Abstract
Prostate cancer is a heterogeneous disease, and its management is now evolving to become more personalized and to incorporate new targeted therapies. With these new changes comes a demand for molecular imaging techniques that can not only detect disease but also assess biology and treatment response. This review article summarizes current molecular imaging approaches in prostate cancer (e.g. 99mTc bone scintigraphy and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography) and highlights emerging clinical and preclinical imaging agents, with an emphasis on mechanism and clinical application. Emerging agents at various stages of clinical translation include radiolabeled analogs of lipid, amino acid, and nucleoside metabolism, as well as agents more specifically targeting prostate cancer biomarkers including androgen receptor, prostate-specific membrane antigen and others. We also highlight new techniques and targeted contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. For all these imaging techniques, a growing and important unmet need is for well-designed prospective clinical trials to establish clear indications with clinical benefit in prostate cancer.
Keywords: Molecular imaging, prostate cancer, positron emission tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, single photon emission computed tomography, prostate-specific membrane antigen, androgen receptor
Introduction
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in American men, with an estimated annual incidence of 241,740 and mortality of 28,170 in 2012 [1]. The disease spectrum is extremely broad, ranging from indolent asymptomatic disease to aggressive metastatic disease. For this reason, clinical management is individualized based on risk factors including stage, serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level, and pathologic Gleason score, as outlined in the risk stratification schema of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network [2, 3]. Local treatment options include radical prostatectomy, external beam radiation, and brachytherapy with radioactive seed implantation. However, recent data increasingly supports the management of very low risk disease with active surveillance, as these patients are often over-treated [4, 5].
For patients with intermediate to high-risk or metastatic disease, the mainstay of systemic treatment is androgen deprivation therapy. Until recently, there were no effective treatment options for castrate-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), but in the past 5 years several agents have shown a significant survival benefit in CRPC and join docetaxel [6] as therapeutic options in this clinical scenario. These include the anti-microtubule agent cabazitaxel [7], the oral CYP17 inhibitor abiraterone (that decreases testosterone production) [8, 9], the androgen receptor antagonist enzalutamide [10], and the autologous cancer vaccine sipuleucel-T [11]. With these new agents, the landscape for treatment of metastatic prostate cancer is changing rapidly.
The trend toward more personalized care and development of new combination therapies for prostate cancer raises a demand for more specialized biomarkers and imaging techniques. Serum PSA testing remains the standard of care for detection and monitoring, but it has been limited by a low specificity (20-40%) that is only partially improved by adaptations such as PSA density, PSA velocity, and free PSA [12]. Likewise, imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT) and 99mTc-based bone scintigraphy have been limited by low accuracy, low-specificity, and inability to detect nodal disease for bone scintigraphy [13]. There is particular clinical need for improved imaging sensitivity for detection of micrometastatic disease during initial workup and for discrimination of locoregional versus distant disease in the setting of PSA relapse. Improved intraprostatic imaging could also influence local treatment choices and/or treatment planning. However, beyond the need for improved detection of disease, there is a challenge for molecular imaging to assess disease biology (e.g. indolent vs. aggressive) and treatment response (e.g. to androgen-deprivation and new CRPC treatments). This review article will summarize the many existing and emerging molecular imaging techniques for prostate cancer, with particular emphasis on their potential for mechanism-based and personalized approaches to disease management.
Imaging prostate cancer: present
Traditional prostate cancer anatomic imaging techniques include transrectal ultrasound (TRUS), CT and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [14]. TRUS has become an essential tool for guidance of interventions such as prostate biopsies and radioactive seed placement by anatomical imaging of the prostate gland but has a limited role for detection of prostate cancer [15]. CT is commonly used for initial staging of intermediate to high-risk disease, to evaluate for pelvic lymphadenopathy and gross extraprostatic disease extension. However, its sensitivity for detection of nodal metastases is only about 35% [13]. T2-weighted endorectal MRI has shown superior soft tissue resolution compared to CT for evaluating local tumor extent, especially with the use of an endorectal coil. MRI has many potential applications in prostate cancer, including initial staging, biopsy guidance, surgical planning, radiation planning, and restaging after PSA relapse [16]. However, it has not yet become widely accepted, partly due to unclear indications and high inter-observer variability.
At large referral centers with expert radiologists, multiparametric MRI is increasingly being utilized with diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), MR spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) and/or dynamic contrast enhancement (DCE-MRI). DWI represents the functional environment of water in tissue and the cellular status of normal and pathologic tissue and therefore is an indicator for characterization and differentiation of benign versus malignant lesions [17]. MRSI can improve prostate cancer specificity and assess tumor aggressiveness by detecting metabolic signatures characteristic of disease. In particular, the ratio of choline plus creatine to citrate in prostate voxels has demonstrated a positive predictive value (PPV) of 90% in combination with MRI [18]. On DCE-MRI, prostate tumors show early enhancement and washout, and this technique can further improve specificity and tumor localization. Multiparametric MRI may be especially valuable for characterization of intraprostatic lesions in patients managed with active surveillance and in patients with PSA relapse after radiation [19, 20].
Prostate cancer most frequently metastasizes to the bone with a predominantly osteoblastic (sclerotic) pathogenesis. Therefore, the mainstay of imaging for advanced prostate cancer is 99mTc-labeled biphosphonate (e.g. 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate [MDP]) bone scintigraphy, which is based on the incorporation of biphosphonate analogue into hydroxyapatite crystals and collagen matrix. This molecular imaging technique is used for initial staging of intermediate to high-risk disease and for restaging after PSA relapse. It has high sensitivity and the ability to survey the entire skeleton with a simple planar scan [13]. However, it has limited specificity and is not sensitive enough to detect micrometastases. Single-photon-emission-tomography (SPECT) and SPECT/CT have been shown to improve the sensitivity and reduce the number of equivocal reports for detection of bone metastases in prostate cancer [21, 22]. Quantitative analysis using the bone scan index (BSI) has recently been shown to be prognostic for survival, and BSI is also under investigation for assessment of treatment response [23, 24].
Images of bone metastases on positron-emission-tomography (PET) may be achieved with 18F-sodium fluoride which is also incorporated into hydroxyapatite crystals in bone. 18F-NaF PET has recently demonstrated higher sensitivity than 99mTc bone scan or SPECT for prostate cancer bone metastases, and incorporation of bone findings from CT with PET/CT provides improved specificity [21]. In a limited study, whole-body DWI MRI demonstrated a higher specificity but lower sensitivity compared with 18F-NaF PET/CT [25]. Another advantage of 18F-NaF PET is the shorter scan time compared to bone scans. 18F-NaF was approved by the FDA in 1972 for use with planar gamma scanners but had poor resolution compared to 99mTc-MDP. However, the recent positive PET results and widespread availability of PET have prompted the initiation of a large ongoing prospective study of 18F-NaF by the National Oncology PET Registry (NOPR) through the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) (http://www.cancerpetregistry.org/).
