; Pred., prediction; Tol., tolerant.
Identification of New Variants by NGS
The results of NGS screening in our cohort of 79 patients are summarized in Table 2. We identified 82 variants by NGS in total; 53 missense, 13 splice-site alterations, 10 nonsense, four frameshifts, one in-frame deletion, and one intronic variant of unknown effect (Tables 2, 4). Of a total of 84 different variants identified in this study by APEX and NGS, there were two “NGS false-negative” variants (p.R1129H and p.Q1513fs), which were detected on APEX array, but were not detected by NGS (Table 2, patients 25 and 38).
Table 4.
Numbers and Types of Variants Detected by APEX Technology and NGS
|
Total |
Null |
Non-Null |
Benign Missense |
|||||
|
Splice-Site Altering |
Nonsense |
Frameshift |
Unknown |
In-Frame Deletion |
Disease-Causing Missense |
|||
| Variants detected by prescreening with APEX | 42 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 23 | 8 |
| New variants detected by NGS alone | 42 (33) | 9 (7) | 6 (4) | 3 (3) | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | 20 (16) | 3 (2) |
| Gross total | 84 (33) | 13 (7) | 10 (4) | 5 (3) | 1 (0) | 1 (1) | 43 (16) | 11 (2) |
Numbers in parentheses indicate the numbers of novel variants that have never been reported. Two variants were detected only on APEX array, but not identified by NGS; one frameshift variant (p.Q1513fs) and one disease-causing missense variant (p.R1129H).
A total of 42 additional variants, which were not detected by APEX, were identified in 45 (57%) patients screened by NGS (Tables 2, 4). Three variants (p.R219*, p.R1108C, and p.S1071fs) found by NGS, were not identified by APEX at the prescreening stage despite being represented on the array (“APEX false-negative”; Table 2, patients 11, 16, 25, and 61). Three (3/45) subjects had two new variants and 42 (42/45) individuals had one new variant (Table 2). Of the 42 new variants detected by NGS, there were 23 missense, 9 splice-site alterations, 6 nonsense, 3 frameshifts, and 1 in-frame deletion (Table 4).
Of the 42 new variants identified by NGS, 33 (79%) were novel, including 18 missense, 7 splice-site alterations, 4 nonsense, 3 frameshifts, and 1 in-frame deletion (Tables 2, 4, 5). Seven variants identified only by NGS already were known, but not yet added to the ABCA4 array by the time of the prescreening of those samples.
Table 5.
In Silico Molecular Genetic Analysis for Novel ABCA4 Variants Identified by NGS
|
Exon/ IVS |
DNA Change |
Protein Change/ Effect |
N
of Alleles Identified |
Pt |
SIFT |
Polyphen2 |
HSF Matrix |
Allele Freq. by EVS |
Reference |
Comments |
|||||
|
Pred. |
Tol. Index (0–1) |
Pred. |
Hum Var Score (0–1) |
Site |
Wt CV |
Mt CV |
CV % Variation |
||||||||
| 3 | c.180delG | p.M61fs | 1 | 35 | ND | ||||||||||
| IVS7 | c.859-9T>C | Splice site | 1 | 5 | Acc. | 78.18 | 76.99 | Possibly site broken (−1.52) | ND | Possibly disease-causing | |||||
| 11 | c.1433T>C | p.I478T | 1 | 1 | Tol. | B | 0.007 | No change | ND | Benign | |||||
| 11 | c.1519G>T | p.D507Y | 1 | 20 | Del. | 0.01 | POD | 0.641 | No change | 1/13006 | dbSNP (rs148234178) | ||||
| 12 | c.1749G>C | p.K583N | 1 | 68 | Del. | 0.04 | POD | 0.893 | Acc. | 66.17 | 37.22 | Site broken (−43.75) | 1/13006 | dbSNP (rs145265791) | |
| 14 | c.1982_ 1983insG | p.A662fs | 1 | 69 | ND | ||||||||||
| 15 | c.2297G>T | p.G766V | 1 | 1 | Tol. | NA | POD | 0.557 | Don. | 69.18 | 42.34 | Site broken (−38.79) | ND | ||
| 15 | c.2345G>A | p.W782* | 1 | 3 | ND | ||||||||||
| 16 | c.2510T>C | p.L837P | 1 | 72 | Tol. | NA | POD | 0.905 | No change | ND | |||||
