Abstract
Studies were undertaken to improve the production of histoplasmin for use in complement-fixation tests and in the determination of H and M antibodies. A shake culture method performed at 25 C was developed with a yeast-phase inoculum. Eight strains of Histoplasma were tested in three synthetic media to evaluate the effects of strain and medium on H and M antigen production. Intrastrain variation was negligible, and antigen production was reproducible. All of the strains produced H antigen; six strains produced both H and M antigens, and two produced only H antigen. The time of H and M antigen appearance varied with the medium; M antigen appearance was dependent upon the strain and medium used. Titers of M antigen appeared to be greater in stagnant culture.
Full text
PDF


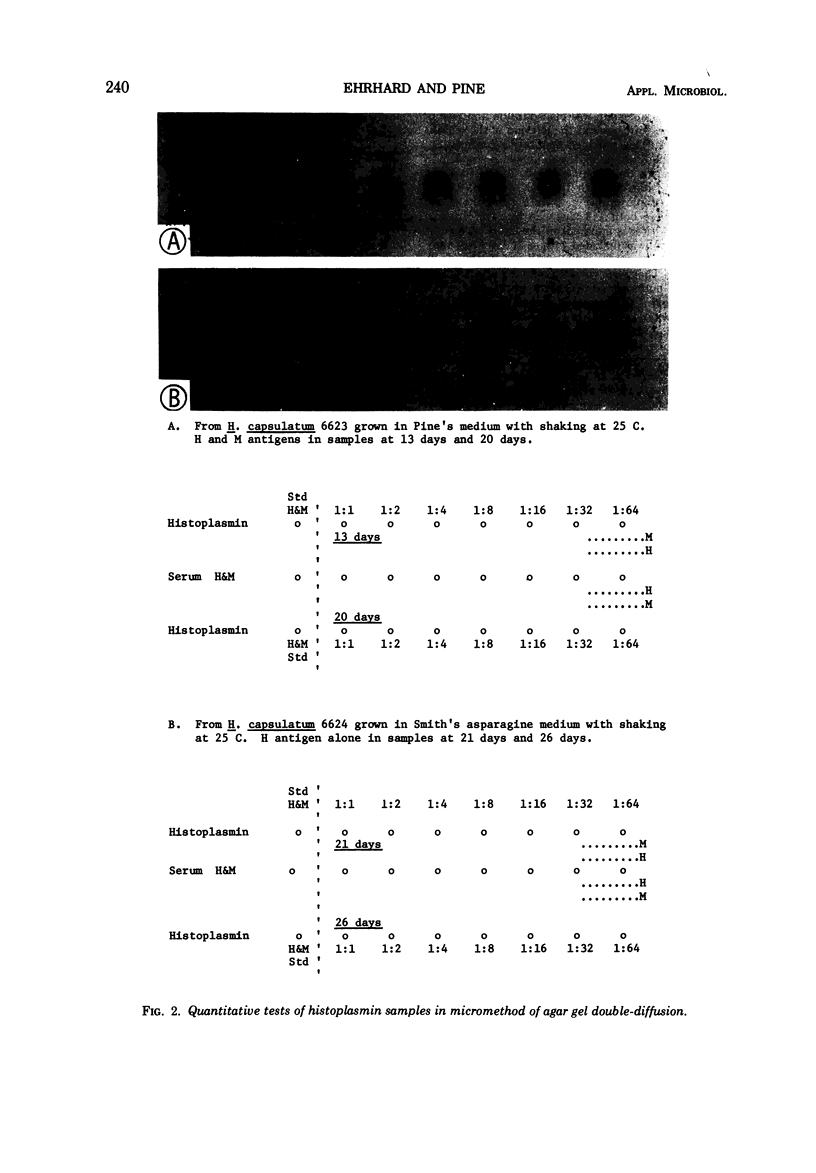


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABERNATHY R. S., HEINER D. C. Precipitation reaction in agar in North American blastomycosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Apr;57:604–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busey J. F., Hinton P. F. Precipitins in histoplasmosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Oct;92(4):637–639. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.92.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWLE A. J. A simplified micro double-diffusion agar precipitin technique. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Nov;52(5):784–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman N. L., Spouse R. F., Larsh H. W. Histoplasmin potency as affected by culture age. Sabouraudia. 1968 Oct;6(4):273–284. doi: 10.1080/00362176885190551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINER D. C. Diagnosis of histoplasmosis using precipitin reactions in agargel. Pediatrics. 1958 Oct;22(4 Pt 1):616–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN L., BRANDT B., MCLAUGHLIN D. EVALUATION OF THE FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY AND AGAR GEL PRECIPITIN TESTS FOR DETECTING HISTOPLASMA ANTIBODIES IN ANTICOMPLEMENTARY SERA. Am J Hyg. 1964 Mar;79:181–185. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN L., SCHUBERT J. H., KAPLAN W. Fluorescent antibody inhibition test for histoplasmosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Jun;59:1033–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L., Blumer S. Development and use of a polyvalent conjugate to differentiate Histoplasma capsulatum and Histoplasma duboisii from other pathogens. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1243–1246. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1243-1246.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klite P. D. The interpretation of agar-gel precipitin reactions in histoplasmosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Nov;66(5):770–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVeigh I., Morton K. Nutritional studies of Histoplasma capsulatum. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1965 Apr 14;25(3):294–308. doi: 10.1007/BF02049917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINE L., KAUFMAN L., BOONE C. J. COMPARATIVE FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY STAINING OF HISTOPLASMA CAPSULATUM AND HISTOPLASMA DUBOISII WITH A SPECIFIC ANTI-YEAST PHASE H. CAPSULATUM CONJUGATE. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1964 Dec 31;24:315–326. doi: 10.1007/BF02053642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINE L. Studies on the growth of Histoplasma capsulatum. I. Growth of the yeast phase in liquid media. J Bacteriol. 1954 Dec;68(6):671–679. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.6.671-679.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINE L. Studies on the growth of Histoplasma capsulatum. III Effect of thiamin and other vitamins on the growth of the yeast and mycelial phases of Histoplasma capsulatum. J Bacteriol. 1957 Aug;74(2):239–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.2.239-245.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L. Growth of Histoplasma capsulatum. VI. Maintenance of the mycelial phase. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Mar;19(3):413–420. doi: 10.1128/am.19.3.413-420.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Public Health Weekly Reports for NOVEMBER 23, 1945. Public Health Rep. 1945 Nov 23;60(47):1383–1413. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUBERT J. H., AJELLO L., COOPER J. S., RUNYON L. C. Evaluation of histoplasmin and yeast phase antigens derived from a single strain of Histoplasma capsulatum in the complement fixation test. J Bacteriol. 1955 May;69(5):558–562. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.5.558-562.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUBERT J. H., LYNCH H. J., Jr, AJELLO L. Evaluation of the agar-plate precipitin test for histoplasmosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Dec;84:845–849. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.84.6.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUBERT J., AJELLO L., STANFORD S., GRANT V. Q. Variation in complement fixation antigen production by different strains of Histoplasma capsulatum grown on two media. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Jan;41(1):91–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvin S. B., Hottle G. A. Factors Influencing Histoplasmin Formation. J Bacteriol. 1948 Nov;56(5):541–546. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.5.541-546.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert J. H., Wiggins G. L. Additional studies of histoplasmin formation. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1966 Nov 10;30(2):81–91. doi: 10.1007/BF02130354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert J. H., Wiggins G. L. Preliminary studies of H and M components of histoplasmin for skin tests and serology. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Oct;92(4):640–641. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.92.4.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADSWORTH C. A slide microtechnique for the analysis of immune precipitates in gel. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1957;10(6):355–360. doi: 10.1159/000228394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIGGINS G. L., SCHUBERT J. H. RELATIONSHIP OF HISTOPLASMIN AGAR-GEL BANDS AND COMPLEMENT-FIXATION TITERS IN HISTOPLASMOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:589–596. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.589-596.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]