18F-FDG PET has been of limited use in prostate cancer due to the relatively low uptake in the setting of biochemical recurrence or castrate-dependent disease and the nonspecific uptake of 18F-FDG in prostatitis or benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) for primary disease. However, there is evidence that 18F-FDG PET may be useful for restaging after PSA relapse and for assessment of treatment response in CRPC [26-29]. In particular, 18F-FDG PET is most useful for evaluating lymph node and bone metastases in patients with PSA > 2.4 ng/mL and PSA velocity > 1.3 ng/mL/yr [28]. In a recent study by Meirelles et al., 18F-FDG PET showed higher sensitivity than 99mTc bone scan for bone metastases due to CRPC [30].
A number of molecular imaging agents have been developed to target the biomarker, prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA), an integral membrane glycoprotein that is highly upregulated in prostate cancer. A mouse monoclonal antibody against PSMA, 111In-capromab pendetide (ProstaScint™), was approved by the FDA in 1996 and initially showed potential for restaging after PSA relapse. However, this agent repeatedly failed in the clinical setting, likely due to poor pharmacokinetics and failure to reach its target epitope on the intracellular portion of PSMA [31-33]. Other emerging techniques based on PSMA are quite promising and will be discussed below.
Imaging prostate cancer: experimental and near-term future
An expanding number of molecular imaging agents for prostate cancer are currently being tested in humans, and we anticipate that several of these will gather widespread clinical application in the near future. In broad categories, these probes include: lipid components (11C/18F-choline and 11C-acetate), amino acids (11C-methionine, 18F-FACBC leucine analog, and 18F-glutamine), nucleoside analogs (18F-FMAU thymidine analog), molecular targeting agents (18F-FDHT for androgen receptor; 111In-J591, 18F-DCFBC and others for PSMA), and macrophage targeting agents (lymphotropic nanoparticles for MRI). We will address each of these categories with special emphasis on mechanism and potential clinical application (summarized in Table 1). However, for all of these agents, the greatest need is for prospective, controlled clinical trials to establish clear indications for use in prostate cancer.
Table 1.
Current molecular imaging agents in prostate cancer (in clinical use or trials).
| Agent | Technique | Half-life | Mechanism | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18F-FDG | PET | 110 min | Glucose analog | PSA relapse |
| 99mTc-MDP | Planar/ SPECT |
6 hr | Bone targeting (hydroxyapatite) |
Bone metastases |
| 18F-NaF | PET | 110 min | Bone targeting (hydroxyapatite) |
Bone metastases |
|
111In-capromab pendetide |
SPECT | 67 hr | PSMA binding (antibody) | PSA relapse |
| 11C/18F -choline | PET | 20 min/ 110 min |
Lipid metabolism agent | PSA relapse |
| 11C-acetate | PET | 20 min | Lipid metabolism agent | PSA relapse |
| 18F-FACBC | PET | 110 min | L-leucine amino acid analog | TBD |
| 11C-methionine | PET | 20 min | Amino acid | Initial staging |
| 18F-FMAU | PET | 110 min | Thymidine analog | TBD |
| 18F-FDHT | PET | 110 min | Androgen receptor binding (testosterone-based) |
Treatment response |
| 111In-J591 | SPECT | 67 hr | PSMA binding (antibody) | TBD |
| 18F-DCFBC | PET | 110 min | PSMA binding (urea-based) | TBD |
| 68Ga-PSMA | PET | 68 min | PSMA binding (urea-based) | TBD |
| Ferumoxtran | MRI | N/A | Macrophage targeting (nanoparticles) |
Lymph node metastases |
Lipid metabolism agents
The development of 18F-choline has recently been expertly reviewed by Bauman et al. and will therefore only be summarized here [34]. Briefly, prostate cancer cells have been shown to have increased fatty acid metabolism with up-regulation and increased activity of lipogenic enzymes [35]. 11C/18F-choline and 11C-acetate in prostate cancer have been associated with choline kinase [36, 37] and fatty acid synthase [38], respectively. The major advantage of 18F-choline is its longer half-life compared to 11C-choline (110 min vs. 20 min). However, 18F-choline has more urinary excretion with bladder accumulation. These agents are not ideal for initial staging due to false positives in prostatitis and BPH and false negatives in small (<5 mm) or necrotic tumors [39]. However, they have shown promise for restaging after PSA relapse, with high sensitivity for local recurrence, nodal metastases and bone metastases [40-43]. A recent study by Giovacchini et al. showed that 11C-choline uptake correlates with PSA velocity and doubling time in the setting of PSA relapse [44]. Furthermore, Souvatzoglou and Rigatti have demonstrated the potential application of 11C-choline for personalized image-guided salvage radiation or lymph node dissection [45, 46]. The utility of 11C-choline after PSA relapse was further highlighted by its recent FDA approval for this indication at the Mayo Clinic. Like 11C-choline, 11C-acetate may be best used for restaging, and studies have shown enhanced sensitivity compared to 18F-FDG [47, 48]. A direct comparison of 11C-acetate and 11C-choline by Kotzerke et al. showed no clear clinical differences between these agents [49].
Amino acid analogs
The amino acids leucine, methionine, and glutamine are effectively taken up by many tumors due to increased amino acid transport and metabolism. The most promising of these agents for prostate cancer imaging has been anti-1-amino-3-18F-fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid (anti-18F-FACBC), an L-leucine analog with excellent tumor uptake and minimal urinary excretion. This probe has shown early clinical success in imaging primary and recurrent disease in the prostate, pelvic lymph nodes and bone, with improved sensitivity compared to 111In-capromab pendetide (Figure 1) [50-52]. Another amino acid, 11C-methionine, has recently shown potential for initial evaluation of low and high grade primary prostate tumors and for guidance of prostate biopsies in patients with elevated PSA and multiple negative biopsies [53, 54]. Finally, glutamine metabolism is upregulated in many tumors, and 18F-labeled glutamine analogs are now emerging for imaging prostate cancer [55].
