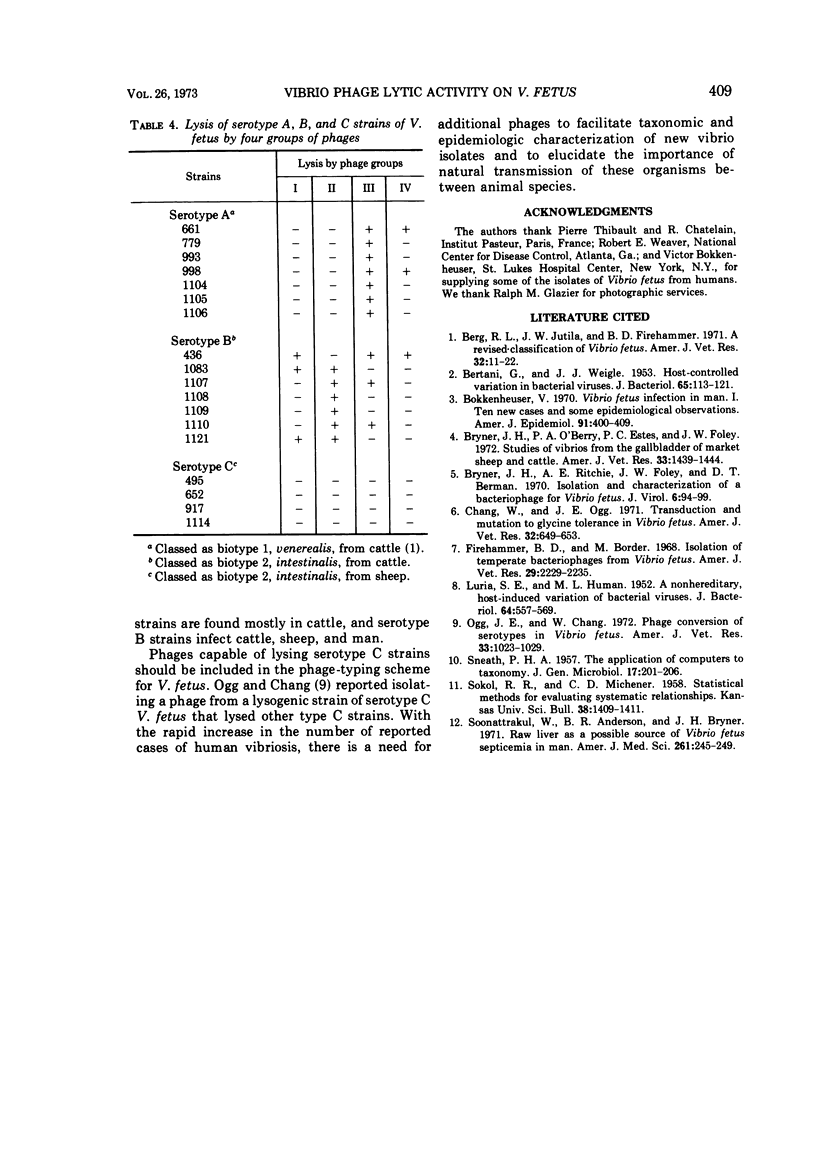
Abstract
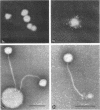
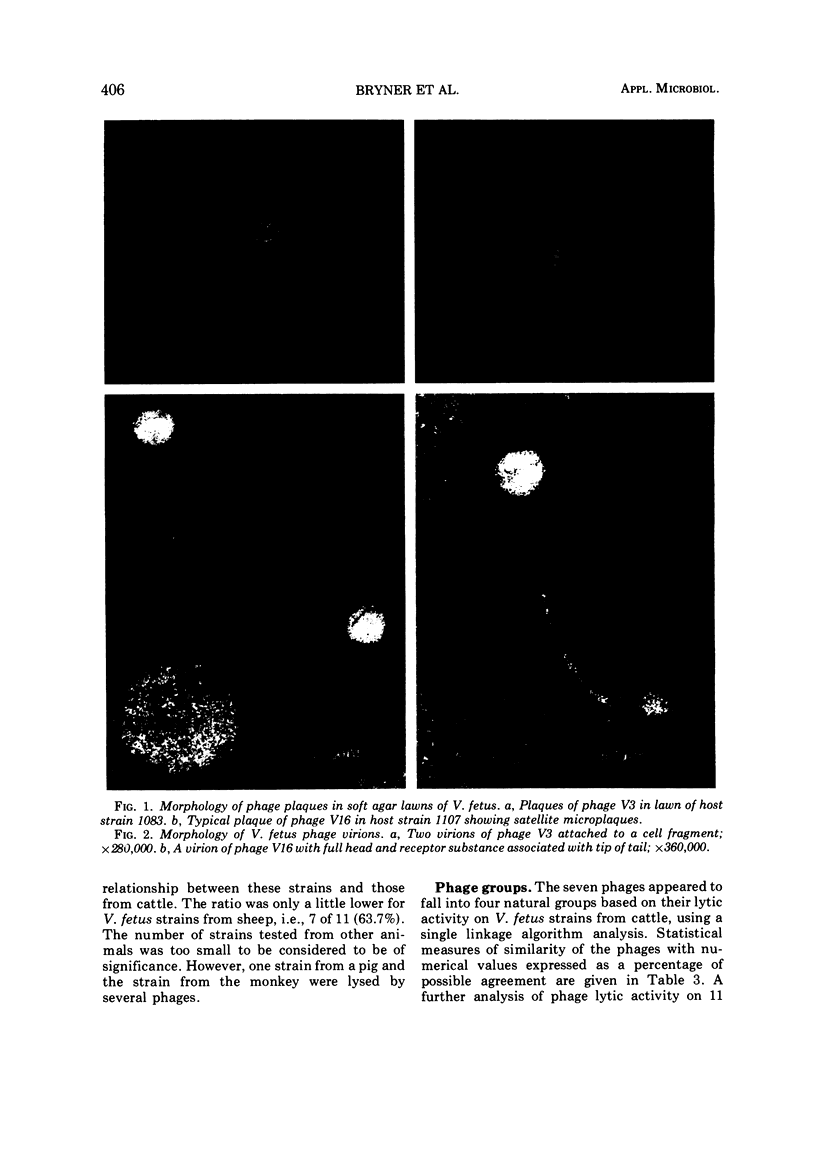
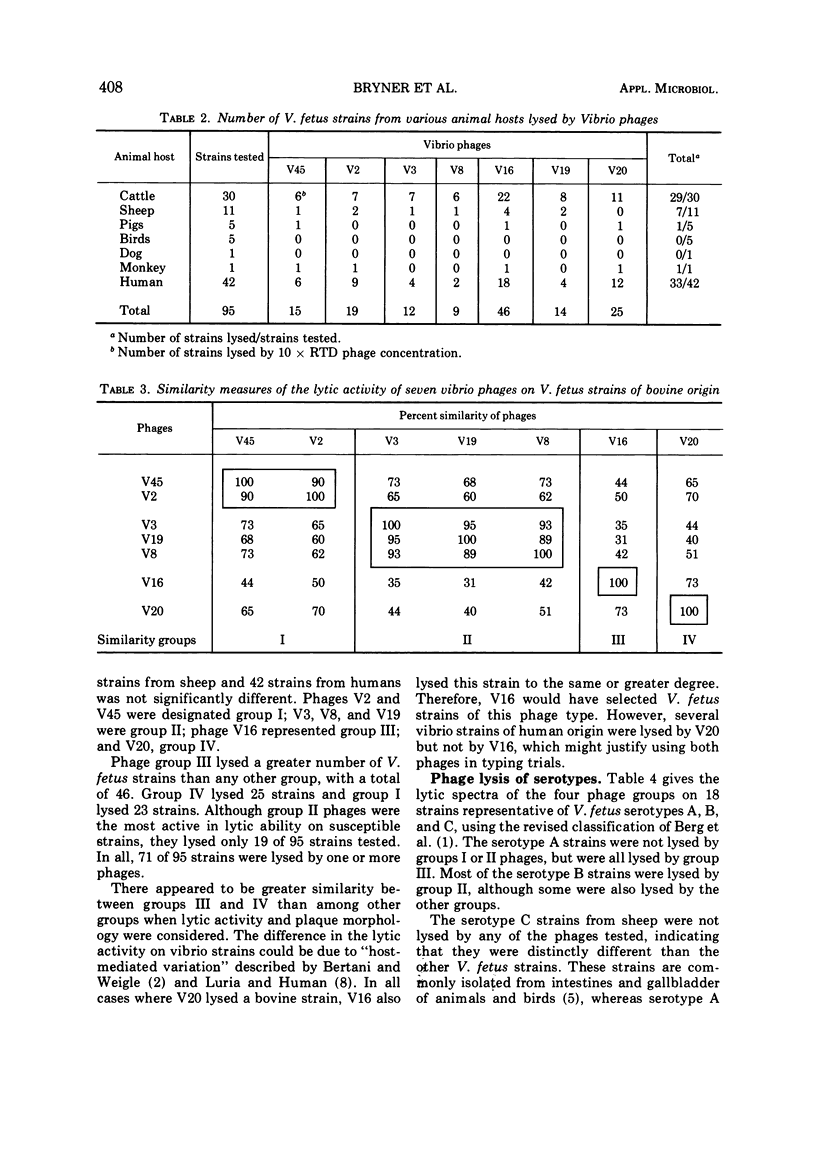
Five phages isolated from lysogenic strains of Vibrio fetus var. venerealis and two from V. fetus var. intestinalis were tested for lytic activity on 95 V. fetus strains from various animal and human hosts. In addition, virion and plaque morphology of the seven phages were compared. Electron micrographs showed that all were the kite-tailed variety with minor variations in head and tail dimensions. Plaques of V45 and V2 were small, clear and irregular; those of V3, V8, and V19 were large, clear and regular at the edge; the plaques of V16 and V20 were intermediate in size, clear, and very irregular at the edge with satellite plaques. The number of strains lysed by one or more phages were as follows: 29 of 30 from cattle; 7 of 11 from sheep; 1 of 5 from pigs; 1 of 1 from a monkey; and 33 of 42 from human hosts. Four natural groups of phages were derived by statistical measures of percentage of similarity in lytic activity. Group III lysed more strains (46 of 95) than any of the others. Twenty-five strains were lysed by group IV, 23 strains by group I, and 19 strains by group II. Results