Abstract
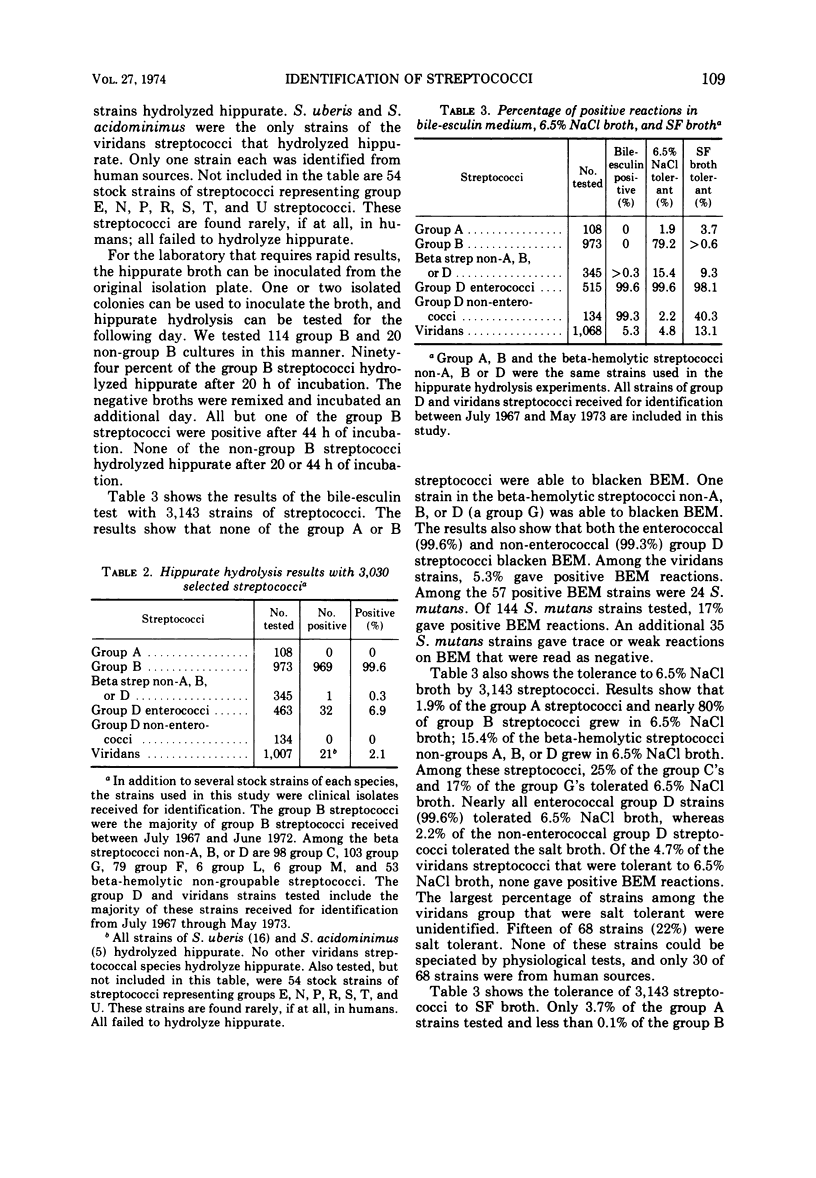
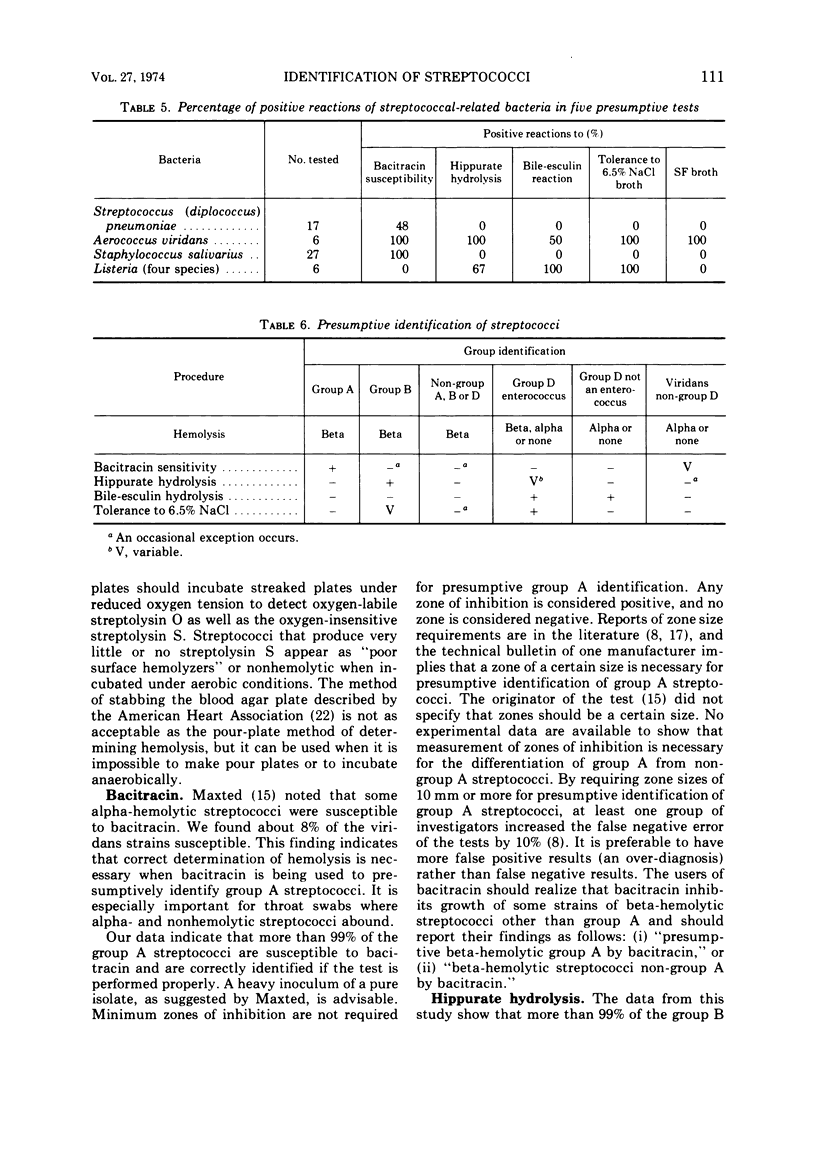
A battery of five tests was used for presumptive identification of the pathogenic streptococci. The non-serological methods included determination of hemolysis for all strains, bacitracin susceptibility for group A streptococci, hippurate hydrolysis by group B streptococci, and bile-esculin reaction for group D streptococci. Enterococcal group D streptococci were differentiated from non-enterococcal group D streptococci by 6.5% NaCl tolerance. Two other categories of streptococci resulted: beta-hemolytic streptococci non-groups A, B, or D; and alpha- or nonhemolytic streptococci, not enterococci, not further identified (viridans streptococci). The tests were used as a battery and not as single entities. In this manner more than 99% of the group A, 99% of the group B, 81% of the beta-hemolytic streptococci non-group A, B, or D, 99% of the group D enterococci, 97% of the group D non-enterococci, and 94% of the viridans streptococci were correctly identified.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. J., Barrett F. F., Gordon R. C., Yow M. D. Suppurative meningitis due to streptococci of Lancefield group B: a study of 33 infants. J Pediatr. 1973 Apr;82(4):724–729. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80606-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton L. L., Feigin R. D., Lins R. Group B beta hemolytic streptococcal meningitis in infants. J Pediatr. 1973 Apr;82(4):719–723. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80605-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunstein H., Tucker E. B., Gibson B. C. Identification and significance of Streptococcus agalactiae (Lancefield group B). Am J Clin Pathol. 1969 Feb;51(2):207–213. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/51.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ederer G. M., Herrmann M. M., Bruce R., Matsen J. M., Chapman S. S. Rapid extraction method with pronase B for grouping beta-hemolytic streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):285–288. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.285-288.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. Comparison of several laboratory media for presumptive identification of enterococci and group D streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Aug;26(2):138–145. doi: 10.1128/am.26.2.138-145.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Moody M. D. Presumptive identification of group D streptococci: the bile-esculin test. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):245–250. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.245-250.