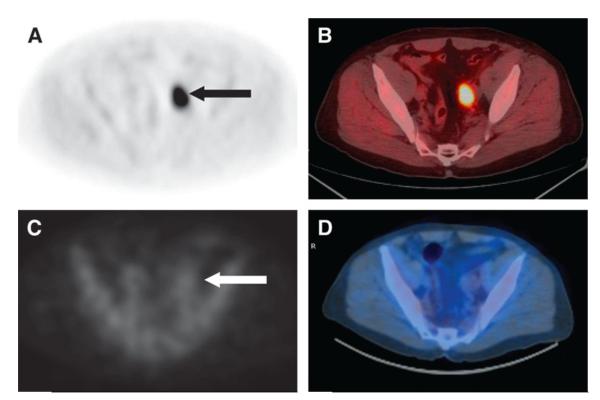
Figure 1.
Axial anti-18F-FACBC PET (A) and PET/CT (B) images in a 67-y-old patient with PSA relapse show intense activity in the left external iliac nodes (black arrow). In the same patient, axial 111In-capromab pendetide SPECT (C) and SPECT/CT (D) images demonstrate no significant activity in this region (white arrow). Reproduced with permission from Schuster et al [52].
Nucleoside analogs
The thymidine analogs 18F-2′-fluoro-5-methyl-1-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl uracil (FMAU) and 18F-3′-fluoro-3′ deoxythymidine (FLT) are biomarkers of cellular proliferation. 18FFMAU has been evaluated in a phase 0 study of multiple cancers and showed uptake in primary prostate cancer as well as bone metastases [56]. Furthermore, preclinical studies have demonstrated that 18F-FMAU uptake is associated with androgen signaling, with increased uptake in castrated animals [57]. 18F-FLT has shown promise in many cancers for evaluation of early treatment response, and it is currently being tested in prostate cancer clinical trials after preclinical success in prostate models [58].
Molecular targeting agents
Direct imaging of androgen receptors in prostate cancer is now possible using 18F-16β-fluoro-5α-dihydrotestosterone (FDHT), and receptor binding specificity has been proven in humans by blocking with flutamide or testosterone [59, 60]. 18F-FDHT has shown a 78% tumor localization rate in patients with metastatic disease, but it is most unique in its successful application for PET pharmacodynamics in a phase I-II trial of the new androgen receptor antagonist enzalutamide for CRPC [60, 61]. In this study by Scher et al., PET imaging of 22 patients showed decreased 18F-FDHT binding after 4 weeks of enzalutamide therapy (at all doses) compared to baseline (Figure 2) [61]. This serves as a proof of principle for the application of molecular imaging agents for prostate cancer drug development and for assessment of individual treatment response [26, 59, 60].
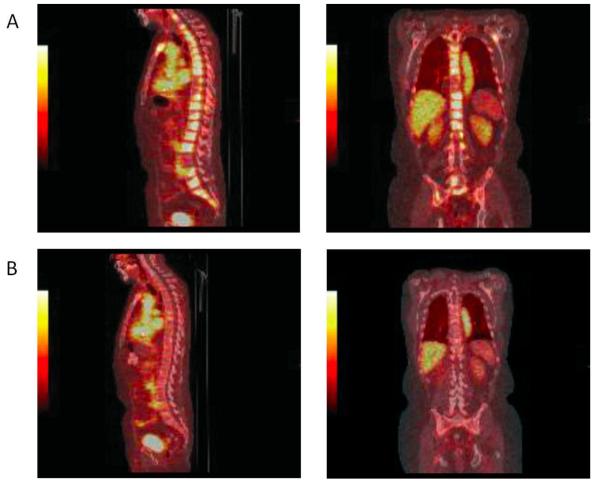
Figure 2.
18F-FDHT PET images at baseline (A) and after 4 weeks of treatment with enzalutamide (B). The sagittal and coronal images were taken 1 h after administration of 18F-FDHT. After four weeks, they show a reduction in 18F-FDHT accumulation in tumor within the vertebrae, compared with the cardiac and aortic blood pool. Reproduced with permission from Scher et al [61].
As noted above, PSMA is a well-characterized biomarker that has been recognized as a molecular imaging target in prostate cancer for many years. PSMA expression is associated with aggressive disease biology, and it is also upregulated by androgen deprivation [62-64]. Though clinical results with 111In-capromab pendetide have been disappointing, other promising PSMA probes are now entering clinical trials, including antibodies and small molecules. The monoclonal antibody J591, developed by Bander et al., targets the extracellular portion of PSMA and has been labeled with several PET and SPECT radionuclides [65-67]. In early phase studies, 111In-J591 has shown accurate detection of prostate cancer bone and soft tissue metastases, as well as uptake in the tumor neovasculature of many solid tumors (where PSMA is also expressed) [65, 68]. The PET agent 89Zr-desferrioxamine B (DFO)-J591 has shown excellent tumor uptake and retention in preclinical models and is now entering clinical trials [69]. Figure 3 shows specific uptake of 89Zr-DFO-J591 in PSMA-positive LNCaP xenografts (tumor-to-muscle ratio of 26:1 at 144 hr) but not in PSMA-negative PC3 xenografts (tumor-to-muscle ratio of 5:1 at 144 hr) [69]. Other antibody-based agents in preclinical development include 64Cu-J591, which has been used to demonstrate PSMA upregulation after androgen blockade, 64Cu-3/A12, a monoclonal antibody to the extracellular portion of PSMA, and 89Zr-(DFO)-7E11, a monoclonal antibody to the intracellular portion of PSMA [70-72].
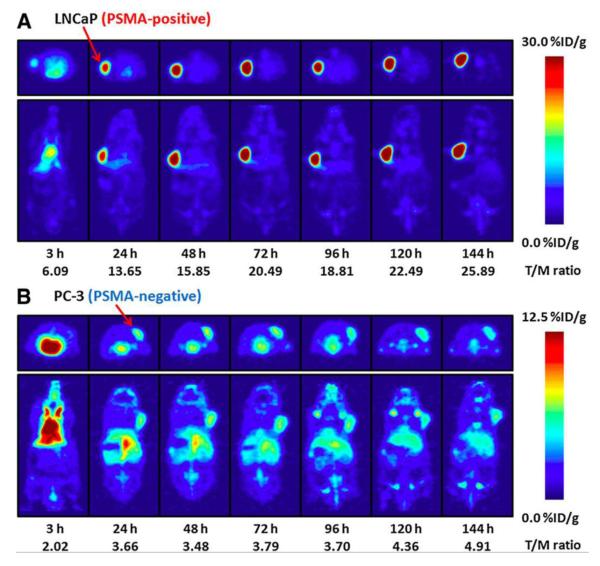
Figure 3.
