Abstract
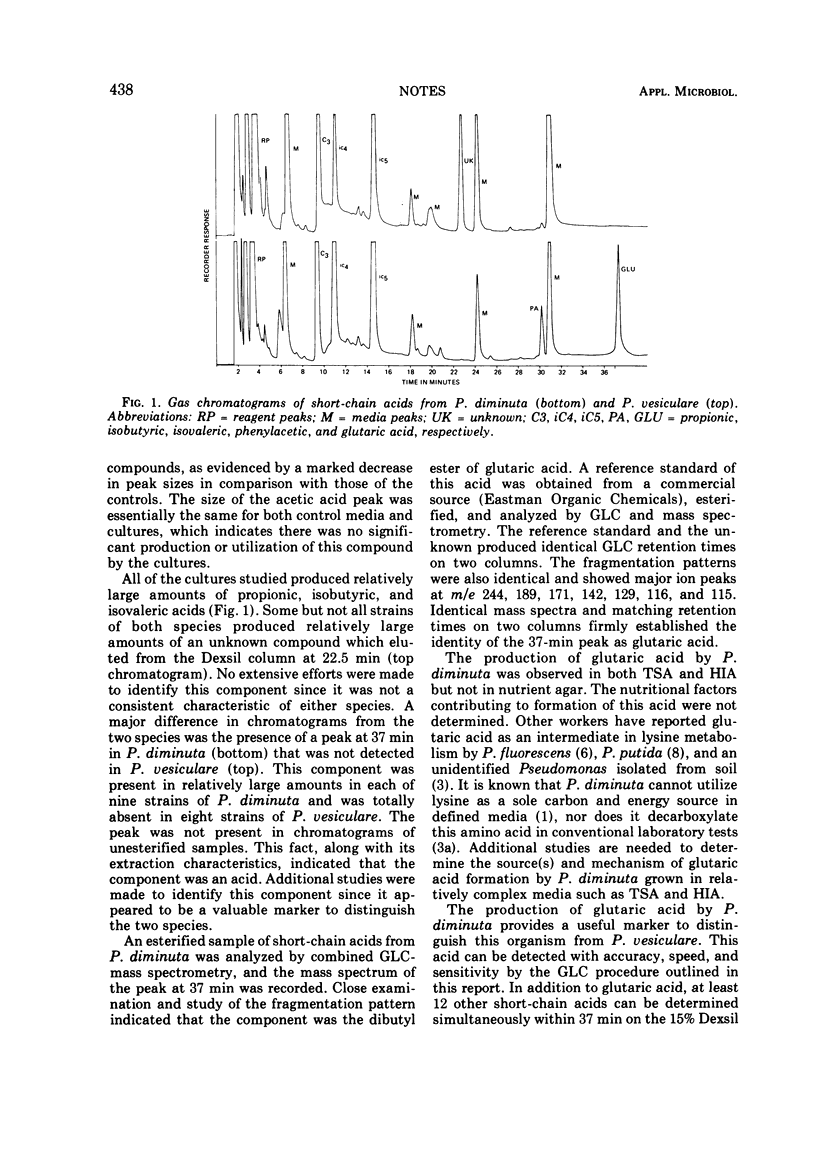
A gas-liquid chromatographic procedure was used to determine short-chain acids produced by Pseudomonas diminuta and P. vesiculare after growth on Trypticase soy agar. Each of nine strains of P. diminuta produced glutaric acid, whereas none of the strains of P. vesiculare produced this acid.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard R. W., Doudoroff M., Stanier R. Y., Mandel M. Taxonomy of the aerobic psuedomonads: Pseudomonas diminuta and P. vesiculare. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Oct;53(3):349–361. doi: 10.1099/00221287-53-3-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Weaver R. E., Tatum H. W., Billingsley S. A. Differentiation between Pseudomonas testosteroni and P. acidovorans by gas chromatography. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Sep;18(9):1477–1482. doi: 10.1139/m72-226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ICHIHARA A., ICHIHARA E. A. Metabolism of L-lysine by bacterial enzymes. V. Glutaric semialdehyde dehydrogenase. J Biochem. 1961 Feb;49:154–157. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. A., Moss C. W. Gas-liquid chromatography of short-chain fatty acids on Dexsil 300 GC. J Chromatogr. 1972 Dec 20;74(2):335–338. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)86164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Samuels S. B., Weaver R. E. Cellular fatty acid composition of selected Pseudomonas species. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):596–598. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.596-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUMA S., ISHIMURA Y., NAKAZAWA T., OKAZAKI T., HAYAISHI O. ENZYMIC STUDIES ON THE METABOLISM OF GLUTARATE IN PSEUDOMONAS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3915–3926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett M. J., Manclark C. R. Nonfermentative bacilli associated with man. I. Nomenclature. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Aug;54(2):155–163. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/54.2.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz M. S., Rodwell V. W. Delta-aminovaleramidase of Pseudomonas putida. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3091–3096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels S. B., Moss C. W., Weaver R. E. The fatty acids of Pseudomonas multivorans (Pseudomonas cepacia) and Pseudomonas kingii. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Feb;74(2):275–279. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-2-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


