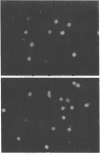
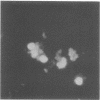
Abstract
Because no fully satisfactory diagnostic method has been available for use in pneumocystis infection, an attempt was made to apply the fluorescent antibody technique in the identification of Pneumocystis carinii. Hyperimmune sera were prepared in rabbits against P. carinii from human and rat sources. After proper adsorption, these antisera were conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate and used as reagents in a direct fluorescent antibody procedure. Each of the two reagents was found to stain trypsin-treated P. carinii organisms from either human or rat sources, indicating the presence of common antigens. Stained organisms were demonstrated in the hypopharyngeal material from rats in which pneumocystis infection had been activated by the administration of corticosteroid. From the results reported here, the procedure outlined is considered sufficiently sensitive and specific to justify tests on pneumocystis infections in man. The findings in a series of specimens from human subjects will be reported separately. The method also provides an extended approach to related research problems. The need for controls of the procedure at all points is emphasized.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradshaw M., Myerowitz R. L., Schneerson R., Whisnant J. K., Robbins J. B. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Nov;73(5):775–777. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-5-775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzosko W. J., Madaliński K., Krawczyński K., Nowoslawski A. Immunohistochemistry in studies on the pathogenesis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in infants. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 21;177:156–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb35042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., KAPLAN M. H. Localization of antigen in tissue cells; improvements in a method for the detection of antigen by means of fluorescent antibody. J Exp Med. 1950 Jan 1;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1084/jem.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENDRICK P. L., ELDERING G., EVELAND W. C. Fluorescent antibody techniques. Methods for identification of Bordetella pertussis. Am J Dis Child. 1961 Feb;101:149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Hughes W. T., Feldman S. Studies of morphology and immunofluorescence of Pneumocystis carinii. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Oct;141(1):304–309. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. K., Jones R. H., Eveland W. C. Fluorescent antibody studies on experimental pneumocytosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Feb;136(2):675–679. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL J. D., EVELAND W. C., SMITH C. W. Superiority of fluorescein isothiocyanate (Riggs) for fluorescent-antibody technic with a modification of its application. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Aug-Sep;98(4):898–900. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGGS J. L., LOH P. C., EVELAND W. C. A simple fractionation method for preparation of fluorescein-labeled gamma globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Dec;105:655–658. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repsher L. H., Schröter G., Hammond W. S. Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis by means of endobronchial brush biopsy. N Engl J Med. 1972 Aug 17;287(7):340–341. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197208172870708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. A review. Pediatr Res. 1967 Mar;1(2):131–158. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196703000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells A. F., Miller C. E., Nadel M. K. Rapid fluorescein and protein assay method for fluorescent-antibody conjugates. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):271–275. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.271-275.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]