Abstract
Autonomic regulation processes in striated muscles are largely mediated by cAMP/PKA-signaling. In order to achieve specificity of signaling its spatial-temporal compartmentation plays a critical role. We discuss here how specificity of cAMP/PKA-signaling can be achieved in skeletal muscle by spatio-temporal compartmentation. While a microdomain containing PKA type I in the region of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) is important for postsynaptic, activity-dependent stabilization of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR), PKA type I and II microdomains in the sarcomeric part of skeletal muscle are likely to play different roles, including the regulation of muscle homeostasis. These microdomains are due to specific A-kinase anchoring proteins, like rapsyn and myospryn. Importantly, recent evidence indicates that compartmentation of the cAMP/PKA-dependent signaling pathway and pharmacological activation of cAMP production are aberrant in different skeletal muscles disorders. Thus, we discuss here their potential as targets for palliative treatment of certain forms of dystrophy and myasthenia. Under physiological conditions, the neuropeptide, α-calcitonin-related peptide, as well as catecholamines are the most-mentioned natural triggers for activating cAMP/PKA signaling in skeletal muscle. While the precise domains and functions of these first messengers are still under investigation, agonists of β2-adrenoceptors clearly exhibit anabolic activity under normal conditions and reduce protein degradation during atrophic periods. Past and recent studies suggest direct sympathetic innervation of skeletal muscle fibers. In summary, the organization and roles of cAMP-dependent signaling in skeletal muscle are increasingly understood, revealing crucial functions in processes like nerve-muscle interaction and muscle trophicity.
Keywords: adrenoceptors, AKAP, endplate, dystrophy, PKA, metabolism, neuromuscular junction, skeletal muscle
Introduction
A variety of hormones and other first messengers employ cAMP-dependent signal transduction to exert their effects (Beavo and Brunton, 2002). Sympathetic activation of adrenergic receptors (or adrenoceptors) by catecholamines is the classical paradigm in this context. In skeletal muscle, catecholamines regulate many physiological functions, including force production (Oliver and Schäfer, 1895; Arreola et al., 1987; Cairns and Dulhunty, 1993a,b; Decostre et al., 2000), blood flow (Marshall, 1982; Saltin et al., 1998; Joyner and Casey, 2009), and metabolism (Gross et al., 1976; Navegantes et al., 2000, 2002). These effects might be mediated through endocrine delivery of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla, but adrenergic nerve terminals make also close contact with striated muscle fibers (Barker and Saito, 1981; Tadaki et al., 1995), suggesting direct release of norepinephrine onto muscle fibers in a neurotransmitter-like or paracrine fashion as it occurs at the heart (Zaglia et al., 2013). However, these aspects of adrenergic signaling on skeletal muscle are far from being established and are currently under investigation (see also below).
In skeletal muscle, catecholamines stimulate primarily β2-adrenergic receptors (β2-ARs). These are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which mostly couple to Gαs and thus activate adenylyl cyclase (AC) (Liggett and Raymond, 1993), leading to an increase in cAMP levels, activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) (Beavo and Brunton, 2002; Altarejos and Montminy, 2011). In parallel, cAMP signals through the “exchange protein activated directly by cAMP” (Epac) (Bos, 2003), and it regulates cyclic-nucleotide gated (CNGs) channels (Beavo and Brunton, 2002). The attenuation of cAMP effects is coordinated by the activation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDEs), which are classified into 11 major families (PDE1-11) (Bloom, 2002; Omori and Kotera, 2007). In skeletal muscle, PDE4 appears to contribute to the majority of cAMP hydrolysis, accounting for more than 80% of the total PDE activity in this tissue (Bloom, 2002). Notably, a couple of different cAMP-regulating GPCRs are typically co-expressed in one and the same cell raising the evident issue of how the small inconspicuous molecule, cAMP, can trigger specific responses upon activation of a certain GPCR. This is also true for striated muscle where a plethora of physiological functions are subject to cAMP-dependent signaling. For skeletal muscle, Berdeaux and Stewart have recently reviewed the different functions of this pathway very nicely (Berdeaux and Stewart, 2012). Furthermore, lists of GPCRs (albeit likely not complete) expressed in heart and skeletal muscles can be found in reviews from Tang (Tang and Insel, 2004) and Jean-Baptiste (Jean-Baptiste et al., 2005), respectively. So, how is specificity gained in cAMP-dependent signaling pathways? The strongest current line of evidence supports a microdomain hypothesis, wherein spatial and temporal segregation of local rises of cAMP plus scaffolding of essential downstream effectors and targets of cAMP play pivotal roles (Steinberg and Brunton, 2001; Zaccolo et al., 2002; Zaccolo, 2011; Edwards et al., 2012). Central players in this scenario are variability of PKA isoforms, A kinase-anchoring proteins (AKAPs), and PDEs. In its inactive state, PKA is comprised of four subunits, i.e., two regulatory (PKA-R) and two catalytic subunits (PKA-C) (Taylor et al., 2008). Upon binding of cAMP to regulatory subunits, catalytic subunits are activated and detach from regulatory subunits in order to phosphorylate targets. In mammals, four isoforms of PKA-R are present, named as type Iα, Iβ, IIα, IIβ. While PDEs impair cAMP from spreading all over the cell through hydrolysis of the second messenger (Conti and Beavo, 2007; Francis et al., 2011), AKAPs serve as scaffolds integrating and anchoring many relevant partners of a GPCR-linked signaling pathway (Scott et al., 2013). Indeed, AKAPs not only bind to PKA (hence their name) but often also to GPCRs, ACs, PDEs, protein phosphatases, and target molecules (Edwards et al., 2012). Thereby, they integrate entire signaling complexes and guarantee high efficiency and fidelity of signal transduction. AKAPs belong to a large heterogeneous group of proteins, which do not share sequence homology but a set of functional properties. They typically exhibit a subcellular targeting domain, interaction domains with other components of signal pathways, and an amphipathic α-helical domain that serves as interaction terminal with PKA-R (Scott et al., 2013). Indeed, the PKA-R expose an N-terminal stretch called dimerization/docking- (D/D-) domain that combines with the AKAP α-helical parts at varying intensities and specificities. A typical and widely used means to test the functional impact of AKAP-PKA interaction is by introducing “AKAP disruptor peptides” which mimic the AKAP interaction domain and thereby release PKA-R from its normal microdomain (Scott et al., 2013). In summary, a large part of cAMP-dependent signaling specificity appears to arise from the interplay between PDEs and AKAPs and is sometimes subsumed under the term “PKA microdomain hypothesis,” recently described in depth in a couple of excellent reviews (Zaccolo, 2011; Edwards et al., 2012; Scott et al., 2013). The present contribution first addresses, how the “PKA microdomain hypothesis” applies to skeletal muscle and what are potential links to skeletal muscle diseases. In a second part, we review the current knowledge on how catecholamines regulate muscle trophicity.
PKA microdomains in skeletal muscle
Investigations dealing with the PKA microdomain hypothesis usually address differential distribution patterns of distinct PKA-R isoforms. Owing to its highly regular striated patterning of sarcomeres, the contractile units of striated muscle, this tissue is particularly amenable to investigating the distribution of PKA-R isoforms relative to sarcomeric marker proteins. Another region of interest is the nerve-muscle synapse, termed as endplate or neuromuscular junction (NMJ), which instructs the rest of the muscle fiber to contract upon stimulation. For both parts there is now information concerning PKA-R distribution, alterations in diseased muscle, as well as causes underlying and consequences of these alterations. In the following we will describe the current state of knowledge regarding these points.
Subsynaptic PKA microdomains
The NMJ is the synapse between motoneuron and muscle fiber and as such exerts the control over skeletal muscle contraction. The latter is triggered upon release of the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine, which activates postsynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChR) leading to an endplate potential and ultimately to muscle contraction. Notably, AChR reaches extremely high densities at the postsynaptic membrane of about 10,000 molecules per square micron and under normal conditions AChRs are metabolically very stable with a half-life of about 13 days (Fambrough, 1979). Principal functions attributed to cAMP/PKA-dependent signaling at the NMJ are synapse stabilization and the metabolic control of AChR stability and function (Li et al., 2001; Lanuza et al., 2002; Li et al., 2002; Nelson et al., 2003). In situ hybridization showed a peculiar accumulation of PKA-RIα transcripts in the NMJ region (Imaizumi-Scherrer et al., 1996) and immunohistochemical analyses found both, PKA-RIα and PKA-RIIα to be enriched close to the postsynaptic membrane (Perkins et al., 2001). However, different studies using fusions of different PKA-R D/D-domains with fluorescent proteins only revealed PKA-RIα but not PKA-RIIα in numerous punctiform structures just beneath the postsynaptic membrane (Barradeau et al., 2001, 2002; Röder et al., 2010; Choi et al., 2012). What do these puncta represent? The involvement of PKA signaling in AChR stabilization suggested them to be intracellular AChR carriers. As bona fide transmembrane proteins, the subunits of the pentameric AChR are generated and assembled in the endoplasmic reticulum, from where they are routed over the Golgi apparatus to the plasma membrane (Marchand et al., 2000, 2002; Marchand and Cartaud, 2002; Wanamaker and Green, 2005, 2007). Using different elegant labeling approaches with the highly AChR-selective snake venom, α-bungarotoxin, Engel et al. showed by electron microscopy that AChR is endocytosed in membrane-bound carriers (Engel et al., 1977; Fumagalli et al., 1982) and several groups established an activity-dependent metabolic stabilization of AChR (Fambrough, 1979; Levitt et al., 1980; Loring and Salpeter, 1980; Levitt and Salpeter, 1981; Stanley and Drachman, 1981, 1983; Salpeter and Loring, 1985; Shyng et al., 1991; Xu and Salpeter, 1997, 1999). Next, Akaaboune et al. demonstrated that AChR is recycled to the postsynaptic membrane in an activity-dependent manner (Akaaboune et al., 1999; Bruneau et al., 2005; Bruneau and Akaaboune, 2006). At this point a large part of the lifecycle of AChRs was described phenomenologically. However, amongst other open questions it remained unclear, what molecules underlie the regulatory decision-making (e.g., dwell at postsynaptic membrane vs. endocytose; recycle vs. degrade) and which machinery would support these processes. Most knowledge was gathered regarding the clustering of AChRs at the membrane, which is mediated by the release of neuronal agrin (Nitkin et al., 1987), binding of agrin to the MuSK co-receptor, LRP4, and activation of the receptor-tyrosine kinase MuSK (Kim et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2008; Zong et al., 2012; Burden et al., 2013; Hubbard and Gnanasambandan, 2013). This then triggers AChR clustering by a yet ill-defined mechanism, which involves the receptor-associated protein of the synapse, rapsyn (Gillespie et al., 1996; Apel et al., 1997; Glass and Yancopoulos, 1997; Ruegg and Bixby, 1998; Fuhrer et al., 1999; Gautam et al., 1999).
