Abstract
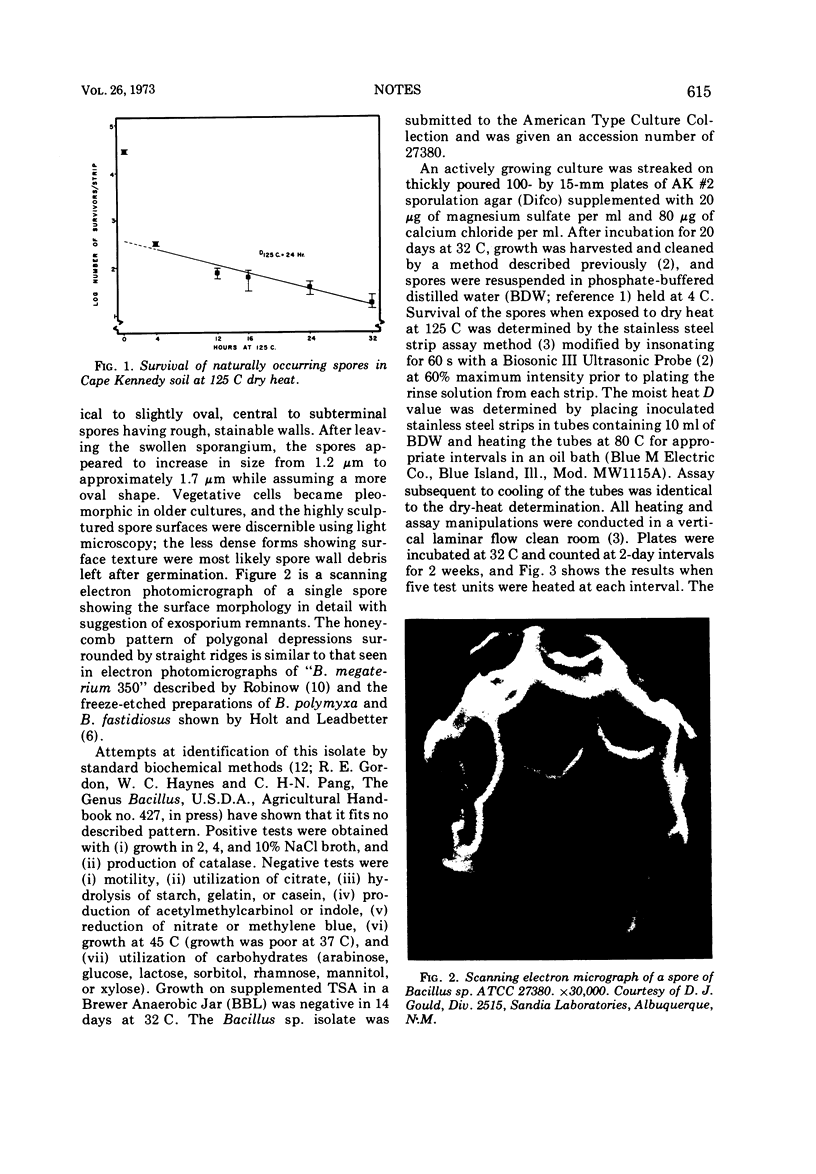
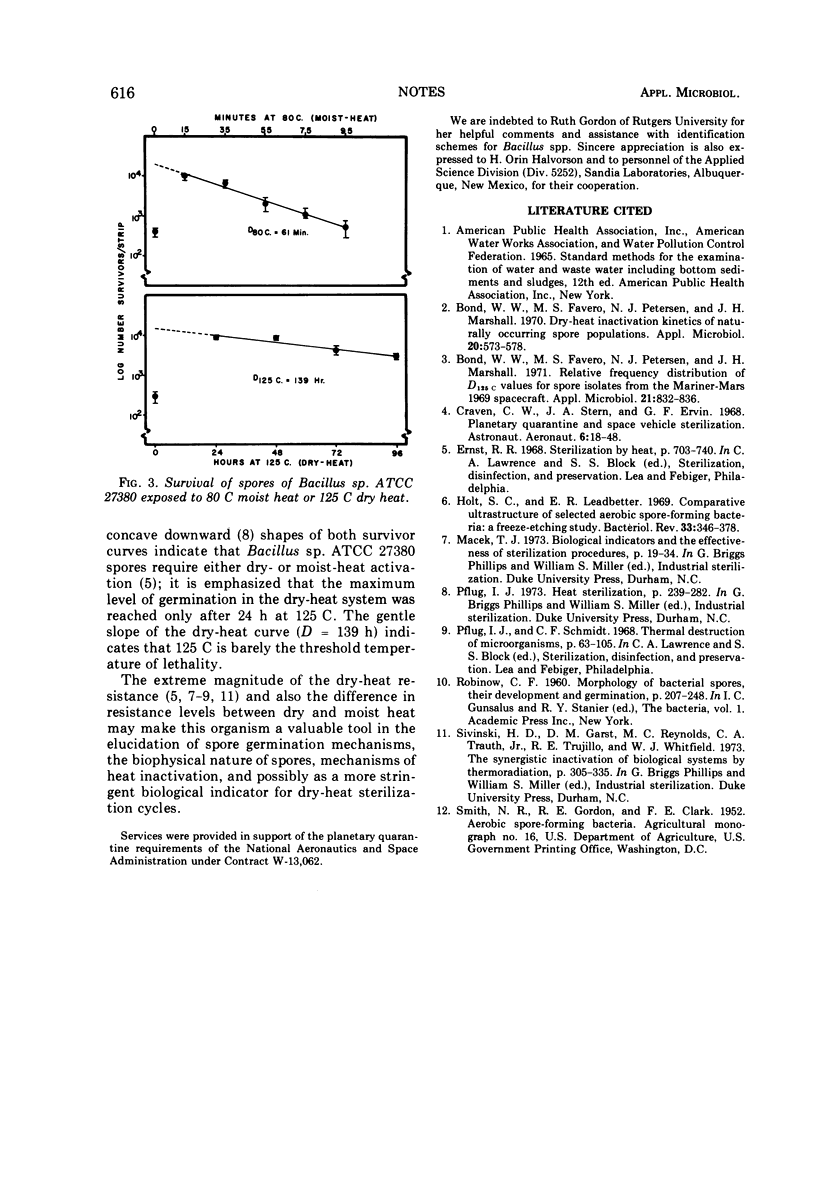
An unusual mesophilic Bacillus sp. was isolated from heated soil, and a cleaned spore preparation showed extraordinary resistance to dry heat (D125C = 139 h) and relative sensitivity to moist heat (D80C = 61 min). Biochemical tests and morphology fit no described species.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bond W. W., Favero M. S., Petersen N. J., Marshall J. H. Dry-heat inactivation kinetics of naturally occurring spore populations. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Oct;20(4):573–578. doi: 10.1128/am.20.4.573-578.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond W. W., Favero M. S., Petersen N. J., Marshall J. H. Relative frequency distribution of d(125 C) values for spore isolates from the mariner-Mars 1969 spacecraft. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):832–836. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.832-836.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R. Comparative ultrastructure of selected aerobic spore-forming bacteria: a freeze-etching study. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Jun;33(2):346–378. doi: 10.1128/br.33.2.346-378.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]