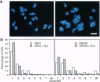
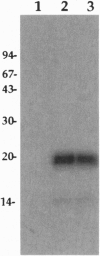
Abstract
We have created a strain of Dictyostelium that is deficient for the Ca2+/calmodulin-independent MLCK-A. This strain undergoes cytokinesis less efficiently than wild type, which results in an increased frequency of multinucleate cells when grown in suspension. The MLCK-A-cells are able, however, to undergo development and to cap crosslinked surface receptors, processes that require myosin heavy chain. Phosphorylated regulatory light chain (RLC) is still present in MLCK-A-cells, indicating that Dictyostelium has one or more additional protein kinases capable of phosphorylating RLC. Concanavalin A treatment was found to induce phosphorylation of essentially all of the RLC in wild-type cells, but RLC phosphorylation levels in MLCK-A-cells are unaffected by concanavalin A. Thus MLCK-A is regulated separately from the other MLCK(s) in the cell.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abu-Elneel K., Karchi M., Ravid S. Dictyostelium myosin II is regulated during chemotaxis by a novel protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 12;271(2):977–984. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano M., Ito M., Kimura K., Fukata Y., Chihara K., Nakano T., Matsuura Y., Kaibuchi K. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase). J Biol Chem. 1996 Aug 23;271(34):20246–20249. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.34.20246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlot C. H., Devreotes P. N., Spudich J. A. Chemoattractant-elicited increases in Dictyostelium myosin phosphorylation are due to changes in myosin localization and increases in kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3918–3926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlot C. H., Spudich J. A., Devreotes P. N. Chemoattractant-elicited increases in myosin phosphorylation in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Ostrow B. D., Tafuri S. R., Chisholm R. L. Targeted disruption of the Dictyostelium RMLC gene produces cells defective in cytokinesis and development. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 2):1933–1944. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. L., Kowalczyk P. A., Ho G., Chisholm R. L. Targeted disruption of the Dictyostelium myosin essential light chain gene produces cells defective in cytokinesis and morphogenesis. J Cell Sci. 1995 Oct;108(Pt 10):3207–3218. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.10.3207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Côte G. P., Bukiejko U. Purification and characterization of a myosin heavy chain kinase from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1065–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lozanne A., Spudich J. A. Disruption of the Dictyostelium myosin heavy chain gene by homologous recombination. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1086–1091. doi: 10.1126/science.3576222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynes J. L., Firtel R. A. Molecular complementation of a genetic marker in Dictyostelium using a genomic DNA library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7966–7970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishkind D. J., Wang Y. L. New horizons for cytokinesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;7(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke J., Kessin R. A defined minimal medium for axenic strains of Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith L. M., Downs S. M., Spudich J. A. Myosin light chain kinase and myosin light chain phosphatase from Dictyostelium: effects of reversible phosphorylation on myosin structure and function. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1309–1323. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger J. A., Firtel R. A. Analysis of G alpha 4, a G-protein subunit required for multicellular development in Dictyostelium. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):38–49. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insall R., Kuspa A., Lilly P. J., Shaulsky G., Levin L. R., Loomis W. F., Devreotes P. CRAC, a cytosolic protein containing a pleckstrin homology domain, is required for receptor and G protein-mediated activation of adenylyl cyclase in Dictyostelium. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(6):1537–1545. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.6.1537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitanishi-Yumura T., Fukui Y. Actomyosin organization during cytokinesis: reversible translocation and differential redistribution in Dictyostelium. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;12(2):78–89. doi: 10.1002/cm.970120203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht D. A., Loomis W. F. Antisense RNA inactivation of myosin heavy chain gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1081–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.3576221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolman M. F., Futey L. M., Egelhoff T. T. Dictyostelium myosin heavy chain kinase A regulates myosin localization during growth and development. J Cell Biol. 1996 Jan;132(1-2):101–109. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu S., Hosoya H. Phosphorylation by MAPKAP kinase 2 activates Mg(2+)-ATPase activity of myosin II. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996 Jun 25;223(3):741–745. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.0966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuczmarski E. R. Partial purification of two myosin heavy chain kinases from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1986 Dec;7(6):501–509. doi: 10.1007/BF01753566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. S., Levitan I. B. Concanavalin A: a tool to investigate neuronal plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Jul;14(7):273–277. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90136-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manjarrez-Hernandez H. A., Baldwin T. J., Aitken A., Knutton S., Williams P. H. Intestinal epithelial cell protein phosphorylation in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea. Lancet. 