Abstract
MoaA/MoaC catalyze a remarkable rearrangement reaction in which guanosine-5′-triphosphate (GTP) is converted to cyclicpyranopterin monophosphate (cPMP). In this reaction, the C8 of GTP is inserted between the C2′ and the C3′ carbons of the GTP ribose. Previous experiments with GTP isotopomers demonstrated that the ribose C3′ hydrogen atom is abstracted by the adenosyl radical. This led to a novel mechanistic proposal involving an intermediate with a bond between the C8 of guanine and C3′ of the ribose. This paper describes the use of 2′,3′-dideoxyGTP to trap this intermediate.
MoaA/MoaC catalyzes the first step in molybdopterin biosynthesis, converting GTP, 1 to cyclicpyranopterin monophosphate (cPMP, 2)1. MoaA/MoaC catalyzes a remarkable rearrangement reaction in which the C8 of GTP, 1 is inserted into the ribose C2′–C3′ bond (Figure 1).2 Previous experiments with GTP isotopomers demonstrated that the ribose C3′ hydrogen atom is abstracted by the adenosyl radical. This led to a mechanistic proposal involving an intermediate with a bond between the C8 of guanine and C3′ of the ribose (Figure 2).3 In this proposal, the 5′-dA radical 3, generated by reductive cleavage of S-Adenosyl methionine (AdoMet), abstracts the 3′ hydrogen atom from GTP to give 4, which then undergoes cyclization to give 6. Reduction of this radical by the purine liganded iron sulfur cluster to 7 followed by hydrolysis to 8 and a benzilic like rearrangement to 9 completes the insertion of the purine carbon into the ribose. Ring opening of 9 followed by dehydration of 10 and a conjugate addition gives 12. Cyclization to 13 followed by a final tautomerization completes the formation of the reaction product 23. While ribose and deoxyribose radicals have been extensively studied in the context of enzymes such as ribonucleotide reductase and DNA damage by radiation or radical-generating antibiotics, addition of a C3′ centered radical to C8 of a purine has never been reported 5,6,7. The successful trapping of an analog of 8 would provide a critical test of the proposed mechanism. In this communication, we describe the use of 2′,3′-dideoxy-GTP 14 as a substrate analog to achieve this trap-trapping.
Figure 1.
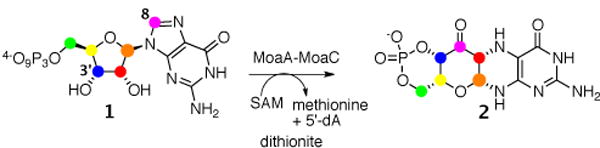
The early reactions in molybdopterin biosynthesis: MoaA/MoaC-catalyzed transformation of GTP (1) to cyclicpyranopterin monophosphate (2). Color shows the atom transfer pattern derived from previous labeling studies.2,4,8
Figure 2.
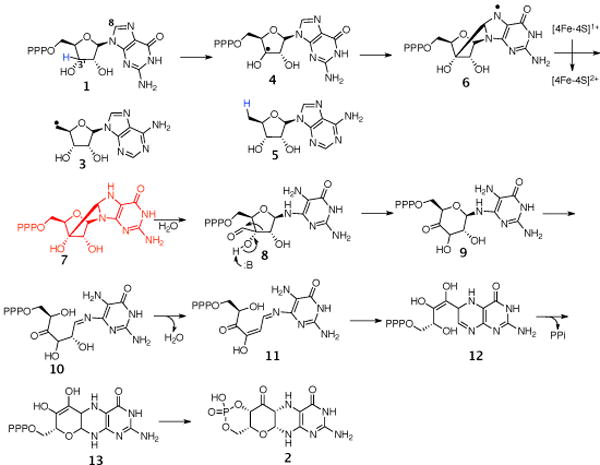
Mechanistic proposal for the MoaA/MoaC-catalyzed reaction.
LCMS analysis of the MoaA/2′,3′-dideoxyGTP 14 reaction mixture demonstrated the formation of a new product eluting at 19.6 min (Figure 3A). ESl-MS (positive mode) analysis of this product demonstrated that its mass [M+H]+ was 490.0 Da - two Da less than the [M+H]+ of the substrate. We considered two possible structures for this product (16 and 20, Figure 3D). To test for the formation of 16, the enzymatic product was dephosphorylated by phosphatase treatment and compared to an authentic sample of 17 (synthesis described in S.l.) by LCMS. Figures 3C and Figures S28 and S29 demonstrate that the retention time of 17 and its MS/MS spectrum are different from the enzymatic product. This excludes the possibility that MoaA catalyzes the formation of 16 from 14.
Figure 3.
