Abstract
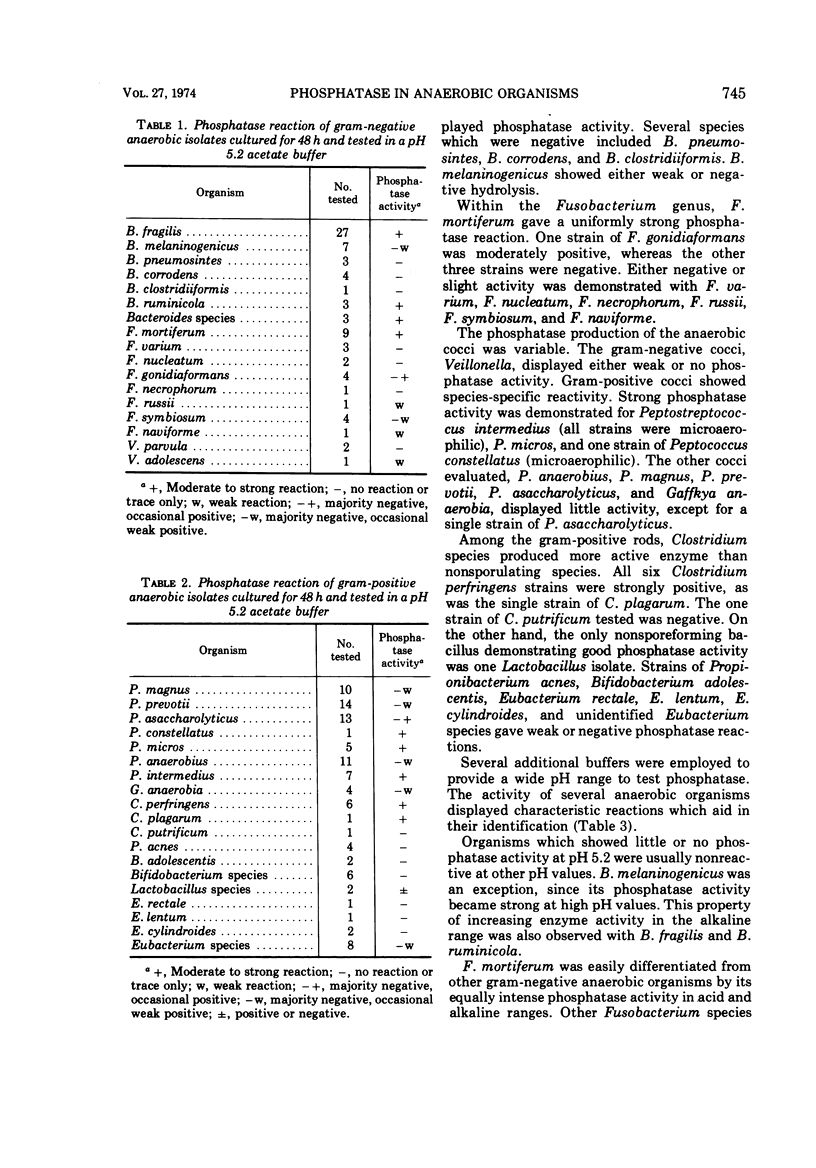
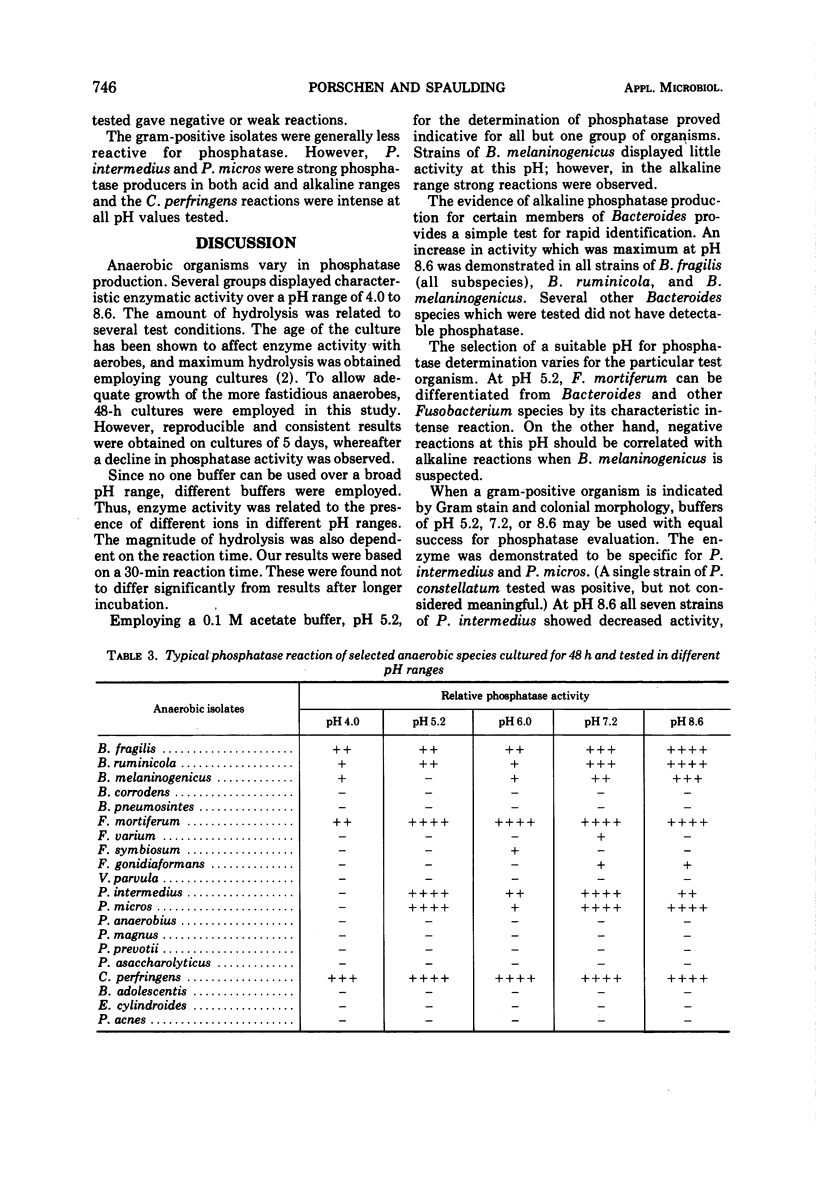
Anaerobic organisms were tested for phosphatase activity in different pH ranges. Several groups of organisms displayed characteristic patterns. Bacteroides fragilis, B. melaninogenicus, and B. ruminicola produced phosphatase with strongest activity at pH 8.6. Fusobacterium mortiferum was the only species of this genus to show strong hydrolysis. The enzyme was active in both acid and alkaline ranges. The activity of gram-positive organisms was variable, the most active groups being Clostridium perfringens, Peptostreptococcus intermedius, P. micros, and Peptococcus constellatus. The incorporation of phosphatase activity into the identification scheme of anaerobes seems feasible. There was a correlation of hydrolysis with several important pathogens.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARBER M., KUPER S. W. A. Identification of Staphylococcus pyogenes by the phosphatase reaction. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1951 Jan;63(1):65–68. doi: 10.1002/path.1700630108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNES E. H., MORRIS J. F. A quantitative study of the phosphatase activity of Micrococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jan;73(1):100–104. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.1.100-104.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANNON F. D., HAWN C. V. PHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS: CORRELATION OF ENZYME PRODUCTION WITH RESISTANCE TO PENICILLIN AND PHAGE PATTERN. J Bacteriol. 1963 Nov;86:1052–1056. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.5.1052-1056.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F., Blasi D., Dayton S. L. Phosphatase activity among Candida species and other yeasts isolated from clinical material. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):364–367. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.364-367.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf P. L., von der Muehll E., Ludwick M. A new test to differentiate Serratia from Enterobacter. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Feb;57(2):241–243. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/57.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



