Abstract
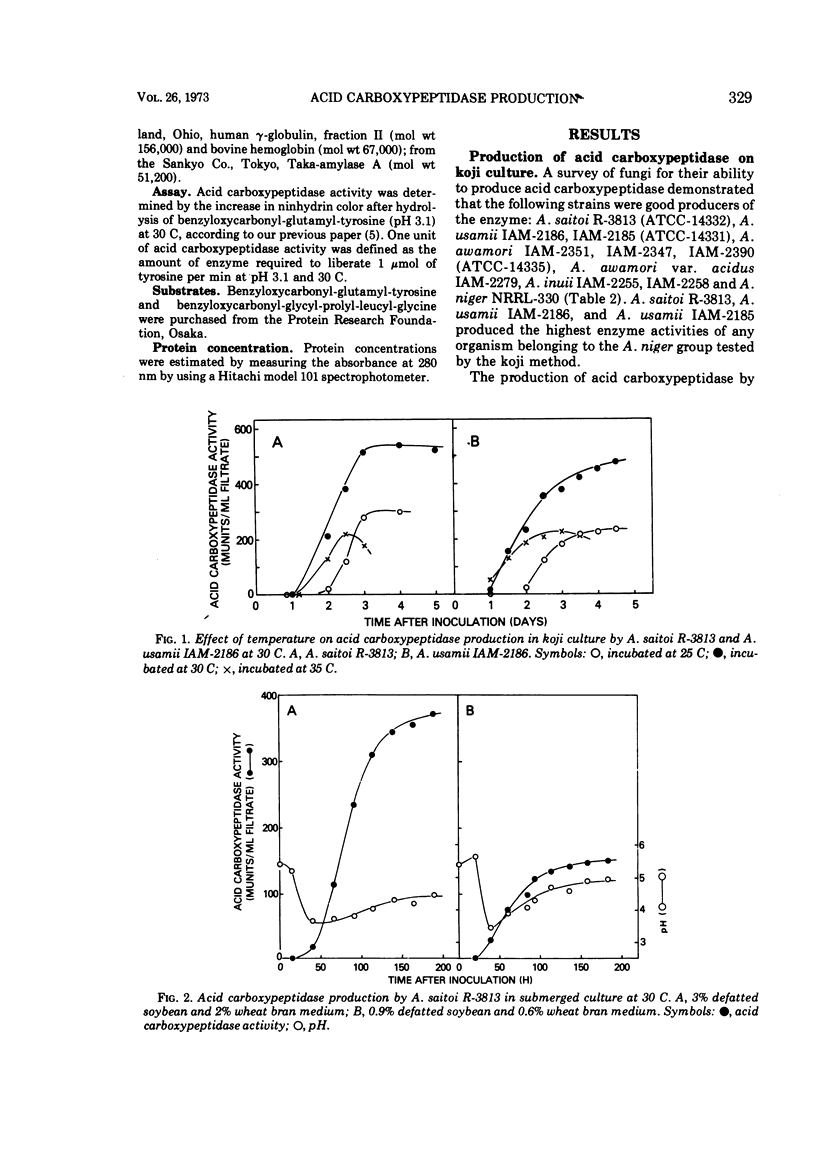
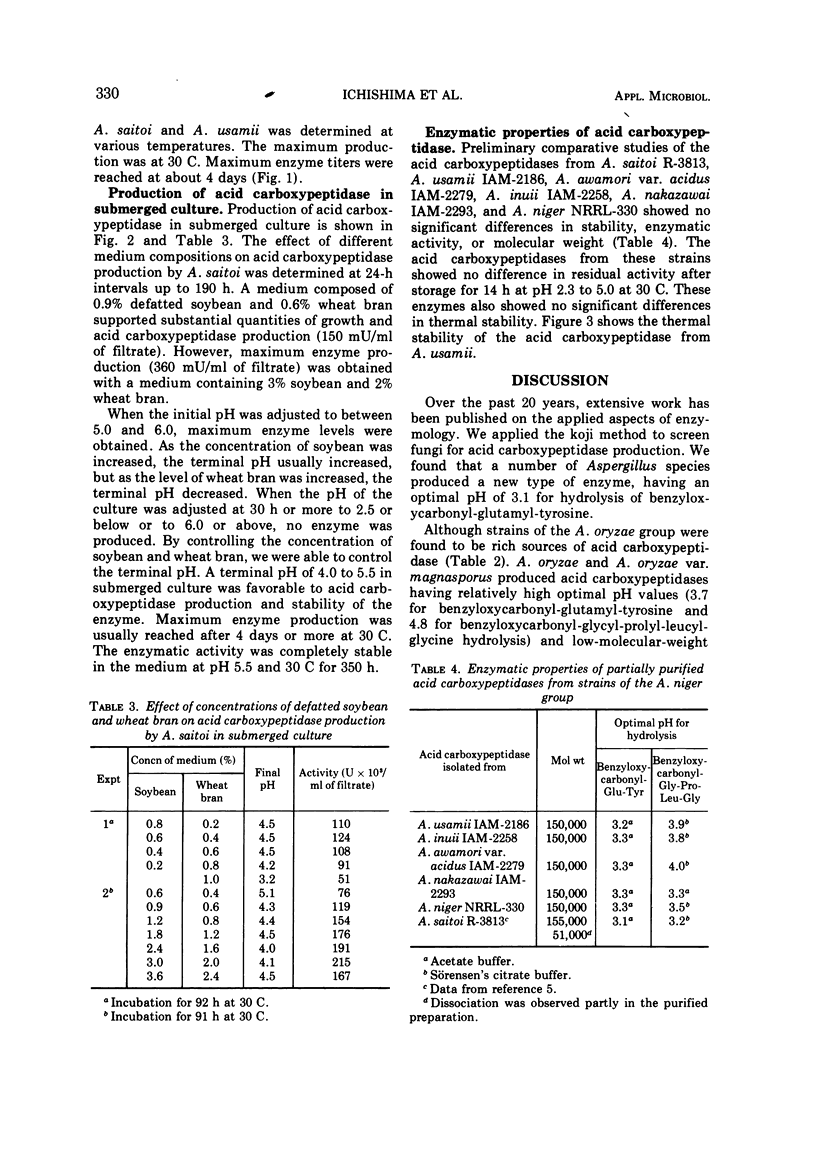
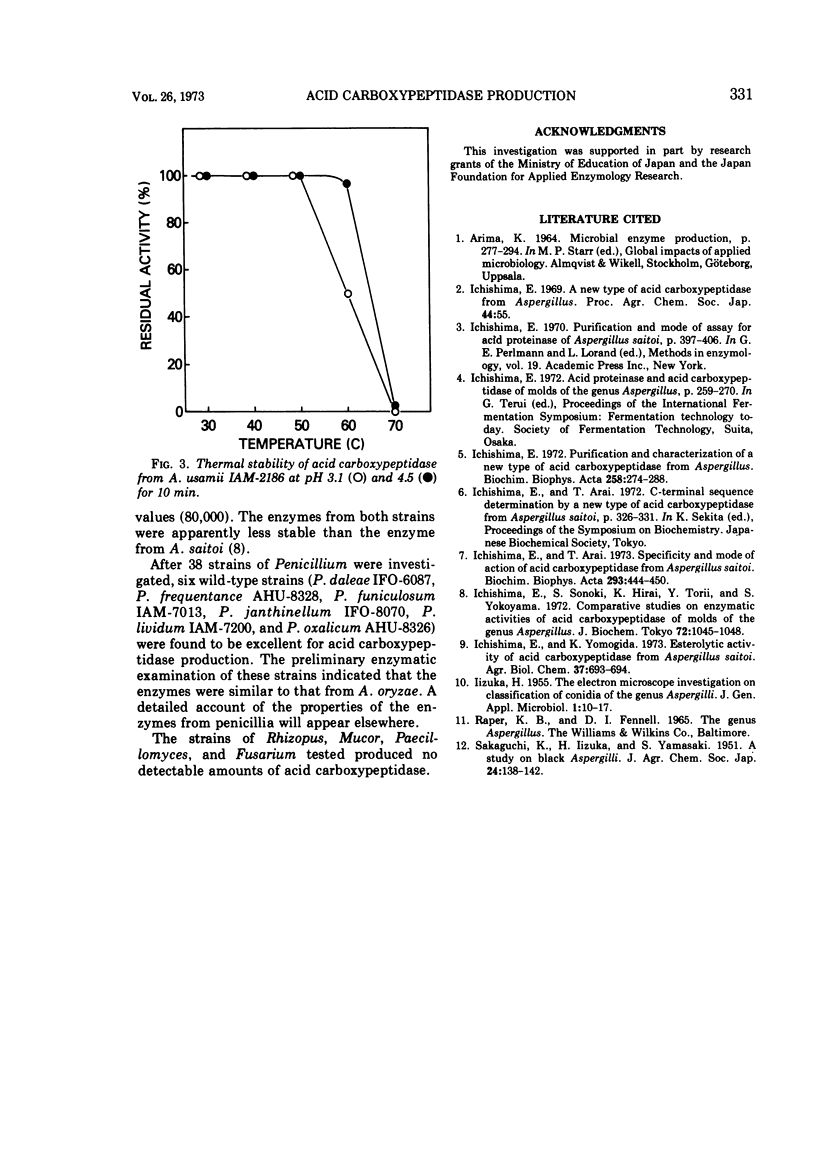
The ability of 88 fungi, which had been obtained as high-potency strains for acid proteinase production, to produce a new type of acid carboxypeptidase (having on optimal pH of about 3 for hydrolysis of benzyloxycarbonyl-glutamyltyrosine) in surface koji culture was determined. Among the aspergilli, substantial amounts of this new acid carboxypeptidase were produced by Aspergillus saitoi, A. usamii, A. awamori, A. inuii, and A. niger. Maximum yields of acid carboxypeptidase per gram of substrate were obtained by submerged culture in a medium containing 0.9% defatted soybean and 0.6% wheat bran. However, the maximum enzyme concentration per milliliter was obtained with a medium containing 3% defatted soybean and 2% wheat bran. The terminal pH could be controlled by varying the concentrations of soybean oil meal and wheat bran. The maximum enzyme production was reached after 4 days or more at 30 C.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ichishima E., Arai T. Specificity and mode of action of acid carboxypeptidase from Aspergillus saitoi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 15;293(2):444–450. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichishima E. Purification and characterization of a new type of acid carboxypeptidase from Aspergillus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 20;258(1):274–288. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90985-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichishima E., Sonoki S., Hirai K., Torii Y., Yokoyama S. Comparative study on enzymatic properties of acid carboxypeptidase of molds of the genus Aspergillus. J Biochem. 1972 Oct;72(4):1045–1048. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


