Abstract
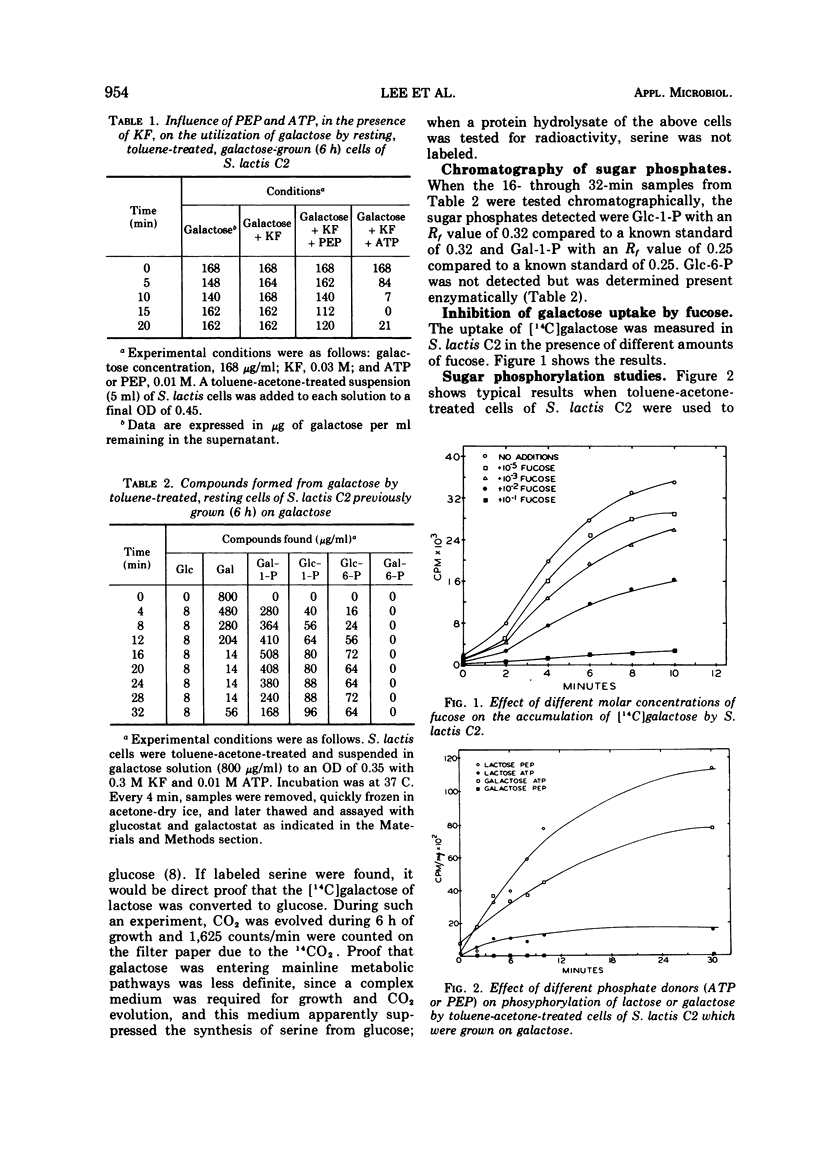
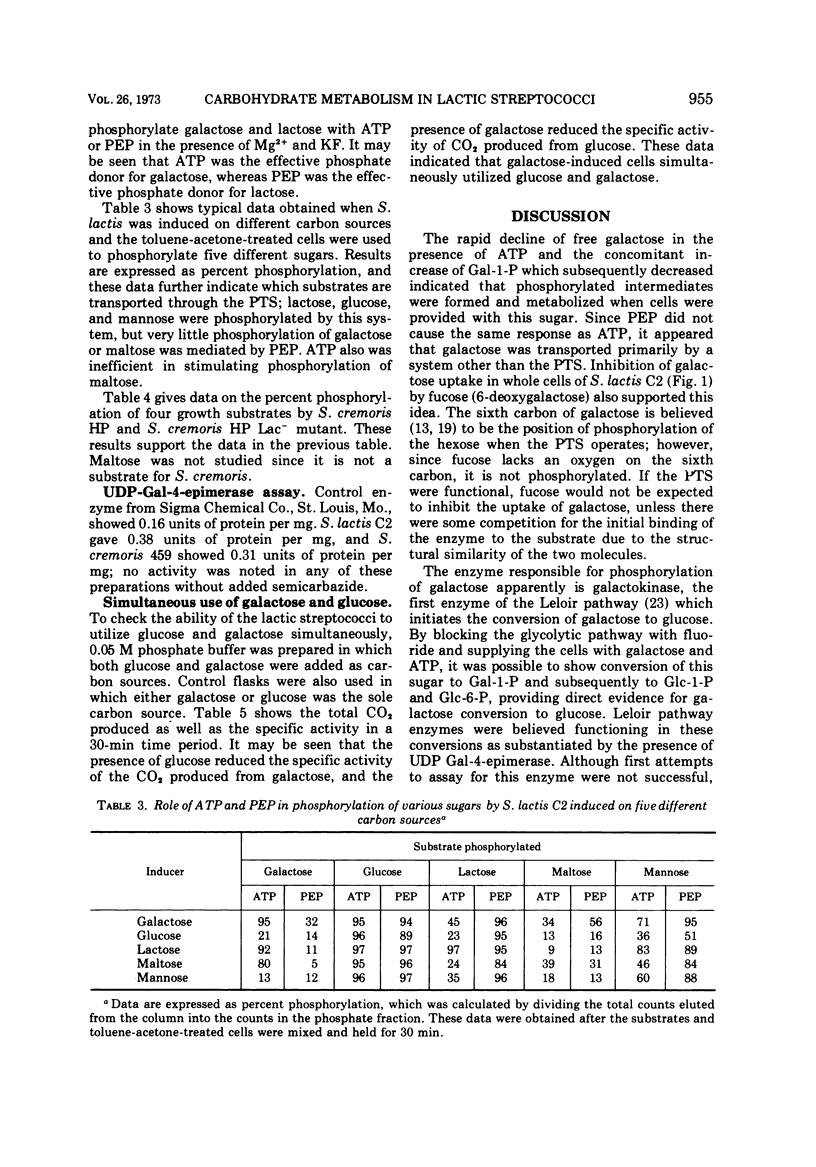
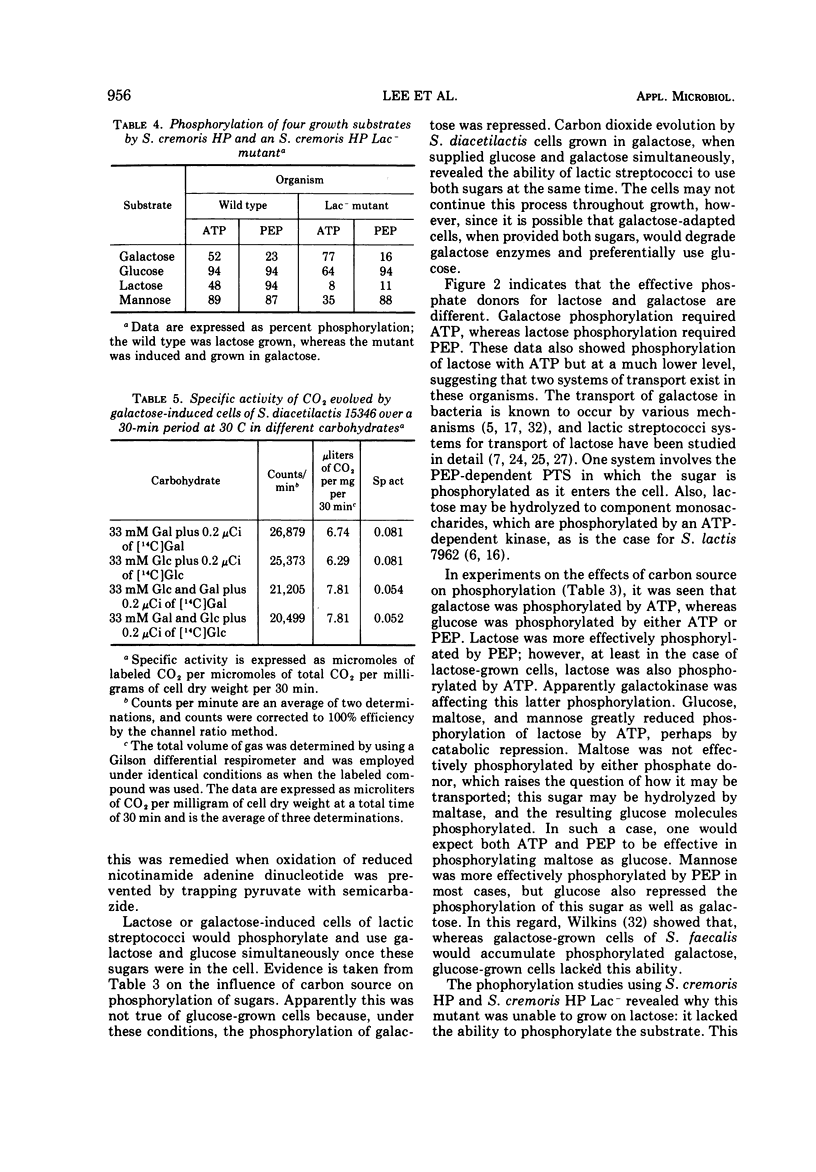
Phosphorylation of free galactose by lactic streptococci was mediated by an adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-dependent kinase. The phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) phosphotransferase system (PTS) was involved to a limited extent in transport of the sugar. The conversion of free galactose to glucose also was demonstrated, and uridine diphosphogalactose-4-epimerase was demonstrated to account for this change. Galactose, supplied as lactose, was phosphorylated during transport by means of the PTS with PEP as the phosphate donor. Data also indicated that galactose derived from lactose was catabolized by the glycolytic pathway. Results showed the participation of ATP or PEP, or both, in the phosphorylation of five growth sugars for lactic streptococci, namely, galactose, glucose, lactose, maltose, and mannose. Free galactose was phosphorylated exclusively by ATP except when cells were grown on galactose; in this case, slight involvement of PEP in phosphorylation also was noted. Lactose phosphorylation was much more effective with PEP except when cells were grown on lactose, in which case ATP was equally effective. Glucose was phosphorylated to about the same degree by either ATP or PEP.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUSSE M. STOFFWECHSELPHYSIOLOGISCHE UNTERSUCHUNGEN AN AROMABILDENDEN MILCHSAEUREKOKKEN. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1963 Dec;191:437–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett D. L., Anderson R. L. Lactose and D0galactose metabolism in Staphylococcus aureus: pathway of D-galactose 6-phosphate degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):641–647. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90761-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CITTI J. E., SANDINE W. E., ELLIKER P. R. BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF STREPTOCOCCUS LACTIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:937–942. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.937-942.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citti J. E., Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Lactose and maltose uptake by Streptococcus lactis. J Dairy Sci. 1967 Apr;50(4):485–487. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(67)87451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan J. B., Morse M. L. Carbohydrate transport in Staphylococcus aureus. 