As for the metabolic stabilization of AChRs different lines of evidence indicate the involvement of the neuropeptide, α-calcitonin-gene related peptide (αCGRP), and of cAMP/PKA-dependent pathways (Poyner, 1992). αCGRP was found to raise postsynaptic cAMP levels in the PKA-RIα microdomain (Röder et al., 2010) and to rapidly phosphorylate the α- and δ-subunit of AChR (Miles et al., 1987, 1989). Furthermore, αCGRP treatment changed the electrophysiological characteristics of AChR (Mulle et al., 1988) and it rescued denervation-induced fragmentation of NMJs (Röder et al., 2010). Furthermore, αCGRP was described to counteract PKC-induced destabilization of AChRs (Li et al., 2001, 2002) and to stimulate AChR gene expression (New and Mudge, 1986; Fontaine et al., 1987) as well as synaptic strength (Lu et al., 1993). Experiments using AKAP disruptor peptides suggested that the proper localization of PKA-RIα on the aforementioned subsynaptic puncta is essential for AChR stabilization (Röder et al., 2010) and in vivo imaging and biochemical assays revealed that many of these structures indeed contain endocytosed AChR (Röder et al., 2010). Altogether these findings suggest that the PKA-RIα positive puncta represent αCGRP-sensitive PKA microdomains on endocytic carriers containing AChR. The actin-dependent motor protein, myosin Va, was found to be crucial for tethering these carriers in close proximity to the NMJ (Röder et al., 2010) (for schematic, see Figure 1), but which is the AKAP used for anchoring PKA-RIα to the AChR-laden carriers? Previous reports suggested D-AKAP1 (Barradeau et al., 2001, 2002; Perkins et al., 2001) as a candidate. However, this was purely based on the general enrichment of this protein underneath the NMJ. A recent study followed another rationale and looked for a protein that would (1) target to AChR, (2) exhibit an AKAP-typical α-helical coiled-coil domain and (3) have interaction domains with other signaling components, and, based on these pre-requisites, tested the hypothesis that rapsyn serves as AKAP at this place. Rapsyn is a 43 kDa protein, that was originally co-purified with AChR from Torpedo electroplax and that quantitatively and strongly interacts with AChR (Sobel et al., 1977; Neubig et al., 1979; Porter and Froehner, 1985; Froehner, 1993). From N- to C-terminus, rapsyn contains a myristoylation site, seven tetratricopeptide repeats, an amphipathic α-helical region, a RING-domain, and PKA- and PKC-phosphorylation consensus sites (Ramarao and Cohen, 1998; Ramarao et al., 2001). Notably, full-length rapsyn but not rapsyn lacking its α-helical domain co-precipitated with PKA-RIα (Choi et al., 2012). In silico modeling identified functional sequence homology of that region with PKA-interaction domains of different AKAPs, and rapsyn interacted with PKA-RIα in a bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay both, in cells and in vivo (here in subsynaptic puncta) (Choi et al., 2012). Finally, over-expression of a peptide derived from the rapsyn α-helical coiled-coil domain displaced PKA-RIα from the NMJ puncta and severely impaired AChR stability (Choi et al., 2012), strongly arguing for rapsyn as the AKAP responsible for linking PKA-RIα to the subsynaptic PKA microdomain (for schematic, see Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Schematic model of the hypothetic assembly of a PKA microdomain beneath the NMJ. Amongst other potential roles at the NMJ, PKA-RI is critical for proper lifetime regulation of AChR. At least a part of these regulatory processes appears to be linked to the endocytosis/recycling of AChR. From the endocytic compartment, AChRs may either return to the postsynaptic membrane (recycling) or be routed to a degradation pathway. To carry out its function, PKA-RI needs to be recruited to endocytic/recycling vesicles which transport AChR and those vesicles are to be tethered close to the postsynaptic membrane in order to receive local rises of cAMP levels. Anchoring of PKA-RI to these vesicles is mediated by rapsyn, while myo5a serves to restrain endocytic/recycling vesicles in the actin-rich cortex underneath the NMJ. First messengers triggering the relevant local rises in cAMP levels are still elusive and they might originate from motoneurons, sympathetic nervous system or other sites.
NMJ structure and stability of AChR strongly suffer in muscles from the mdx mouse model for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) (Torres and Duchen, 1987; Lyons and Slater, 1991; Xu and Salpeter, 1997; Grady et al., 2000; Shiao et al., 2004), in which cAMP signaling is aberrant (Reynolds et al., 2008). That does, of course, not mean that the altered signaling is the underlying cause for the NMJ phenomena, but the typical subsynaptic enrichment of PKA-RIα was lacking in about half of all fibers in mdx muscles, microdomain specificity to different GPCR agonists was subverted, and AChR turnover was inversely correlated with PKA-RIα accumulation beneath the NMJ (Röder et al., 2012). Altogether this set of data suggests a link between defect subsynaptic microdomain formation of PKA-RIα in dystrophic muscles and the observed alterations in NMJ morphology and AChR stability. In general, the concept of an AChR stabilizing role of cAMP was also tested in the context of another devastating group of muscle diseases, i.e., congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS). These are rare genetic diseases that affect either pre- or postsynaptic components of the NMJ and lead to impaired neuromuscular transmission and muscle weakness (Palace and Beeson, 2008). Many forms of CMS also present low levels of AChR at the NMJ. Although the underlying mechanisms for that might differ between distinct mutations, the finding that sympathomimetic substances, such as ephedrine and salbutamol, can significantly improve these patients' symptoms (Edgeworth, 1930; Schara et al., 2009; Lashley et al., 2010; Liewluck et al., 2011; Finlayson et al., 2013), suggests an involvement of catecholamines in AChR turnover. Since ephedrine and salbutamol both can activate β2-ARs and thus affect cAMP production, this could point to a possible role of cAMP in stabilizing AChR and/or leading to higher AChR expression. Certainly, further research is needed to better understand these effects.
