Abstract
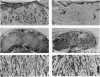
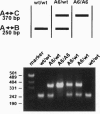
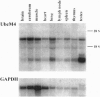
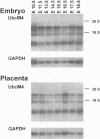
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2 or Ubc) constitute a family of conserved proteins that play a key role in ubiquitin-dependent degradation of proteins in eukaryotes. We describe here a transgenic mouse strain where retrovirus integration into an Ubc gene, designated UbcM4, results in a recessive-lethal mutation. UbcM4 is the mouse homologue of the previously described human UbcH7 that is involved in the in vitro ubiquitination of several proteins including the tumor suppressor protein p53. The provirus is located in the first intron of the gene. When both alleles are mutated the level of steady-state mRNA is reduced by about 70%. About a third of homozygous mutant embryos die around day 11.5 of gestation. Embryos that survive that stage are growth retarded and die perinatally. The lethal phenotype is most likely caused by impairment of placenta development as this is the only organ that consistently showed pathological defects. The placental labyrinth is drastically reduced in size and vascularization is disturbed. The UbcM4 mouse mutant represents the first example in mammals of a mutation in a gene involved in ubiquitin conjugation. Its recessive-lethal phenotype demonstrates that the ubiquitin system plays an essential role during mouse development.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artelt P., Grannemann R., Stocking C., Friel J., Bartsch J., Hauser H. The prokaryotic neomycin-resistance-encoding gene acts as a transcriptional silencer in eukaryotic cells. Gene. 1991 Mar 15;99(2):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90134-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barklis E., Mulligan R. C., Jaenisch R. Chromosomal position or virus mutation permits retrovirus expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90596-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld N., Gonen H., Mayer A., Smith C. E., Siegel N. R., Schwartz A. L., Ciechanover A. Purification and characterization of a novel species of ubiquitin-carrier protein, E2, that is involved in degradation of non-"N-end rule" protein substrates. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9574–9581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90396-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copp A. J. Death before birth: clues from gene knockouts and mutations. Trends Genet. 1995 Mar;11(3):87–93. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(00)89008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross J. C., Werb Z., Fisher S. J. Implantation and the placenta: key pieces of the development puzzle. Science. 1994 Dec 2;266(5190):1508–1518. doi: 10.1126/science.7985020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemot F., Nagy A., Auerbach A., Rossant J., Joyner A. L. Essential role of Mash-2 in extraembryonic development. Nature. 1994 Sep 22;371(6495):333–336. doi: 10.1038/371333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurtner G. C., Davis V., Li H., McCoy M. J., Sharpe A., Cybulsky M. I. Targeted disruption of the murine VCAM1 gene: essential role of VCAM-1 in chorioallantoic fusion and placentation. Genes Dev. 1995 Jan 1;9(1):1–14. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system for protein degradation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:761–807. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicke L., Riezman H. Ubiquitination of a yeast plasma membrane receptor signals its ligand-stimulated endocytosis. Cell. 1996 Jan 26;84(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80982-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser M. Ubiquitin, proteasomes, and the regulation of intracellular protein degradation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;7(2):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S. The ubiquitin-conjugation system. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:179–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratochwil K., von der Mark K., Kollar E. J., Jaenisch R., Mooslehner K., Schwarz M., Haase K., Gmachl I., Harbers K. Retrovirus-induced insertional mutation in Mov13 mice affects collagen I expression in a tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90795-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwee L., Baldwin H. S., Shen H. M., Stewart C. L., Buck C., Buck C. A., Labow M. A. Defective development of the embryonic and extraembryonic circulatory systems in vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM-1) deficient mice. Development. 1995 Feb;121(2):489–503. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.2.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinger L., Varshavsky A. Selective arrangement of ubiquitinated and D1 protein-containing nucleosomes within the Drosophila genome. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E., Bestor T. H., Jaenisch R. Targeted mutation of the DNA methyltransferase gene results in embryonic lethality. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):915–926. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90611-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui S., Sandberg A. A., Negoro S., Seon B. K., Goldstein G. Isopeptidase: a novel eukaryotic enzyme that cleaves isopeptide bonds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1535–1539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuschewski K., Hauser H. P., Treier M., Jentsch S. Identification of a novel family of ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes with distinct amino-terminal extensions. J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 2;271(5):2789–2794. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.5.2789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer R. J., Arnold J., László L., Landon M., Lowe J. Ubiquitin in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 13;1089(2):141–157. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muralidhar M. G., Thomas J. B. The Drosophila bendless gene encodes a neural protein related to ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes. Neuron. 1993 Aug;11(2):253–266. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90182-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuber U., Schwarz S., Kaiser P., Schneider R., Scheffner M. Cloning of human ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes UbcH6 and UbcH7 (E2-F1) and characterization of their interaction with E6-AP and RSP5. J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 2;271(5):2795–2800. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.5.2795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh C. E., McMahon R., Benzer S., Tanouye M. A. bendless, a Drosophila gene affecting neuronal connectivity, encodes a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme homolog. J Neurosci. 1994 May;14(5 Pt 2):3166–3179. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-05-03166.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orian A., Whiteside S., Israël A., Stancovski I., Schwartz A. L., Ciechanover A. Ubiquitin-mediated processing of NF-kappa B transcriptional activator precursor p105. Reconstitution of a cell-free system and identification of the ubiquitin-carrier protein, E2, and a novel ubiquitin-protein ligase, E3, involved in conjugation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 15;270(37):21707–21714. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.37.21707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Nuber U., Huibregtse J. M. Protein ubiquitination involving an E1-E2-E3 enzyme ubiquitin thioester cascade. Nature. 1995 Jan 5;373(6509):81–83. doi: 10.1038/373081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C., Bladt F., Goedecke S., Brinkmann V., Zschiesche W., Sharpe M., Gherardi E., Birchmeier C. Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor is essential for liver development. Nature. 1995 Feb 23;373(6516):699–702. doi: 10.1038/373699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seperack P. K., Mercer J. A., Strobel M. C., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Retroviral sequences located within an intron of the dilute gene alter dilute expression in a tissue-specific manner. EMBO J. 1995 May 15;14(10):2326–2332. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07227.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seufert W., Futcher B., Jentsch S. Role of a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in degradation of S- and M-phase cyclins. Nature. 1995 Jan 5;373(6509):78–81. doi: 10.1038/373078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stancovski I., Gonen H., Orian A., Schwartz A. L., Ciechanover A. Degradation of the proto-oncogene product c-Fos by the ubiquitin proteolytic system in vivo and in vitro: identification and characterization of the conjugating enzymes. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;15(12):7106–7116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.12.7106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara Y., Minowa O., Mori C., Shiota K., Kuno J., Noda T., Kitamura N. Placental defect and embryonic lethality in mice lacking hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. Nature. 1995 Feb 23;373(6516):702–705. doi: 10.1038/373702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Rayburn H., Hynes R. O. Cell adhesion events mediated by alpha 4 integrins are essential in placental and cardiac development. Development. 1995 Feb;121(2):549–560. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.2.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]