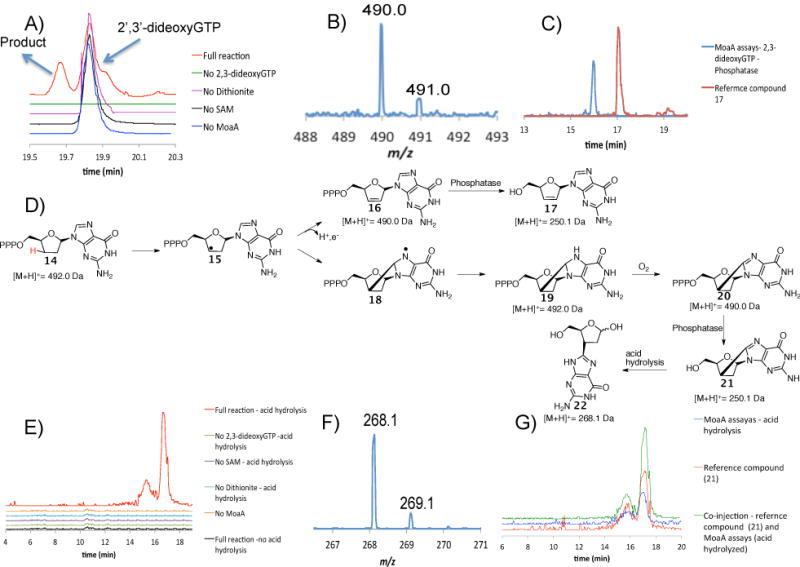
Analysis of the product formed when 2′,3′-dideoxyGTP 14 is treated with MoaA. A) LC analysis of the MoaA reaction mixture and controls. Red trace is the full reaction where all the components are present. Green, pink, black and blue traces are for reaction mixtures where either 2′,3′-dideoxyGTP, dithionite, SAM or MoaA is absent respectively. The unidentified signal at 19.9 min has the same [M+H]+ as 2′,3′-dideoxyGTP. B) MS of the compound eluting at 19.6 min. The [M+H]+ is 490.0 Da -two Da less than the [M+H]+ of the substrate 14. C) Extracted Ion Chromatograms for [M+H]+ = 250.0 Da demonstrate that compound 17 is different from the dephosphorylated enzymatic product. D) Mechanistic analysis to suggest possible products formed from 2′,3′-dideoxyGTP 14. E) Extracted Ion Chromatograms for [M+H]+ = 268.1 Da demonstrate that the [M+H]+ = 268.1 Da signal is seen only in reaction mixtures with all the components present after phosphatase treatment and acid hydrolysis. The two compounds with [M+H]+ = 268.1 Da are most likely a consequence of hemiacetal isomerization during the acid hydrolysis. F) MS of the compound formed by acid hydrolysis of the dephosphorylated enzymatic product ([M+H]+ = 268.1 Da). G) Extracted Ion Chromatograms for [M+H]+ = 268.1 Da demonstrate that the derivatized enzymatic product has the same mass and co-elutes with compound 22.
The MS/MS spectrum of 17 showed fragmentation of the N-glycosyl bond to form guanine (152.0 Da, Figure S23). This fragmentation was not detected for the dephosphorylated enzymatic product (Figure S24) suggesting an additional bond between the sugar and the base consistent with 20. Unfortunately, NMR characterization of the enzymatic product was not possible. Only small quantities were formed because 2′,3′-dideoxyGTP 14 is a poor substrate (there is no evidence for enzyme modification by MS analysis). An identification strategy, involving comparison with a reference compound, was therefore adopted. If 19 is the product structure, oxidation and dephosphorylation, followed by N-glycosyl bond cleavage would give 22 which can be synthesized as a reference (see SI). To test this, the enzymatic product was derivatized by treating the MoaA reaction mixture with phosphatase followed by acid at 65°C for 2 hrs. The extracted ion chromatograms for 268.1 Da (22 + H+ + H2O) are shown in Figure 3E and demonstrate that the acid treatment generates isomers of the product as expected from ring opening of the hemiacetal. The derivatized enzymatic product coelutes with the synthetic reference, (also generates isomers on acid treatment (see SI) and is identical by LCMS analysis. Thus, the enzymatic reaction of 2′,3′-dideoxy-GTP, 14 supports the formation of the remarkable reaction intermediate 7 in the MoaA-catalyzed reaction.
A mechanistic proposal for the formation of 22, is described in Figure 4. The 5′-dA radical 4 abstracts the 3′ hydrogen atom from 2′,3′-dideoxyGTP 14, to give 15, which then undergoes cyclization to give 18. Reduction of this radical by the purine liganded iron sulfur cluster gives 19 which on aerobic oxidation results in the formation of 20. Phosphatase treatment of 20 followed by acid hydrolysis gives 22 as a mixture of isomers.
Figure 4.

Mechanistic proposal for the MoaA catalyzed reaction and subsequent derivatization of 2′,3′-dideoxyGTP 14
While this paper was under review, an important new paper on the mechanism of MoaA/MoaC appeared in the literature9. This paper suggests that compound 7 is the product of MoaA and demonstrates that 7 is a substrate for MoaC. Both papers provide support for the unprecedented bond formation between C3′ of the ribose and C8 of the purine using different but complementary approaches.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (DK44083) and by the Robert A. Welch Foundation (A-0034)
Footnotes
Supporting Information : The experimental procedures are mentioned in the supporting information. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org
References
- 1.Fisher M, Thony B, Leimkuhler S. Comprehensive Natural Products II Chemistry. Biology. 2010;7:628–640. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Johnson J, Wuebbens M, Rajagopalan K. J Biol Chem. 1989;264(23):13440–13447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mehta A, Hanes J, Abdelwahed S, Hilmey D, Hañzelmann P, Begley T. Biochemistry. 2013;52:1134–36. doi: 10.1021/bi3016026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lees NS, Häzelmann P, Hernandez HL, Subramanian S, Schindelin H, Johnson MK, Hoffman BM. JACS. 2009;131(26):9184–91850. doi: 10.1021/ja903978u. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Stubbe J, Nocera D, Yee C, Chang M. Chem Rev. 2003;103(6):2167–2202. doi: 10.1021/cr020421u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chatgilialoglu C, Ferreri C, Terzidis M. Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40:1368–1382. doi: 10.1039/c0cs00061b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Greenberg MD, editor. Radical and Radical Ion Reactivity in Nucleic Acid Chemistry. 2009. pp. 1–443. (Wiley Series of Reactive intermediates in Chemistry and Biology). [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wuebbens M, Rajagopalan K. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:1082–1087. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.3.1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hover B, Loksztejn A, Ribeiro A, Yokoyama K. JACS. 2013;135(18):7019–7032. doi: 10.1021/ja401781t. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


