Abstract
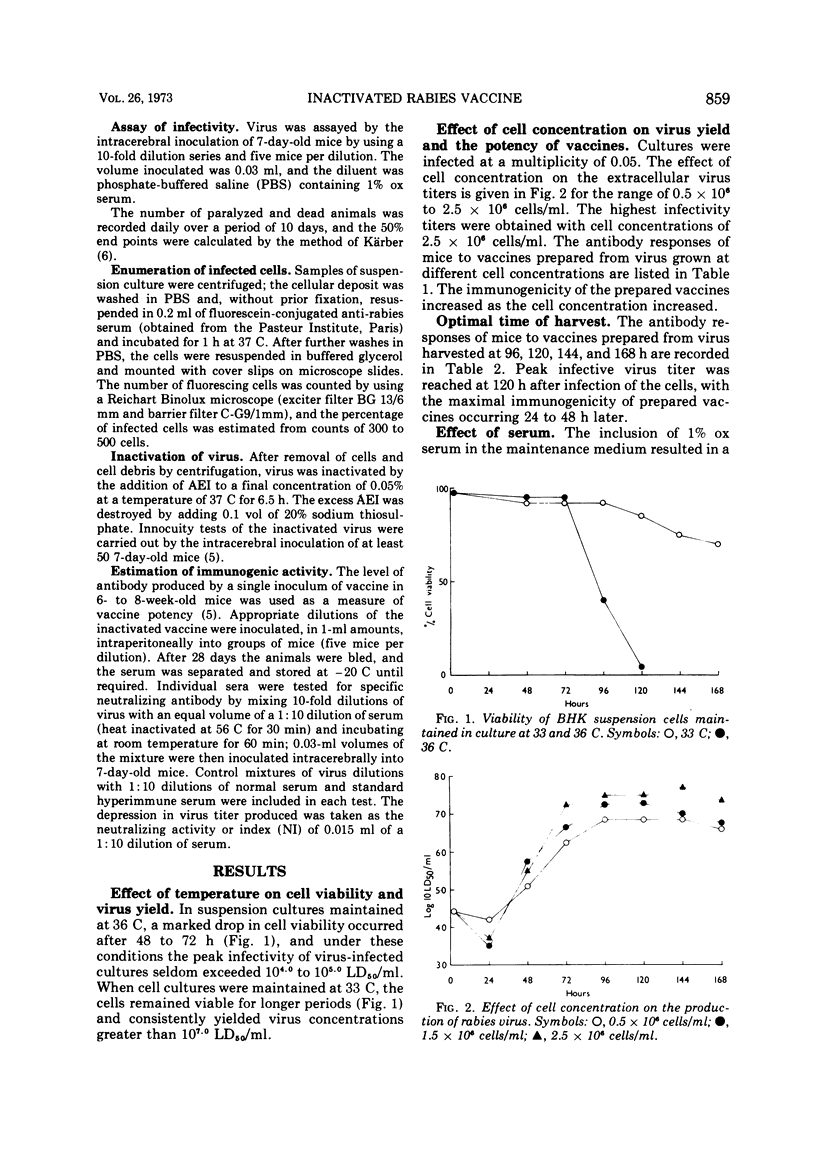
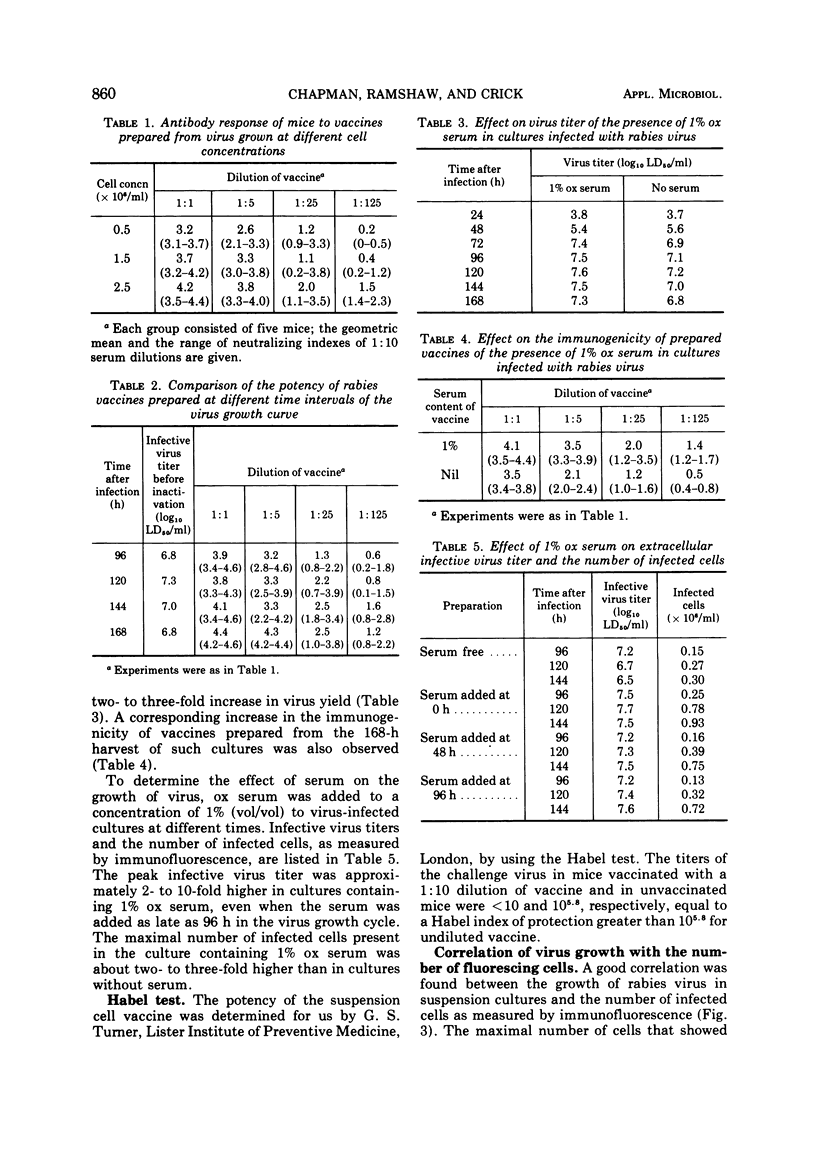
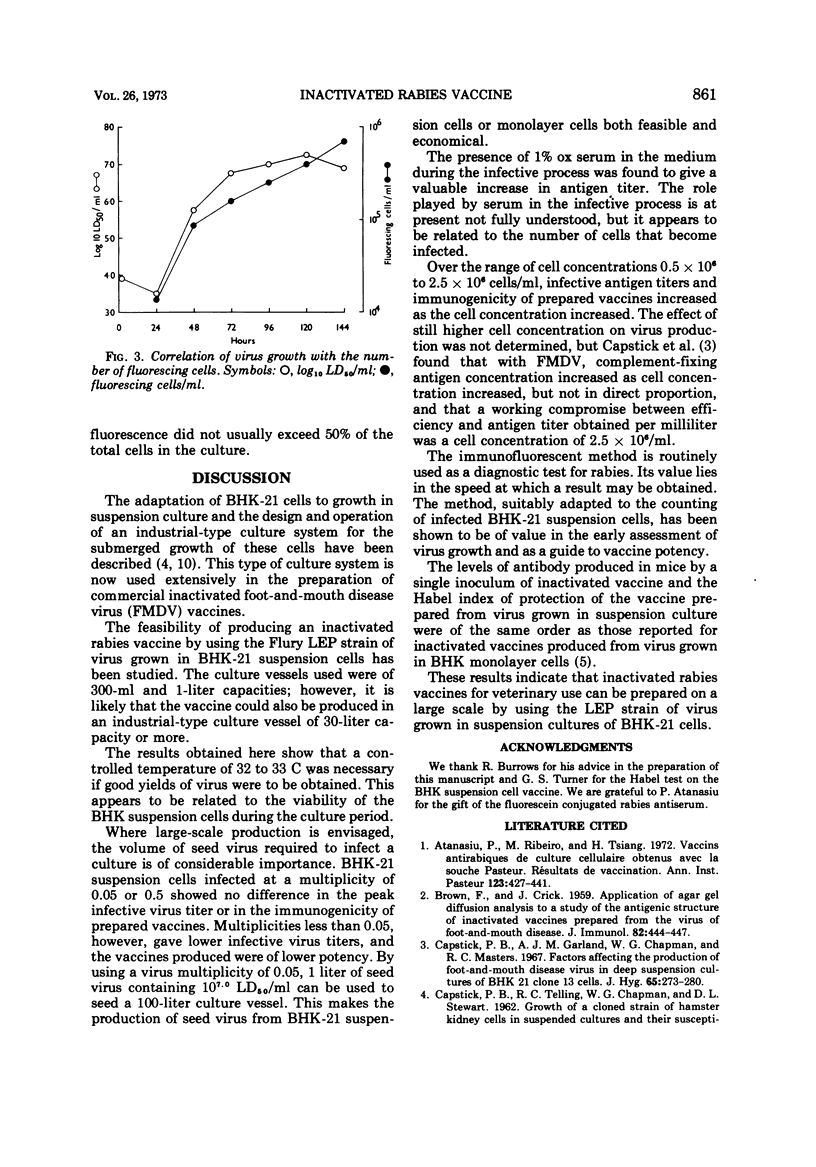
Suspension cultures of BHK-21 cells maintained at 32 to 33 C were infected with the Flury LEP strain of rabies virus. By using a cell concentration of 2.0 × 106 to 2.5 × 106 cells per ml infected at a multiplicity of 0.05, high titers of extracellular virus were reached in 96 to 120 h, and potent inactivated vaccines were prepared from culture fluids harvested between 96 to 168 h. The addition of 1% bovine serum to the maintenance medium resulted in an increase in virus yields and vaccine potency. Estimation of the number of infected cells by immunofluorescent procedures proved a rapid and reliable guide to the virus content of suspension cultures.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atanasiu P., Ribeiro M., Tsiang H. Vaccins antirabiques de culture cellulaire obtenus avec la souche Pasteur. Résultats de vaccination. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Sep;123(3):427–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN F., CRICK J. Application of agar-gel diffusion analysis to a study of the antigenic structure of inactivated vaccines prepared from the virus of foot-and-mouth disease. J Immunol. 1959 May;82(5):444–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capstick P. B., Garland A. J., Chapman W. G., Masters R. C. Factors affecting the production of foot-and-mouth disease virus in deep suspension cultures of BHK21 clone 13 cells. J Hyg (Lond) 1967 Sep;65(3):273–280. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400045794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick J., Brown F. An inactivated baby hamster kidney cell rabies vaccine for use in dogs and cattle. Res Vet Sci. 1971 Mar;12(2):156–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., STOKER M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:147–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. M., Burrows T. M. Improvements in the design of laboratory apparatus for the suspended culture of tissue cells. Lab Pract. 1966 Aug;15(8):864–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


