Abstract
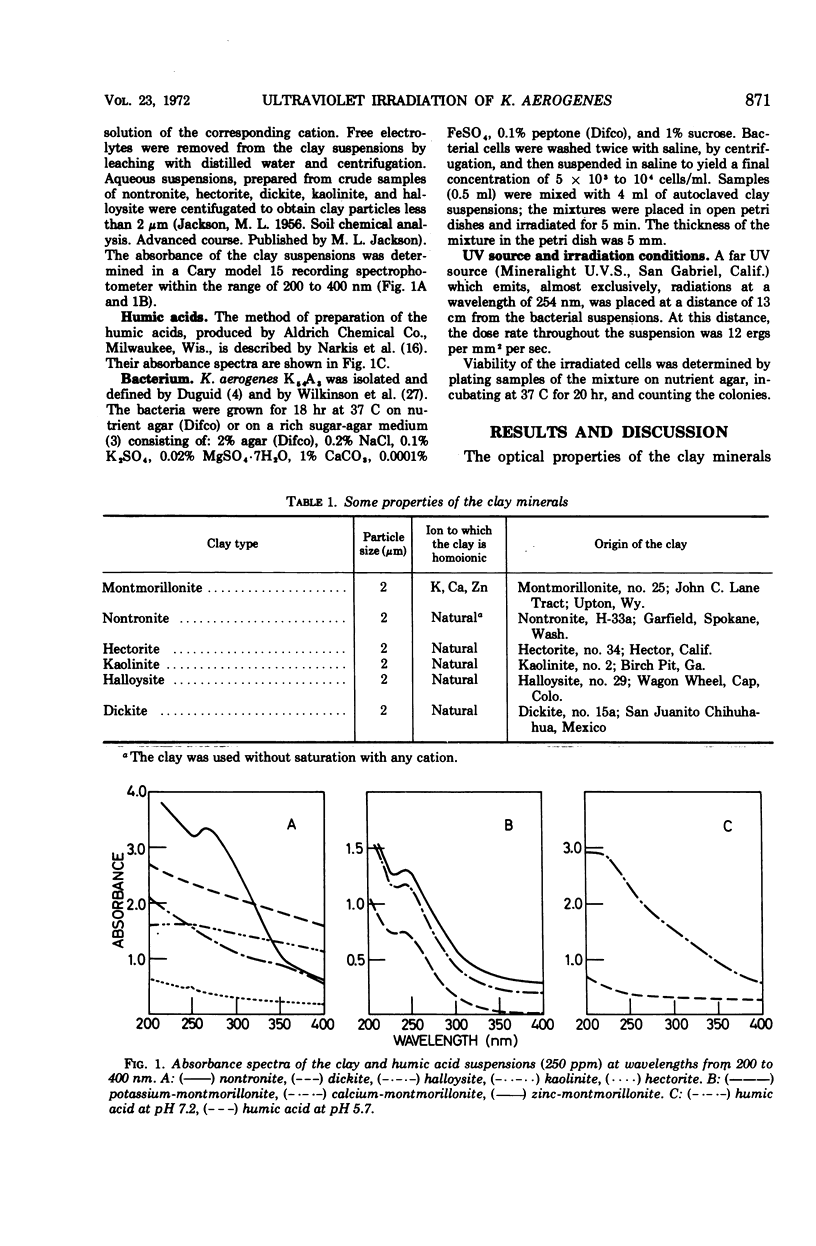
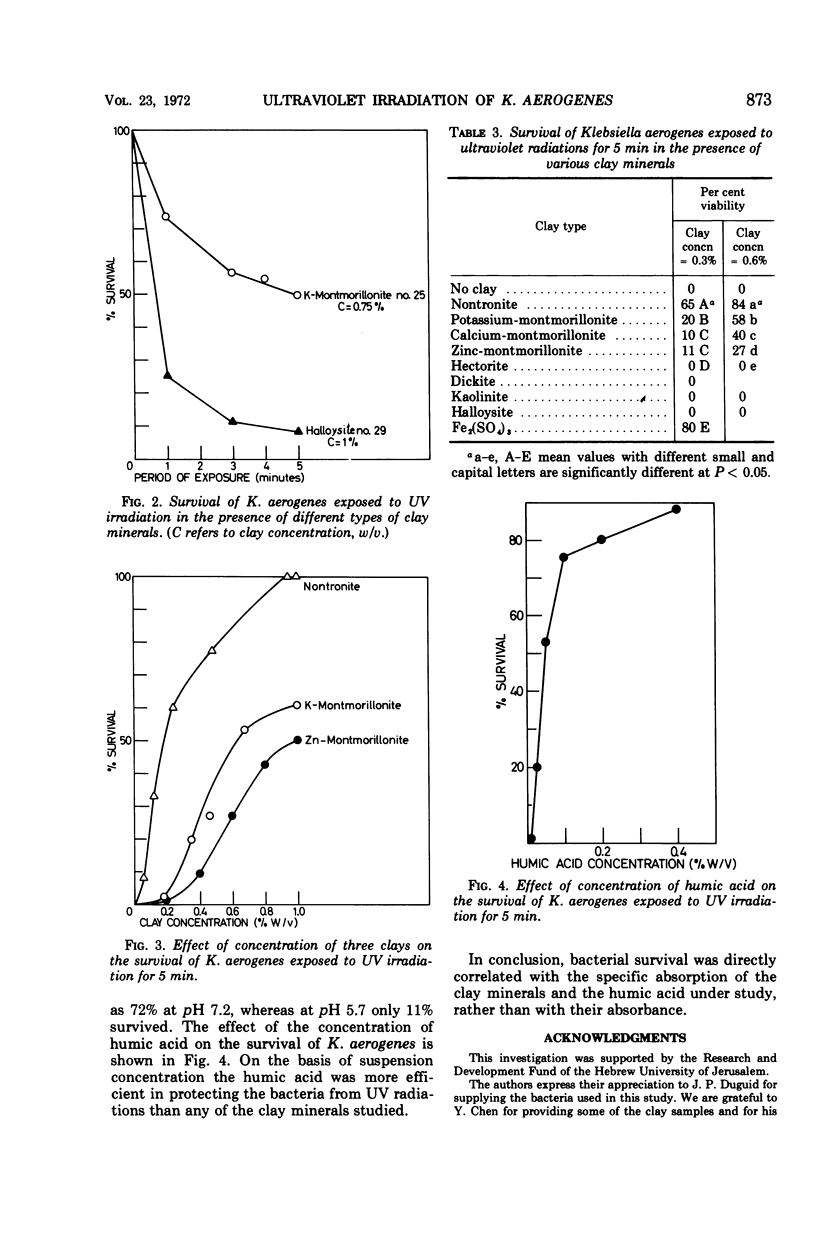
The effect of various clay minerals and humic acid on the survival of Klebsiella aerogenes exposed to ultraviolet (UV) irradiation was investigated. A protective effect was observed and found to depend on the specific light absorption and light scattering properties of the clay minerals and the humic acid used. The higher the specific absorption, the better was the survival of K. aerogenes after UV irradiation. Bacterial survival was lower in clays saturated with divalent cations (Ca, Zn) than in those homoionic to monovalent cations (K).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DUGUID J. P. The demonstration of bacterial capsules and slime. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1951 Oct;63(4):673–685. doi: 10.1002/path.1700630413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall K. C. Interaction between colloidal montmorillonite and cells of Rhizobium species with different inogenic surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 1;156(1):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro T., Stotzky G. Sorption between microorganisms and clay minerals as determined by the electrical sensing zone particle analyser. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Apr;14(4):299–307. doi: 10.1139/m68-049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotzky G. Influence of clay minerals on microorganisms. 3. Effect of particle size, cation exchange capacity, and surface area on bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Dec;12(6):1235–1246. doi: 10.1139/m66-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotzky G. Influence of clay minerals on microorganisms. II. Effect of various clay species, homoionic clays, and other particles on bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Aug;12(4):831–848. doi: 10.1139/m66-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotzky G., Rem L. T. Influence of clay minerals on microorganisms. I. Montmorillonite and kaolinite on bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Jun;12(3):547–563. doi: 10.1139/m66-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotzky G., Rem L. T. Influence of clay minerals on microorganisms. IV. Montmorillonite and kaolinites on fungi. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Nov;13(11):1535–1550. doi: 10.1139/m67-202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON J. F., DUGUID J. P., EDMUNDS P. N. The distribution of polysaccharide production in Aerobacter and Escherichia strains and its relation to antigenic character; with a note on the influence of potassium deficiency upon production of polysaccharide by Aerobacter aerogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Aug;11(1):59–72. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