Temporal PET images of 89Zr-DFO-J591 in mice bearing LNCaP xenografts (PSMA-positive, A) or PC-3 xenografts (PSMA-negative, B). Axial and coronal planar images at the center of the tumors show PSMA-specific uptake and retention of 89Zr-DFO-J591. Mean tumor-to-muscle ratios and upper thresholds of scale are shown. Reproduced with permission from Holland et al [69].
Our group and others have developed small molecules targeting PSMA in order to improve tumor uptake and clearance from non-target sites [73, 74]. A low-molecular-weight, urea-based inhibitor of PSMA, 18F-N-[N-[(S)-1,3-dicarboxypropyl]carbamoyl]-4-fluorobenzyl-L-cysteine (18F-DCFBC) has now been evaluated in a phase 0 trial for progressive metastatic prostate cancer. Bone and soft tissue metastases were successfully visualized by PET, including probable early bone lesions that were not seen on CT or 99mTc-MDP bone scan (Figure 4) [75]. A second-generation low-molecular weight 18F-fluorine labeled PSMA targeting agent, 2-(3-[1-Carboxy-5-[(6-[18F]fluoro-pyridine-3-carbonyl)-amino]-pentyl]-ureido)-pentanedioic acid (18F-DCFPyL), has also been developed with preclinical studies demonstrating high tumor to background ratio at two hours post-injection of 39.4 ± 5.4 percent injected dose per gram of tissue (%ID/g) evident within the PSMA expressing tumor xenografts [76]. A PSMA-targeting SPECT agent 99mTc-trofolastat, developed by Molecular Insight Pharmaceuticals, has also shown rapid uptake in human bone and soft tissue metastases and is now in phase II trials [77]. We have also synthesized a 99mTc-radiolabeled PSMA agent, which in preclinical studies demonstrates tumor-to-background ratio of 44:1 at 120 min post-injection [78]. In addition, another urea-based inhibitor, Glu-NH-CO-NH-Lys-(Ahx)-[68Ga(HBED-CC)] (68Ga-PSMA), was recently tested in 37 prostate cancer patients and showed a median tumor-to-background ratio of 28:1 at 3 hours post-injection [79, 80]. Other urea-based agents with even higher binding affinities are in preclinical development [81].
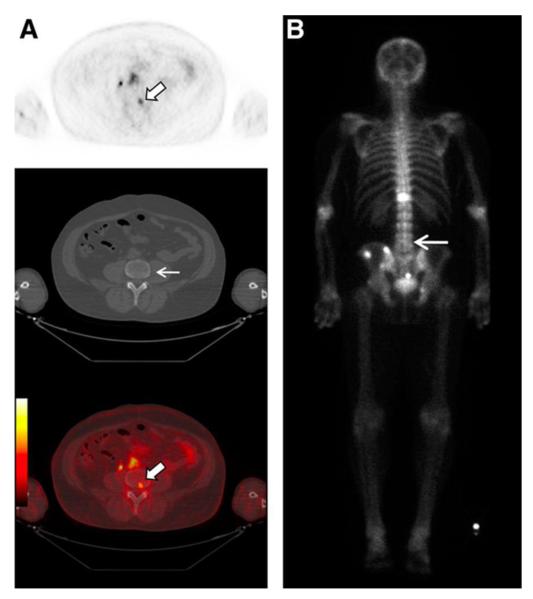
Figure 4.
18F-DCFBC PET images in a patient with progressive metastatic prostate cancer. An area of focal 18F-DCFBC uptake in the L4 vertebral body on PET and fused PET/CT (thick arrows, A) showed no correlative abnormality on CT (thin arrow, A) or bone scan (arrow, B). Reproduced with permission from Cho et al [75].
Macrophage targeting agents
A class of functional MRI contrast agents has been developed to target macrophages within lymph nodes, a technique termed lymphotropic nanoparticle-enhanced MRI (LNMRI) or MR lymphangiography. These agents are composed of inert ultra-small supraparamagnetic iron oxide (USPIO) particles (e.g. ferumoxtran) that are phagocytosed by macrophages and decrease T2-weighted signal in non-tumor areas. They have shown excellent sensitivity and specificity for pelvic nodal metastases measuring at least 5 mm [82]. Indeed, a prospective multicenter study of 375 intermediate to high-risk patients confirmed that LN-MRI had significantly higher sensitivity and negative predictive value for detection of nodal metastases compared to CT [83]. This technique could be quite valuable for surgical or radiation treatment planning, as omission of pelvic nodal dissection and/or irradiation could significantly reduce toxicity.
Imaging prostate cancer: new compounds
There are many new compounds under investigation for imaging prostate cancer and, as expected, most are highly specific molecular targeting agents. This trend is consistent with the changing clinical and experimental landscape of prostate cancer, moving toward a more mechanism-based approach to this heterogeneous disease. In the following section, we highlight recent preclinical studies, particularly focusing on those published in the past few years (summarized in Table 2).
Table 2.
Future molecular imaging agents in prostate cancer (in preclinical testing).