PKA microdomains at the sarcomeric region
Sarcomeric PKA microdomain organization was addressed either by immunohistochemical staining of PKA-R isoforms (Perkins et al., 2001) or by expression studies using fluorescent protein-labeled Epac-based cAMP biosensors (Nikolaev et al., 2004) targeted to PKA microdomains by virtue of D/D domains (Di Benedetto et al., 2008) specific for either PKA-RIα (RIα-EPAC-camps) or PKA-RIIα (RIIα-EPAC-camps) (Röder et al., 2009). Both approaches yielded essentially identical results (for schematic, see Figure 2). While PKA-RIα was found in a broad band overlapping with the sarcomeric actin filaments, PKA-RIIα exhibited highly confined striated localization that coincided with both, the m-band and the z-line. Experiments using over-expression of AKAP disruptor peptides showed that this peculiar distribution pattern is largely based on AKAP-dependent subcellular targeting (Röder et al., 2009). Harnessing the cAMP-sensor domain of the EPAC-camps biosensors furthermore showed a differential sensitivity of the two microdomains. While the cAMP concentration in the RIα-microdomain was elevated in the presence of the agonist, αCGRP, the RIIα-microdomain responded to norepinephrine with increased cAMP levels (Röder et al., 2009). Both effects were ablated by AKAP disruptor peptides (Röder et al., 2009). These data demonstrate that the sarcomeric region of skeletal muscle exhibits clearly defined and functionally distinct PKA microdomains, which are organized by specific AKAPs. At present, it is unclear which AKAP(s) mediate the anchoring of PKA-RIα and PKA-RIIα to the different domains in the sarcomeric region but one eminent protein, myospryn, is certainly carrying out a part of this function. This 449 kDa heavy protein with the official gene name CMYA5 (cardiomyopathy-associated 5) was identified by expression profiling of a cardiac muscle library and has since been found to interact specifically with PKA-RIIα but not (or hardly) with the other PKA-R isoforms (Reynolds et al., 2007). Intriguingly, endogenous myospryn localization in the sarcomere exhibited the expected m- and z-line expression pattern fitting to PKA-RIIα distribution (Reynolds et al., 2007) while in another study myospryn showed only faint m-line and strong I-band distribution (Sarparanta et al., 2010). Whether this could indicate natural variability or be due to other factors is unclear, but myospryn is now widely considered to be an important determinant for PKA microdomain formation in skeletal and heart muscle. In the recent past, more and more proteins were found to interact with myospryn, including the structural proteins α-actinin (Durham et al., 2006), desmin (Kouloumenta et al., 2007), dystrophin (Reynolds et al., 2008), and titin (Sarparanta et al., 2010), as well as proteolytic enzymes such as the muscle-specific protease, calpain 3 (Sarparanta et al., 2010), and the protein phosphatase calcineurin (Kielbasa et al., 2011). Notably, these proteins all play important roles in muscle integrity and metabolic adaptations suggesting a mediator role of myospryn in these processes (Sarparanta, 2008). This is corroborated by feedback loops: Expression of myospryn is modulated by the cAMP-dependent CREB pathway, and it is known to be a direct target of the myocyte enhancer factor MEF2A (Durham et al., 2006). Furthermore, absence or malfunction of myospryn is observed in a couple of muscle diseases including tibial and limb-girdle muscular dystrophies (TMD and LGMD2J, respectively) (Sarparanta et al., 2010) as well as the most abundant and severe form of muscular dystrophies, i.e., DMD (Reynolds et al., 2008). Notably, in the DMD mouse model, mdx, myospryn showed altered subcellular distribution and specific PKA activity was strongly reduced (Reynolds et al., 2008). This also fits to another study, where PKA-RIα distribution in the sarcomeres was altered and, in particular, the microdomain selectivity to respond to the specific agonists, norepinephrine and αCGRP, was completely subverted (Röder et al., 2009). In summary, although the precise function of cAMP microdomain organization in skeletal muscle sarcomeres is still elusive, there are correlations between aberrant cAMP signaling and severe muscle diseases. Based on this rationale, urocortins were tested as therapeutics against muscular dystrophy (Hinkle et al., 2007; Reutenauer-Patte et al., 2012). Urocortins are neuropeptides that bind to the GPCRs, corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) receptors (CRFR), of which CRF2R is highly abundant in skeletal muscle. Notably, in dystrophic mdx mice treatment with urocortins significantly ameliorated a set of symptoms, ranging from fiber necrosis to muscle function. Possible mechanisms of action might include cAMP-induced activation of PKA and Epac, which in turn may address altered Ca2+ handling in skeletal muscle fibers (Reutenauer-Patte et al., 2012).
Figure 2.
PKA-R isoforms display differential distribution patterns in skeletal muscle sarcomeres. Immunohistochemical and GFP-based sensor analyses showed that PKA-RIα essentially co-distributes with microfilaments and PKA-RIIα with m-bands and z-lines. These distribution patterns are the most prevalent in mouse muscle. They are based on AKAP-binding and can be subverted in diseased muscle, such as upon dystrophy. AKAPs relevant for these distribution patterns are still elusive, but myospryn is very likely to participate in the anchoring of PKA-RIIα.
Mechanisms of cAMP-induced effects on skeletal muscle protein metabolism
Skeletal muscle constitutes about 40–60% of our body masses. It is, thus, not only driving locomotion but also represents a major metabolic organ due to its enormous energy expenditure, its capability to take up glucose in an insulin-dependent manner, and its role as amino acid-source during catabolic conditions (Sandri, 2008; Glass, 2010). All these functions are intimately linked to the sarcomeres, which constitute the vast excess of skeletal muscle tissue. GPCR- and cAMP-mediated signaling can act on different time scales, ranging from the seconds to days range, correlating to either direct activation of targets (e.g., by PKA-dependent phosphorylation) or to changes in transcriptional profiles (e.g., by modulation of CREB activity). In contrast to their catabolic effects on lipids and carbohydrate metabolism, catecholamines exert an anabolic effect on skeletal muscle protein metabolism (Navegantes et al., 2002). This effect is mediated by β2-ARs and involves cAMP signaling (Navegantes et al., 2000, 2002). Numerous studies have shown that β2-adrenergic agonists, such as clenbuterol (“older” generation) and formoterol (“newer” generation), induce hypertrophy of skeletal muscle in rodents, large animals and humans (Lynch and Ryall, 2008). β-agonist-induced hypertrophy seems to be specific for striated muscle, since smooth muscles do not increase in size in response to these agents (Reeds et al., 1986) and β2-adrenergic agonists inhibit smooth muscle cell proliferation (Southgate and Newby, 1990; Tomlinson et al., 1994; Indolfi et al., 1997). Experiments conducted in β2-AR−/− mice (Hinkle et al., 2002) have convincingly shown that β2-AR is responsible for this anabolic effect. Indeed, β2-AR−/− mice display decreased cross-sectional area of type I and IIA fibers compared with age-matched wildtype mice (Bacurau et al., 2009), an effect that is associated with lower muscle cAMP levels (Gonçalves et al., 2009).
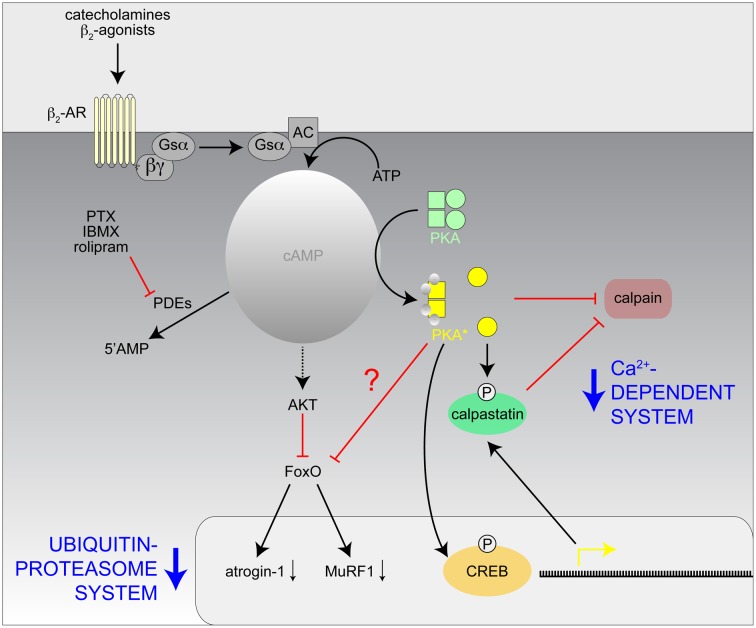
The molecular mechanisms by which cAMP signaling induces growth and muscle-sparing responses are uncertain and may involve an increase in the rate of protein synthesis and/or a decrease in protein degradation (Navegantes et al., 2002; Lynch and Ryall, 2008). A large body of evidence indicates that the in vivo effects of cAMP-inducing agents are in part due to inhibition of muscle proteolysis (Figure 3). Indeed, both chemical and surgical sympathectomy in fed rats lead to an increase in the activity of the Ca2+-dependent proteolytic system, which suggests the existence of an adrenergic tonus on skeletal muscle that keeps this pathway inhibited under normal conditions (Navegantes et al., 1999, 2001). Accordingly, the administration of β2-adrenergic agonists is accompanied by a reduction in calpain 1 activity and an increase in the activity of calpastatin, an endogenous inhibitor of calpains (Bardsley et al., 1992; Parr et al., 1992). More recently, it has been demonstrated that β2-adrenergic agonists might attenuate muscle atrophy through inhibitory effects on the ubiquitin-proteasome system, the main intracellular pathway for protein degradation in skeletal muscle (Yimlamai et al., 2005; Gonçalves et al., 2012). This effect is mediated through a cAMP/Akt-dependent pathway (Kline et al., 2007; Gonçalves et al., 2009, 2012), which leads to the phosphorylation of Foxo3a and, consequently, the suppression of atrogin-1/MAFbx and MuRF1, two ubiquitin E3-ligases involved in muscle atrophy (Bodine et al., 2001; Centner et al., 2001; Lecker et al., 2004; Sandri et al., 2004). Moreover, treatment with PDE inhibitors increased muscle cAMP levels and decreased the rate of total protein degradation in muscles from diabetic (Baviera et al., 2007) and fasted rodents (Lira et al., 2007) through a clear reduction in the activity of the Ca2+-dependent proteolytic system and the ubiquitin-proteasome system. The fact that the antiproteolytic effect of both β2 agonists (Gonçalves et al., 2012) and PDE inhibitors (Baviera et al., 2007) in vitro was inhibited by H89, a PKA inhibitor, and mimicked by 6-BNZ-cAMP, a PKA activator, further supports the idea that activation of the cAMP cascade via a PKA-dependent pathway is one of the regulatory mechanism(s) to prevent excessive skeletal muscle protein breakdown. Given that in dystrophic muscle the Ca2+-dependent proteolytic system and the ubiquitin-proteasomal system are activated on the one hand (Kar and Pearson, 1976; Spencer and Tidball, 1996; Kumamoto et al., 2000) and PKA signaling, on the other hand, is disturbed (Reynolds et al., 2008; Röder et al., 2009), it is reasonable to suggest that increased calpain and proteasome activities contribute to dystrophic pathology and, by extension, that protease inhibition by cAMP-inducing agents could be a treatment strategy for DMD.
