Abstract
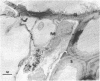
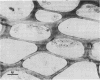
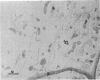
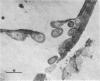
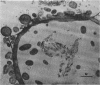
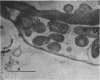
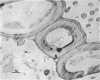
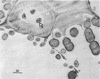
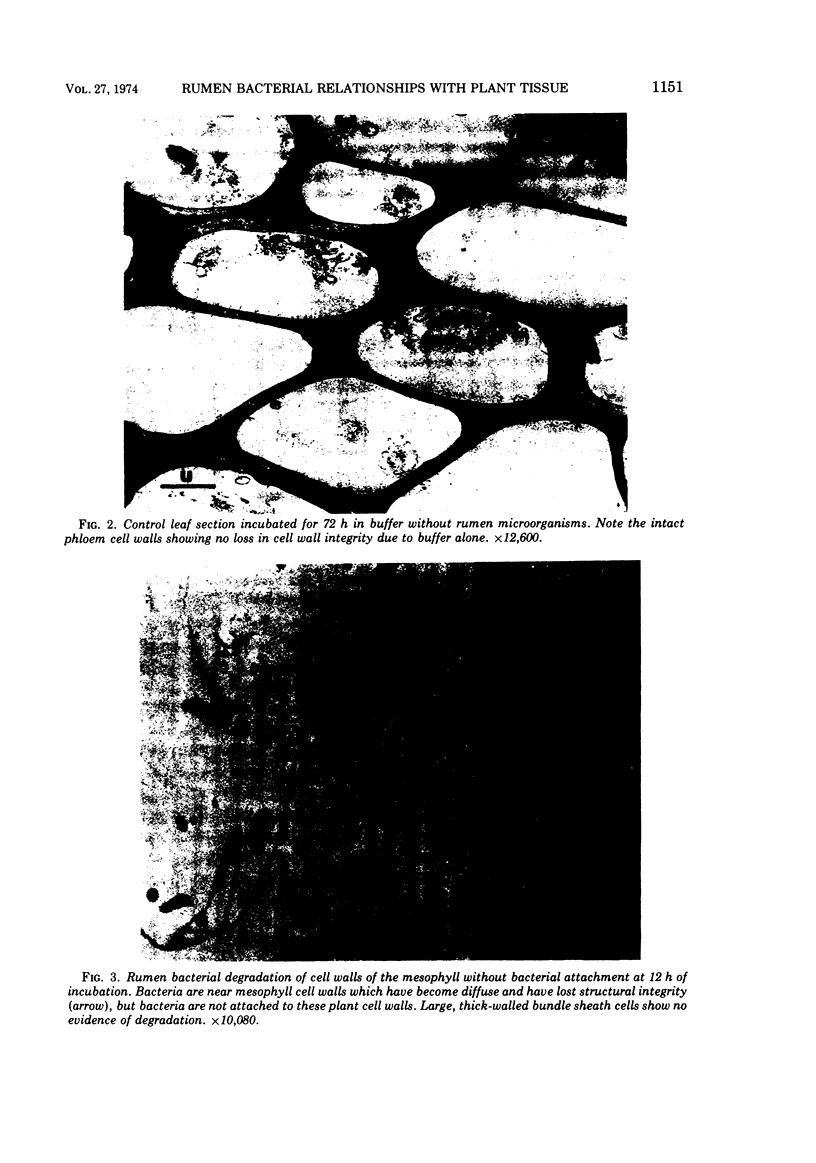
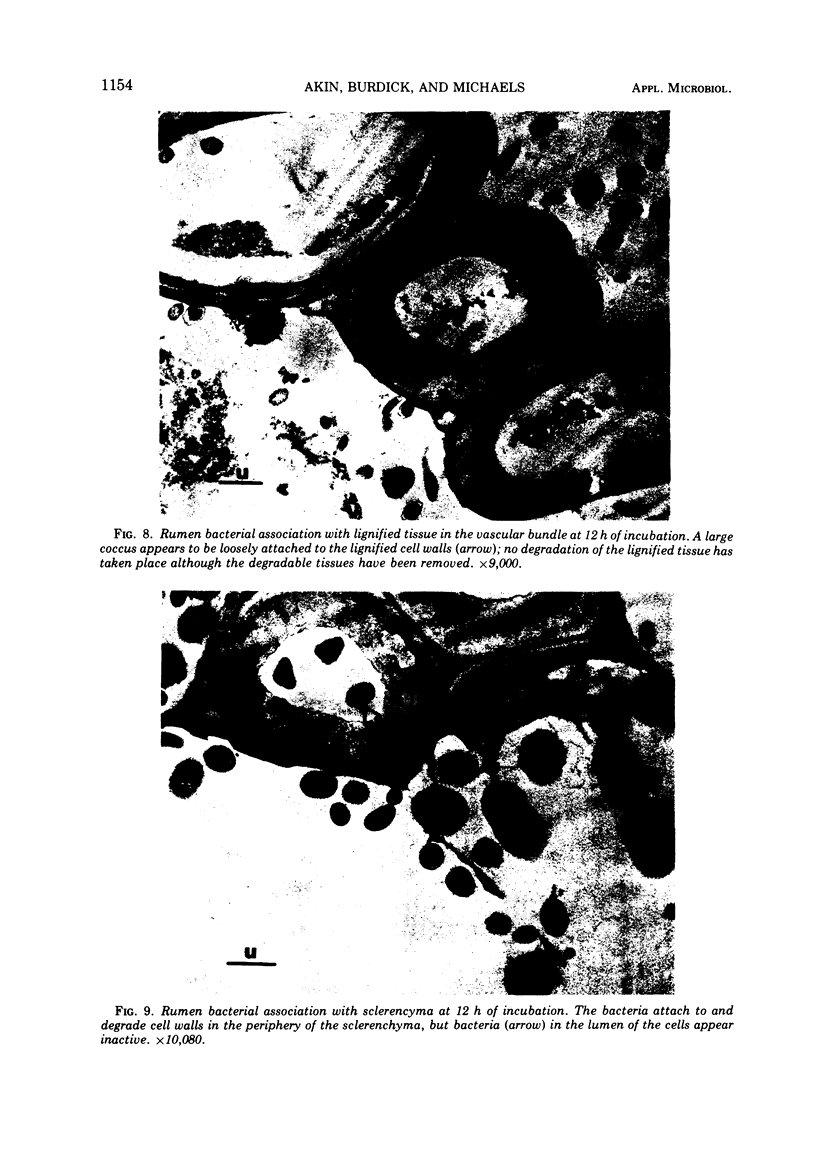
The mode of rumen bacterial degradation of cell walls in coastal bermudagrass [Cynodon dactylon (L) Pers.] differed with the plant tissue type. Bacteria degraded thin, primary cell walls of mesophyll and phloem apparently by extracellular enzymes and without prior attachment; thick-walled bundle sheath and epidermal cells apparently were degraded after bacterial attachment, in some types by an extracellular substance, to the plant cell walls. Rumen bacteria split the nondegraded cuticle from the epidermis by preferentially attacking the cell just underneath the cuticle. The propensity for bacterial attachment to lignified cells of the vascular tissue was low, and bacterial degradation of these cells did not occur after 72 h of incubation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coen J. A., Dehority B. A. Degradation and utilization of hemicellulose from intact forages by pure cultures of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Sep;20(3):362–368. doi: 10.1128/am.20.3.362-368.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker R. F., Richards G. N., Playne M. J. Digestion of polysaccharide constituents of tropical pasture herbage in the bovine rumen. I. Townsville Stylo (Stylosanthes humilis). Carbohydr Res. 1972 Apr;22(1):173–185. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)85736-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurti C. R., Kitts W. D. Preparation and properties of cellulases from rumen microorganisms. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Dec;15(12):1373–1379. doi: 10.1139/m69-248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. R., Yu I., Hungate R. E. Factors affecting cellulolysis by Ruminococcus albus. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):729–737. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.729-737.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]