| Agent | Technique | Half-life | Mechanism/ Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18F-FLT | PET | 110 min | Thymidine analog |
| 89Zr-(DFO)-J591 | PET | 78 hr | PSMA (antibody) |
| 64Cu-J591 | PET | 13 hr | PSMA (antibody) |
| 99mTc-trofolastat | SPECT | 6 hr | PSMA (small molecule) |
| 89Zr-(DFO)-5A10 | PET | 78 hr | free PSA (antibody) |
|
111In-DOTA- ZIGF1R:4551 |
SPECT | 67 hr | Insulin-like growth factor receptor (Affibody) |
| 99mTc-bombesin | SPECT | 6 hr | Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (small molecule) |
| 64Cu-TP3939 | PET | 13 hr | Vasoactive pituitary adenylate cyclase- activating peptide receptor (small molecule) |
|
64Cu-DOTA- EpCAM mAb |
PET | 13 hr | Epithelial cellular adhesion molecule (antibody) |
| 131I-NM404 | SPECT | 8 d | Phospholipid ether |
| M13-SBP-MNP | MRI | N/A | Tumor matrix glycoproteins (bacteriophage with nanoparticles and peptide) |
| Gd-DOTA-CLT1 | MRI | N/A | Fibrin-fibronectin (small molecule) |
| Hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate/lactate |
MRSI | N/A | Metabolite analog |
New compounds for PET or SPECT
A large variety of molecular targets are now being explored for imaging prostate cancer, including tumor receptors and other specific biomarkers. A free PSA antibody (5A10) conjugated with 89Zr-(DFO) has been used in preclinical CRPC models to measure androgen receptor-dependent changes in tumor PSA expression [84]. This technique has the potential to measure treatment response to anti-androgens and other therapies. A group in Sweden has recently focused on the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R), which is involved in androgen independence and is an emerging drug target. Their Affibody-based agent 111In-DOTA-ZIGF1R:4551 showed IGF-1R-specific uptake in DU-145 xenografts with a tumor-to-blood ratio of 3:1 at 8 hours [85]. A series of 99mTc-labeled bombesin compounds have been developed to target the gastrin-releasing peptide receptor, which is overexpressed in many cancers, and they have shown tumor-to-muscle ratios of up to 24:1 at 24 hours in PC3 xenografts [86]. The vasoactive pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide receptor-1 (VPAC1) is expressed in all prostate cancers, and a VPAC1-targeting peptide probe 64Cu-TP3939 has shown uptake in PC3 xenografts with a tumor-to-muscle ratio of 6:1 at 24 hours [87]. Hall et al. recently developed a monoclonal antibody to the epithelial cellular adhesion molecule EpCAM (expressed in many cancers) that is dual labeled with 64Cu-DOTA and IRDye 800CW. In an orthotopic PC3 xenograft model, they demonstrated 87% accuracy for identification of nodal metastases [88]. Counsell et al. has developed multiple radiolabeled versions of phospholipid ethers, which are abundant in a variety of tumors, and they have shown tumor uptake of up to 18% of the injected dose per gram at day 5 for 131I-NM404 in PC3 xenografts [89, 90].
New compounds for MRI or MRSI
Several groups have recently targeted extracellular matrix proteins to improve MRI contrast enhancement in prostate cancer models. Ghosh et al. used a novel M13 bacteriophage as a carrier for multiple iron oxide nanoparticles and a peptide targeting the tumor matrix glycoprotein SPARC (M13-SBP-MNP). They showed excellent nanoparticle delivery and MRI contrast in prostate cancer xenograft models [91]. Another group used a small molecule approach, targeting fibrin-fibronectin complexes with the cyclic peptide CLT1 conjugated to Gd-DOTA. They showed high binding specificity and improved MRI contrast compared to non-targeted Gd-DOTA in an orthotopic PC3 model [92].
Hyperpolarized 13C can be used as a contrast agent for MRI or MRSI, as it briefly retains its nuclear polarization after injection. Using a fast MRSI technique with 13C-labeled pyruvate and lactate in the transgenic adenocarcinoma of mouse prostate (TRAMP) model, Chen et al. effectively detected prostate tumors and correlated 13C-lactate uptake with tumor grade [93, 94]. In addition, Yaligar et al. recently demonstrated that increased 13C-lactate correlated with tumor aggression in prostate cancer models [95]. Therefore, this technique shows promise for not only detecting tumors but also assessing their biology.
Conclusion
As the management of prostate cancer becomes more personalized and new treatments become available, there is increasing clinical demand for molecular imaging beyond 99mTc bone scintigraphy and 18F-FDG PET. In this review, we have highlighted the great number and variety of emerging molecular imaging agents for prostate cancer. Many of these have been tested in early phase clinical trials and have shown excellent potential for detection of primary and metastatic disease. We are particularly encouraged by several recent studies that demonstrate proof of principle for the use of molecular imaging to assess specific tumor biology or treatment response in prostate cancer. However, larger controlled trials will be necessary to establish clear clinical indications for these agents.
Acknowledgment
Dr. Thomas M. Link reviewed this article.
Footnotes
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines Conflict of Interest Ana P. Kiess, Steve Y. Cho, and Martin G. Pomper declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as:
*Of importance
**Of major importance
- 1.American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts & Figures 2012. American Cancer Society; Atlanta: 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Thompson I, Thrasher JB, Aus G, et al. Guideline for the management of clinically localized prostate cancer: 2007 update. The Journal of urology. 2007;177(6):2106–31. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2007.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.National Comprehensive Cancer Network Prostate Cancer Clinical Practice Guidelines. (Version 2.2013) 2013 May 28; Available from: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/prostate.pdf.
- 4.Klotz L, Zhang L, Lam A, et al. Clinical results of long-term follow-up of a large, active surveillance cohort with localized prostate cancer. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2010;28(1):126–31. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.24.2180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hayes JH, Ollendorf DA, Pearson SD, et al. Active surveillance compared with initial treatment for men with low-risk prostate cancer: a decision analysis. JAMA : the journal of the American Medical Association. 2010;304(21):2373–80. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.1720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Petrylak DP, Tangen CM, Hussain MH, et al. Docetaxel and estramustine compared with mitoxantrone and prednisone for advanced refractory prostate cancer. The New England journal of medicine. 2004;351(15):1513–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa041318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.de Bono JS, Oudard S, Ozguroglu M, et al. Prednisone plus cabazitaxel or mitoxantrone for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer progressing after docetaxel treatment: a randomised open-label trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9747):1147–54. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61389-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.de Bono JS, Logothetis CJ, Molina A, et al. Abiraterone and increased survival in metastatic prostate cancer. The New England journal of medicine. 2011;364(21):1995–2005. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1014618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ryan CJ, Smith MR, de Bono JS, et al. Abiraterone in metastatic prostate cancer without previous chemotherapy. The New England journal of medicine. 2013;368(2):138–48. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1209096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Scher HI, Fizazi K, Saad F, et al. Increased survival with enzalutamide in prostate cancer after chemotherapy. The New England journal of medicine. 2012;367(13):1187–97. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1207506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kantoff PW, Higano CS, Shore ND, et al. Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. The New England journal of medicine. 2010;363(5):411–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1001294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Prensner JR, Rubin MA, Wei JT, Chinnaiyan AM. Beyond PSA: the next generation of prostate cancer biomarkers. Science translational medicine. 2012;4(127):127rv3. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hricak H, Choyke PL, Eberhardt SC, et al. Imaging prostate cancer: a multidisciplinary perspective. Radiology. 2007;243(1):28–53. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2431030580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cho SY, Pomper MG. Molecular imaging in prostate cancer. In: Pomper MG, Gelovani JG, editors. Molecular imaging in oncology. Informa Healthcare; New York: 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shinohara K, Wheeler TM, Scardino PT. The appearance of prostate cancer on transrectal ultrasonography: correlation of imaging and pathological examinations. The Journal of urology. 1989;142(1):76–82. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)38666-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sciarra A, Barentsz J, Bjartell A, et al. Advances in magnetic resonance imaging: how they are changing the management of prostate cancer. European urology. 2011;59(6):962–77. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.02.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bonekamp D, Jacobs MA, El-Khouli R, et al. Advancements in MR imaging of the prostate: from diagnosis to interventions. Radiographics. 2011;31(3):677–703. doi: 10.1148/rg.313105139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mueller-Lisse UG, Scherr MK. Proton MR spectroscopy of the prostate. European journal of radiology. 2007;63(3):351–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2007.06.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vargas HA, Akin O, Afag A, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging for predicting prostate biopsy findings in patients considered for active surveillance of clinically low risk prostate cancer. The Journal of urology. 2012;188(5):1732–8. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.07.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Akin O, Gultekin DH, Vargas HA, et al. Incremental value of diffusion weighted and dynamic contrast enhanced MRI in the detection of locally recurrent prostate cancer after radiation treatment: preliminary results. European radiology. 2011;21(9):1970–8. doi: 10.1007/s00330-011-2130-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Even-Sapir E, Metser U, Michani E, et al. The detection of bone metastases in patients with high-risk prostate cancer: 99mTc-MDP Planar bone scintigraphy, single- and multi-field-of-view SPECT, 18F-fluoride PET, and 18F-fluoride PET/CT. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 2006;47(2):287–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Helyar V, Mohan HK, Barwick T, et al. The added value of multislice SPECT/CT in patients with equivocal bony metastasis from carcinoma of the prostate. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37(4):706–13. doi: 10.1007/s00259-009-1334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dennis ER, Jia X, Mezheritskiy IS, et al. Bone scan index: a quantitative treatment response biomarker for castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2012;30(5):519–24. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.36.5791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ulmert D, Kaboteh R, Fox JJ, et al. A novel automated platform for quantifying the extent of skeletal tumour involvement in prostate cancer patients using the Bone Scan Index. European urology. 2012;62(1):78–84. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.01.037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mosavi F, Johansson S, Sandberg DT, et al. Whole-body diffusion-weighted MRI compared with (18)F-NaF PET/CT for detection of bone metastases in patients with high-risk prostate carcinoma. AJR. American journal of roentgenology. 2012;199(5):1114–20. doi: 10.2214/AJR.11.8351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Fox JJ, Schoder H, Larson SM. Molecular imaging of prostate cancer. Current opinion in urology. 2012;22(4):320–7. doi: 10.1097/MOU.0b013e32835483d5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chang CH, Wu HC, Tsai JJ, et al. Detecting metastatic pelvic lymph nodes by 18F-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography in patients with prostate-specific antigen relapse after treatment for localized prostate cancer. Urologia internationalis. 2003;70(4):311–5. doi: 10.1159/000070141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schoder H, Herrmann K, Gonen M, et al. 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography for the detection of disease in patients with prostate-specific antigen relapse after radical prostatectomy. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2005;11(13):4761–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Morris MJ, Akhurst T, Larson SM, et al. Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography as an outcome measure for castrate metastatic prostate cancer treated with antimicrotubule chemotherapy. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2005;11(9):3210–6. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Meirelles GS, Schoder H, Ravizzini GC, et al. Prognostic value of baseline [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and 99mTc-MDP bone scan in progressing metastatic prostate cancer. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2010;16(24):6093–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Deb N, Goris M, Trisler K, et al. Treatment of hormone-refractory prostate cancer with 90Y-CYT-356 monoclonal antibody. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 1996;2(8):1289–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Thomas CT, Bradshaw PT, Pollock BH, et al. Indium-111-capromab pendetide radioimmunoscintigraphy and prognosis for durable biochemical response to salvage radiation therapy in men after failed prostatectomy. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2003;21(9):1715–21. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.05.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wilkinson S, Chodak G. The role of 111indium-capromab pendetide imaging for assessing biochemical failure after radical prostatectomy. The Journal of urology. 2004;172(1):133–6. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000132138.02846.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bauman G, Belhocine T, Kovacs M, et al. 18F-fluorocholine for prostate cancer imaging: a systematic review of the literature. Prostate cancer and prostatic diseases. 2012;15(1):45–55. doi: 10.1038/pcan.2011.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zadra G, Photopoulos C, Loda M. The fat side of prostate cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.03.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Contractor K, Challapalli A, Barwick T, et al. Use of [11C]choline PET-CT as a noninvasive method for detecting pelvic lymph node status from prostate cancer and relationship with choline kinase expression. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(24):7673–83. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Henriksen G, Herz M, Hauser A, et al. Synthesis and preclinical evaluation of the choline transport tracer deshydroxy-[18F]fluorocholine ([18F]dOC) Nucl Med Biol. 2004;31(7):851–8. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2004.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Vavere AL, Kridel SJ, Wheeler FB, Lewis JS. 1-11C-acetate as a PET radiopharmaceutical for imaging fatty acid synthase expression in prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2008;49(2):327–34. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.107.046672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *39.Souvatzoglou M, Weirich G, Schwarzenboeck S, et al. The sensitivity of [11C]choline PET/CT to localize prostate cancer depends on the tumor configuration. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2011;17(11):3751–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2093. This prospective study correlates histology of prostatectomy specimens with 11C-choline PET/CT images, showing the potential for false positives in prostatitis and BPH and false negatives in small (<5 mm) or necrotic tumors.
- 40.Castellucci P, Fuccio C, Nanni C, et al. Influence of trigger PSA and PSA kinetics on 11C-Choline PET/CT detection rate in patients with biochemical relapse after radical prostatectomy. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 2009;50(9):1394–400. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.108.061507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Picchio M, Castellucci P. Clinical Indications of C-Choline PET/CT in Prostate Cancer Patients with Biochemical Relapse. Theranostics. 2012;2(3):313–7. doi: 10.7150/thno.4007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Castellucci P, Fuccio C, Rubello D, et al. Is there a role for (11)C-choline PET/CT in the early detection of metastatic disease in surgically treated prostate cancer patients with a mild PSA increase <1.5 ng/ml? European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. 2011;38(1):55–63. doi: 10.1007/s00259-010-1604-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Picchio M, Spinapolice EG, Fallanca F, et al. [11C]Choline PET/CT detection of bone metastases in patients with PSA progression after primary treatment for prostate cancer: comparison with bone scintigraphy. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. 2012;39(1):13–26. doi: 10.1007/s00259-011-1920-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *44.Giovacchini G, Picchio M, Parra RG, et al. Prostate-specific antigen velocity versus prostate-specific antigen doubling time for prediction of 11C choline PET/CT in prostate cancer patients with biochemical failure after radical prostatectomy. Clinical nuclear medicine. 2012;37(4):325–31. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0b013e31823363b0. In this retrospective study, high PSA velocity predicted for 11C-choline PET uptake in men with PSA relapse, showing the value of 11C-choline for detecting aggressive recurrent disease.