Figure 3.
Hypothetical model of the mechanisms involved with the inhibition of the Ca2+-dependent and Ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic systems in skeletal muscle by catecholamines and β2-agonists. AC, adenylate cyclase; CREB, cAMP response element binding protein; IBMX, isobutylmethylxanthine; PKA*, activated PKA; PTX, pentoxifylline; ?, unknown effect.
On the origin and destination of catecholamines in skeletal muscle
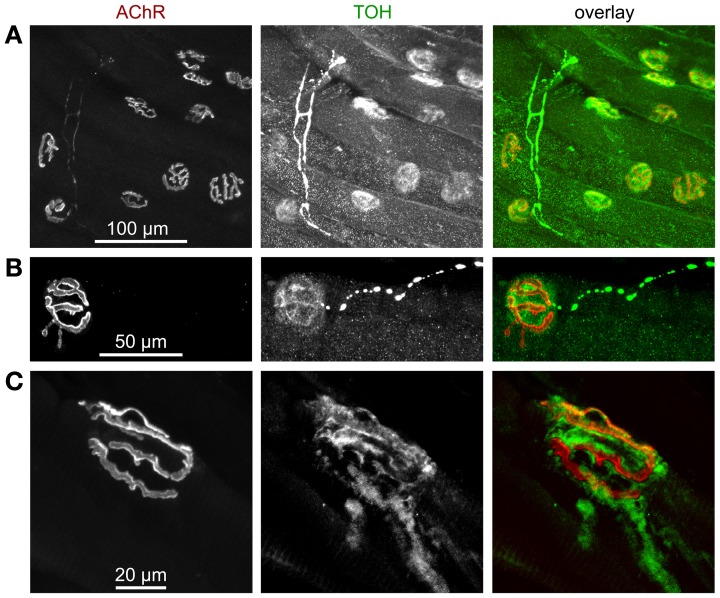
It is general knowledge that sympathetic first messengers can be released from either adrenal medulla as hormones or from sympathetic neurons as neurotransmitters directly onto target tissues (Mason, 1968). However, surprisingly little is known about the real contributions of these different modes of sympathetic activities in most tissues (Daly and McGrath, 2011) and this holds true also for skeletal muscle. Yet, to our knowledge, there are a few studies reporting on direct innervation of skeletal muscle fibers by non-myelinated, noradrenergic fibers (Boeke, 1909a,b, 1913; Barker and Saito, 1981; Tadaki et al., 1995), suggesting that sympathetic actions on skeletal muscle are at least partially mediated by neural mechanisms. Accordingly, a study using surgical ablation of sympathetic ganglia, which innervate hind limb muscles have shown that direct innervation of skeletal muscles by autonomic nerves is critical for muscle homeostasis (Navegantes et al., 2004) and a wealth of investigations has dealt with the effects of sympathetic agonists on skeletal muscle force potentiation and release of acetylcholine from motoneurons (see, e.g., Oliver and Schäfer, 1895; Goffart and Ritchie, 1952; Krnjevic and Miledi, 1958; Bowman and Raper, 1967). The latter are processes, which are likely to need fast regulation in the course of fight-or-flight situations. This triggered us to reinvestigate the distribution of sympathetic innervation in skeletal muscle and to address differences between sympathetic targets in healthy and dystrophic muscles. Thus, we first studied the distribution of the sympathetic neuron marker, tyrosine hydroxylase (TOH) in longitudinal sections of mouse hindlimb muscle and found this marker protein to be concentrated on top of most NMJs (Figure 4A). This is in accordance with previous studies carried out in several vertebrate species, including man (Chan-Palay et al., 1982a,b). In many cases, enrichments of TOH immunostaining in proximity to NMJs were connected to pearl chain-like processes, which are likely to represent sympathetic axons (Figure 4B). Notably, while previous investigators performed immunostainings on transverse muscle sections and thus proposed TOH to be present in the motoneuronal presynaptic portion of NMJs (Chan-Palay et al., 1982a,b), the analysis of our longitudinal slices revealed that TOH immunofluorescence does not match postsynaptic AChR staining as it would be typical for motoneuronal markers, but was mostly just in the gaps between the NMJ pretzel structure (Figure 4C). That fits to the older observations from Boeke based on tissue silver impregnation (Boeke, 1909a,b, 1913) and corroborates his suggestion that sympathetic neurons run and terminate next to motoneurons. Future investigations should be carried out to further strengthen this finding.
Figure 4.
Tyrosine hydroxylase (TOH) immunofluorescence is present in sparse axon-like processes and at NMJs. Mouse hindlimb muscles were sectioned and then stained with α-bungarotoxin-AlexaFluor555 (AChR) and an antibody against TOH. Then, confocal microscopy was performed. All panels show maximum z-projections of several optical slices. From left to right, fluorescence signals of AChR, TOH, and overlays are depicted. In overlays, AChR and TOH appear in red and green, respectively. (A) Overview picture showing that most NMJs display enrichments of TOH immunofluorescence. (B) Note thin and pearl chain-like TOH-positive process that ends next to TOH-positive accumulation, which shows a complementary distribution with respect to AChR. (C) Detail of a NMJ with TOH staining complementary to AChR labelling and with emanating axon-like process.
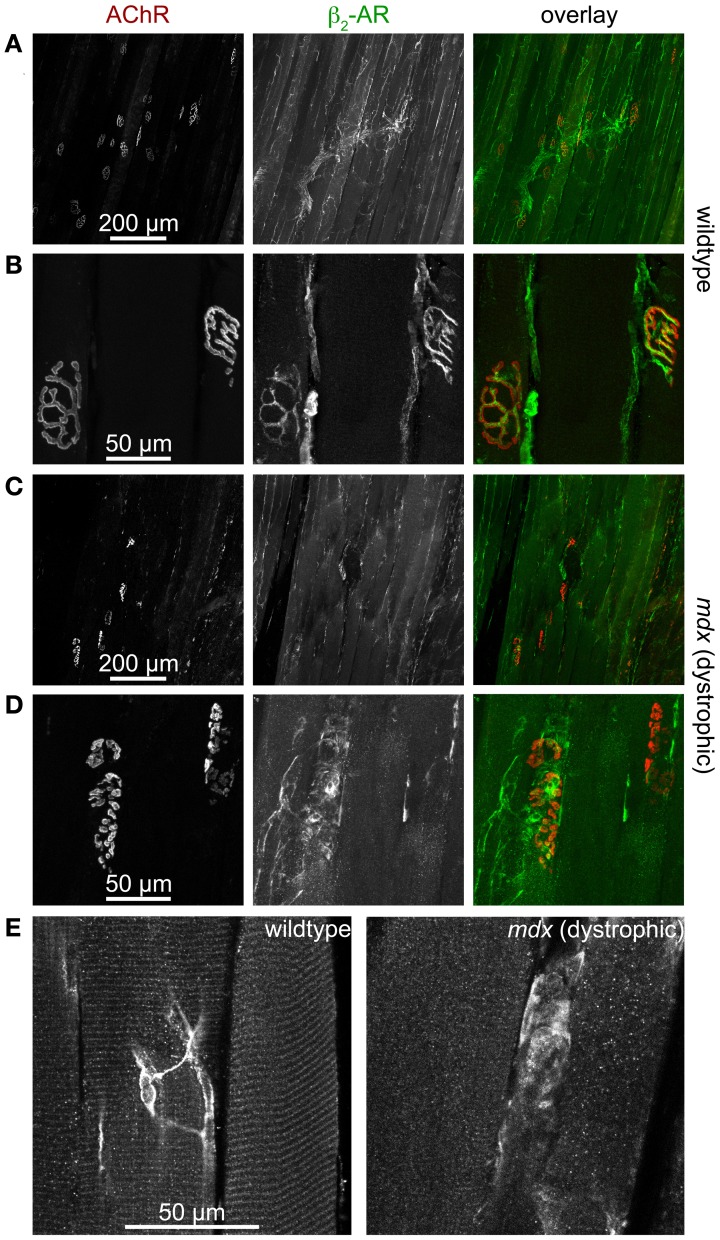
Next, we addressed the expression pattern of β2-AR in hindlimb muscle. This showed immunohistochemical signals of β2-AR in at least four different locations: (1) larger blood vessels (not depicted), (2) motoneurons (Figures 5A,B), (3) muscle fibers (Figure 5E, left panel), and (4) ill-defined anastomotic fibers (Figure 5E, on left panel see central part of the picture). Since the presence of β2-AR had been found by staining and anticipated to be present due to functional roles in blood vessels (Daly and McGrath, 2011), motoneurons (Melamed et al., 1976; Wohlberg et al., 1986; Bondok et al., 1988; Adachi et al., 1992; Parkis et al., 1995; Zeman et al., 2004; Tartas et al., 2010; Noga et al., 2011; Baker and Baker, 2012) and muscle fibers (Gross et al., 1976; Cairns and Dulhunty, 1993a,b; Cairns et al., 1993; Kokate et al., 1993; Navegantes et al., 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004; Prakash et al., 1999; Decostre et al., 2000; Gonçalves et al., 2012), our findings in wildtype muscles were corroborating previous reports. However, the difference between wildtype and dystrophic mdx muscles was striking, both with respect to neuronal as well as muscle staining: First, while the typical pretzel-shaped postsynaptic AChR signals in wildtype muscle were perfectly mirrored by presynaptic β2-AR staining (Figures 5A,B) in almost fibers, this was much rarer the case in mdx synapses (Figures 5C,D), which were also highly fragmented as reported previously (Torres and Duchen, 1987; Lyons and Slater, 1991; Grady et al., 2000). Second, while β2-AR immunofluorescence displayed a highly regular striated patterning in wildtype muscle (Figure 5E, left panel), it was almost uniformly distributed in many fibers from mdx muscles (Figure 5E, right panel). In summary, these data show that there are significant differences in distribution of β2-AR between healthy and dystrophic muscles. In the context of the PKA microdomain hypothesis this could be an additional level of dysregulation leading to alterations of cAMP with all the sequelae as discussed before.