| 16 | c.2568C>A | p.Y856* | 1 | 5 | ND | ||||||||||
| 18 | c.2686A>G | p.K896E | 1 | 53 | Tol. | NA | B | 0.002 | ND | Benign | |||||
| 20 | c.2942C>T | p.P981L | 1 | 19 | Del. | 0.00 | POD | 0.813 | No change | 1/13006 | dbSNP (rs147826775) | ||||
| 20 | c.2972G>T | p.G991V | 1 | 70 | Del. | NA | PRD | 0.998 | Donor | 64.62 | 91.45 | New site (41.53) | ND | ||
| IVS20 | c.3050+1G>C | Splice site | 1 | 54 | Acc. | 86.43 | 57.49 | Site broken (−33.49) | ND | ||||||
| IVS21 | c.3191-1G>T | Splice site | 1 | 26 | Acc. | 94.38 | 65.44 | WT site broken (−30.67) | ND | ||||||
| 22 | c.3289A>T | p.R1097* | 1 | 71 | ND | ||||||||||
| 22 | c.3299T>A | p.I1100N | 1 | 23 | Del. | NA | PRD | 0.986 | No change | ND | |||||
| 23 | c.3370G>T | p.D1124Y | 1 | 62 | Del. | NA | PRD | 0.998 | No change | ND | |||||
| 23 | c.3392delC/ 3393C>G | p.A1131Gfs | 1 | 55 | ND | ||||||||||
| 23 | c.3398T>C | p.I1133T | 1 | 27 | Del. | NA | B | 0.100 | No change | ND | Possibly disease-causing | ||||
| 27 | c.4070C>A | p.A1357E | 1 | 28 | Del. | NA | PRD | 0.94 | Acc. | 40.92 | 69.86 | New site (+70.74) | ND | ||
| IVS30 | c.4539+2T>G | Splice site | 1 | 56 | Don. | 79.18 | 52.35 | WT site broken (−33.89) | ND | ||||||
| 31 | c.4552A>C | p.S1518R | 1 | 57 | Del. | NA | POD | 0.871 | Acc. | 76.3 | 47.36 | Site broken (−37.94) | ND | ||
| 31 | c.4634G>A | p.S1545N | 2 | 21, 25 | Tol. | NA | B | 0.253 | Acc. | 80.04 | 51.1 | Site broken (−36.16) | ND | ||
| 33 | c.4773G>C | Splice site | 1 | 29 | Don. | 84.58 | 73.57 | Site broken (−13.02) | ND | ||||||
| 35 | c.4978delC | p.L1661* | 1 | 24 | ND | ||||||||||
| 36 | c.5041_5055del GTGGTTGCCATCTGC | p.V1681_C1685del | 1 | 40 | NA | ND | db SNP (rs62646872) | ||||||||
| 36 | c.5088C>G | p.S1696R | 1 | 10 | Tol. | NA | PRD | 0.780 | Don. | 59.34 | 86.17 | New site (45.23) | ND | ||
| 39 | c.5578C>T | p.R1860W | 1 | 38 | Del. | 0.02 | B | 0.025 | No change | ND | db SNP (rs200849015) | ||||
| IVS42 | c.5899-3_ 5899-2delTA | Splice site | 1 | 66 | NA | ND | |||||||||
| IVS42 | c.5899-2delA | Splice site | 1 | 58 | Acc. | 82.1 | 28.26 | WT site broken (−65.58) | ND | ||||||
| 45 | c.6209C>G | p.T2070R | 1 | 52 | Tol. | NA | PRD | 0.996 | Acc. | 57.41 | 86.36 | New site (50.42) | ND | ||
| 46 | c.6385A>G | p.S2129G | 1 | 43 | Del. | NA | B | 0.001 | ND | Possibly disease-causing | |||||
Splice-site alteration (described as splice site) includes the change expected to affect splicing, for example, when the splice donor or splice acceptor site is changed, and the change that might affect splicing, for example, changes close to the splice donor or splice acceptor site, or in the first or last nucleotide of an exon. SIFT (version 4.0.4) results are reported to be tolerant if tolerance index is ≥0.05 or deleterious if tolerance index is <0.05. Polyphen-2 (vision 2.1) appraises mutations qualitatively as benign, possibly damaging or probably damaging based on the model's false positive rate. The cDNA is numbered according to Ensemble transcript ID ENST00000370225, in which +1 is the A of the translation start codon. Human splicing finder version 2.4.1 was applied to predict the effect of each variant on splicing. The result from the HSF matrix indicates the values for the Wt and mutant sequences. The larger the difference in values between the Wt and the mutant sequences suggests a greater chance that the variant can affect splicing. EVS denotes variants in the Exome Variant Server, NHLBI Exome Sequencing Project, Seattle, WA (accessed 01/04/2013; available in the public domain at http://snp.gs.washington.edu/EVS).
