Abstract
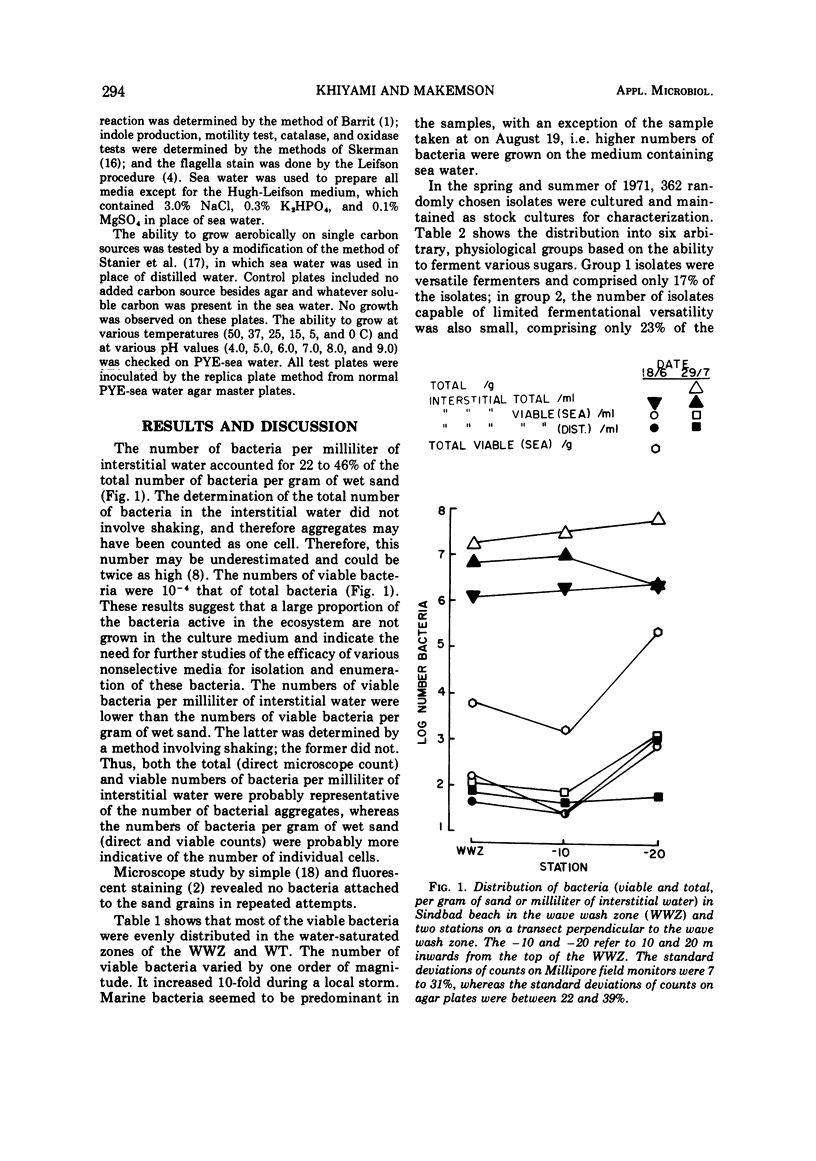
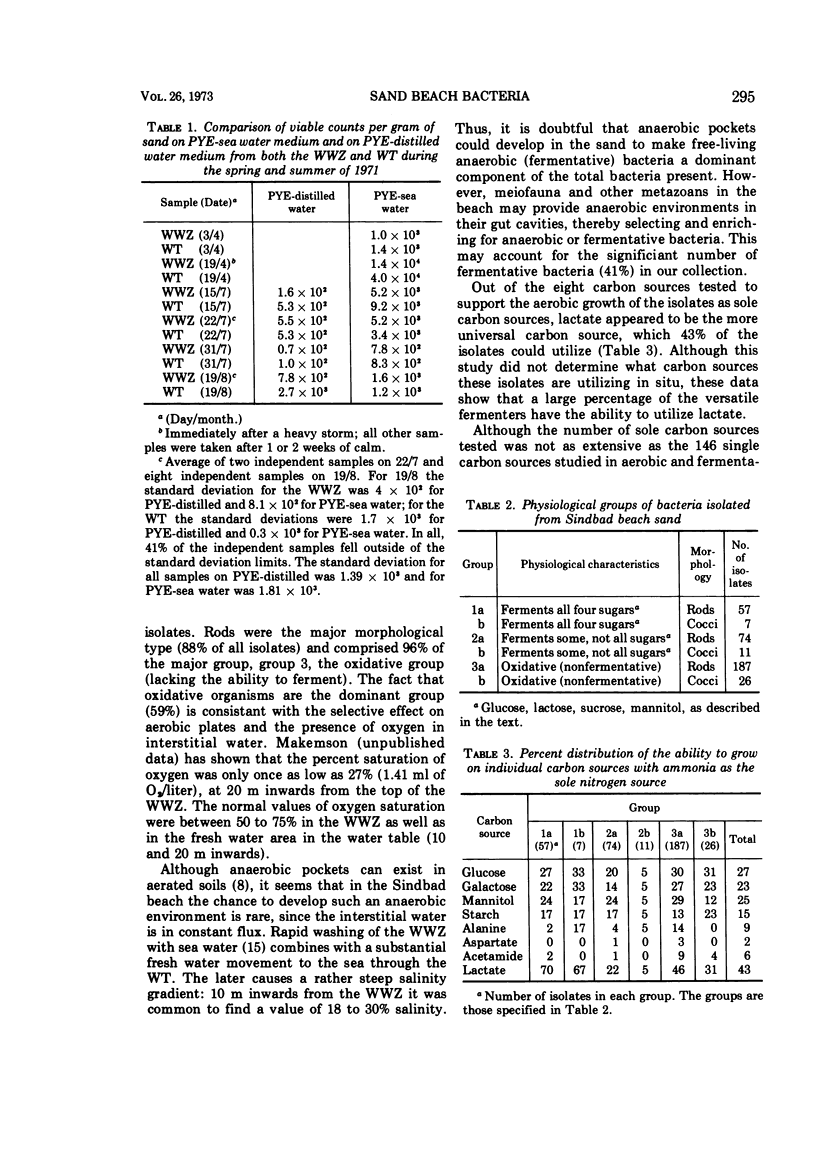
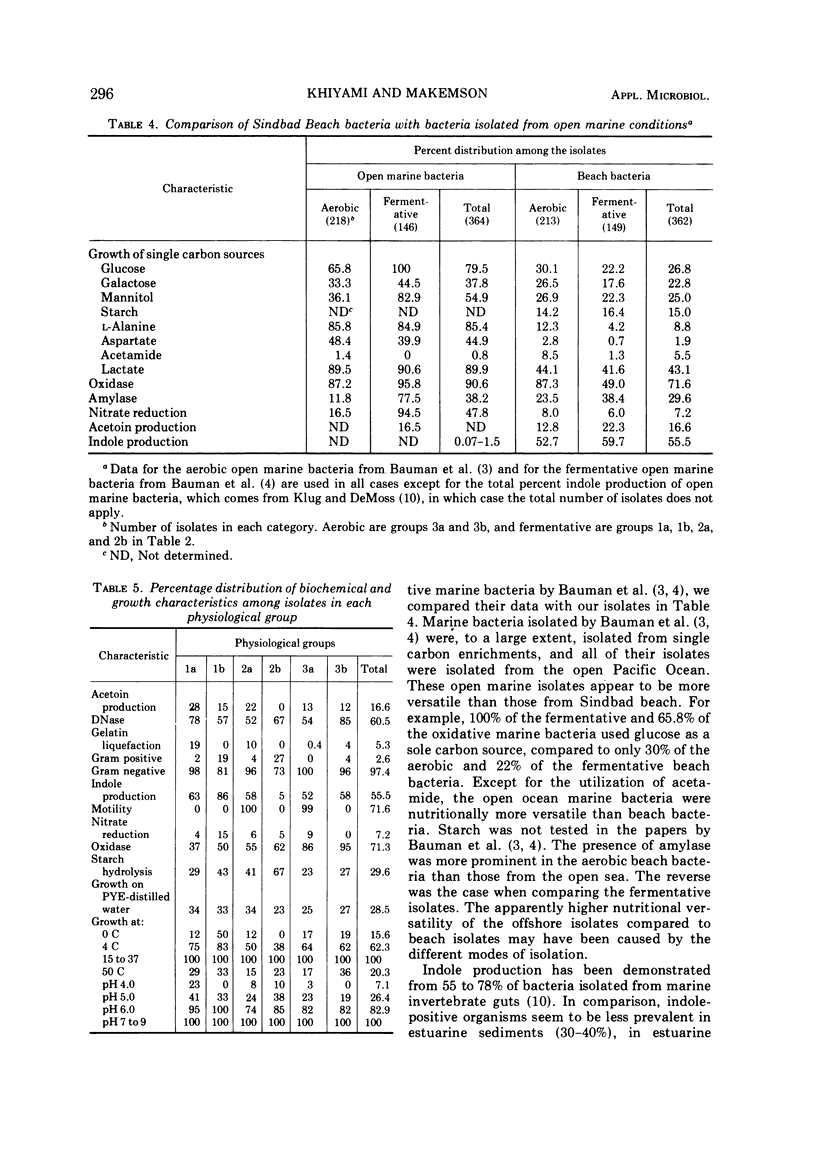
Bacteria in the water-saturated sand of a relatively unpolluted sand beach were enumerated by direct microscope and viable counting. The number of interstitial bacteria was estimated to be a significant fraction of the total number of bacteria present. Three hundred sixty-two strains were isolated and submitted to cultural and biochemical tests. Fermentational abilities and the production of indole suggested that a significant number of these bacteria were symbiotically associated with resident metazoans.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batoosingh E., Anthony E. H. Direct and indirect observations of bacteria on marine pebbles. Can J Microbiol. 1971 May;17(5):655–664. doi: 10.1139/m71-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann L., Baumann P., Mandel M., Allen R. D. Taxonomy of aerobic marine eubacteria. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):402–429. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.402-429.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Baumann L., Mandel M. Taxonomy of marine bacteria: the genus Beneckea. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):268–294. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.268-294.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGH R., LEIFSON E. The taxonomic significance of fermentative versus oxidative metabolism of carbohydrates by various gram negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):24–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.1.24-26.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug M. J., DeMoss R. D. Tryptophanase-positive bacteria in the marine environment. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):283–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.283-285.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Genigeorgis C., Hoeprich P. D. Metachromatic agar-diffusion methods for detecting staphylococcal nuclease activity. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):585–587. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.585-587.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