Figure 5.
β2-AR-immunofluorescence is found in motoneurons and muscle fibers and is severely altered in dystrophic muscle. Mouse hindlimb muscles of wildtype (A,B,E left) or dystrophic mdx mice (C,D,E right) were sectioned and then stained with α-bungarotoxin-AlexaFluor555 (AChR) and an antibody against β2-AR. Then, confocal microscopy was performed. (A–D) Show maximum z-projections of several optical slices, in (E) single optical slices are depicted. From left to right, fluorescence signals of AChR, β2-AR, and overlays are depicted. In overlays, AChR and β2-AR appear in red and green, respectively. In wildtype muscles, β2-AR immunofluorescence covers entire motor nerve bundles (A) and perfectly matches the AChR arborized structures in the NMJ (B). This is typical for the distribution of motoneuronal markers. Conversely, β2-AR immunofluorescence is much sparser in dystrophic muscle (C) and exhibits only partial overlap with AChR staining (D). In muscle fibers of wildtype animals (E left) β2-AR is found in triple striations per sarcomer, similar to the distribution of PKA-RIIα (see Figure 2). This striation is mostly absent in dystrophic muscle (E right), where β2-AR distribution is often uniform along the fibers. Finally, anostomotic β2-AR-positive, axon-like processes of unknown identity are also often seen running along muscle fibers (E left).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. M. Mongillo (Padua/Italy), Dr. S. Schiaffino (Padua/Italy), and Dr. M. Zaccolo (Oxford/UK) for helpful discussions. Rüdiger Rudolf is supported by DFG grants RU923/7-1 and RU923/8-1, Siegfried Labeit by EU-network SarcoSI and DFG grant LA668/15-1, and Danilo Lustrino, Ísis C. Kettelhut and Luiz C. C. Navegantes by CNPQ (305149/2012-1) and FAPESP (12/05697-7 and 12/24524-6.) grants. We acknowledge support by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and Open Access Publishing Fund of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology.
References
- Adachi S., Oka J., Nagao T., Fukuda H. (1992). Activation of beta-adrenergic receptor induces Na(+)-dependent inward currents in acutely dissociated motoneurons of bullfrog spinal cord. Brain Res. 571, 79–88 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90511-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaaboune M., Culican S. M., Turney S. G., Lichtman J. W. (1999). Rapid and reversible effects of activity on acetylcholine receptor density at the neuromuscular junction in vivo. Science 286, 503–507 10.1126/science.286.5439.503 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altarejos J. Y., Montminy M. (2011). CREB and the CRTC co-activators: sensors for hormonal and metabolic signals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 12, 141–151 10.1038/nrm3072 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apel E. D., Glass D. J., Moscoso L. M., Yancopoulos G. D., Sanes J. R. (1997). Rapsyn is required for MuSK signaling and recruits synaptic components to a MuSK-containing scaffold. Neuron 18, 623–635 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80303-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arreola J., Calvo J., Garcia M. C., Sanchez J. A. (1987). Modulation of calcium channels of twitch skeletal muscle fibres of the frog by adrenaline and cyclic adenosine monophosphate. J. Physiol. 393, 307–330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacurau A. V., Jardim M. A., Ferreira J. C., Bechara L. R., Bueno C. R., Jr., Alba-Loureiro T. C., et al. (2009). Sympathetic hyperactivity differentially affects skeletal muscle mass in developing heart failure: role of exercise training. J. Appl. Physiol. 106, 1631–1640 10.1152/japplphysiol.91067.2008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker M. R., Baker S. N. (2012). Beta-adrenergic modulation of tremor and corticomuscular coherence in humans. PLoS ONE 7:e49088 10.1371/journal.pone.0049088 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardsley R. G., Allcock S. M., Dawson J. M., Dumelow N. W., Higgins J. A., Lasslett Y. V., et al. (1992). Effect of beta-agonists on expression of calpain and calpastatin activity in skeletal muscle. Biochimie 74, 267–273 10.1016/0300-9084(92)90125-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Saito M. (1981). Autonomic innervation of receptors and muscle fibres in cat skeletal muscle. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 212, 317–332 10.1098/rspb.1981.0042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barradeau S., Imaizumi-Scherrer T., Weiss M. C., Faust D. M. (2001). Muscle-regulated expression and determinants for neuromuscular junctional localization of the mouse RIalpha regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98, 5037–5042 10.1073/pnas.081393598 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barradeau S., Imaizumi-Scherrer T., Weiss M. C., Faust D. M. (2002). Intracellular targeting of the type-I alpha regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 12, 235–241 10.1016/S1050-1738(02)00167-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baviera A. M., Zanon N. M., Carvalho Navegantes L. C., Migliorini R. H., Do Carmo Kettelhut I. (2007). Pentoxifylline inhibits Ca2+-dependent and ATP proteasome-dependent proteolysis in skeletal muscle from acutely diabetic rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 292, E702–E708 10.1152/ajpendo.00147.2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Brunton L. L. (2002). Cyclic nucleotide research – still expanding after half a century. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 710–718 10.1038/nrm911 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berdeaux R., Stewart R. (2012). cAMP signaling in skeletal muscle adaptation: hypertrophy, metabolism, and regeneration. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 303, E1–E17 10.1152/ajpendo.00555.2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom T. J. (2002). Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozymes expressed in mouse skeletal muscle. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 80, 1132–1135 10.1139/y02-149 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodine S. C., Latres E., Baumhueter S., Lai V. K., Nunez L., Clarke B. A., et al. (2001). Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science 294, 1704–1708 10.1126/science.1065874 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. (1909a). Die motorische Endplatte bei den höheren Vertebraten, ihre Entwickelung, Form und Zusammenhang mit der Muskelfaser. Anat. Anz. 35, 240–256 [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. (1909b). Ueber eine aus marklosen Fasern hervorgehende zweite Art von hypolemmalen Nervenendplatten bei den quergestreiften Muskelfasern der Vertebraten. Anat. Anz. 35, 481–484 [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. (1913). Die doppelte (motorische und sympathische) efferente Innervation der quergestreiften Muskelfasern. Anat. Anz. 44, 343–356 [Google Scholar]
- Bondok A. A., Botros K. G., El-Mohandes E. A. (1988). Fluorescence histochemical study of the localisation and distribution of beta-adrenergic receptor sites in the spinal cord and cerebellum of the chicken. J. Anat. 160, 167–174 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L. (2003). Epac: a new cAMP target and new avenues in cAMP research. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 733–738 10.1038/nrm1197 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman W. C., Raper C. (1967). Adrenotropic receptors in skeletal muscle. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 139, 741–753 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb41241.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruneau E., Sutter D., Hume R. I., Akaaboune M. (2005). Identification of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor recycling and its role in maintaining receptor density at the neuromuscular junction in vivo. J. Neurosci. 25, 9949–9959 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3169-05.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruneau E. G., Akaaboune M. (2006). The dynamics of recycled acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction in vivo. Development 133, 4485–4493 10.1242/dev.02619 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burden S. J., Yumoto N., Zhang W. (2013). The Role of MuSK in Synapse Formation and Neuromuscular Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 5:a009167 10.1101/cshperspect.a009167 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns S. P., Dulhunty A. F. (1993a). Beta-adrenergic potentiation of E-C coupling increases force in rat skeletal muscle. Muscle Nerve 16, 1317–1325 10.1002/mus.880161208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns S. P., Dulhunty A. F. (1993b). The effects of beta-adrenoceptor activation on contraction in isolated fast- and slow-twitch skeletal muscle fibres of the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 110, 1133–1141 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13932.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns S. P., Westerblad H., Allen D. G. (1993). Changes of tension and [Ca2+]i during beta-adrenoceptor activation of single, intact fibres from mouse skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch. 425, 150–155 10.1007/BF00374515 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centner T., Yano J., Kimura E., McElhinny A. S., Pelin K., Witt C. C., et al. (2001). Identification of muscle specific ring finger proteins as potential regulators of the titin kinase domain. J. Mol. Biol. 306, 717–726 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4448 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V., Engel A. G., Palay S. L., Wu J. Y. (1982a). Synthesizing enzymes for four neuroactive substances in motor neurons and neuromuscular junctions: light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 6717–6721 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6717 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V., Engel A. G., Wu J. Y., Palay S. L. (1982b). Coexistence in human and primate neuromuscular junctions of enzymes synthesizing acetylcholine, catecholamine, taurine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 7027–7030 10.1073/pnas.79.22.7027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. R., Berrera M., Reischl M., Strack S., Albrizio M., Roder I. V., et al. (2012). Rapsyn mediates subsynaptic anchoring of PKA type I and stabilisation of acetylcholine receptor in vivo. J. Cell Sci. 125, 714–723 10.1242/jcs.092361 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti M., Beavo J. (2007). Biochemistry and physiology of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: essential components in cyclic nucleotide signaling. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 76, 481–511 10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.060305.150444 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly C. J., McGrath J. C. (2011). Previously unsuspected widespread cellular and tissue distribution of beta-adrenoceptors and its relevance to drug action. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 32, 219–226 10.1016/j.tips.2011.02.