In Silico Molecular Genetic Analysis for New Variants Identified by NGS
In silico analysis of the 42 variants identified by NGS, including the 9 previously reported variants and the 33 novel variants, are shown in Tables 3 and 5, respectively.
Of the 9 previously reported variants that were detected by NGS, there were 4 null variants (2 nonsense and 2 splice-site alterations); 4 disease-causing missense variants, with deleterious or damaged protein function predicted by SIFT and Polyphen2; and one benign missense variant (p.D2177N, Table 3).
Deleterious or damaged protein function was predicted by SIFT and Polyphen2 in 16 of 18 novel missense variants (Table 5). Two variants (p.I478T and p.K896E) were predicted to be tolerated and benign. The predicted effects on splicing of these 16 missense variants, one variant resulting in a nucleotide substitution at the end of exon 33 (c.4773G>C), and five intronic variants, were assessed using the HSF program. Altered splicing was suggested for 7 of the missense variants, the (c.4773G>C) variant, and all 5 intronic variants (Table 5). The allele frequencies for the 33 novel variants were, at most, 1 in 13006, suggesting that these are all very rare. Overall, 31 of the 33 novel variants were considered disease-causing, except for only the two missense variants, p.I478T and p.K896E (Table 5).
Disease-Causing Variants
A total of 73 (31 novel and 42 previously identified) disease-causing variants was identified in this cohort of 79 patients (Table 4). The distribution of the number of alleles in the cohort is summarized in Table 6. One patient (1%) harbored three disease-causing variants, 36 (46%) had two disease-causing variants, 36 (46%) had one disease-causing variant, and six patients (7%) remained with no disease-causing variant identified (Table 6).
Table 6.
Distribution of 79 Patients With ABCA4-Related Retinal Disease Based on Number of Identified Disease-Causing Variants
|
Comprehensive Screening With APEX and NGS |
|||||
|
No Disease-Causing Variant |
1 Disease-Causing Variant |
2 Disease-Causing Variants |
3 Disease-Causing Variants |
||
| Prescreening with APEX | 1 disease causing-variant, n = 66 | 29 | 36 | 1 | |
| No disease-causing variants, n = 13 | 6 | 7 | |||
| Total, n = 79 | 6 | 36 | 36 | 1 | |
Discussion
Our study reports the molecular genetic findings using a PCR-enrichment–based NGS strategy in a large well-characterized British cohort with a clinical diagnosis of ABCA4-associated retinal disease. The NGS revealed two or more disease-causing variants in 37 (47%) of 79 patients, in whom only one variant was detected in prescreening with APEX array technology.
Of the 66 subjects with one disease-causing allele identified previously by APEX, the second disease-causing allele was identified in 37 individuals (56%). In keeping with our findings, Zernant et al. reported that the same NGS strategy identified the second disease-causing allele in 48% of their cohort who also only had one allele found previously with APEX.5 These findings suggest that many disease-associated mutations in the ABCA4 gene are very rare and yet unknown, supporting the validity of the PCR-enrichment–based NGS method either as the screening method of choice, or as an additional screening method for patients in whom APEX does not reveal two variants. Of note, the NGS method is cost- and time-efficient at this time only for large (at least 96 samples) cohorts.
