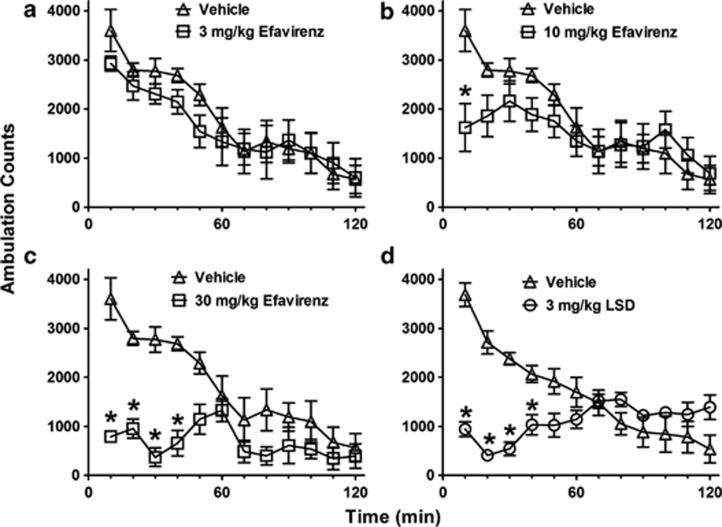
Figure 2.
Efavirenz dose-dependently depresses open-field locomotor activity in a novel environment in mice similar to lysergic acid diethylamine (LSD). The ambulation data are shown for groups of eight mice as mean (±SE) counts within 10-min periods for separate groups of eight mice injected intraperitoneally with vehicle, efavirenz, or LSD. (a) At a dose of 3 mg/kg, efavirenz had no effect on ambulation. (b) At a dose of 10 mg/kg, efavirenz decreased ambulation only during the first 10 min. (c) At a dose of 30 mg/kg, efavirenz produced near-maximal suppression of ambulation that was sustained for 40 min. (d) LSD (3 mg/kg) produces a more potent sustained decrease in ambulation similar to that produced by 30 mg/kg efavirenz. The asterisks (*) indicate a significant difference from vehicle control (P<0.05).