3. Studies of the transport process. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 4;112(1):63–73. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6585(96)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland S. E., Speck M. L., Woodard J. R., Jr Stimulation of lactic streptococci in milk by -galactosidase. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jan;23(1):21–25. doi: 10.1128/am.23.1.21-25.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W., Egan J. B., Morse M. L. Carbohydrate transport in Staphylococcus aureus. V. The accumulation of phosphorylated carbohydrate derivatives, and evidence for a new enzyme-splitting lactose phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):274–279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W., Egan J. B., Morse M. L. Carbohydrate transport in Staphylococcus aureus. VI. The nature of the derivatives accumulated. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1881–1885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W., Penberthy W. K., Hill K. L., Morse M. L. Metabolism of lactose by Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2187–2188. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2187-2188.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W., Penberthy W. K., Hill K. L., Morse M. L. Phosphotransferase system of Staphylococcus aureus: its requirement for the accumulation and metabolism of galactosides. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):383–388. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.383-388.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNDIG W., GHOSH S., ROSEMAN S. PHOSPHATE BOUND TO HISTIDINE IN A PROTEIN AS AN INTERMEDIATE IN A NOVEL PHOSPHO-TRANSFERASE SYSTEM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1067–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. Role of metabolic energy in the transport of -galactosides by Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):784–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.784-789.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerwar G. K., Gordon A. S., Kaback H. R. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated membrane vesicles. IV. Galactose transport by isolated membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):291–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg H. L., Reeves R. E. Correlation between hexose transport and phosphotransferase activity in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;126(5):1241–1243. doi: 10.1042/bj1261241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LELOIR L. F. The enzymatic transformation of uridine diphosphate glucose into a galactose derivative. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Sep;33(2):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laue P., MacDonald R. E. Identification of thiomethyl-beta-D-galactoside 6-phosphate accumulated by Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 10;243(3):680–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A., Zottola E. A. Loss of lactose metabolism in lactic streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jun;23(6):1090–1096. doi: 10.1128/am.23.6.1090-1096.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Walter L. A., Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Involvement of phosphoenolpyruvate in lactose utilization by group N streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):603–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.603-610.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L., Miller A., 3rd, Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Mechanisms of lactose utilization by lactic acid streptococci: enzymatic and genetic analyses. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):804–809. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.804-809.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premi L., Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Lactose-hydrolyzing enzymes of Lactobacillus species. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jul;24(1):51–57. doi: 10.1128/am.24.1.51-57.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Eberhard S. J., Dingle S. L., McDowell T. D. Distribution of the phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):808–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.808-813.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDINE W. E., ELLIKER P. R., HAYS H. Cultural studies on Streptococcus diacetilactis and other members of the lactic Streptococcus group. Can J Microbiol. 1962 Apr;8:161–174. doi: 10.1139/m62-021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Roseman S. Sugar transport. VII. Lactose transport in Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):966–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins P. O. Transport and binding of galactose by Streptococcus faecalis. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Dec;16(12):1145–1151. doi: 10.1139/m70-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