Of the 13 patients with initially no disease-causing variant found by APEX, one disease-causing ABCA4 allele was identified in seven subjects (54%) by NGS, with six remaining with no likely disease-causing allele (46%). Further screening with NGS, including screening all intronic regions, and upstream and downstream control regions of the ABCA4 gene, as well as other candidate genes, in larger well-characterized cohorts will be needed to identify fully all pathogenic alleles in these patients. It recently has been proposed that intronic and synonymous variants may account for a significant proportion of the remaining disease-causing variants not identified with exomic NGS.5,39
There were two “NGS false negative” variants (p.R1129H and p.Q1513fs) and three “APEX false negative” variants (p.R219*, p.R1108C, and p.S1071fs) in our cohort. The missense variant p.R1129H was not detected by NGS, most likely due to allele-specific amplification. The frameshift variant c.4537_4538insC, p.Q1513fs, is located in a homopolymer of seven C-nucleotides, where an insertion of another C nucleotide presents a challenge to identify by the Roche 454 sequencing platform. The “APEX false negative” variants were caused by technical issues with the specific array, ABCR400 (432 mutations on the chip) in 2005. Two of those variants, p.R1108C, and p.S1071fs, were detected by APEX in other patients (Table 2). Nevertheless, these findings suggest that combined APEX/NGS analysis may be worthy of consideration for comprehensive mutation detection.
In silico molecular genetic analysis was performed for all 84 variants identified in our cohort, with 73 of these determined to be likely disease-causing. Review of the clinical findings of the six patients harboring only one, likely benign, missense variant, revealed that they had a less typical (“atypical”) phenotype for ABCA4-associated retinal disease, including an absence of flecks in all patients, significant peripheral retinal bone spicule pigmentation in three subjects, geographic-like atrophy in one individual, a subtle atrophic change confined to the fovea in one patient, and a lack of peripapillary sparing on AF imaging in three subjects. In this study, patients with bilateral macular atrophy, with or without surrounding flecks, potentially were included as having Stargardt disease, with other less typical (“atypical”) findings also having been reported in ABCA4-associated retinal disease.18,40,41 However, other genes associated with autosomal recessive macular dystrophy, autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophy, and autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa also should be considered for these patients with no identified likely disease-causing ABCA4 alleles, in addition to the possibility of missed ABCA4 alleles due to the inherent limitations of the molecular testing approach.
In our cohort, in keeping with previous reports, there was one well-known intronic variant (c.5461-10T>C) of equivocal pathogenicity following detailed in silico analysis,4,5,16; highlighting the need for an effective assay to determine functionally the effects of ABCA4 variants, or alternatively to consider investigating mRNA expression. The allele, c.5461-10T>C, was the most common in our cohort, with 8/79 patients (10%) harboring this variant. Interestingly, the second allele was not identified in six of these patients. However, co-segregation of c.5461-10T>C with the disease has been documented in several studies, thereby strongly suggesting its disease-causation.4
In summary, we have demonstrated the validity and utility of ABCA4 mutation screening with an NGS-based protocol in a large British cohort, with successful identification of the new disease-causing alleles in approximately half of the cases harboring one allele detected by prescreening with APEX technology. The identification of both disease-causing alleles will improve the accuracy of diagnosis and the counselling of patients, and also will assist in more effective patient selection of genetically confirmed participants for current and future clinical trials for ABCA4-associated retinal disease.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patients who kindly agreed to take part in this study and colleagues who referred individuals to us at Moorfields Eye Hospital, and those who contributed to the assembly of the ABCA4 panel, particularly Naushin Waseem, Bev Scott, and Sophie Devery. The authors also thank Graham E. Holder, Anthony G. Robson, and Magella M. Neveu for interpretation of electrophysiologic data, and Yozo Miyake, Arundhati Dev Borman, Rajarshi Mukherjee, Eva Lenassi, Panagiotis I. Sergouniotis, and Aman Chandra for their insightful comments.
