Abstract
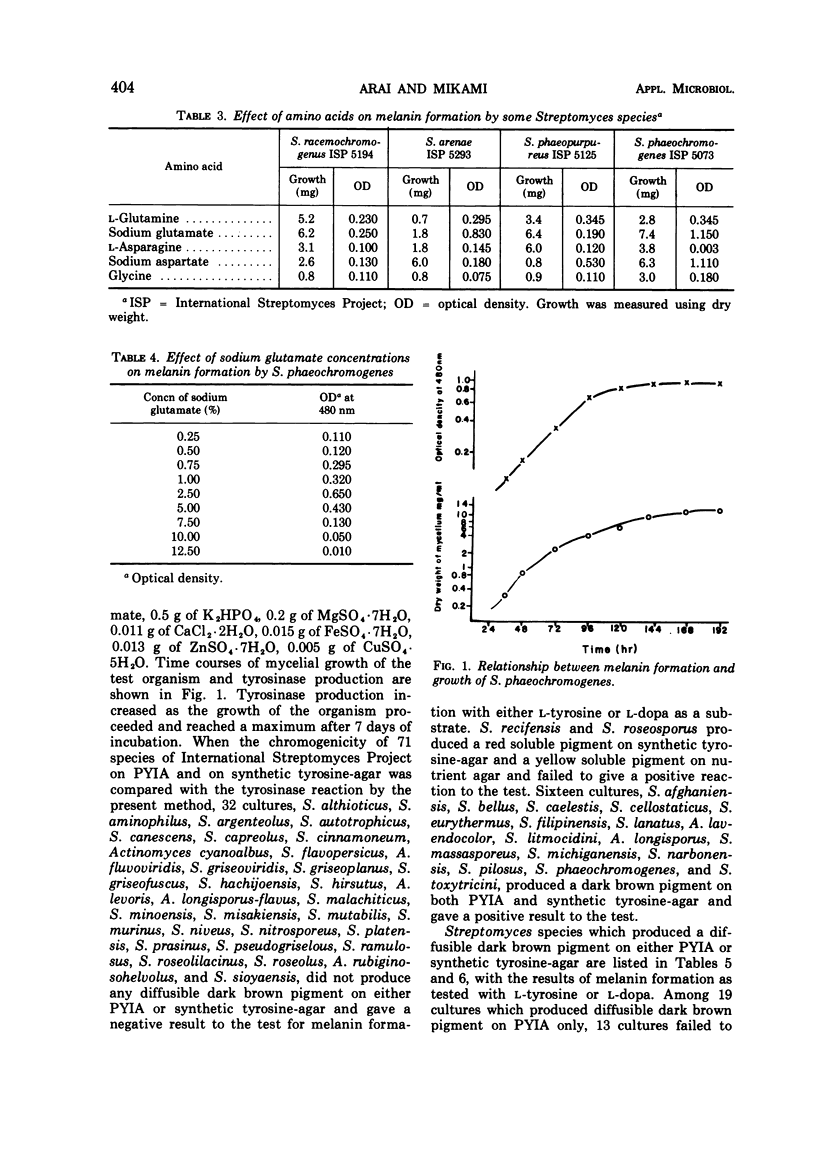
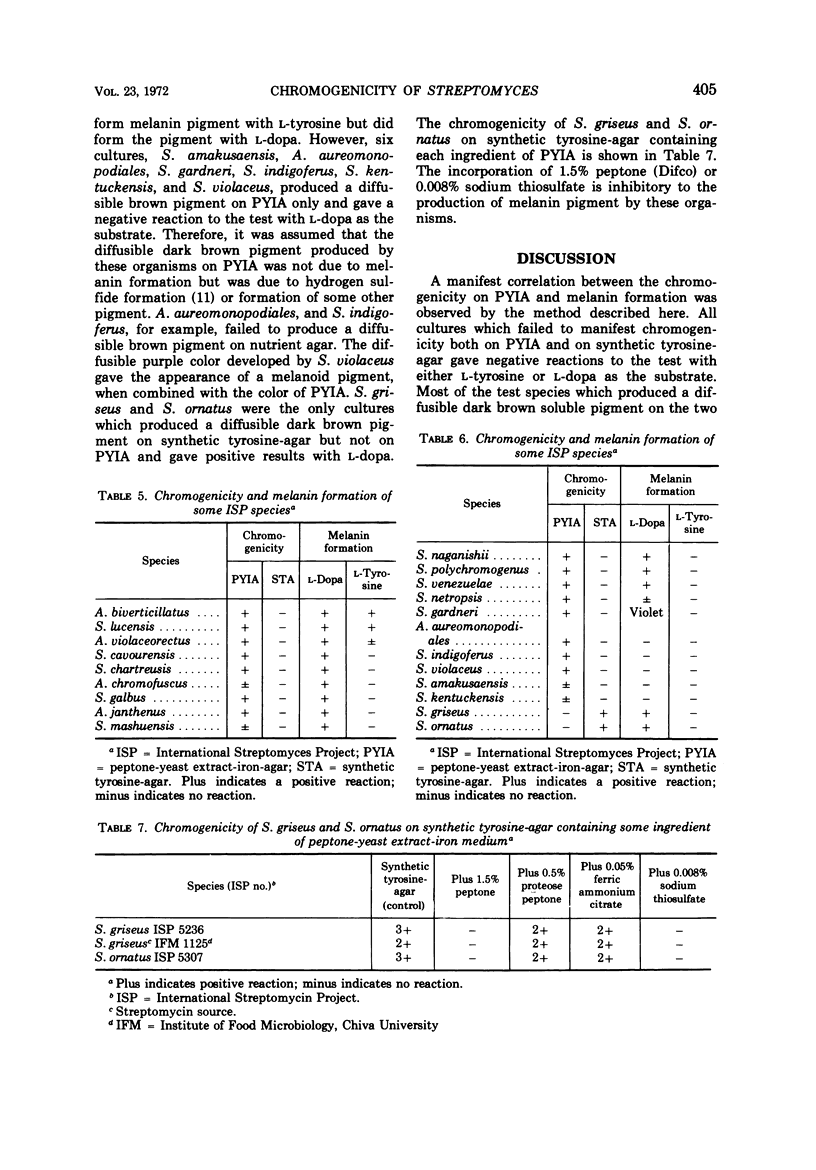
A simplified technique to detect polyphenol oxidase and melanin formation by Streptomyces culture filtrates was developed. The procedure involves the direct assay of pigment formation by the culture filtrate with 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine (L-dopa) as a substrate. Among cultures of the International Streptomyces Project, 34 failed to produce a diffusible dark brown pigment on peptone-yeast extract-iron-agar and synthetic tyrosine-agar and gave a negative reaction to the melanin formation test. Sixteen cultures produced a diffusible dark brown pigment on both peptone-yeast extract-iron-agar and synthetic tyrosine-agar and gave positive reactions to the test with either L-tyrosine or L-dopa as substrate. Twenty-one cultures produced a diffusible dark brown pigment on peptone-yeast extract-iron-agar, but failed to do so on synthetic tyrosine-agar. Most of these cultures gave a positive reaction to the test when L-dopa was used as the substrate. The correlation between chromogenicity on complex organic media and melanin formation was more clearly established with L-dopa as substrate than with synthetic tyrosine-agar in the present test. The melanin formation test by the present technique, instead of chromogenicity on complex organic media, is recommended as a key feature for the classification of Streptomyces.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- TRESNER H. D., DANGA F. Hydrogen sulfide production by Streptomyces as a criterion for species differentiation. J Bacteriol. 1958 Sep;76(3):239–244. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.3.239-244.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenova G. M. Melanoidnye pigmenty aktinomitsetov. Mikrobiologiia. 1965 Mar-Apr;34(2):278–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



