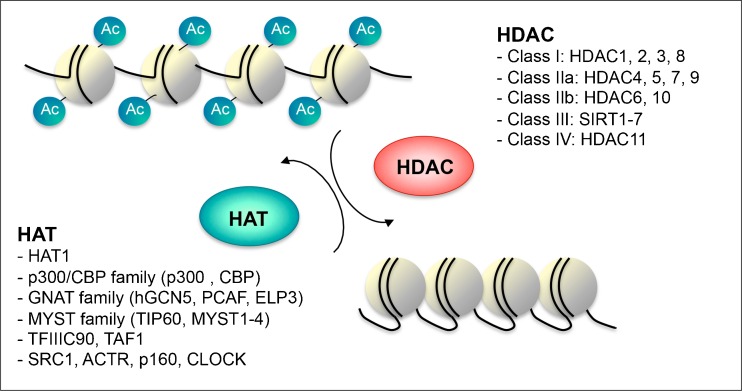
Fig. 1.
Histone acetyletransferase (HAT) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) families. Illustration of chromatin conformation according to the HAT/HDAC balance. The acetylation levels of nucleosome histone tails, at lysine residues, are determined through the interplay between acetylation and deacetylation mechanisms engaged respectively through HATs and HDACs enzymes. The different families and classes of enzymes are noted. Ac = Acetyl; CBP = cyclic adenomonophosphate response element-binding (CREB) binding protein; GNAT = Gcn5-related N-acetyltransferases; hGCN5 = human general control of amino acid synthesis protein 5-like 2; PCAF = p300/CBP-associated factor; ELP3 = elongation protein 3; MYST = MOZ/YBF2/SAS2/TIP60; TIP60 = TAT interacting proteins 60; TFIIIC90 = transcription factor IIIC 90kDa; TAF1 = TATA Box Binding Protein-Associated Factor, SRC1 = steroid receptor coactivator 1; ACTR = SRC-3, steroid receptor coactivator/AIB-1, Activated In Breast cancer-1/TRAM-1, thyroid hormone receptor activator molecule 1/ NCOA3, nuclear receptor coactivator 3