Abstract
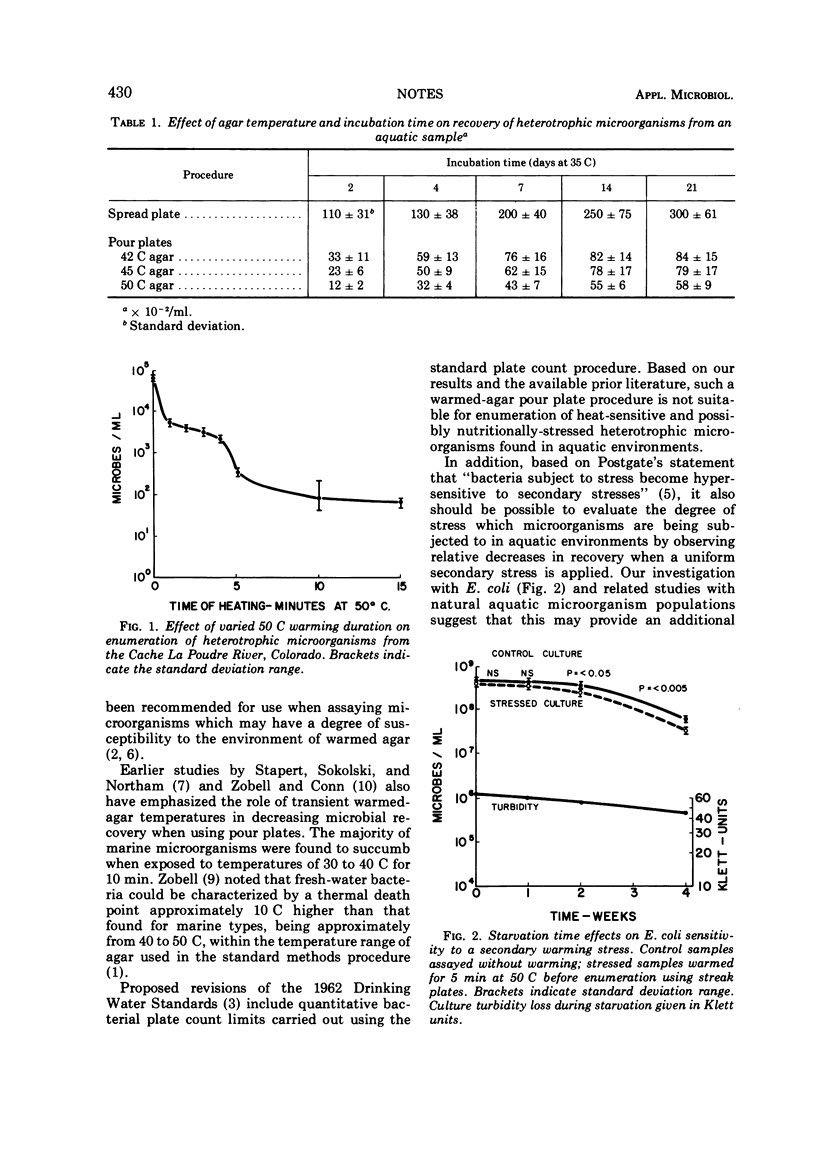
Heterotrophic microorganisms in water samples are susceptible to the transient stress of warmed agar used in the standard methods pour plate procedure, causing significantly decreased recoveries in comparison with a spread plate technique. Microbial starvation can increase susceptibility to a transient warming stress. The standard plate count procedure, as presently described, should not be considered for quantitation of microorganisms from aquatic environments.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hayasaka S., Klein D. A. Structural effects on Arthrobacter methylene hydroxylase activity. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1141–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1141-1146.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B., Speck M. L. Discrepancies in the enumeration of Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):494–498. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.494-498.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN Soestbergen A. A., Lee C. H. Pour plates or streak plates? Appl Microbiol. 1969 Dec;18(6):1092–1093. doi: 10.1128/am.18.6.1092-1093.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zobell C. E., Conn J. E. Studies on the Thermal Sensitivity of Marine Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1940 Aug;40(2):223–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.40.2.223-238.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