- 45.Souvatzoglou M, Krause BJ, Purschel A, et al. Influence of (11)C-choline PET/CT on the treatment planning for salvage radiation therapy in patients with biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer. Radiotherapy and oncology : journal of the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology. 2011;99(2):193–200. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2011.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rigatti P, Suardi N, Briganti A, et al. Pelvic/retroperitoneal salvage lymph node dissection for patients treated with radical prostatectomy with biochemical recurrence and nodal recurrence detected by [11C]choline positron emission tomography/computed tomography. European urology. 2011;60(5):935–43. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.07.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Oyama N, Miller TR, Dehdashti F, et al. 11C-acetate PET imaging of prostate cancer: detection of recurrent disease at PSA relapse. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 2003;44(4):549–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Albrecht S, Buchegger F, Soloviev D, et al. (11)C-acetate PET in the early evaluation of prostate cancer recurrence. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. 2007;34(2):185–96. doi: 10.1007/s00259-006-0163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kotzerke J, Volkmer BG, Glatting G, et al. Intraindividual comparison of [11C]acetate and [11C]choline PET for detection of metastases of prostate cancer. Nuklearmedizin. Nuclear medicine. 2003;42(1):25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Schuster DM, Taleghani PA, Nieh PT, et al. Characterization of primary prostate carcinoma by anti-1-amino-2-[(18)F] -fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid (anti-3-[(18)F] FACBC) uptake. American journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. 2013;3(1):85–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Amzat R, Taleghani PA, Savir-Baruch B, et al. Unusual presentations of metastatic prostate carcinoma as detected by anti-3 F-18 FACBC PET/CT. Clinical nuclear medicine. 2011;36(9):800–2. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0b013e318219b47e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Schuster DM, Votaw JR, Nieh PT, et al. Initial experience with the radiotracer anti-1-amino-3-18F-fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid with PET/CT in prostate carcinoma. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 2007;48(1):56–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Toth G, Lengyel Z, Balkay L, et al. Detection of prostate cancer with 11C-methionine positron emission tomography. The Journal of urology. 2005;173(1):66–9. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000148326.71981.44. discussion 69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Shiiba M, Ishihara K, Kimura G, et al. Evaluation of primary prostate cancer using 11C-methionine-PET/CT and 18F-FDG-PET/CT. Annals of nuclear medicine. 2012;26(2):138–45. doi: 10.1007/s12149-011-0551-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Rajagopalan KN, DeBerardinis RJ. Role of glutamine in cancer: therapeutic and imaging implications. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 2011;52(7):1005–8. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.110.084244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sun H, Sloan A, Mangner TJ, et al. Imaging DNA synthesis with [18F]FMAU and positron emission tomography in patients with cancer. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. 2005;32(1):15–22. doi: 10.1007/s00259-004-1713-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Jadvar H, Yap LP, Park R, et al. [18F]-2′-Fluoro-5-methyl-1-beta-D-arabinofuranosyluracil (18F-FMAU) in prostate cancer: initial preclinical observations. Molecular imaging. 2012;11(5):426–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Oyama N, Hasegawa Y, Kiyono Y, et al. Early response assessment in prostate carcinoma by (1)(8)F-fluorothymidine following anticancer therapy with docetaxel using preclinical tumour models. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. 2011;38(1):81–9. doi: 10.1007/s00259-010-1613-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dehdashti F, Picus J, Michalski JM, et al. Positron tomographic assessment of androgen receptors in prostatic carcinoma. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. 2005;32(3):344–50. doi: 10.1007/s00259-005-1764-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Larson SM, Morris M, Gunther I, et al. Tumor localization of 16beta-18F-fluoro-5alpha-dihydrotestosterone versus 18F-FDG in patients with progressive, metastatic prostate cancer. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 2004;45(3):366–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- **61.Scher HI, Beer TM, Higano CS, et al. Antitumour activity of MDV3100 in castration-resistant prostate cancer: a phase 1-2 study. Lancet. 2010;375(9724):1437–46. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60172-9. This phase I-II trial of the androgen receptor antagonist enzalutamide was accompanied by 18F-FDHT PET imaging showing decreased binding after 4 weeks of enzalutamide therapy. This demonstrates the utility of molecular imaging for drug development and assessing individual treatment response.
- 62.Chang SS, Reuter VE, Heston WD, Gaudin PB. Comparison of anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen antibodies and other immunomarkers in metastatic prostate carcinoma. Urology. 2001;57(6):1179–83. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(01)00983-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Perner S, Hofer MD, Kim R, et al. Prostate-specific membrane antigen expression as a predictor of prostate cancer progression. Hum Pathol. 2007;38(5):696–701. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2006.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Sweat SD, Pacelli A, Murphy GP, Bostwick DG. Prostate-specific membrane antigen expression is greatest in prostate adenocarcinoma and lymph node metastases. Urology. 1998;52(4):637–40. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(98)00278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bander NH, Trabulsi EJ, Kostakoglu L, et al. Targeting metastatic prostate cancer with radiolabeled monoclonal antibody J591 to the extracellular domain of prostate specific membrane antigen. The Journal of urology. 2003;170(5):1717–21. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000091655.77601.0c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Bander NH, Milowskiy MI, Nanus DM, et al. Phase I trial of 177lutetium-labeled J591, a monoclonal antibody to prostate-specific membrane antigen, in patients with androgen-independent prostate cancer. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23(21):4591–601. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.05.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Milowsky MI, Nanus DM, Kostakoglu L, et al. Phase I trial of yttrium-90-labeled anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen monoclonal antibody J591 for androgen-independent prostate cancer. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2004;22(13):2522–31. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.09.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Milowsky MI, Nanus DM, Kostakoglu L, et al. Vascular targeted therapy with anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen monoclonal antibody J591 in advanced solid tumors. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2007;25(5):540–7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.07.8097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *69.Holland JP, Divilov V, Bander NH, et al. 89Zr-DFO-J591 for immunoPET of prostate-specific membrane antigen expression in vivo. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 2010;51(8):1293–300. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.110.076174. This preclinical study of the PSMA-targeting antibody PET agent 89Zr-DFO-J591 showed excellent tumor uptake and retention in LNCaP xenografts.