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decostre V., Gillis J. M., Gailly P. (2000). Effect of adrenaline on the post-tetanic potentiation in mouse skeletal muscle. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 21, 247–254 10.1023/A:1005685900196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Benedetto G., Zoccarato A., Lissandron V., Terrin A., Li X., Houslay M. D., et al. (2008). Protein kinase A type I and type II define distinct intracellular signaling compartments. Circ. Res. 103, 836–844 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.174813 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham J. T., Brand O. M., Arnold M., Reynolds J. G., Muthukumar L., Weiler H., et al. (2006). Myospryn is a direct transcriptional target for MEF2A that encodes a striated muscle, alpha-actinin-interacting, costamere-localized protein. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 6841–6849 10.1074/jbc.M510499200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgeworth H. (1930). A report of progress on the use of ephedrine in a case of myasthenia gravis. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 94, 1136 10.1001/jama.1930.27120410003009c [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards H. V., Christian F., Baillie G. S. (2012). cAMP: novel concepts in compartmentalised signalling. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 23, 181–190 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.09.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Lindstrom J. M., Lambert E. H., Lennon V. A. (1977). Ultrastructural localization of the acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis and in its experimental autoimmune model. Neurology 27, 307–315 10.1212/WNL.27.4.307 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M. (1979). Control of acetylcholine receptors in skeletal muscle. Physiol. Rev. 59, 165–227 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlayson S., Spillane J., Kullmann D. M., Howard R., Webster R., Palace J., et al. (2013). Slow channel congenital myasthenic syndrome responsive to a combination of fluoxetine and salbutamol. Muscle Nerve 47, 279–282 10.1002/mus.23534 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine B., Klarsfeld A., Changeux J. P. (1987). Calcitonin gene-related peptide and muscle activity regulate acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit mRNA levels by distinct intracellular pathways. J. Cell Biol. 105, 1337–1342 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1337 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis S. H., Blount M. A., Corbin J. D. (2011). Mammalian cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: molecular mechanisms and physiological functions. Physiol. Rev. 91, 651–690 10.1152/physrev.00030.2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C. (1993). Regulation of ion channel distribution at synapses. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 16, 347–368 10.1146/annurev.ne.16.030193.002023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrer C., Gautam M., Sugiyama J. E., Hall Z. W. (1999). Roles of rapsyn and agrin in interaction of postsynaptic proteins with acetylcholine receptors. J. Neurosci. 19, 6405–6416 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fumagalli G., Engel A. G., Lindstrom J. (1982). Ultrastructural aspects of acetylcholine receptor turnover at the normal end-plate and in autoimmune myasthenia gravis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 41, 567–579 10.1097/00005072-198211000-00001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautam M., Dechiara T. M., Glass D. J., Yancopoulos G. D., Sanes J. R. (1999). Distinct phenotypes of mutant mice lacking agrin, MuSK, or rapsyn. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 114, 171–178 10.1016/S0165-3806(99)00013-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie S. K., Balasubramanian S., Fung E. T., Huganir R. L. (1996). Rapsyn clusters and activates the synapse-specific receptor tyrosine kinase MuSK. Neuron 16, 953–962 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80118-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. J. (2010). Signaling pathways perturbing muscle mass. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 13, 225–229 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32833862df [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. J., Yancopoulos G. D. (1997). Sequential roles of agrin, MuSK and rapsyn during neuromuscular junction formation. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 7, 379–384 10.1016/S0959-4388(97)80066-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goffart M., Ritchie J. M. (1952). The effect of adrenaline on the contraction of mammalian skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 116, 357–371 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves D. A., Lira E. C., Baviera A. M., Cao P., Zanon N. M., Arany Z., et al. (2009). Mechanisms involved in 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate-mediated inhibition of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in skeletal muscle. Endocrinology 150, 5395–5404 10.1210/en.2009-0428 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves D. A., Silveira W. A., Lira E. C., Graca F. A., Paula-Gomes S., Zanon N. M., et al. (2012). Clenbuterol suppresses proteasomal and lysosomal proteolysis and atrophy-related genes in denervated rat soleus muscles independently of Akt. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 302, E123–E133 10.1152/ajpendo.00188.2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady R. M., Zhou H., Cunningham J. M., Henry M. D., Campbell K. P., Sanes J. R. (2000). Maturation and maintenance of the neuromuscular synapse: genetic evidence for roles of the dystrophin–glycoprotein complex. Neuron 25, 279–293 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80894-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. R., Mayer S. E., Longshore M. A. (1976). Stimulation of glycogenolysis by beta adrenergic agonists in skeletal muscle of mice with the phosphorylase kinase deficiency mutation (I strain). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 198, 526–538 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle R. T., Hodge K. M., Cody D. B., Sheldon R. J., Kobilka B. K., Isfort R. J. (2002). Skeletal muscle hypertrophy and anti-atrophy effects of clenbuterol are mediated by the beta2-adrenergic receptor. Muscle Nerve 25, 729–734 10.1002/mus.10092 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle R. T., Lefever F. R., Dolan E. T., Reichart D. L., Dietrich J. A., Gropp K. E., et al. (2007). Corticortophin releasing factor 2 receptor agonist treatment significantly slows disease progression in mdx mice. BMC Med. 5:18 10.1186/1741-7015-5-18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. R., Gnanasambandan K. (2013). Structure and activation of MuSK, a receptor tyrosine kinase central to neuromuscular junction formation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1834, 2166–2169 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.02.034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi-Scherrer T., Faust D. M., Benichou J. C., Hellio R., Weiss M. C. (1996). Accumulation in fetal muscle and localization to the neuromuscular junction of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A regulatory and catalytic subunits RI alpha and C alpha. J. Cell Biol. 134, 1241–1254 10.1083/jcb.134.5.1241 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Indolfi C., Avvedimento E. V., Di Lorenzo E., Esposito G., Rapacciuolo A., Giuliano P., et al. (1997). Activation of cAMP-PKA signaling in vivo inhibits smooth muscle cell proliferation induced by vascular injury. Nat. Med. 3, 775–779 10.1038/nm0797-775 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean-Baptiste G., Yang Z., Khoury C., Gaudio S., Greenwood M. T. (2005). Peptide and non-peptide G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) in skeletal muscle. Peptides 26, 1528–1536 10.1016/j.peptides.2005.03.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner M. J., Casey D. P. (2009). The catecholamines strike back. What NO does not do. Circ. J. 73, 1783–1792 10.1253/circj.CJ-09-0559 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kar N. C., Pearson C. M. (1976). A calcium-activated neutral protease in normal and dystrophic human muscle. Clin. Chim. Acta 73, 293–297 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90175-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielbasa O. M., Reynolds J. G., Wu C. L., Snyder C. M., Cho M. Y., Weiler H., et al. (2011). Myospryn is a calcineurin-interacting protein that negatively modulates slow-fiber-type transformation and skeletal muscle regeneration. FASEB J. 25, 2276–2286 10.1096/fj.10-169219 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim N., Stiegler A. L., Cameron T. O., Hallock P. T., Gomez A. M., Huang J. H., et al. (2008). Lrp4 is a receptor for Agrin and forms a complex with MuSK. Cell 135, 334–342 10.1016/j.cell.2008.10.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline W. O., Panaro F. J., Yang H., Bodine S. C. (2007). Rapamycin inhibits the growth and muscle-sparing effects of clenbuterol. J. Appl. Physiol. 102, 740–747 10.1152/japplphysiol.00873.2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokate T. G., Heiny J. A., Sperelakis N. (1993). Stimulation of the slow calcium current in bullfrog skeletal muscle fibers by cAMP and cGMP. Am. J. Physiol. 265, C47–C53 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouloumenta A., Mavroidis M., Capetanaki Y. (2007). Proper perinuclear localization of the TRIM-like protein myospryn requires its binding partner desmin. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 35211–35221 10.1074/jbc.M704733200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjevic K., Miledi R. (1958). Some effects produced by adrenaline upon neuromuscular propagation in rats. J. Physiol. 141, 291–304 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto T., Fujimoto S., Ito T., Horinouchi H., Ueyama H., Tsuda T. (2000). Proteasome expression in the skeletal muscles of patients with muscular dystrophy. Acta Neuropathol. 100, 595–602 10.1007/s004010000229 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanuza M. A., Garcia N., Santafe M., Gonzalez C. M., Alonso I., Nelson P. G., et al. (2002). Pre- and postsynaptic maturation of the neuromuscular junction during neonatal synapse elimination depends on protein kinase C. J. Neurosci. Res. 67, 607–617 10.1002/jnr.10122 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lashley D., Palace J., Jayawant S., Robb S., Beeson D. (2010). Ephedrine treatment in congenital myasthenic syndrome due to mutations in DOK7. Neurology 74, 1517–1523 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181dd43bf [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecker S. H., Jagoe R. T., Gilbert A., Gomes M., Baracos V., Bailey J., et al. (2004). Multiple types of skeletal muscle atrophy involve a common program of changes in gene expression. FASEB J. 18, 39–51 10.1096/fj.03-0610com [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt T. A., Loring R. H., Salpeter M. M. (1980). Neuronal control of acetylcholine receptor turnover rate at a vertebrate neuromuscular junction. Science 210, 550–551 10.1126/science.7423205 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt T. A., Salpeter M. M. (1981). Denervated endplates have a dual population of junctional acetylcholine receptors. Nature 291, 239–241 10.1038/291239a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M. X., Jia M., Jiang H., Dunlap V., Nelson P. G. (2001). Opposing actions of protein kinase A and C mediate Hebbian synaptic plasticity. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 871–872 10.1038/nn0901-871 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M. X., Jia M., Yang L. X., Dunlap V., Nelson P. G. (2002). Pre- and postsynaptic mechanisms in Hebbian activity-dependent synapse modification. J. Neurobiol. 52, 241–250 10.1002/neu.10089 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liewluck T., Selcen D., Engel A. G. (2011). Beneficial effects of albuterol in congenital endplate acetylcholinesterase deficiency and Dok-7 myasthenia. Muscle Nerve 44, 789–794 10.1002/mus.22176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liggett S. B., Raymond J. R. (1993). Pharmacology and molecular biology of adrenergic receptors. Baillieres Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 7, 279–306 10.1016/S0950-351X(05)80178-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lira E. C., Graca F. A., Gonçalves D. A., Zanon N. M., Baviera A. M., Strindberg L., et al. (2007). Cyclic adenosine monophosphate-phosphodiesterase inhibitors reduce skeletal muscle protein catabolism in septic rats. Shock 27, 687–694 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31802e43a6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loring R. H., Salpeter M. M. (1980). Denervation increases turnover rate of junctional acetylcholine receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 2293–2297 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2293 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B., Fu W. M., Greengard P., Poo M. M. (1993). Calcitonin gene-related peptide potentiates synaptic responses at developing neuromuscular junction. Nature 363, 76–79 10.1038/363076a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch G. S., Ryall J. G. (2008). Role of beta-adrenoceptor signaling in skeletal muscle: implications for muscle wasting and disease. Physiol. Rev. 88, 729–767 10.1152/physrev.00028.2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons P. R., Slater C. R. (1991). Structure and function of the neuromuscular junction in young adult mdx mice. J. Neurocytol. 20, 969–981 10.1007/BF01187915 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchand S., Bignami F., Stetzkowski-Marden F., Cartaud J. (2000). The myristoylated protein rapsyn is cotargeted with the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor to the postsynaptic membrane via the exocytic pathway. J. Neurosci. 20, 521–528 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchand S., Cartaud J. (2002). Targeted trafficking of neurotransmitter receptors to synaptic sites. Mol. Neurobiol. 26, 117–135 10.1385/MN:26:1:117 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchand S., Devillers-Thiery A., Pons S., Changeux J. P., Cartaud J. (2002). Rapsyn escorts the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor along the exocytic pathway via association with lipid rafts. J. Neurosci. 22, 8891–8901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. M. (1982). The influence of the sympathetic nervous system on individual vessels of the microcirculation of skeletal muscle of the rat. J. Physiol. 332, 169–186 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. W. (1968). A review of psychoendocrine research on the sympathetic-adrenal medullary system. Psychosom. Med. 30(Suppl.), 631–653 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melamed E., Lahav M., Atlas D. (1976). Histochemical evidence for beta-adrenergic receptors in the rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 116, 511–515 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90499-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles K., Anthony D. T., Rubin L. L., Greengard P., Huganir R. L. (1987). Regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor phosphorylation in rat myotubes by forskolin and cAMP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 6591–6595 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6591 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles K., Greengard P., Huganir R. L. (1989). Calcitonin gene-related peptide regulates phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in rat myotubes. Neuron 2, 1517–1524 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90198-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulle C., Benoit P., Pinset C., Roa M., Changeux J. P. (1988). Calcitonin gene-related peptide enhances the rate of desensitization of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in cultured mouse muscle cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 5728–5732 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5728 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navegantes L. C., Machado C. R., Resano N. M., Migliorini R. H., Kettelhut I. C. (2003). Beta2-agonists and cAMP inhibit protein degradation in isolated chick (Gallus domesticus) skeletal muscle. Br. Poult. Sci. 44, 149–154 10.1080/0007166031000085355 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navegantes L. C., Migliorini R. H., Do Carmo Kettelhut I. (2002). Adrenergic control of protein metabolism in skeletal muscle. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 5, 281–286 10.1097/00075197-200205000-00007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navegantes L. C., Resano N. M., Baviera A. M., Migliorini R. H., Kettelhut I. C. (2004). Effect of sympathetic denervation on the rate of protein synthesis in rat skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 286, E642–E647 10.1152/ajpendo.00371.2003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navegantes L. C., Resano N. M., Migliorini R. H., Kettelhut I. C. (1999). Effect of guanethidine-induced adrenergic blockade on the different proteolytic systems in rat skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 277, E883–E889 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navegantes L. C., Resano N. M., Migliorini R. H., Kettelhut I. C. (2000). Role of adrenoceptors and cAMP on the catecholamine-induced inhibition of proteolysis in rat skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 279, E663–E668 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navegantes L. C., Resano N. M., Migliorini R. H., Kettelhut I. C. (2001). Catecholamines inhibit Ca(2+)-dependent proteolysis in rat skeletal muscle through beta(2)-adrenoceptors and cAMP. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 281, E449–E454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Lanuza M. A., Jia M., Li M. X., Tomas J. (2003). Phosphorylation reactions in activity-dependent synapse modification at the neuromuscular junction during development. J. Neurocytol. 32, 803–816 10.1023/B:NEUR.0000020625.70284.a6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubig R. R., Krodel E. K., Boyd N. D., Cohen J. B. (1979). Acetylcholine and local anesthetic binding to Torpedo nicotinic postsynaptic membranes after removal of nonreceptor peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 690–694 10.1073/pnas.76.2.690 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New H. V., Mudge A. W. (1986). Calcitonin gene-related peptide regulates muscle acetylcholine receptor synthesis. Nature 323, 809–811 10.1038/323809a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaev V. O., Bunemann M., Hein L., Hannawacker A., Lohse M. J. (2004). Novel single chain cAMP sensors for receptor-induced signal propagation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 37215–37218 10.1074/jbc.C400302200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitkin R. M., Smith M. A., Magill C., Fallon J. R., Yao Y. M., Wallace B. G., et al. (1987). Identification of agrin, a synaptic organizing protein from Torpedo electric organ. J. Cell Biol. 105, 2471–2478 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2471 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noga B. R., Johnson D. M., Riesgo M. I., Pinzon A. (2011). Locomotor-activated neurons of the cat. II. Noradrenergic innervation and colocalization with NEalpha 1a or NEalpha 2b receptors in the thoraco-lumbar spinal cord. J. Neurophysiol. 105, 1835–1849 10.1152/jn.00342.2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver G., Schäfer E. A. (1895). The physiological effects of the extracts of the suprarenal capsules. J. Physiol. 18, 230–276 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omori K., Kotera J. (2007). Overview of PDEs and their regulation. Circ. Res. 100, 309–327 10.1161/01.RES.0000256354.95791.f1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palace J., Beeson D. (2008). The congenital myasthenic syndromes. J. Neuroimmunol. 201–202, 2–5. 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.05.030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkis M. A., Bayliss D. A., Berger A. J. (1995). Actions of norepinephrine on rat hypoglossal motoneurons. J. Neurophysiol. 74, 1911–1919 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parr T., Bardsley R. G., Gilmour R. S., Buttery P. J. (1992). Changes in calpain and calpastatin mRNA induced by beta-adrenergic stimulation of bovine skeletal muscle. Eur. J. Biochem. 208, 333–339 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17191.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins G. A., Wang L., Huang L. J., Humphries K., Yao V. J., Martone M., et al. (2001). PKA, PKC, and AKAP localization in and around the neuromuscular junction. BMC Neurosci. 2:17 10.1186/1471-2202-2-17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter S., Froehner S. C. (1985). Interaction of the 43K protein with components of Torpedo postsynaptic membranes. Biochemistry 24, 425–432 10.1021/bi00323a028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poyner D. R. (1992). Calcitonin gene-related peptide: multiple actions, multiple receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 56, 23–51 10.1016/0163-7258(92)90036-Y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash Y. S., Van Der Heijden H. F., Gallant E. M., Sieck G. C. (1999). Effect of beta-adrenoceptor activation on [Ca2+]i regulation in murine skeletal myotubes. Am. J. Physiol. 276, C1038–C1045 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramarao M. K., Bianchetta M. J., Lanken J., Cohen J. B. (2001). Role of rapsyn tetratricopeptide repeat and coiled-coil domains in self-association and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor clustering. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 7475–7483 10.1074/jbc.M009888200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramarao M. K., Cohen J. B. (1998). Mechanism of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor cluster formation by rapsyn. