Abstract
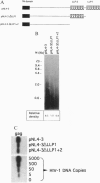
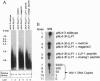
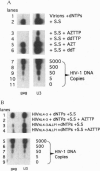
Reverse transcription of HIV-1, without detergent or amphipathic peptide-induced permeability of the viral envelope, has been demonstrated to occur in the intact HIV-1 virion. In this report, we demonstrate that the amphipathic domains in the C terminus of the transmembrane glycoprotein (gp41) account for the natural permeability of the HIV-1 envelope to deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, the substrates for DNA polymerization. In addition, nonphysiological deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, such as 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine 5'-triphosphate and 3'-deoxythymidine 5'-triphosphate, can also penetrate the viral envelope, incorporate into, and irreversibly terminate reverse transcripts. As a result, viral infectivity is potently inhibited. Since the lentiviral envelope with these newly demonstrated characteristics can serve as a delivery pathway for anti-reverse transcription agents, we propose a unique strategy to prevent HIV-1 interand, possibly, intrahost transmission.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Gendelman H. E., Koenig S., Folks T., Willey R., Rabson A., Martin M. A. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.284-291.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloia R. C., Jensen F. C., Curtain C. C., Mobley P. W., Gordon L. M. Lipid composition and fluidity of the human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):900–904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloia R. C., Tian H., Jensen F. C. Lipid composition and fluidity of the human immunodeficiency virus envelope and host cell plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5181–5185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnér E. S., Valentin A., Eriksson S. Thymidine and 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine metabolism in human peripheral blood lymphocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages. A study of both anabolic and catabolic pathways. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10968–10975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo J., Boceta M., González M. E., Michel M., Carrasco L. Membrane permeabilization by different regions of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein gp41. J Virol. 1995 Jul;69(7):4095–4102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.7.4095-4102.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone L. R., Skalka A. M. Viral DNA synthesized in vitro by avian retrovirus particles permeabilized with melittin. II. Evidence for a strand displacement mechanism in plus-strand synthesis. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):117–126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.117-126.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borroto-Esoda K., Boone L. R. Equine infectious anemia virus and human immunodeficiency virus DNA synthesis in vitro: characterization of the endogenous reverse transcriptase reaction. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1952–1959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1952-1959.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Emerman M., Tiollais P., Sonigo P. The cytoplasmic domain of simian immunodeficiency virus transmembrane protein modulates infectivity. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4395–4403. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4395-4403.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernomordik L., Chanturiya A. N., Suss-Toby E., Nora E., Zimmerberg J. An amphipathic peptide from the C-terminal region of the human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein causes pore formation in membranes. J Virol. 1994 Nov;68(11):7115–7123. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.11.7115-7123.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debyser Z., Vandamme A. M., Pauwels R., Baba M., Desmyter J., De Clercq E. Kinetics of inhibition of endogenous human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcription by 2',3'-dideoxynucleoside 5'-triphosphate, tetrahydroimidazo-[4,5,1-jk][1,4]-benzodiazepin-2(1H)-thion e, and 1-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)methyl]-6-(phenylthio)thymine derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11769–11776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubay J. W., Roberts S. J., Hahn B. H., Hunter E. Truncation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein cytoplasmic domain blocks virus infectivity. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6616–6625. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6616-6625.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl P. L., Doms R. W., Moss B. Oligomeric structure of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabuzda D. H., Lever A., Terwilliger E., Sodroski J. Effects of deletions in the cytoplasmic domain on biological functions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoproteins. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3306–3315. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3306-3315.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawrisch K., Han K. H., Yang J. S., Bergelson L. D., Ferretti J. A. Interaction of peptide fragment 828-848 of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type I with lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 30;32(12):3112–3118. doi: 10.1021/bi00063a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom H. R., Hausmann E. H., Ozel M., Pauli G., Koch M. A. Fine structure of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and immunolocalization of structural proteins. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffar O. K., Dowbenko D. J., Berman P. W. The cytoplasmic tail of HIV-1 gp160 contains regions that associate with cellular membranes. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):439–441. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90054-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffar O. K., Dowbenko D. J., Berman P. W. Topogenic analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein, gp160, in microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1677–1687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch V. M., Edmondson P., Murphey-Corb M., Arbeille B., Johnson P. R., Mullins J. I. SIV adaptation to human cells. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):573–574. doi: 10.1038/341573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Wooley D. P., Naidu Y. M., Kestler H. W., 3rd, Daniel M. D., Li Y., Desrosiers R. C. Significance of premature stop codons in env of simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4709–4714. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4709-4714.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau N. R., Page K. A., Littman D. R. Pseudotyping with human T-cell leukemia virus type I broadens the human immunodeficiency virus host range. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):162–169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.162-169.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. J., Hu W., Fisher A. G., Looney D. J., Kao V. F., Mitsuya H., Ratner L., Wong-Staal F. Role of the carboxy-terminal portion of the HIV-1 transmembrane protein in viral transmission and cytopathogenicity. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Aug;5(4):441–449. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. J., Vogel P., Alexander N. J., Sutjipto S., Hendrickx A. G., Marx P. A. Localization of SIV in the genital tract of chronically infected female rhesus macaques. Am J Pathol. 1992 Sep;141(3):655–660. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. A., Cloyd M. W., Liebmann J., Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Islam K. R., Wang S. Z., Mietzner T. A., Montelaro R. C. Alterations in cell membrane permeability by the lentivirus lytic peptide (LLP-1) of HIV-1 transmembrane protein. Virology. 1993 Sep;196(1):89–100. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. A., Garry R. F., Jaynes J. M., Montelaro R. C. A structural correlation between lentivirus transmembrane proteins and natural cytolytic peptides. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Jun;7(6):511–519. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya H., Broder S. Inhibition of the in vitro infectivity and cytopathic effect of human T-lymphotrophic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus (HTLV-III/LAV) by 2',3'-dideoxynucleosides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1911–1915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker W. B., White E. L., Shaddix S. C., Ross L. J., Buckheit R. W., Jr, Germany J. M., Secrist J. A., 3rd, Vince R., Shannon W. M. Mechanism of inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase and human DNA polymerases alpha, beta, and gamma by the 5'-triphosphates of carbovir, 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine, 2',3'-dideoxyguanosine and 3'-deoxythymidine. A novel RNA template for the evaluation of antiretroviral drugs. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1754–1762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poumbourios P., el Ahmar W., McPhee D. A., Kemp B. E. Determinants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein oligomeric structure. J Virol. 1995 Feb;69(2):1209–1218. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.2.1209-1218.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter G. D., Jr, Mulligan M. J., Lydy S. L., Compans R. W. Cell fusion activity of the simian immunodeficiency virus envelope protein is modulated by the intracytoplasmic domain. Virology. 1993 Nov;197(1):255–264. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira A. I., Marx P. A., Patterson B. K., Mahoney J., Koup R. A., Wolinsky S. M., Ho D. D. Cellular targets of infection and route of viral dissemination after an intravaginal inoculation of simian immunodeficiency virus into rhesus macaques. J Exp Med. 1996 Jan 1;183(1):215–225. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivas S. K., Srinivas R. V., Anantharamaiah G. M., Segrest J. P., Compans R. W. Membrane interactions of synthetic peptides corresponding to amphipathic helical segments of the human immunodeficiency virus type-1 envelope glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7121–7127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H. 1,4-Diaminobutane (putrescine), spermidine, and spermine. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:285–306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Törnevik Y., Jacobsson B., Britton S., Eriksson S. Intracellular metabolism of 3'-azidothymidine in isolated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Sep;7(9):751–759. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venable R. M., Pastor R. W., Brooks B. R., Carson F. W. Theoretically determined three-dimensional structures for amphipathic segments of the HIV-1 gp41 envelope protein. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Feb;5(1):7–22. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C., Spies C. P., Compans R. W. The human and simian immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein transmembrane subunits are palmitoylated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Oct 10;92(21):9871–9875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.21.9871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yong W. H., Wyman S., Levy J. A. Optimal conditions for synthesizing complementary DNA in the HIV-1 endogenous reverse transcriptase reaction. AIDS. 1990 Mar;4(3):199–206. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199003000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Martin B., Chen H. C. Antimicrobial activity of synthetic magainin peptides and several analogues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):910–913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Bagasra O., Niikura M., Poiesz B. J., Pomerantz R. J. Intravirion reverse transcripts in the peripheral blood plasma on human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected individuals. J Virol. 1994 Nov;68(11):7591–7597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.11.7591-7597.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Dornadula G., Pomerantz R. J. Endogenous reverse transcription of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in physiological microenviroments: an important stage for viral infection of nondividing cells. J Virol. 1996 May;70(5):2809–2824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.5.2809-2824.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Dornadula G., Wu Y., Havlir D., Richman D. D., Pomerantz R. J. Kinetic analysis of intravirion reverse transcription in the blood plasma of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected individuals: direct assessment of resistance to reverse transcriptase inhibitors in vivo. J Virol. 1996 Jan;70(1):628–634. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.1.628-634.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Duan L. X., Dornadula G., Pomerantz R. J. Increasing transduction efficiency of recombinant murine retrovirus vectors by initiation of endogenous reverse transcription: potential utility for genetic therapies. J Virol. 1995 Jun;69(6):3929–3932. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.6.3929-3932.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]