- **70.Evans MJ, Smith-Jones PM, Wongvipat J, et al. Noninvasive measurement of androgen receptor signaling with a positron-emitting radiopharmaceutical that targets prostate-specific membrane antigen. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011;108(23):9578–82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1106383108. This preclinical study used 64Cu-J591 PET to quantitatively measure PSMA expression, showing that PSMA is upregulated by antiandrogen therapy. This provides an important proof of principle for using molecular imaging as a biomarker of receptor signaling.
- 71.Ruggiero A, Holland JP, Hudolin T, et al. Targeting the internal epitope of prostate-specific membrane antigen with 89Zr-7E11 immuno-PET. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 2011;52(10):1608–15. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.111.092098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Elsasser-Beile U, Reischl G, Wiehr S, et al. PET imaging of prostate cancer xenografts with a highly specific antibody against the prostate-specific membrane antigen. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 2009;50(4):606–11. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.108.058487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Foss CA, Mease RC, Cho SY, et al. GCPII imaging and cancer. Curr Med Chem. 2011;19(9):1346–59. doi: 10.2174/092986712799462612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Mease RC, Foss CA, Pomper MG. PET Imaging in Prostate Cancer: Focus on Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013;13(8):951–62. doi: 10.2174/1568026611313080008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *75.Cho SY, Gage KL, Mease RC, et al. Biodistribution, Tumor Detection, and Radiation Dosimetry of 18F-DCFBC, a Low-Molecular-Weight Inhibitor of Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen, in Patients with Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 2012;53(12):1883–91. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.112.104661. In this phase 0 clinical trial of the PSMA-targeting small molecule PET agent 18F-DCFBC, bone and soft tissue metastases were successfully visualized in men with progressive disease, including early bone lesions that were not visible on CT or 99mTc bone scan.
- 76.Chen Y, Pullambhatla M, Foss CA, et al. 2-(3-{1-Carboxy-5-[(6-[18F]fluoro pyridine-3-carbonyl)-amino]-pentyl}-ureido)-pen tanedioic acid, [18F]DCFPyL, a PSMA-based PET imaging agent for prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(24):7645–53. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Osborne JR, Hassan N, Vallabhajosula S, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology. Chicago: 2012. Tc-99m Labeled Small Molecule Inhibitors of Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA): New Molecular Imaging Probes to detect Metastatic Prostate Adenocarcinoma. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Banerjee SR, Foss CA, Castanares M, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of technetium-99m- and rhenium-labeled inhibitors of the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) J Med Chem. 2008;51(15):4504–17. doi: 10.1021/jm800111u. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Afshar-Oromieh A, Haberkorn U, Eder M, et al. [68Ga]Gallium-labelled PSMA ligand as superior PET tracer for the diagnosis of prostate cancer: comparison with 18F-FECH. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. 2012;39(6):1085–6. doi: 10.1007/s00259-012-2069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Afshar-Oromieh A, Malcher A, Eder M, et al. PET imaging with a [(68)Ga]gallium-labelled PSMA ligand for the diagnosis of prostate cancer: biodistribution in humans and first evaluation of tumour lesions. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. 2012 doi: 10.1007/s00259-012-2298-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Chen Y, Pullambhatla M, Banerjee SR, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of low molecular weight fluorescent imaging agents for the prostate-specific membrane antigen. Bioconjugate chemistry. 2012;23(12):2377–85. doi: 10.1021/bc3003919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Harisinghani MG, Barentsz J, Hahn PF, et al. Noninvasive detection of clinically occult lymph-node metastases in prostate cancer. The New England journal of medicine. 2003;348(25):2491–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Heesakkers RA, Hovels AM, Jager GJ, et al. MRI with a lymph-node-specific contrast agent as an alternative to CT scan and lymph-node dissection in patients with prostate cancer: a prospective multicohort study. The lancet oncology. 2008;9(9):850–6. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ulmert D, Evans MJ, Holland JP, et al. Imaging androgen receptor signaling with a radiotracer targeting free prostate-specific antigen. Cancer discovery. 2012;2(4):320–7. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Tolmachev V, Malmberg J, hofstrom C, et al. Imaging of insulinlike growth factor type 1 receptor in prostate cancer xenografts using the affibody molecule 111In-DOTA-ZIGF1R:4551. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 2012;53(1):90–7. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.111.090829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Yu Z, Carlucci G, Ananias HJ, et al. Evaluation of a technetium-99m labeled bombesin homodimer for GRPR imaging in prostate cancer. Amino acids. 2012 doi: 10.1007/s00726-012-1369-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Zhang K, Aruva MR, Shanthly N, et al. PET imaging of VPAC1 expression in experimental and spontaneous prostate cancer. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 2008;49(1):112–21. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.107.043703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Hall MA, Pinkston KL, Wilganowski N, et al. Comparison of mAbs targeting epithelial cell adhesion molecule for the detection of prostate cancer lymph node metastases with multimodal contrast agents: quantitative small-animal PET/CT and NIRF. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 2012;53(9):1427–37. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.112.106302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Counsell RE, Schwendner SW, Meyer KL, et al. Tumor visualization with a radioiodinated phospholipid ether. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 1990;31(3):332–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Pinchuk AN, Rampy MA, Longino MA, et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship effects on the tumor avidity of radioiodinated phospholipid ether analogues. Journal of medicinal chemistry. 2006;49(7):2155–65. doi: 10.1021/jm050252g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Ghosh D, Lee Y, Thomas S, et al. M13-templated magnetic nanoparticles for targeted in vivo imaging of prostate cancer. Nature nanotechnology. 2012;7(10):677–82. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2012.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Wu X, Burden-Gulley SM, Yu GP, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of a peptide targeted small molecular Gd-DOTA monoamide conjugate for MR molecular imaging of prostate cancer. Bioconjugate chemistry. 2012;23(8):1548–56. doi: 10.1021/bc300009t. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Chen AP, Albers MJ, Cunningham CH, et al. Hyperpolarized C-13 spectroscopic imaging of the TRAMP mouse at 3T-initial experience. Magnetic resonance in medicine : official journal of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine / Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2007;58(6):1099–106. doi: 10.1002/mrm.21256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Albers MJ, Bok R, Chen AP, et al. Hyperpolarized 13C lactate, pyruvate, and alanine: noninvasive biomarkers for prostate cancer detection and grading. Cancer research. 2008;68(20):8607–15. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Yaligar J, Thakur SB, Bokacheva L, et al. Lactate MRSI and DCE MRI as surrogate markers of prostate tumor aggressiveness. NMR in biomedicine. 2012;25(1):113–22. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]