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95, 4007–4012 10.1073/pnas.95.7.4007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeds P. J., Hay S. M., Dorwood P. M., Palmer R. M. (1986). Stimulation of muscle growth by clenbuterol: lack of effect on muscle protein biosynthesis. Br. J. Nutr. 56, 249–258 10.1079/BJN19860104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reutenauer-Patte J., Boittin F. X., Patthey-Vuadens O., Ruegg U. T., Dorchies O. M. (2012). Urocortins improve dystrophic skeletal muscle structure and function through both PKA- and Epac-dependent pathways. Am. J. Pathol. 180, 749–762 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.10.038 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. G., McCalmon S. A., Donaghey J. A., Naya F. J. (2008). Deregulated protein kinase A signaling and myospryn expression in muscular dystrophy. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 8070–8074 10.1074/jbc.C700221200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. G., McCalmon S. A., Tomczyk T., Naya F. J. (2007). Identification and mapping of protein kinase A binding sites in the costameric protein myospryn. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1773, 891–902 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.04.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röder I. V., Choi K. R., Reischl M., Petersen Y., Diefenbacher M. E., Zaccolo M., et al. (2010). Myosin Va cooperates with PKA RIalpha to mediate maintenance of the endplate in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 2031–2036 10.1073/pnas.0914087107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röder I. V., Lissandron V., Martin J., Petersen Y., Di Benedetto G., Zaccolo M., et al. (2009). PKA microdomain organisation and cAMP handling in healthy and dystrophic muscle in vivo. Cell. Signal. 21, 819–826 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.01.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röder I. V., Strack S., Reischl M., Dahley O., Khan M. M., Kassel O., et al. (2012). Participation of myosin Va and Pka type I in the regeneration of neuromuscular junctions. PLoS ONE 7:e40860 10.1371/journal.pone.0040860 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruegg M. A., Bixby J. L. (1998). Agrin orchestrates synaptic differentiation at the vertebrate neuromuscular junction. Trends Neurosci. 21, 22–27 10.1016/S0166-2236(97)01154-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salpeter M. M., Loring R. H. (1985). Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in vertebrate muscle: properties, distribution and neural control. Prog. Neurobiol. 25, 297–325 10.1016/0301-0082(85)90018-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltin B., Radegran G., Koskolou M. D., Roach R. C. (1998). Skeletal muscle blood flow in humans and its regulation during exercise. Acta Physiol. Scand. 162, 421–436 10.1046/j.1365-201X.1998.0293e.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri M. (2008). Signaling in muscle atrophy and hypertrophy. Physiology (Bethesda) 23, 160–170 10.1152/physiol.00041.2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri M., Sandri C., Gilbert A., Skurk C., Calabria E., Picard A., et al. (2004). Foxo transcription factors induce the atrophy-related ubiquitin ligase atrogin-1 and cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Cell 117, 399–412 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00400-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarparanta J. (2008). Biology of myospryn: what's known? J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 29, 177–180 10.1007/s10974-008-9165-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarparanta J., Blandin G., Charton K., Vihola A., Marchand S., Milic A., et al. (2010). Interactions with M-band titin and calpain 3 link myospryn (CMYA5) to tibial and limb-girdle muscular dystrophies. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 30304–30315 10.1074/jbc.M110.108720 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schara U., Barisic N., Deschauer M., Lindberg C., Straub V., Strigl-Pill N., et al. (2009). Ephedrine therapy in eight patients with congenital myasthenic syndrome due to DOK7 mutations. Neuromuscul. Disord. 19, 828–832 10.1016/j.nmd.2009.09.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. D., Dessauer C. W., Tasken K. (2013). Creating order from chaos: cellular regulation by kinase anchoring. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 53, 187–210 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-011112-140204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiao T., Fond A., Deng B., Wehling-Henricks M., Adams M. E., Froehner S. C., et al. (2004). Defects in neuromuscular junction structure in dystrophic muscle are corrected by expression of a NOS transgene in dystrophin-deficient muscles, but not in muscles lacking alpha- and beta1-syntrophins. Hum. Mol. Genet. 13, 1873–1884 10.1093/hmg/ddh204 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyng S. L., Xu R., Salpeter M. M. (1991). Cyclic AMP stabilizes the degradation of original junctional acetylcholine receptors in denervated muscle. Neuron 6, 469–475 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90254-W [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel A., Weber M., Changeux J. P. (1977). Large-scale purification of the acetylcholine-receptor protein in its membrane-bound and detergent-extracted forms from Torpedo marmorata electric organ. Eur. J. Biochem. 80, 215–224 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11874.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate K., Newby A. C. (1990). Serum-induced proliferation of rabbit aortic smooth muscle cells from the contractile state is inhibited by 8-Br-cAMP but not 8-Br-cGMP. Atherosclerosis 82, 113–123 10.1016/0021-9150(90)90150-H [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer M. J., Tidball J. G. (1996). Calpain translocation during muscle fiber necrosis and regeneration in dystrophin-deficient mice. Exp. Cell Res. 226, 264–272 10.1006/excr.1996.0227 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. F., Drachman D. B. (1981). Denervation accelerates the degradation of junctional acetylcholine receptors. Exp. Neurol. 73, 390–396 10.1016/0014-4886(81)90274-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. F., Drachman D. B. (1983). Rapid degradation of “new” acetylcholine receptors at neuromuscular junctions. Science 222, 67–69 10.1126/science.6623057 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg S. F., Brunton L. L. (2001). Compartmentation of G protein-coupled signaling pathways in cardiac myocytes. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 41, 751–773 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.41.1.751 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadaki N., Hisa Y., Uno T., Koike S., Okamura H., Ibata Y. (1995). Neurotransmitters for the canine inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 113, 755–759 10.1016/S0194-5998(95)70016-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Insel P. A. (2004). GPCR expression in the heart; “new” receptors in myocytes and fibroblasts. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 14, 94–99 10.1016/j.tcm.2003.12.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartas M., Morin F., Barriere G., Goillandeau M., Lacaille J. C., Cazalets J. R., et al. (2010). Noradrenergic modulation of intrinsic and synaptic properties of lumbar motoneurons in the neonatal rat spinal cord. Front Neural Circuits 4:4 10.3389/neuro.04.004.2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Kim C., Cheng C. Y., Brown S. H., Wu J., Kannan N. (2008). Signaling through cAMP and cAMP-dependent protein kinase: diverse strategies for drug design. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1784, 16–26 10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.10.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson P. R., Wilson J. W., Stewart A. G. (1994). Inhibition by salbutamol of the proliferation of human airway smooth muscle cells grown in culture. Br. J. Pharmacol. 111, 641–647 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14784.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres L. F., Duchen L. W. (1987). The mutant mdx: inherited myopathy in the mouse. Morphological studies of nerves, muscles and end-plates. Brain 110(Pt. 2), 269–299 10.1093/brain/110.2.269 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanamaker C. P., Green W. N. (2005). N-linked glycosylation is required for nicotinic receptor assembly but not for subunit associations with calnexin. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 33800–33810 10.1074/jbc.M501813200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanamaker C. P., Green W. N. (2007). Endoplasmic reticulum chaperones stabilize nicotinic receptor subunits and regulate receptor assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 31113–31123 10.1074/jbc.M705369200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlberg C. J., Davidoff R. A., Hackman J. C. (1986). Analysis of the responses of frog motoneurons to epinephrine and norepinephrine. Neurosci. Lett. 69, 150–155 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90594-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu R., Salpeter M. M. (1997). Acetylcholine receptors in innervated muscles of dystrophic mdx mice degrade as after denervation. J. Neurosci. 17, 8194–8200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu R., Salpeter M. M. (1999). Rate constants of acetylcholine receptor internalization and degradation in mouse muscles. J. Cell. Physiol. 181, 107–112 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yimlamai T., Dodd S. L., Borst S. E., Park S. (2005). Clenbuterol induces muscle-specific attenuation of atrophy through effects on the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. J. Appl. Physiol. 99, 71–80 10.1152/japplphysiol.00448.2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaccolo M. (2011). Spatial control of cAMP signalling in health and disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 11, 649–655 10.1016/j.coph.2011.09.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaccolo M., Magalhaes P., Pozzan T. (2002). Compartmentalisation of cAMP and Ca(2+) signals. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14, 160–166 10.1016/S0955-0674(02)00316-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaglia T., Milan G., Franzoso M., Bertaggia E., Pianca N., Piasentini E., et al. (2013). Cardiac sympathetic neurons provide trophic signal to the heart via beta2-adrenoceptor-dependent regulation of proteolysis. Cardiovasc. Res. 97, 240–250 10.1093/cvr/cvs320 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeman R. J., Peng H., Etlinger J. D. (2004). Clenbuterol retards loss of motor function in motor neuron degeneration mice. Exp. Neurol. 187, 460–467 10.1016/j.expneurol.2004.03.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B., Luo S., Wang Q., Suzuki T., Xiong W. C., Mei L. (2008). LRP4 serves as a coreceptor of agrin. Neuron 60, 285–297 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.10.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zong Y., Zhang B., Gu S., Lee K., Zhou J., Yao G., et al. (2012). Structural basis of agrin-LRP4-MuSK signaling. Genes Dev. 26, 247–258 10.1101/gad.180885.111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]