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. Recognition of group D streptococcal species of human origin by biochemical and physiological tests. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jun;23(6):1131–1139. doi: 10.1128/am.23.6.1131-1139.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franciosi R. A., Knostman J. D., Zimmerman R. A. Group B streptococcal neonatal and infant infections. J Pediatr. 1973 Apr;82(4):707–718. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80604-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. F., Jr Reisolation of Staphylococcus salivarius from the human oral cavity. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1281–1286. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1281-1286.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES W. F., Jr, FELDMAN H. A., FINLAND M. Susceptibility of hemolytic streptococci, other than those of group D, to eleven antibiotics in vitro. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957 Feb;27(2):159–169. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/27.2.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXTED W. R. The use of bacitracin for identifying group A haemolytic streptococci. J Clin Pathol. 1953 Aug;6(3):224–226. doi: 10.1136/jcp.6.3.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr Group B streptococci: the new challenge in neonatal infections. J Pediatr. 1973 Apr;82(4):703–706. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80603-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F., Dayton S. L., Chipps D. D. Autograft rejection in acutely burned patients: relation to colonization by Streptococcus agalactiae. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Mar;25(3):493–495. doi: 10.1128/am.25.3.493-495.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toala P., McDonald A., Wilcox C., Finland M. Susceptibility of group D streptococcus (enterococcus) to 21 antibiotics in vitro, with special reference to species differences. Am J Med Sci. 1969 Dec;258(6):416–430. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196912000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Facklam R. R., Wortham E. C. Distribution by serological type of group B streptococci isolated from a variety of clinical material over a five-year period (with special reference to neonatal sepsis and meningitis). Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):228–235. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.228-235.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Thacker L. G., Facklam R. R. Nonhemolytic group B streptococci of human, bovine, and ichthyic origin. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):496–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.496-498.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