Supported by grants from the National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centre at Moorfields Eye Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and UCL Institute of Ophthalmology; Foundation Fighting Blindness (USA); Fight For Sight; Moorfields Eye Hospital Special Trustees; Macular Disease Society; National Eye Institute/NIH Grants EY021163, EY019861, and EY019007 (Core Support for Vision Research); unrestricted funds from Research to Prevent Blindness (New York, NY) to the Department of Ophthalmology; Columbia University; Suzuken Memorial Foundation; Mitsukoshi Health and Welfare Foundation; Daiwa Anglo-Japanese Foundation; and Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (Japan); and by a Foundation Fighting Blindness Career Development Award (MM). The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Disclosure: K. Fujinami, None; J. Zernant, None; R.K. Chana, None; G.A. Wright, None; K. Tsunoda, None; Y. Ozawa, None; K. Tsubota, None; A.R. Webster, None; A.T. Moore, None; R. Allikmets, None; M. Michaelides, None
References
- 1. Allikmets R, Singh N, Sun H, et al. A photoreceptor cell-specific ATP-binding transporter gene (ABCR) is mutated in recessive Stargardt macular dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1997; 15: 236– 246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Michaelides M, Chen LL, Brantley MA Jr, et al. ABCA4 mutations and discordant ABCA4 alleles in patients and siblings with bull's-eye maculopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. 2007; 91: 1650– 1655 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Burke TR, Tsang SH. Allelic and phenotypic heterogeneity in ABCA4 mutations. Ophthalmic Genet. 2011; 32: 165– 174 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Fujinami K, Lois N, Davidson AE, et al. A longitudinal study of Stargardt disease: clinical and electrophysiological assessment, progression and genotype correlations. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013; 155: 1075– 1088 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Zernant J, Schubert C, Im KM, et al. Analysis of the ABCA4 gene by next-generation sequencing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52: 8479– 8487 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Fujinami K, Akahori M, Fukui M, Tsunoda K, Iwata T, Miyake Y. Stargardt disease with preserved central vision: identification of a putative novel mutation in ATP-binding cassette transporter gene. Acta Ophthalmol. 2011; 89: 297– 298 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Webster AR, Heon E, Lotery AJ, et al. An analysis of allelic variation in the ABCA4 gene. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001; 42: 1179– 1189 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Cremers FP, van de Pol DJ, van Driel M, et al. Autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa and cone-rod dystrophy caused by splice site mutations in the Stargardt's disease gene ABCR. Hum Mol Genet. 1998; 7: 355– 362 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Martinez-Mir A, Paloma E, Allikmets R, et al. Retinitis pigmentosa caused by a homozygous mutation in the Stargardt disease gene ABCR. Nat Genet. 1998; 18: 11– 12 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Rozet JM, Gerber S, Souied E, et al. Spectrum of ABCR gene mutations in autosomal recessive macular dystrophies. Eur J Hum Genet. 1998; 6: 291– 295 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Lewis RA, Shroyer NF, Singh N, et al. Genotype/phenotype analysis of a photoreceptor-specific ATP-binding cassette transporter gene, ABCR, in Stargardt disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1999; 64: 422– 434 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Rozet JM, Gerber S, Ghazi I, et al. Mutations of the retinal specific ATP binding transporter gene (ABCR) in a single family segregating both autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa RP19 and Stargardt disease: evidence of clinical heterogeneity at this locus. J Med Genet. 1999; 36: 447– 451 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Yatsenko AN, Shroyer NF, Lewis RA, Lupski JR. Late-onset Stargardt disease is associated with missense mutations that map outside known functional regions of ABCR (ABCA4). Hum Genet. 2001; 108: 346– 355 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Jaakson K, Zernant J, Kulm M, et al. Genotyping microarray (gene chip) for the ABCR (ABCA4) gene. Hum Mutat. 2003; 22: 395– 403 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Fishman GA, Stone EM, Grover S, Derlacki DJ, Haines HL, Hockey RR. Variation of clinical expression in patients with Stargardt dystrophy and sequence variations in the ABCR gene. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999; 117: 504– 510 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Papaioannou M, Ocaka L, Bessant D, et al. An analysis of ABCR mutations in British patients with recessive retinal dystrophies. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000; 41: 16– 19 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Rivera A, White K, Stohr H, et al. A comprehensive survey of sequence variation in the ABCA4 (ABCR) gene in Stargardt disease and age-related macular degeneration. Am J Hum Genet. 