Abstract
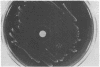
Growth of Peptostreptococcus anaerobius was shown to be totally inhibited by sodium polyanethol sulfonate (SPS). Other anaerobic cocci grew in the presence of SPS although some strains of Peptococcus prevotii and Peptococcus magnus showed delayed growth. A SPS disk assay for the presumptive identification of P. anaerobius is described.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belding M. E., Klebanoff S. J. Effect of sodium polyanetholesulfonate on antimicrobial systems in blood. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):691–698. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.691-698.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundt E. A., Andrews B. E., Erno H., Kunze M., Black F. T. The sensitivity of mycoplasmatales to sodium-polyanethol-sulfonate and digitonin. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1973 Oct;225(1):104–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambe D. W., Jr, McPhedran A. M., Mertz J. A., Stewart P. Streptobacillus moniliformis isolated from a case of Haverhill fever: biochemical characterization and inhibitory effect of sodium polyanethol sulfonate. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Dec;60(6):854–860. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/60.6.854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]