Abstract
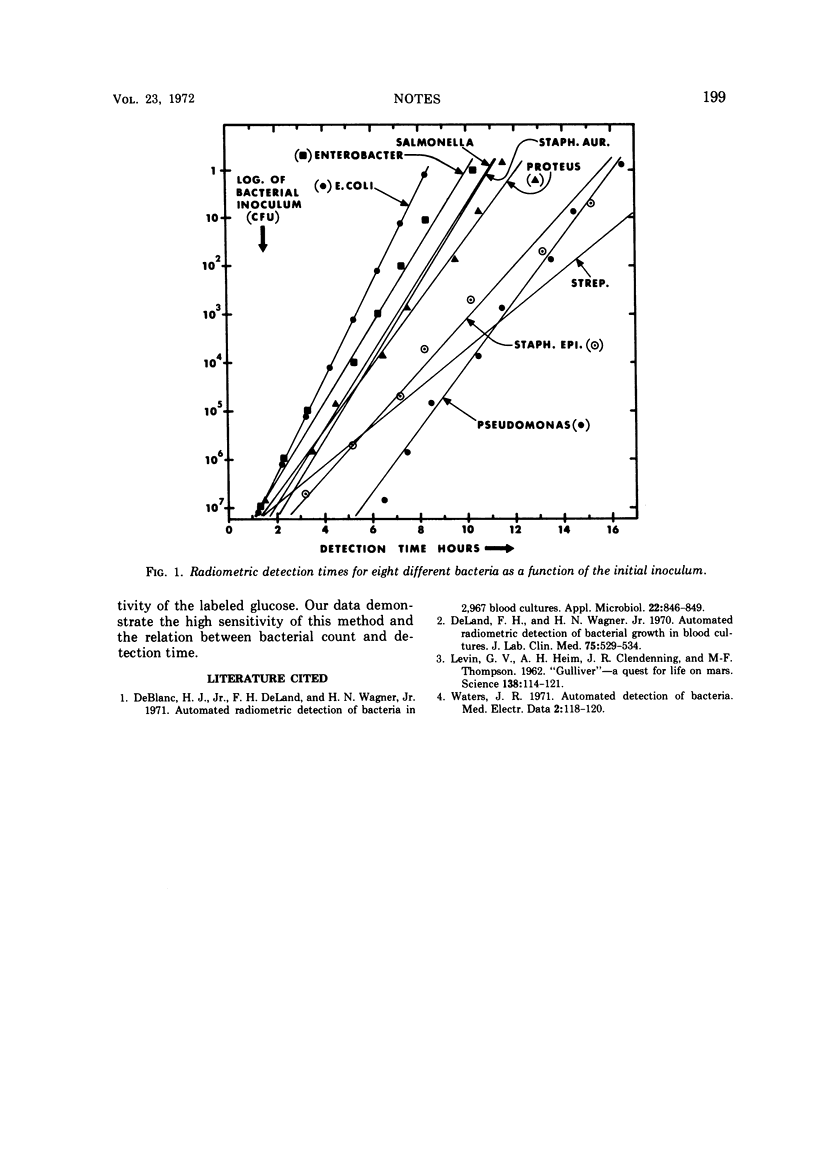
Decimal serial dilutions of eight common bacterial species were prepared, and the detection times were determined by measuring the 14CO2 metabolized from the 14C-labeled glucose substrate. The detection time was proportional to the logarithm of the initial inoculum, and high sensitivity, down to 1 colonyforming unit, was demonstrated.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DeBlanc H. J., Jr, DeLand F., Wagner H. N., Jr Automated radiometric detection of bacteria in 2,967 blood cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):846–849. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.846-849.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLand F., Wagner H. N., Jr Automated radiometric detection of bacterial growth in blood cultures. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Mar;75(3):529–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin G. V., Heim A. H., Clendenning J. R., Thompson M. F. "Gulliver"--A Quest for Life on Mars: Radioisotopes are used in a miniature instrument designed to detect life during early probes of the planet. Science. 1962 Oct 12;138(3537):114–121. doi: 10.1126/science.138.3537.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