2000; 67: 800– 813 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Birch DG, Peters AY, Locke KL, Spencer R, Megarity CF, Travis GH. Visual function in patients with cone-rod dystrophy (CRD) associated with mutations in the ABCA4(ABCR) gene. Exp Eye Res. 2001; 73: 877– 886 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Briggs CE, Rucinski D, Rosenfeld PJ, Hirose T, Berson EL, Dryja TP. Mutations in ABCR (ABCA4) in patients with Stargardt macular degeneration or cone-rod degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001; 42: 2229– 2236 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Fumagalli A, Ferrari M, Soriani N, et al. Mutational scanning of the ABCR gene with double-gradient denaturing-gradient gel electrophoresis (DG-DGGE) in Italian Stargardt disease patients. Hum Genet. 2001; 109: 326– 338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Shroyer NF, Lewis RA, Yatsenko AN, Wensel TG, Lupski JR. Cosegregation and functional analysis of mutant ABCR (ABCA4) alleles in families that manifest both Stargardt disease and age-related macular degeneration. Hum Mol Genet. 2001; 10: 2671– 2678 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Klevering BJ, Blankenagel A, Maugeri A, Cremers FP, Hoyng CB, Rohrschneider K. Phenotypic spectrum of autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophies caused by mutations in the ABCA4 (ABCR) gene. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002; 43: 1980– 1985 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Pang CP, Lam DS. Differential occurrence of mutations causative of eye diseases in the Chinese population. Hum Mutat. 2002; 19: 189– 208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Stenirri S, Fermo I, Battistella S, et al. Denaturing HPLC profiling of the ABCA4 gene for reliable detection of allelic variations. Clin Chem. 2004; 50: 1336– 1343 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Downs K, Zacks DN, Caruso R, et al. Molecular testing for hereditary retinal disease as part of clinical care. Arch Ophthalmol. 2007; 125: 252– 258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Ernest PJ, Boon CJ, Klevering BJ, Hoefsloot LH, Hoyng CB. Outcome of ABCA4 microarray screening in routine clinical practice. Mol Vis. 2009; 15: 2841– 2847 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Xi Q, Li L, Traboulsi EI, Wang QK. Novel ABCA4 compound heterozygous mutations cause severe progressive autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophy presenting as Stargardt disease. Mol Vis. 2009; 15: 638– 645 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Littink KW, Koenekoop RK, van den Born LI, et al. Homozygosity mapping in patients with cone-rod dystrophy: novel mutations and clinical characterizations. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51: 5943– 5951 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Maugeri A, van Driel MA, van de Pol DJ, et al. The 2588G-->C mutation in the ABCR gene is a mild frequent founder mutation in the Western European population and allows the classification of ABCR mutations in patients with Stargardt disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1999; 64: 1024– 1035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Klevering BJ, Yzer S, Rohrschneider K, et al. Microarray-based mutation analysis of the ABCA4 (ABCR) gene in autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophy and retinitis pigmentosa. Eur J Hum Genet. 2004; 12: 1024– 1032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Fujinami K, Sergouniotis PI, Davidson AE, et al. The clinical effect of homozygous ABCA4 alleles in 18 patients [published online ahead of print June 11, 2013] Ophthalmology. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2013.04.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Sergouniotis PI, Davidson AE, Lenassi E, Devery SR, Moore AT, Webster AR. Retinal structure, function, and molecular pathologic features in gyrate atrophy. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119: 596– 605 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Bach M, Brigell MG, Hawlina M, et al. ISCEV standard for clinical pattern electroretinography (PERG): 2012 update. Doc Ophthalmol. 2013; 126: 1– 7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Marmor MF, Fulton AB, Holder GE, Miyake Y, Brigell M, Bach M. ISCEV standard for full-field clinical electroretinography (2008 update). Doc Ophthalmol. 2009; 118: 69– 77 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Lois N, Holder GE, Bunce C, Fitzke FW, Bird AC. Phenotypic subtypes of Stargardt macular dystrophy-fundus flavimaculatus. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001; 119: 359– 369 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Ng PC, Henikoff S. SIFT: predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003; 31: 3812– 3814 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, et al. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods. 2010; 7: 248– 249 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. den Dunnen JT, Antonarakis SE. Mutation nomenclature extensions and suggestions to describe complex mutations: a discussion. Hum Mut. 2000; 15: 7– 12 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Braun TA, Mullins RF, Wagner AH, et al. Non-exomic and synonymous variants in ABCA4 are an important cause of Stargardt disease. Hum Mol Genet. In press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Burke TR, Allikmets R, Smith RT, Gouras P, Tsang SH. Loss of peripapillary sparing in non-group I Stargardt disease. Exp Eye Res. 2010; 91: 592– 600 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Fritsche LG, Fleckenstein M, Fiebig BS, et al. A subgroup of age-related macular degeneration is associated with mono-allelic sequence variants in the ABCA4 gene. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012; 53: 2112– 2118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]