1992 Feb 29;339(8792):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manstein D. J., Titus M. A., De Lozanne A., Spudich J. A. Gene replacement in Dictyostelium: generation of myosin null mutants. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):923–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03453.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruta H., Baltes W., Dieter P., Marmé D., Gerisch G. Myosin heavy chain kinase inactivated by Ca2+/calmodulin from aggregating cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):535–542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01459.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A. A., Luna J. E. The Dictyostelium cytoskeleton. Experientia. 1995 Dec 18;51(12):1135–1143. doi: 10.1007/BF01944731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okagaki T., Ishikawa R., Kohama K. Inhibitory Ca(2+)-regulation of myosin light chain kinase in the lower eukaryote, Physarum polycephalum: role of a Ca(2+)-dependent inhibitory factor. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;56(1):113–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrow B. D., Chen P., Chisholm R. L. Expression of a myosin regulatory light chain phosphorylation site mutant complements the cytokinesis and developmental defects of Dictyostelium RMLC null cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 2):1945–1955. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak C., Spudich J. A., Elson E. L. Capping of surface receptors and concomitant cortical tension are generated by conventional myosin. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):549–551. doi: 10.1038/341549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson B., Spudich J. A. A novel positive selection for identifying cold-sensitive myosin II mutants in Dictyostelium. Genetics. 1995 Jun;140(2):505–515. doi: 10.1093/genetics/140.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz G., Spudich J. A., Parham P. Monoclonal antibodies against seven sites on the head and tail of Dictyostelium myosin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1016–1023. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Perry S. V. An electrophoretic study of the low-molecular-weight components of myosin. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;119(1):31–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1190031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollenz R. S., Chen T. L., Trivinos-Lagos L., Chisholm R. L. The Dictyostelium essential light chain is required for myosin function. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):951–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90614-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport R. Establishment of the mechanism of cytokinesis in animal cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1986;105:245–281. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Spudich J. A. Myosin heavy chain kinase from developed Dictyostelium cells. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):15144–15150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblatt J., Schekman R. A hitchhiker's guide to analysis of the secretory pathway in yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;32:3–36. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satterwhite L. L., Lohka M. J., Wilson K. L., Scherson T. Y., Cisek L. J., Corden J. L., Pollard T. D. Phosphorylation of myosin-II regulatory light chain by cyclin-p34cdc2: a mechanism for the timing of cytokinesis. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):595–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satterwhite L. L., Pollard T. D. Cytokinesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90057-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. R. Regulation of cytoplasmic and smooth muscle myosin. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;3(1):98–104. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90171-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker M. O., Lau W., Shattuck R. L., Kwiatkowski A. P., Matrisian P. E., Guerra-Santos L., Wilson E., Lukas T. J., Van Eldik L. J., Watterson D. M. Use of DNA sequence and mutant analyses and antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to examine the molecular basis of nonmuscle myosin light chain kinase autoinhibition, calmodulin recognition, and activity. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1107–1125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman M. Cultivation and synchronous morphogenesis of Dictyostelium under controlled experimental conditions. Methods Cell Biol. 1987;28:9–29. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney H. L., Bowman B. F., Stull J. T. Myosin light chain phosphorylation in vertebrate striated muscle: regulation and function. Am J Physiol. 1993 May;264(5 Pt 1):C1085–C1095. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.5.C1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. L., Ravid S., Spudich J. A. Control of nonmuscle myosins by phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:721–759. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. L., Spudich J. A. Characterization and bacterial expression of the Dictyostelium myosin light chain kinase cDNA. Identification of an autoinhibitory domain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16044–16049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. L., Spudich J. A. Dictyostelium myosin light chain kinase. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13818–13824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trybus K. M. Filamentous smooth muscle myosin is regulated by phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2887–2894. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trybus K. M. Regulation of smooth muscle myosin. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1991;18(2):81–85. doi: 10.1002/cm.970180202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamakita Y., Yamashiro S., Matsumura F. In vivo phosphorylation of regulatory light chain of myosin II during mitosis of cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):129–137. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeilig C. E., Goldberg N. D. Cell-cycle-related changes of 3':5'-cyclic GMP levels in Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1052–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]