of this study indicate that phage typing should be a practical supplement to other differential tests for V. fetus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERTANI G., WEIGLE J. J. Host controlled variation in bacterial viruses. J Bacteriol. 1953 Feb;65(2):113–121. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.2.113-121.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. L., Jutila J. W., Firehammer B. D. A revised classification of Vibrio fetus. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Jan;32(1):11–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokkenheuser V. Vibrio fetus infection in man. I. Ten new cases and some epidemiologic observations. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Apr;91(4):400–409. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryner J. H., O'Berry P. A., Estes P. C., Foley J. W. Studies of vibrios from gallbladder of market sheep and cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1972 Jul;33(7):1439–1444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryner J. H., Ritchie A. E., Foley J. W., Berman D. T. Isolation and characterization of a bacteriophage for Vibrio fetus. J Virol. 1970 Jul;6(1):94–99. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.1.94-99.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang W., Ogg J. E. Transduction and mutation to glycine tolerance in vibrio fetus. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Apr;32(4):649–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firehammer B. D., Border M. Isolation of temperate bacteriophages from Vibrio fetus. Am J Vet Res. 1968 Nov;29(11):2229–2235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., HUMAN M. L. A nonhereditary, host-induced variation of bacterial viruses. J Bacteriol. 1952 Oct;64(4):557–569. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.4.557-569.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogg J. E., Chang W. Phage conversion of serotypes in Vibrio fetus. Am J Vet Res. 1972 May;33(5):1023–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNEATH P. H. The application of computers to taxonomy. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Aug;17(1):201–226. doi: 10.1099/00221287-17-1-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soonattrakul W., Andersen B. R., Bryner J. H. Raw liver as a possible source of Vibrio fetus septicemia in man. Am J Med Sci. 1971 May;261(5):245–249. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197105000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]